Concept 4.3: A few chemical groups are key to molecular function
1/10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Organic molecule properties
Depends on the carbon skeleton and chemical groups attached to it, giving it unique properties
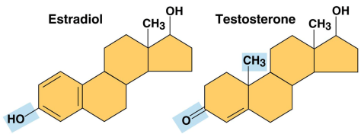
Estradiol and testosterone
Steroids with a common carbon skeleton in the form of four fused rings, differing only in the chemical groups attached to the skeleton’s rings
Functional groups
The components of organic molecules most commonly involved in chemical reactions and molecular properties
Includes groups of:
Hydroxyl
Carbonyl
Carboxyl
Amino
Sulfhydryl
Phosphate
Methyl

Hydroxyl
Functional group with the formula (—OH) or (HO—), also known as alcohol and included in ethanol

Carbonyl
Functional group with the formula (>C=O), also known as ketone or aldehyde and included in acetone or propanal

Carboxyl
Functional group with the formula (—COOH), also known as carboxylic acid or organic acid and included in acetic acid as well as its ionized form

Amino
Functional group with the formula (—NH2), also known as amine and included in glycine as well as its ionized form

Sulfhydryl
Functional group with the formula (—SH) or (HS—), also known as thiol and included in cysteine

Phosphate
Funcational group with the formula (—OPO32-), also known as organic phosphate and included in glycerol phosphate

Methyl
Functional group with the formula (—CH3), also known as methylated compound and included in 5-Methylcytosine
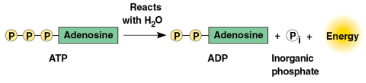
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
An important organic phosphate, consisting of an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of three phosphate groups
Reacts with water easily to release energy for cell utilization