cardiovascular system
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
thoracic inlet
junctional region between the structures of the root of the neck and the contents of the thoracic cavity
what is the average size of the heart ?
250 - 350g
the right atrio-ventricular valve is also known as
tricuspid
the left atrioventricular valve is also known as
bicuspid / mitral
chordae tendineae
tendon-like connective tissue that connects papillary muscle to AV valve cusps
function of papillary muscles
prevent valve prolapse
what are the 4 markers of auscultation
pulmonary, aortic, tricuspid and mitral valves
auscultation
listening to internal structure using stethoscope
what is the pericardial sac ?
double walled membrane enclosing heart
what are the 2 layers of the pericardial sac called ?
serous and fibrous
pericardial cavity
fluid filled area between muscle and cardiac sac that reduces friction
the serous pericardium can further be divided into
parietal and visceral
what is the function of the serous pericardium ?
reduce friction
what is the function of the fibrous pericardium ?
prevents overfilling
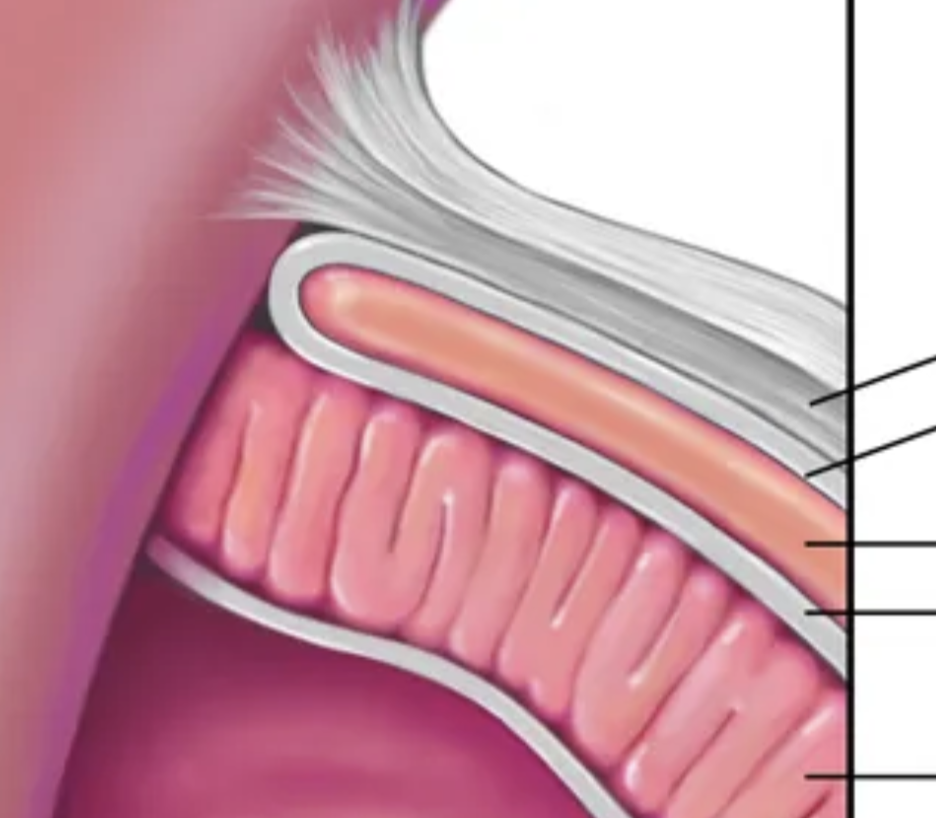
list these structures in descending order
fibrous pericardium, parietal serous, pericardial fluid, visceral serous, myocardium
myocardium
major muscle layer, contracts to force blood out
endocardium
inner layer of muscle, protects heart valves
the left coronary artery bifurcates into…
circumflex and anterior descending/interventricular
the coronary arteries at the edge of the heart are referred to as…
right and left marginal
the left coronary artery supplies blood to how much of the septum ?
2/3
ischemic cardiac disease is the result of…
obstruction of circulation in coronary arteries, lack of oxygen to myocardium
an inferior heart attack occurs where ?
right coronary artery
which artery is referred to as the artery of sudden death ?
left anterior
coronary veins join to form…
coronary sinus
where does the coronary sinus drain into ?
right atrium on posterior side of heart
thoracic inlet
junctional region between the structures of the root of the neck and the contents of the thoracic cavity
the mediastinum is split into superior and inferior by
sternal angle T4/5
what structures lie in the superior mediastinum ?
thymus, aortic arch, SVC, trachea, oesophagus, brachiocephalic veins, phrenic nerves
role of phrenic nerves
control diaphragm
where do you find the sternal angle ?
T4 - attachment at 2nd rib
the sternal angle is also referred to as the…
angle of Louis
where is the heart located ?
middle mediastinum
what other structure lay in the middle mediasternum ?
pericardium, ascending aorta, pulmonary trunk, SVC, cardiac plexus, phrenic nerves
the most anterior compartment of the mediastinum is the…
thymus
the visceral layer of the serous pericardium forms the…
epicardium
what is the cardiac plexus ?
network of nerves at base of heart - cardiac sympathetic nerves and cardiac branches of vagus nerve
3 branches of aortic arch
brachocephalic artery, left common carotid, left subclavian
the common carotid arteries supply…
head and neck
the subclavian arteries supply
upper limbs
the descending aorta splits into the…
posterior intercostal arteries
internal carotid arteries supply…
brain
external carotid arteries supply
face and neck
what is the role of the internal jugular veins ?
drain blood from face neck and brain
left and right JVs join with subclavian vein to form what ?
brachiocephalic veins
left and right brachiocephalic veins join to form
superior vena cava
what is the most common pulse palpation ?
carotid