California Biodiversity Mid Term Flashcards
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Endemic
Species there and nowhere else
Biodiversity Crisis
Rapid, human-caused decline in species populations and ecosystem health
Climate Change
Global climate changing faster than species can adapt
Provisioning Services
Provide food, building materials, energy
Regulating Services
Homeostasis (regulating the ecosytem), food prevention, climate and erosion control
Cultural Services
Benefits that our culture as humans benefit
Ecological Literacy
The ability to understand the natural systems that sustain life on Earth and use that understanding to create sustainable human communities
Naturalist
People who observe, study, and interpret the natural world
Traditional Ecological Knowledge (TEK)
Body of knowledge, beliefs, practices held by indigenous communities about the environment passed down through generations
Benefits of TEK
healthy ecosystem, mutual exchange of give and take, avoid overextracting
Two-Eyed Seeing
Viewing the world through indigenous and Western lenses
Slope
Measurement of the angle of the land face
Aspect
The compass direction that a slope faces
Elevation
Vertical height of a geographical feature on Earth's surface
Topography
Study of the physical features of Earth's surface
Geographic Range
Spatial distribution of a natural feature of organism, where a species is likely to occur
Endangered Species
In significant danger of going extinct in all or a portion of its geographic range
Endangered Species Act (ESA)
Passed in 1973 to protect endangered species
Carolus Linnaeus
Developed binomial system of classification
The Cell Theory
All living things are made of cells
6 kingdoms
Bacteria, archaea, protista, fungi, plantae, animalia
Photosynthetic kingdoms
Protista and plantae
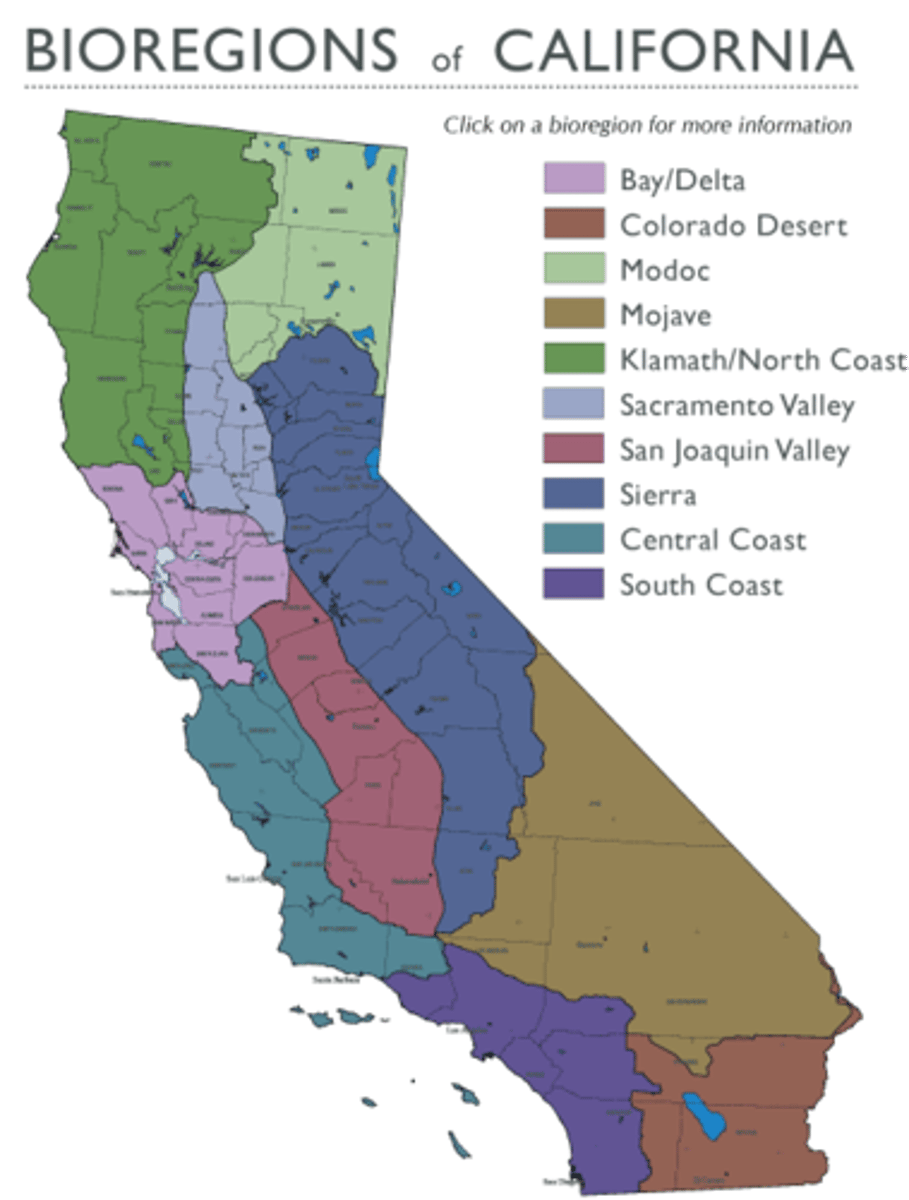
California Bioregions
Klamath, Modoc, Sacramento Valley, Bay Delta, Sierra, San Joaquin Valley, Central Coast, South Coast Mojave, Colorado Desert
Geomorphic
Rock shape - study of Earth's surface and shape (ex: islands, mountains, valleys, rivers, faults)
Convergent
Where 2 continental plates collide
Divergent
Where continental plates move apart and space is filled in
Transform
Two plates slide past each other in opposite directions
Elevation and Zonation
Foothills, chapparral, lower montane forest, upper montane forest, subalphine forest, alphine, great basin woodland
Biotic vs abiotic
alive vs never alive
water in three forms
liquid = water, solid = ice, gas = vapor
Water cycle order
accumulation, evaportation, condensation, precipitation
4 global carbon reservoirs
atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, lithosphere
Sequester
carbon sink
Biomass
is alive, has weight and volume
Effects of industrial revolution on environment
fossil fueled energy transition, air and water pollution, deforestation, habitat destruction, overall carbon emission increase
Carbon cycle 3 forms
solid = coal, graphite, Liquid = mixed as an oil, gas = Carbon dioxide
Pangea
supercontinent that existed during Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras
True
The San Andreas fault is a transform fault
Common rock types
Igneous/Volcanic, metamorphic, sedimentary
Groundwater
Water deep in the ground and is high enough that roots can tap into it for a water source
Runoff
Serves as a reservoir and accumulation plant
Evaporation and Transpiration
The breathing of water by plants
Soil Horizons
Bedrock, parent rock, subsoil, eluviation layer, topsoil, organic layer
Humus
decomposed plant and animal material
Organic
contains carbon
Symbiosis
Mutualistic relationship between two organisms where neither can live without the other
Mutualism
When two species benefit from their relationship
Mycorrhiza
A symbiotic relationship between a fungus and plant
myco = fungus, rrizhal = root
found in 80-90% of plant life
Solstices
apex days
Equinoxes
mid way points
Latitudinal zones of earth
arctic, temperate, tropical, equator
Topographic extremes in California
Death valley, mt witney, clear lake, San Fransisco Bay/Delta
CA Bioregions
Mediterranean climate
What climate does California have?
Endemic Species
Species that occur in one place and no where else
Geiger counter
scientific instrument detecting radioactive particles
Mycelium
Netwrok of thread like fungal structures growing through soil and connects to plant roots
Hub trees
largest and oldest trees in a forest that act like central part in Mycorrhizal network
Aposemitism
advertising toxicity with color
Where does California's water used most?
Human use - 60% and Agricultural use - 40%
Water formula
H + OH = H2O
Acidic
Excess H
Alkali or Basic
Excess OH
pH
potential hydrogen - a substance's ability to attract hydrogen ions
Carbonic Acid formula
H2O + CO2 = H2CO3
Threats to major rivers of CA (Sacramento San Joaquin)
Dams, Pollution, Overextraction, Recharge
Watersheds
where water flows
Refugia
Location that supports an isolated population of a species that might no longer exist lower down
Vernal Pools
pools that accumulate after rain - important for amphibians and birds
Examples of estuaries being productive ecosystems
bacteria decomposes nutrients, breeding and hatching grounds for fish, feeding grounds for birds, incoming tides bring nutrients and oxygen
