Chemistry: topic 1.5 - atomic spectroscopy
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
define spectroscopy
an analytical technique which utilises the interactions between matter and electromagnetic radiation to reveal details of atomic and chemical structure.
2
New cards
How many electron shells
4
3
New cards
What are the subshells within each shell
s, p, d, f
4
New cards
How many orbitals in each sub shell
s=1, p=3, d= 5, f=7
5
New cards
how many electrons to each orbital
2
6
New cards
electrons of each subshell
s=2, p=6, d=10, f=14
7
New cards
Where is the s block on the periodic table
first two columns : H- Be+He

8
New cards
p block
last 6 columns: B-Ne

9
New cards
d block:
middle ten columns: Sc-Zn

10
New cards
aufbau principle
lower energy subshells filled first, then in order of increasing energy
11
New cards
electron config of ions **not in d-block**
electrons are added/removed from highest energy subshell
12
New cards
Exceptions to general electron config
Chromium and copper - both contain half filled 4s subshell - as allows each orbital in the 3d subshell to be half or completely filled which is more stable
13
New cards
electron config of ions in **d-block**
electrons are lost from 4s subshell then 3d sucshell
14
New cards
ground state
lowest energy level of an atom or ion, which electrons naturally occur in
15
New cards
How electrons promoted to higher energy levels?
through absorption of photons (discrete quantised amounts of energy which can be supplied as heat, light or electrical energy,
16
New cards
what happens when electrons in excited state return to lower energy levels?
energy is emitted from atom as electromagnetic radiation, photons.
17
New cards
Why are the series of emitted photons of specific frequency and wavelength unique to the element?
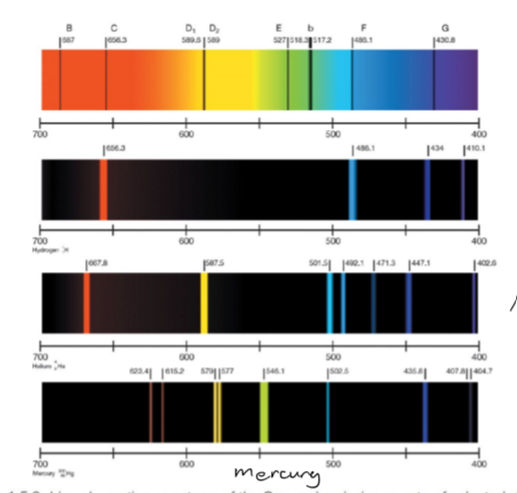
Each element has diff number of electrons, protons and neutrons, therefore are different distances from the nucleus which they travel when promoted to higher energy levels, therefore varying levels of energy are emitted through protons, leading to diff areas of UV energy emissions, the lower the energy the longer the wavelength. **SET of wavelengths is unique not each wavelength.**
18
New cards
define atomic **emission** spectroscopy
an analytical technique with utilises the characteristic emission spectra of elements in their **qualitative** identification. the intensity of the emission can also be used to determine the relative concentrations of elements in the mixtures. looks at wavelengths of photons **emitted**.
19
New cards
atomic absorbtion spectroscopy
a highly sensitive and selective **quantitative** analytical technique used to determine the concentration (in ppm and ppb), mostly of metallic elements in a sample. through **absorbtion** of photons.
20
New cards
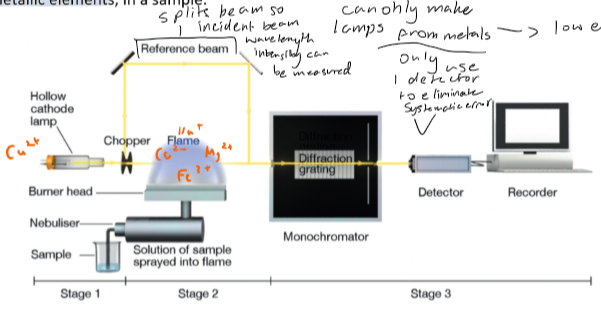
Why are the lamps in AAS mostly made from metals?
As metals have low electronegativity and therefore can be promoted to higher energy levels more easily. have low electronegativity as have low number of valence shell electrons and therefore rather give them up to become cations
21
New cards
Why is the incident beam split before the flame in AAS?
this creates a reference beam of the wavelengths being emitted by the metal in the lamp which can be measured by the same detector which will measure the transmitted beam, limits systematic error as same detector is used.
22
New cards
How AAS work?
1. a hollow cathode lamp is used, the hollow cathode is coated in the element of interest
2. A voltage is applied across the electrodes and the valence shell electrons of the metal are excited to higher energy levels, when they return to ground they emit photons with unique sets of wavelengths
3. The lamp emits a beam which is aligned with the burner head to pass directly through a long flame fulued by the analyte sample
4. A nebuliser system draws up the analyte sample and sprays it into the fuel mixture entering the flame of the burner head
5. The heat from the flame evaporates the solvent and breaks down its compoiunds into atoms and ions in a free atomic state
6. These atoms and ions from the sample absorb available energy from the incident beam, if they contain matching transitions
7. Therefore if the element of interest is present, the transitions will match and atomic absorption then emission will occur
8. As the emission is not limited to a single direction like the lamp, the energy is lost in all directions and very little rejoins the incident beam
9. The transmitted beam is directed to a monochromator
10. The monochromator diffracts the radiation to separate it into individual wavelengths, a wavelength unique to the investigated element is chosen for detection,
11. The intensity of this wavelength is compared between the incident and transmitted beams.
12. the degree of absorbance of the element is found from this
13. The absorbance is proportional to the concentration of the element of the sample and therefore once absorbance is found so can concentration
23
New cards
How is a callibration graph of an element’s absorbance made?
1. prepare a set of standards of known concentration - a blank of distilled water is also included as a reference for callibration
2. measure the absorbance of each standard using AAS
3. plot a callibration graph including a trend line
4. determine the concentration of the sample through estimation based on these known values
24
New cards
When there is more than 1 electron in an orbital what occurs?
the electrons spin in opposite directions due to repulsion