Individual and flock approach to ovine pneumonia
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
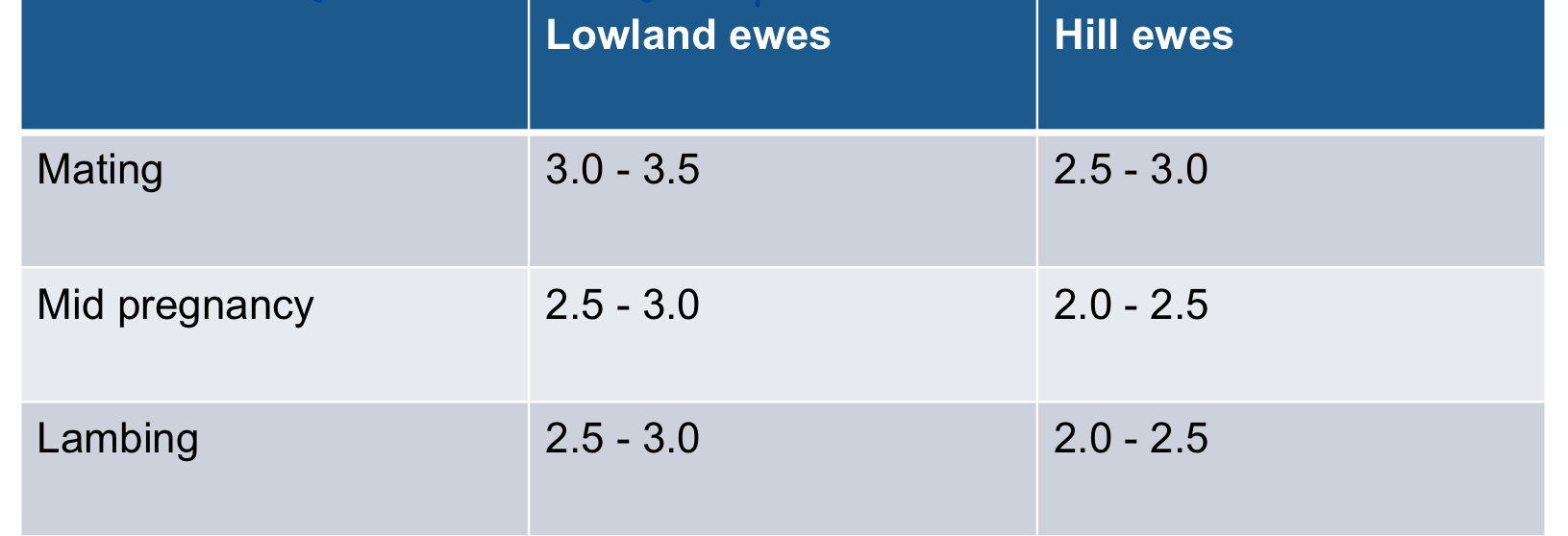
What are the BCS references for sheep in different stages?
fat= good! because thin means vulnerable to disease
What are the general causes of ill thrift?
poor nutrition
parasitism (fluke in adults/ haemonchus as it gets warmer)
chronic respiratory disease
dental disease (molars and incissors)
gastrointestinal disease
lameness
skin disease
others (mastitis, CLA, scrapie)
What are common causes of severe respiratory disease?
chronic suppurative pneumonia (abscessation)
jaagsiekte (ovine pulmonary adenocarcinoma- OPA)
maedi
laryngeal chronditis
pneumonic pasteurellosis
shipping fever
CLA not generally the UK
What are other causes of respiratory disease to remember?
atypical/chronic pneumonia/chronic non-progressive pneumonia (mycoplasma)
lungworms
oestrus ovis (needs heat)
enzootic nasal tumor (not UK)
inhalation pneumonia
tuberculosis
What is the cause of atypical/chronic pneumonia/chronic non-progressive pneumonia?
mycoplasma ovipneumonia
found in normal and diseased lungs
multiple strains in an infection
may have a role in permitting other pathogens ‘in’
usually 4-7 month old lambs
What is the progression in location of atypical/chronic pneumonia/chronic non-progressive pneumonia?
