fission and fusion
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what does radioactive decay, fission and fusion release?
they release nuclear energy because it involves changes in the nucleus of the atom.
define nuclear fission
splitting a large, unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei.
define nuclear fusion
when two small nuclei join together to form a larger nuclei.
what happens with fission for Uranium 235
when a neutron is collided into the Uranium 235 nucleus, the nucleus takes the neutron. Now the nucleus is unstable and splits into two smaller nuclei.
what are the products for fission
kinetic energy
2 or 3 neutrons.
2 smaller nuclei
what is a chain reaction (uranium 235)
when a fission happens, since it releases neutrons. Those neutrons can collide with other Uranium 235 atoms making it fission then it will happen again and again.
what is the purpose of the moderator in the reactor?
the moderator in the reactor is used to slow down the neutrons since it is easier for the uranium 235 to take the neutron into the nucleus, this occurs fission.
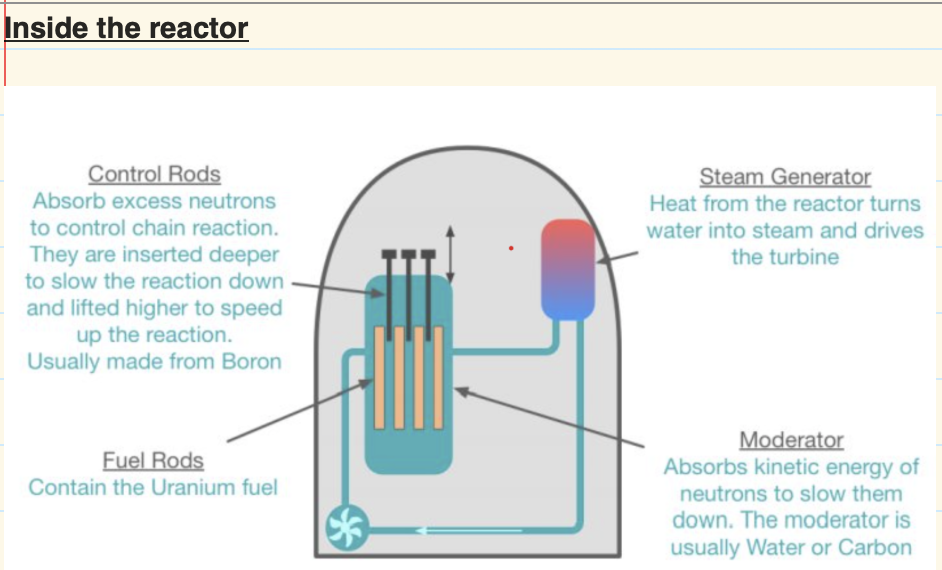
what is the purpose of the control rods in the reactor
they absorb the excess neutrons to control the rate of fission
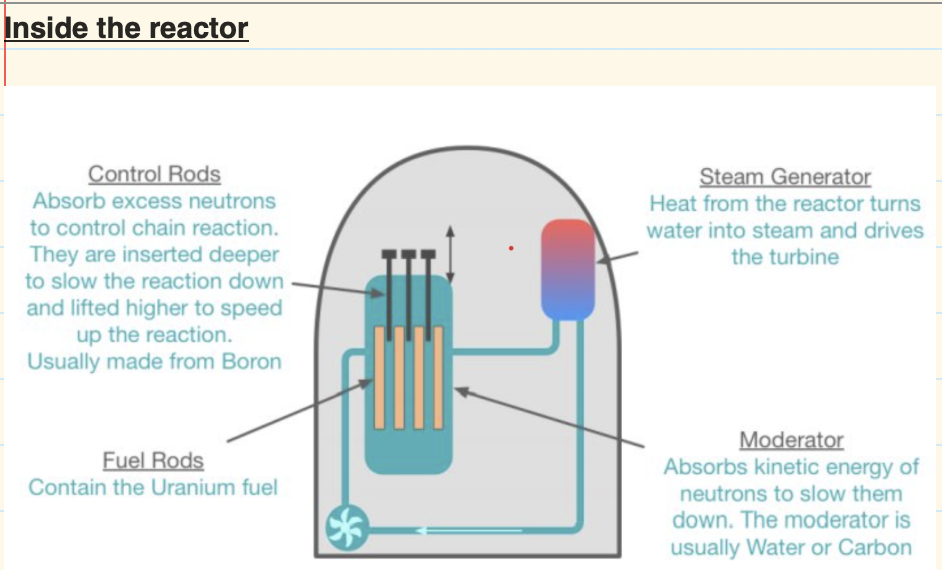
in a nuclear reactor what is the ‘shielding method’
in the reactor (where all of the ionising radiation occurs) around the reactor is thick steel and around the thick steel is a layer of concrete, this shielding method absorbs the ionising radiation that the reactor makes.
what is the difference between fission and fusion
fission
large nucleus→ two smaller nuclei
releases 2-3 neutrons
happens at lower temperatures than nuclear fusion
fusion
two smaller nuclei→large nucleus
releases nuclear energy
happens at high temperatures
in nuclear fusion what happens to the mass of the large nucleus
the large nucleus is slightly less than the total of the two nuclei that has joined together.
why is there a slight loss of mass when nuclear fusion has taken place
some of the mass converted into energy (using einstine’s famous equation)
E =M c (squared)
E =energy released
M = mass lost
c = speed of light.
what do stars get their energy form
nuclear fusion, for example in the sun they contain hydrogen atoms. The hydrogen atoms nuclei are joined together to get helium and release energy that makes the sun shine.
Why does nuclear fusion cannot happen at low temperatures?
they cant do low temperatures because due the protons in the nucleus they cant fuse with low temerpature since they do electrostatic repulsion, but if it is at a high temerpature they can gain a great amount of kinetic energy and it can overcome the electrostatic repulsion.