Unstable Angina
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Unstable Angina (UA)
Progressive & unpredictable; change in previously established stable lesion.
May last for 10 minutes or longer
May occur at rest or during sleep.
Indicates plaque instability; Stable lesion may rupture leading to constriction and thrombosis which can occlude and lead to MI.
Not relieved by NTG SL X 3
UA includes
UA includes ST depression and T wave inversion
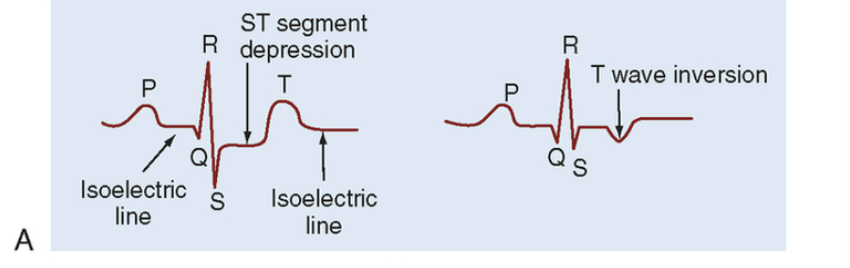
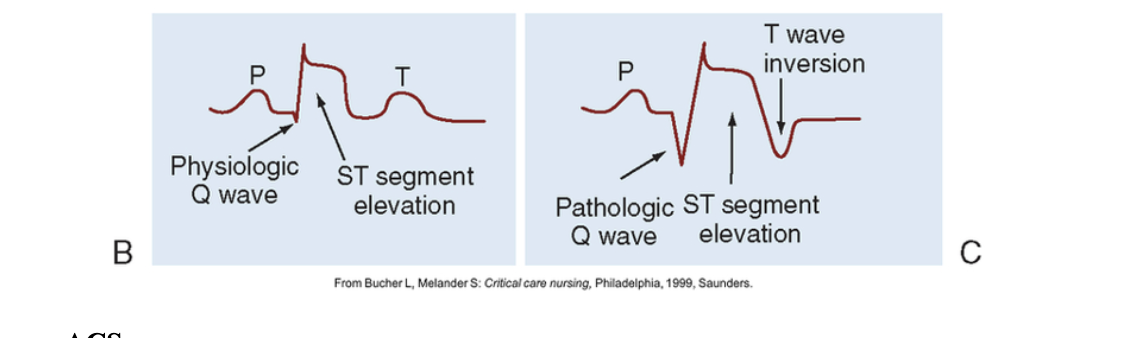
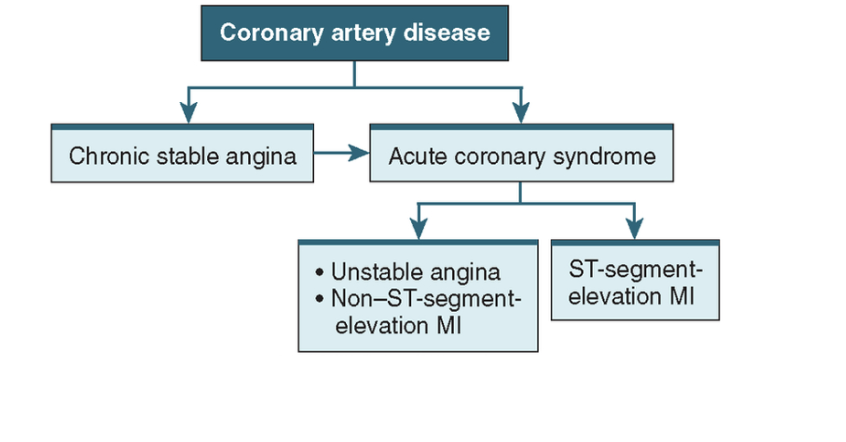
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) includes
Includes UA and non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
ACS
ACS
Within the first 10 seconds of an occlusion, the heart is deprived on O2 and the glucose needed for aerobic metabolism and contractility.
Anaerobic metabolism begins and creates lactic acid (limited O2)
Irreversible damage begins after 20 minutes.