frequently found in the nasal cavity, where it moves from ewe to lamb
then invades the bronchi
What are the clinical signs of that disease?
mild
reduced growth
remember calf ‘cuffing pneumonia’
What is the treatment for that disease?
generally self-limiting
most non-aminoglycoside AB’s (even broad spectrum penicillins)
it’s a slow disease so you have to think improvement will take a fortnight
How do you prevent that disease?
lower stocking densities
avoid multiple stress events
keep healthy sheep
What are causes of chronic suppurative pneumonia?
basically we have no clue why they get it
inhalation of bacteria (eg fusobacterium necrophorum, trueperella pyogenes)
almost always secondary bacterial infection of compromised lung tissue
some will have haematogenous spread from septic focus
secondary to mannheimia haemolytica
What are clinical signs of that disease? And how to diagnose?
weight loss, depression, tachypnea, cough, usually normal temp
may have or may not have these signs
it’s difficult to diagnose- ultrasound may identify pleural abscesses, auscultation?
What is the treatment for it?
most ABs have some effect, however, effectiveness will be improved with drugs concentrating in lungs/abscesses and having long persistence
How do you prevent it?
have healthy sheep
ie control the things one can and the sheep will be in a better place to control infections
can’t actually stop it happening because we don’t actually know how it happens
using pasteurella vaccination?
What is ovine pulmonary adenomatosis (OPA)?
contagious lung tumor
retrovirus (jaagsiekte virus)
long incubation period: 3-4 year old sheep which makes control difficult
secondary bacterial infection (mannheimia haemolytia)
What are signs of OPA?
initial weight loss (appetite maintained) with exercise intolerance, increasingly tachypnoeic, crackles over lung field- loads and loads of fluid
How do you diagnose jaagsiekte?
‘wheelbarrow test’ diagnostic- clear frothy fluid from nostrils
no detectable immune response- no blood tests- it’s an intrinsic virus so it’s part of the sheep genome so it’s seen as self
ultrasound: sharp demarcation from normal lung tissue- basically looking for what looks like liver in the lung and that’s the tumor but it’s tough because the tumor would have to be right up against the body wall where you are scanning
post mortem confirmation of diagnosis
What is the treatment for jaagsiekte?
no treatment: cull affected sheep and offspring
difficult to control: regularly inspect flock for weight loss/signs of respiratory disease
don’t buy it in
What is maedi (ovine progressive pneumonia)?
chronic respiratory disease caused by lentivirus (retrovirus)- closely related to caprine arthritis and encephalitis virus (CAEV)
sheep infected as lambs through milk because it likes to reside in the udder
clinical disease is rare in animals cause of long incubation period
lymphocytic infiltration of lungs, udder, joints, nervous tissue
What are clinical signs of maedi?
exercise intolerance, weight loss, progressive tachypnea/dyspnea, indurative mastitis
How do you diagnose maedi?
detection of antibodies to MVV- AGIDT or ELISA but body is slow to introduce antibodies so there’s a 6 month diagnostic gap
How would maedi affected lungs feel on post mortem?
firm, rubbery, heavy lungs, do not collapse (often concurrent pasteurellosis or jaagsiekte)
How do you control/prevent maedi?
go in and test every 6 months and pull out the positives
test and cull seropositive animals and offspring
artificial rearing of lambs- probability of being affected is low
purchase replacements from accredited MVV free flocks
USA has a genetic test for susceptibility to disease
What is laryngeal chondritis and what are clinical signs?
abscessation of arytenoid cartilages in larynx- non-specific environmental bacteria
CS: progressive, severe inspiratory dyspnea, open mouth breathing, cyanosis, painful larynx- often die
What is treatment?
early cases- corticosteroid (if in respiratory difficulties) and high dose broad spectrum antibiotic for 3-4 weeks
tracheotomy in emergency might save the animal
How is ovine lungworm controlled?
normally non-pathogenic
controlled in young lambs with routine GI nematode treatments
adult sheep seem to develop a degree of immunity
What are the 3 main species of ovine lungworm?
dictyocaulus filaria
muellerius capillaris
protostrongylus, multiple species
Which species of ovine lungworm will show up in almost all sheep you post mortem?
m capillaris and protostrongylus spp