1A
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
Central α-carbon attached to NH2, COOH, H, and R-group
What is the absolute configuration of most amino acids?
L configuration at the α-carbon (S configuration for all except cysteine).
which amino acid is achiral?
glycine
Which amino acid has R configuration?
cysteine (due to sulfur priority)
Molecule with both positive and negative charges but overall neutral.
zwitterion
What is the form of amino acids at physiological pH?
NH3⁺ and COO⁻ (zwitterionic form)
When are amino acids fully protonated?
At low pH (acidic conditions).
When are amino acids fully deprotonated?
At high pH (basic conditions)
Which amino acids are acidic?
Aspartic acid (Asp, D), Glutamic acid (Glu, E).
What are acidic amino acids charges at physiological pH?
Negative (deprotonated carboxylate)
Which amino acids are basic?
Histidine (H), Arginine (R), Lysine (K)
Which basic amino acid is partially protonated at pH 7.4?
Histidine (pKa ~6), often used in enzyme active sites
List nonpolar amino acids.
gly-g. ala-a. pro-p. leu-L. ile-I. met-M. phe-f. trp-W. val-V
where are hydrophobic residues typically found?
Buried in the interior of proteins.
List polar amino acids.
gln-Q, ser-S, cys-C, ala-A, thr-T, tyr- Y
What enables polar residues to hydrogen bond?
OH, SH, and amide groups.
where are hydrophillic/polar amino acids found
on the outside
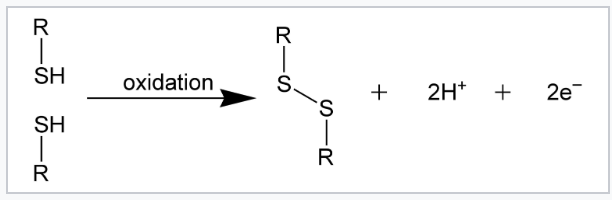
What forms a disulfide bond?
Oxidation of two cysteine residues → cystine.
Where do disulfide bonds typically form?
Extracellular proteins (oxidizing environments).
What breaks disulfide bonds?
Reducing agents (ex. β-mercaptoethanol, DTT).
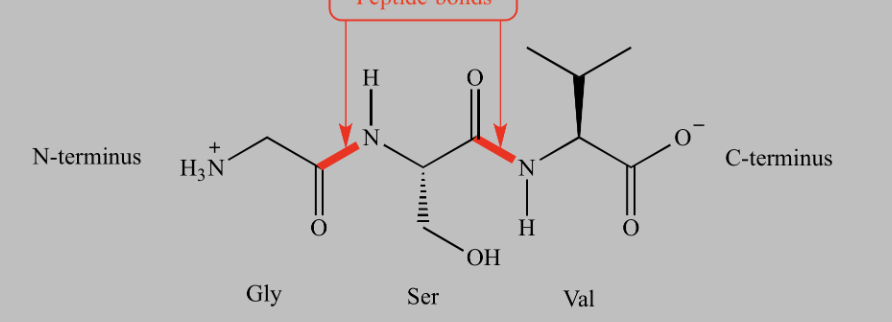
amide bond formed between COOH of one amino acid and NH2 of another.
peptide bond
What type of reaction forms a peptide bond?
dehydration (condensation) reaction
What type of reaction breaks a peptide bond?
hydrolysis-addition of water
What gives the peptide bond partial double-bond character?
Resonance between C=O and C–N.
What is the direction of a polypeptide?
N-terminus → C-terminus.
What conditions cause nonenzymatic hydrolysis?
Strong acid, strong base, or heat.
What enzymes hydrolyze peptide bonds?
proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, pepsin).
What is the significance of hydrolysis in the body?
Protein digestion and turnover.
Linear sequence of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
primary structure
What determines primary structure?
DNA sequence (gene encoding the protein).
What stabilizes secondary structures?
Hydrogen bonding between backbone atoms (C=O and N–H).
Main types of secondary structure?
α-helix and β-sheet.
What amino acid disrupts α-helices?
Proline (rigid ring structure causes kinks).
What stabilizes tertiary structure?
Hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions, disulfide bonds.
Disulfide bonds between cysteine residues
stabilize folded proteins.
What drives hydrophobic collapse?
Nonpolar residues move inward to avoid water.
Causes rigid turns or breaks in helices.
proline in tertiary structure
Association of multiple polypeptide chains (subunits).
quaternary structure
What stabilizes quaternary structure?
Same forces as tertiary: hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, H-bonds, disulfide bonds
Example of a quaternary protein?
Hemoglobin (tetramer).
what causes protein denaturation?
Heat, pH changes, detergents (SDS), organic solvents, reducing agents.
What structure(s) remain intact after denaturation?
primary structure - peptide bonds
What is protein folding driven by?
Hydrophobic effect + formation of stabilizing interactions.
Help proteins fold correctly and prevent aggregation.
chaperones
Why are hydrophobic interactions important for protein stability?
They reduce disruption of water structure and drive folding inwards
example of hydrophobic residues?
Val, Leu, Ile, Phe, Trp.