Myocardial Infarction (MI) Progression
If injury is halted: then non Q wave MI or NSTEMI = partial muscle damage
If not halted: thrombus forms then progression to myocardium (cell death, necrosis) = STEMI
Collateral circulation assists in compensation of decreased circulation
ichemia
lack of o2
injury
muscle dying
infraction
muscle death
Anticoagulants
such as heparin or warfarin, slows down the body's process of making clots.
Antiplatelets,
such as aspirin and clopidogrel, prevent blood cells called platelets from clumping together to form a clot.
Thrombolytics
(…ase, Streptokinase, Alteplase [t-PA]) work by dissolving a major clot quickly
Clinical Manifestations
Chest pain/pressure: heavy, tight, burning, crushing
Pressure that radiates: neck, back, arm, jaw
Dysrhythmia
Dyspnea
Diaphoresis
N, V
Acute Anxiety
Fatigue/weakness
Clammy, cool skin: vasoconstriction
Diagnostics (See CAD PPT)
Cardiac Biomarkers
Troponin T, I, and C
CBC, BMP
12 lead ECG
CXR
Exercise Stress Test
Pharmacologic Stress Test
Echocardiogram or TEE
Cardiac Catheterization
Interventions
Oxygen 2L nc
Pulse oximetry and frequent VS
Cardiac Assessment
Bedrest
Telemetry monitoring
IV access
Medications
Thrombolytics
…ase
Acts directly on clots to cause lysis (not only in heart)
***Within 30 minutes of arrival to ED, not usually after 12 hours after symptoms and must have STEMI (complete blockage)
Know contraindications (Table 37-16)
Before thrombolytic→do all invasive procedures (draw labs, start 2 or 3 IV lines, insert foley)
Thrombolytics with Heparin may be used
thrombolytic recommended dose
Recommended dose is 0.9 mg/kg (not to exceed 90-mg total dose) infused over about 3 hrs with 10% of the total dose administered as an initial intravenous (IV) bolus over 1 minute (by MD).
Thrombolytic Contraindications
No internal bleeding or bleeding tendency (liver failure, Vitamin K deficiency, disseminated intravascular coagulation, Hemophilia, von Willebrand disease)
Cerebral hemorrhage
Ischemic Stroke in the past 3 months
Surgery (within 3 weeks)
Presence of current trauma
Severe uncontrolled HTN→BP > 180/110 mm HG
Thrombolytic Working?
Reperfusion Signs:
Chest pain stops
May observe limited dysrhythmias
ST segment returns to normal
Cardiac markers peak and return to normal
Thrombolytic Working?
side effects:
Reocclusion: Further chest pain - do EKG
Bleeding
Gums or IV sites – Apply pressure
Drop in BP or increase in HR – Stop Med
Change in mental status – Stop Med
Hematuria, Melena – Stop Med
Other Drug Therapy
IV NTG
Ace Inhibitors/ARBs
Β Blockers
Antidysrhythmics
Lipid lowering
Anticoagulants
Antiplatelet
Stool softeners
Anticoagulants…Heparin
25,000 Units in 250 mL D5W IV
Heparin bolus given, followed by maintenance infusion on IV pump
Prevents thrombus formation
Therapeutic effect monitored by Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT). Elevations are seen in patients on heparin therapy
Watch for bleeding
Antidote: Protamine Sulfate
Anticoagulants…Warfarin
Given when baseline established with heparin
Will discontinue heparin after warfarin begins
Oral doses may vary
Therapeutic effect monitored by prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR)
Watch for bleeding
Antidote: Vitamin K
Interventions
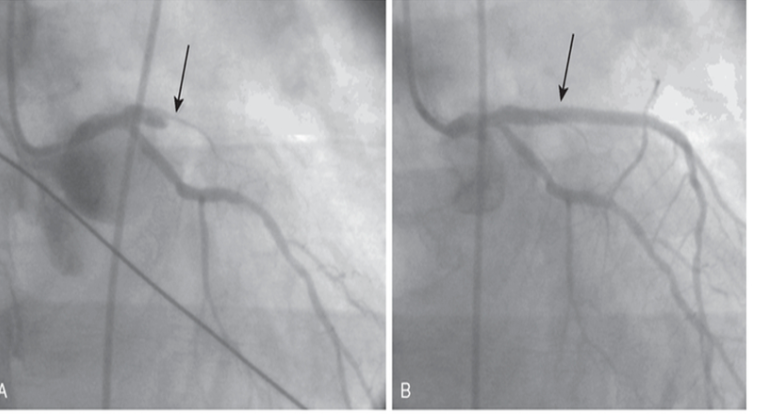
Cardiac Catheterization, Coronary Angiogram, Arteriogram
interventions
Identify, localize CAD
Contrast dye is injected through the catheter. X-ray images are taken to highlight the arteries.