Anadromous
Born in freshwater migrate to salt water and return to fresh water to spawn
Anadromous fish species
Steelhead, rainbow trout, pacific lamprey
California current
slow, cold ocean flowing SOUTH along North American coast
Upwelling
winds push surface water away from shore and suck up nutrient rich cold water from deeper areas
El Nino
Warming of sea surface temperature - moisture
La Nina
Cooling of ocean surface - dryness
Air flows
north pole, subtropical, south pole jet streams
orographic effect
Movement of air masses over land - ocean to land
orographic precipitation
when moist air is lifted over mountain range which forms orographic clouds and release precipitation on WINDWARD side of range
Rain Shadow Effect
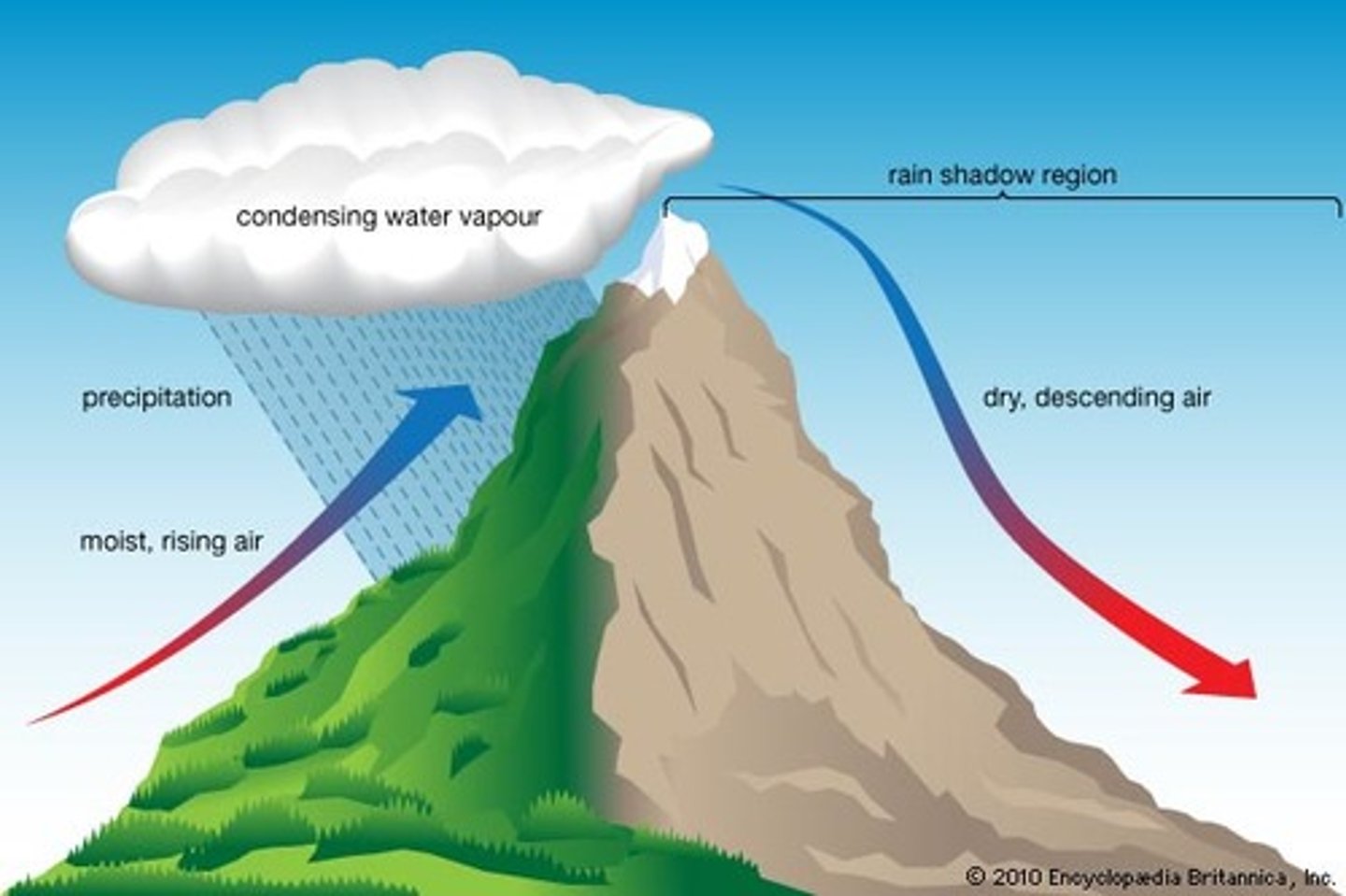
Why do we have a desert in California?
Because the rain shadow effect of going from coast range to great valley to sierra Nevada it gets very dry at the point at the other side of sierra in desert
What are some of the factors that contribute to California's biodiversity?
Abiotic factors: unique geography (highest and lowest points), mediterranean climate (hot dry summers and wet winters)
Biotic factors: Native species (many are endemic), ecosystem interactions (competition, symbiosis, mutualism), Habitat diversity (forests, coasts, grassalnds, etc)
Mammal Characteristics
Warm blooded, give birth to young, nourhsed by milk, have body hair or fur
Diets of animals
Insectavore, Omnivore, Herbivore, Carnivore, Scavenger
Photosynthesis Equation
CO2 + H2O → C6H12O6 + O2
Aerobic Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
True
True or False: Energy flows and matter cycles through ecosystems
Chloroplasts
Photosynthesis occurs in ...
mitochondria
Aerobic Respiration occurs in ...
Food Chain
Process of moving matter/energy through an ecosystem
Carrying capacity
Number of individuals of a species that an environment can support
Niche partitioning
avoiding competition by exploiting another source
Spatial Niche partitioning
using different areas
Dietary Niche partitioning
consuming different foods in the same habitat
Temporal niche partitioning
Species hunt are active or hunt at different times
Ecological niche
the role of an organism in the community
Producer, herbivore, omnivore, carnivore, scavenger, decomposer
California Food web chain
know this
Ansel Adams
Yosemite photographer
Manifest Destiny affects on environment
deforestation, soil exhaustion and dust bowl, habitat destruction, American buffalo habitat near extinction
Gold rush effects on environment
deforestation, toxic pollution, hydraulic mining washed hillsides into rivers, mercury contamination