Pharmaceutical management of cough
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is coughing?
a protective reflex action caused when airway being irritated or obstructed
What are the timelines of cough?
<3 weeks acute, 3-8 weeks subacute, >8 weeks chronic
What do you need to know about acute cough?
most common due to viral upper respiritory tract infection - self-limiting, cough reflex more sensitive in women, common symptom in respitory problems - acute exacerbations and hospitalisations associated with athsma and COPD, seasonal impact
What do you need to know about subactute cough?
sometimes due to overcoming an illness and resolves itself, sometimes it becomming chronic
What do you need to know about chronic cough?
most common dry/minimmally productive, common cause GORD, athsma, rhinits, drugs, environment, red flag symptom
What questions should you ask to explore nature of cough?
character? length of time? colour of any productive? associated symptoms? what time of day? exacerbating features? recently unwell?
What medications can cause cough?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, build off bradykinin in lungs, 15% of people on it
What lifestyle factors can cause cough?
smoking, workplace - dust, housing -mold, both trigger athsma
What past medical history should you be thinking about with cough?
respiritory disease, COPD, CVD, immunosuppressed
What are the 5 common causes of cough (or catorgaries)?
cough varient athsma and eosinophillic bronchitis
GORD
undiagnosed or idiopathic chronic cough
upper airway disease and cough
cough due to other common respiritory diseases such as lower RTI, COPD, bronchiectasis etc.
What causes athsma cough?
allergen gets picked up on by dendritic cells, these recruit TH2 cells which produce cytokinis IL-4 and IL-5, (type 1 sensitivity) causes swollen lining and excess mucus to build up in airway
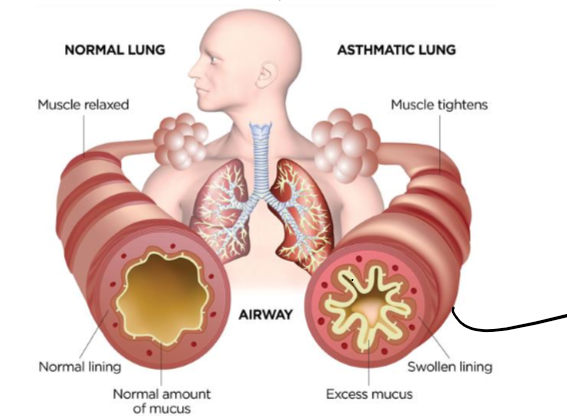
What is CVA?
cough varient athsma, dry cough as only symptom (but other athsma symptoms), eosinophilic inflammation, bronchial hyper-responsiveness, clinical indicator - nocturnal cough, post-exersize, allergen exposure
What is eosinophilic bronchitis?
elevated eosinophils, persistant cough without bronchospasm
What is the treatment for CVA and eosinophilic bronchitis?
elliminate allergen, inhaled corticosteroids (1st line), SABA, antihisamines, Leukotriene receptor antagonists
What does SABA stand for?
short acting beta-2-receptor agonists
How does GORD cause cough?
patients have increased cough reflex sensitivity
How do you treat GORD cough?
as per local guidlines - PPI or H₂ receptor antagonist, eliminate causative medications, livestyle advice, reveiw after 6-8 weeks
How does upper airways disease cause cough?
cough accompanied by nasal stuffiness, sinusitis and post-nasal drip - the sensation of secretions draining into the posterior pharynx from the nose or sinuses (which causes cough
What is the treatment for cough associated with upper airways disease?
Possibly antihistamines (limited efficacy), topical nasal steroids given for 2-8 weeks to patients with cough and post-nasal drip are effective
When should chronic cough be concidered idiopathic?
following full assessment at a specialist cough clinic, often clinical history of reflux cough
What is the main group of people with idiopathic chronic cough?
middle-aged women who have a long standing chronic dry cough which starts around the menopause
What is the treatment for idiopathic chronic cough?
limited to non-specific anti-tussive therapy such as dextromethorphan
When do you need to refer someone with cough?
>3 weeks, suptum colour and thickness, HR>130, chest pain associated, SOB: RR> 30, <92% ox sat, <33% of predicted peak expiratory flow, recurrent nocturnal cough in children, whooping cough/croup in children, suspected adverse drug event, failed meds
What are the treatments for cough not recommended by NICE? why give, why not?
suppressants - where no underlying cause can help with sleep or other stuff
expectorants - apparent promotion of expulsion of bronchal secretions - vomit inducing
demulcents - soothing action (harmless and inexpensive)
What is a non-pharmacological recomendation can you suggest for cough?
honey and lemon if >1 year, fluids, associated fever and pain - paracetamol/ibuprofen, vapour rub, warm, clear fluid, simple linctus cough mixture (think diabetics) , steam
Why is codeine/pholcodeine not used as a antitussive anymore?
both sedating, pholcodeine has fewer side effects and less likely to be abused, opioid related side effects, discontinued as interacts with general anastetics
Dextromethorphan
less sedating, lower potential for abuse, rare report of mania after high dose, short term use only
What is an example of a expectorant?
guaifenesin
What do you need to be aware of for giving antihisamines for cough?
avoid in patients who are taking phenothiazines and tricyclic antidepressants, avoid alcohol
What are some examples of antihistamines?
dphenhydramine, brompheniramine and promethazine
What is an example of sympathomimetics?
pseudoephedrine
What are sympathomimetics?
brochodilator and decongestant, care in high BP, diabetics, coronary artery disease, hyperthyrodism, interactions MOAs, Beta blockers and ticyclic antidepressants
Why was theophulline stopped?
interactions, GI irritation, palpitations, insomnia, headaches
side effects, toxicity dysrhyrthmia, seizures, hypotension (serum), >80mcg/mL
narrow theraputic index
What are some examples of mucolytics?
acetylcysteine, sodium chloride, carbocistiene
What are mucolytics?
inhaled, oral, poor evidence for long term improvement, patient satisfaction - relief 60 secs after inspirations, typically initiated in hospital and then continued, breaks down mucous, often treatment for COPD
What is a red flag for cough in community pharmacy?
how many times are they coming in - repeated chest infections
When would you consider antibiotics for cough associated with respirtory tract infections?
CRP > 100mg/L start treatment, CRP 20-100mg/L delay antibiotic therapy for 3 weeks or symptoms become significantly worse, CRP <20mg/L do not offer antimicrobial agents, broad spectrum agent, explain to patient why deniel
What do you need to know about cough and cold treatment in children?
containing medicines NOT suitable for children <6 years old, 6-12 treatment is 2nd line for max 5 days, codeine linctus for dry unproductive cough not recommended if <18, risk outweighs benifits