Balloon angioplasty and/or Stent placement thru femoral or radial artery
Prep:
Ask about dye allergies
Verify consent for procedure
NPO 6-12 hours prior
IV fluids Sedation given prior
treatment
Treatment: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): Balloon and Stent
Stents are thrombogenic = sticky.
Bare metal = needs anticoagulant rest of life.
Drug-eluting stent = medication on stent to prevent thrombosis. Still need anticoagulants for about 6 mos.
Interventions…Cardiac Catheterization
Interventions…PCI Post-op
Hematoma Prevention
Compression device over artery. Vaso-seal/per-close/Femstop
HOB 30 degrees or less
Bedrest until following day if femoral
Telemetry monitoring and freq VS checks
Distal pulses checks frequently (q 15 mins/1st hr)
I & O, ensure urine output adequate
IV fluids to eliminate dye
Encourage oral fluids to eliminate dye
Assess for complications:
Rupture of dilated artery
Infarction due to plaque breaking off and occluding vessel
Interventions…Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
Requires sternotomy and cardiopulmonary bypass
Uses arteries and veins for grafts
The internal mammary, radial artery, and the saphenous vein are also used for bypass grafts.
Note neurovascular checks on the respective extremity post-op.
CABG surgery remains a palliative treatment for CAD and not a cure.
Interventions…Intraaortic Balloon Pump (IABP)
Sausage-shaped balloon placed in the aorta which inflates and deflates in synchrony with the cardiac cycle (ECG) to reduce afterload and left ventricular diastolic pressure while increasing perfusion of the coronary arteries.
Short term use to decrease cardiac workload and improve organ perfusion
Interventions…IABP complications
Site infection
Arterial trauma or hemorrhage
Thromboembolism
Pneumonia due to immobility
Interventions…Ventricular Assist Device (VAD)
Placed internally or externally, replacing the pumping action of the left ventricle. Blood is shunted from the left atrium to the aorta.
Used for longer term support, but temporary
Used most frequently for failure to wean from cardiopulmonary bypass after surgery
May be bi-ventricular
Interventions…VAD
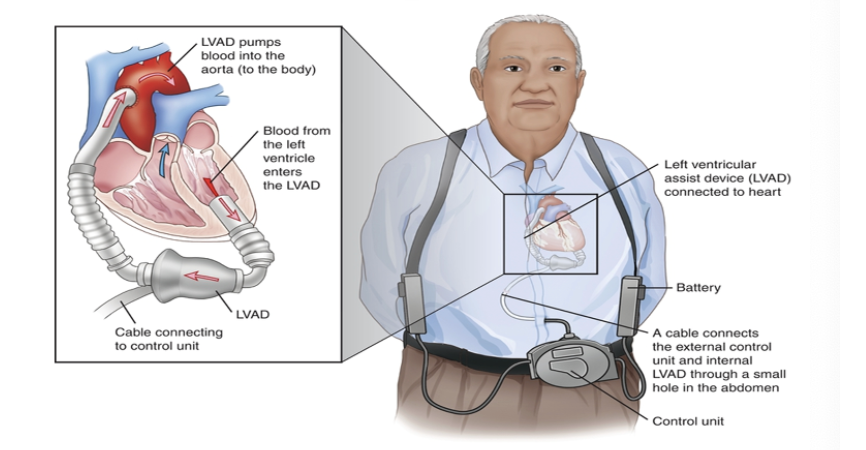
Remodeling
Changes occur in the left ventricular myocardium that lead to progressive decline in left ventricular performance.