Structured shell of water around hydrophobic surfaces.
solvation layer
folding _______ of water
increases entropy
Hydrophobic residues cluster → __________ → entropy increases (favorable).
water becomes less ordered
What thermodynamic force drives folding?
Increase in entropy of water (ΔS > 0), making ΔG negative.
pH where a molecule has no net charge.
isoelectric point (pl)
How do proteins behave at pH < pI?
They are positively charged.
How do proteins behave at pH > pI?
They are negatively charged.
What is pI important for?
Isoelectric focusing.
What does electrophoresis separate molecules by?
charge and size
Which direction do negatively charged proteins migrate?
toward the anode (+).
Separation by size only; ____ denatures proteins and gives uniform negative charge.
SDS
Separates proteins by charge, size, and shape (no denaturation).
native PAGE
Proteins migrate until pH = pI → no movement.
isoelectric focusing
What makes cysteine unique?
Can form disulfide bonds (oxidation).
Where do disulfide bonds form?
Extracellular space (oxidizing)
inside the cytosol =
reducing
What type of bond holds primary structure?
covalent peptide bonds
What type of bond holds secondary structure?
hydrogen bonds
Bind specific molecules to transport, store, or regulate them.
binding proteins
Shape, charge, and chemical complementarity of the binding site determines
specificity
When binding of one ligand influences binding of others (ex: hemoglobin).
positive cooperativity
examples of binding proteins
Hemoglobin (_____)
myoglobin (____)
albumin (____)
DNA-binding transcription factors.
binds O₂, stores O₂, transports fatty acids,
What is the main nonenzymatic protein involved in immunity?
Antibodies (immunoglobulins).
Structure of an antibody?
Two heavy chains + two light chains linked by disulfide bonds.
What part of the antibody binds antigen?
variable region (Fab region).
What determines antigen specificity?
Amino acid sequence in the variable region.
How do antibodies neutralize pathogens?
Binding and blocking, tagging for destruction, or aggregating antigens.
Proteins that convert chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical work.
motor proteins
Major families of motor proteins?
Myosin, kinesin, dynein
responsible for muscle contraction and actin-based movement.
myosin
Moves cargo toward the + end of microtubules (away from nucleus).
kinesin
Moves cargo toward the – end of microtubules (toward nucleus); also drives cilia and flagella movement.
dynein
Conformational changes driven by ATP binding, hydrolysis, and release allow
motor proteins to move directionally
What type of protein is collagen?
Structural protein (not enzymatic).
Structural protein in hair, nails, skin.
keratin
Motor-related protein (polymer) that interacts with myosin.
actin
Structural motif found in antibodies and many cell surface receptors.
immunoglobulin fold
Increase reaction rate by lowering activation energy (Ea) without being consumed
enzymes
Do enzymes change ΔG, ΔH, or Keq?
No. They only affect the reaction rate, not thermodynamic favorability.
oxidation/reduction (ex. dehydrogenases)
Oxidoreductases
transfer functional groups (ex. kinases)
transferases
use water to break bonds (ex. proteases)
hydrolases
break/make bonds without water (ex. aldolase)
lyases
rearrangements (ex. phosphoglucose isomerases
isomerases
bond formation using ATP (ex. DNA ligase)
ligase
enzymes _______ by stabilizing transition state, bringing reactants together, altering local environment, straining substrate bonds.
lower activation energy
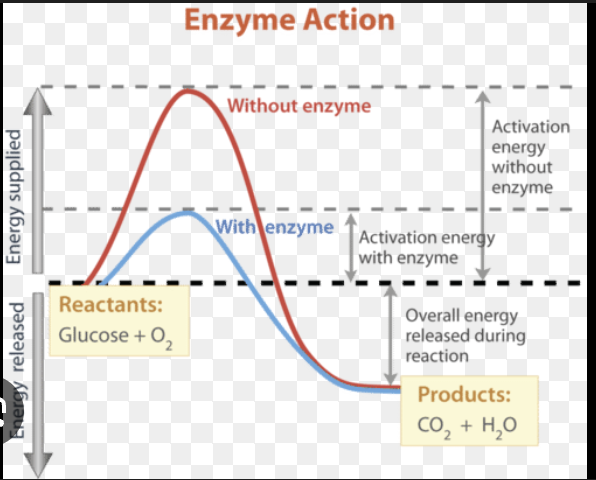
What part of the energy diagram changes with an enzyme?
Activation energy (peak height) decreases; reactants/products remain the same.
What determines enzyme specificity?
Shape, polarity, charge, and chemical complementarity of the active site.
What is substrate binding based on?
Noncovalent interactions (H-bonding, ionic interactions, hydrophobic forces).
Which model does MCAT emphasize?
induced fit
Enzyme and substrate fit perfectly; rigid model.
aactive Site (Lock-and-Key) Model
Enzyme changes shape when substrate binds; more accurate biological model.
Induced-Fit Model?
Inorganic ions (e.g., Mg²⁺, Zn²⁺) required for enzyme activity.
cofactors
Help stabilize negative charges or assist in substrate binding.
metal ions