Ultimately, ventricular remodeling may result in diminished contractile (systolic) function and reduced stroke volume
COMPLICATIONS of MI
Dysrhythmias (freq occur-80-90% of pts)
Heart Failure
Cardiogenic Shock (O2 and nutrients are inadequate to cardiac tissues)
Papillary Muscle Dysfunction infarct at mitral valve
Ventricular Aneurysm or Rupture (heart wall thins and bulges out)
Pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardium)
Cardiac Rehabilitation
During activity – monitor bp/pulse. Check for any increase greater than 20 mm hg or chest pain-intolerance
Cardiac Rehab goal is to change lifestyle to modify risk factors
CAD is a chronic disease
Go to ED if…
Onset of sob/wheezing/racing heart
Onset of new slow pulse rate
Weight gain of 3 lb in 1 week
Dizziness, faintness, extreme fatigue
Chest pain with associated symptoms
CP that is not relieved after 15 minutes/or 3 ntg.
Dilitiazem is used to treat variant angina (Prinzmetal’s) because it does which of the following:
A. Lower blood pressure
B. Slow the heart rate
C. Slow conduction across the myocardium
D. Relax arterial smooth muscle in the coronary arteries
Why is Captopril prescribed for clients who have experienced a recent MI:
A. To restore blood supply to the myocardium
B. To increase myocardial oxygen demand
C. To reduce post-MI Mortality
D. To reduce acute pain associated with MI
A patient is admitted to the cardiac care unit with a diagnosis of Acute Coronary Syndrome after experiencing a sudden onset of chest pain 4 hours ago. The first Troponin-I level is within normal limits. The nurse recognizes that this patient:
A. Has not experienced a myocardial infarction.
B. Should have a second Troponin-I level drawn in 6 hours.
C. Should have a second Troponin-I level repeated immediately.
D. Likely experienced a myocardial infarction within the past 24-48 hours.
During the administration of a thrombolytic
agent to a patient with an acute MI, the nurse should stop the drug infusion if the patient experiences
A. Bleeding from the gums.
B. Surface bleeding from the IV site.
C. A decrease in level of consciousness.
D. A nonsustained episode of ventricular tachycardia.
A patient is scheduled for coronary angiography and possible percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) the nurse explains to the patient that it is used to:
A. Determine structural defects in the heart
B. Locate any coronary artery obstructions and give thrombolytic agents.
C. Measure the amt of blood pumped from the heart
D. Visualize any coronary artery blockages and dilate any obstructed arteries.
A client is receiving NTG IV. The nurse should monitor for the most common side effect which is:
A. Drowsiness
B. Headache
C. Hypotension
D. Nausea
The nurse adjusts the plan of care for a client who is receiving propranolol to include increased monitoring of:
A. Heart rate
B. High blood pressure
C. Glucose
D. Potassium
Which of the following may indicate successful reperfusion after receiving a thrombolytic?
a. Negative creatine phosphokinase isoenzymes
b. Q wave formation
c. Atrial fibrillation
d. Normalization of ST segment
The older patient with coronary artery disease (CAD) is more likely to have what symptom if experiencing cardiac ischemia?
a. Syncope
b. Dyspnea
c. Chest pain
d. Depression
The provider diagnoses the patient with acute stable angina. The provider prescribes the patient NTG SL 5 mg for discharge and instructs him to see his cardiologist. What instructions should be included in teaching the patient about this newly prescribed medication? Select all that apply.
a. Take 3 tabs 5 mins apart when you feel chest pain.
b. Take 1 tabs 5 mins apart X 3 when you feel chest pain.
c. Keep the medication in your pants pocket.
d. If you take 3 tablets and your chest still hurts, call 911.
e. Discontinue the medication if it gives you a headache.
The cardiologist asks the nurse to schedule the patient for a diagnostic cardiac catheterization in the femoral area. Which instructions are the nurse’s highest priority at this time? Select all that apply.
a. Verify consent for the procedure.
b. Question the patient about any dye allergies.
c. Tell the patient that metformin should be withheld the day of the procedure and 48 hours afterward.
d. Shave the patient’s right femoral groin to prepare the catheterization site.
e. Instruct the patient to complete the lab studies in the next day or two.