5.1 Meiosis, 5.2 Meiosis and Genetic Diversity
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Genetics
the study of heredity and heredity variation
Heredity
the transmission of traits from one generation to the next
traits are passed from parent to offspring through genes (segments of DNA that code for heredity, offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes)
Asexual Reproduction
single individual
no fusion of gametes
clones( offspring are exact copies of the parent)
mutations are the only source of variation
can produce asexually through mitosis
Sexual Reproduction
two parents (male/female)
offspring are unique combinations of genes from parents
genetically varied from parents and siblings
meiosis
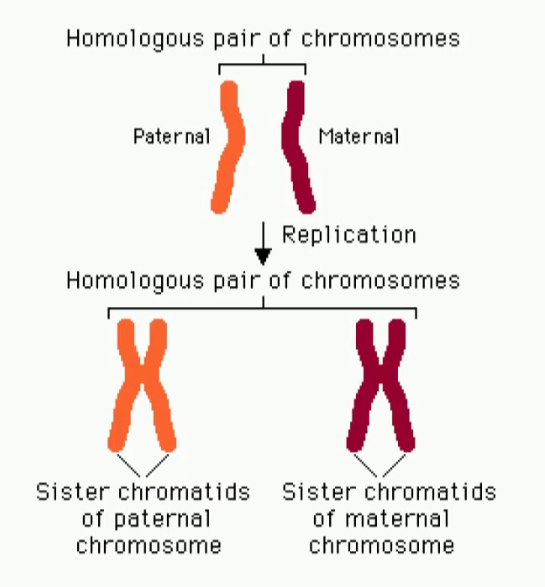
Homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes (same size, length, centromere position) that carry the same genetic information
one homologous chromosome is inherited from mom and one is inherited from dad
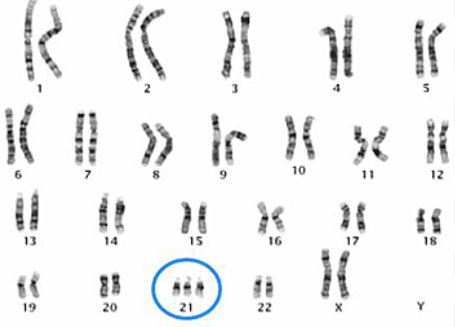
Karyotype
a display of chromosome pairs ordered by size and length
used to see irregularities like down syndrome, turner syndrome, and klinefelter syndrome
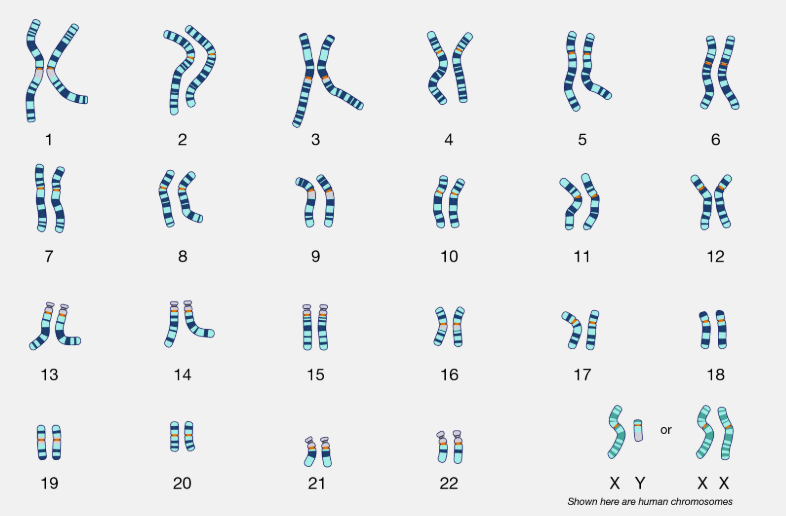
Somatic (body) cells
diploid or 2n
two complete sets of each chromosome
humans: 2n=46
Gametic (sex) cells
haploid or n
one set of each chromosome
humans(sperm and egg) n=23
eukaryotes have DNA that is packaged in chromosomes
there are 2 types of chromosomes
autosomes- chromosomes that do not determine sex (humans have 22 pairs)
sex chromosome is 23rd pair
sex chromosomes- x and y
eggs- X(humans 22+X)
sperm- X or Y (humans 22+X or 22+Y)
all sexually reproducing organisms have both a diploid and haploid number
Life cycle
sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism from conception to its own reproduction
fertilization and meiosis alternative in sexual life cycles
fertilization is when a sperm cell (haploid) fuses with an egg (haploid) to form a zygote (diploid)
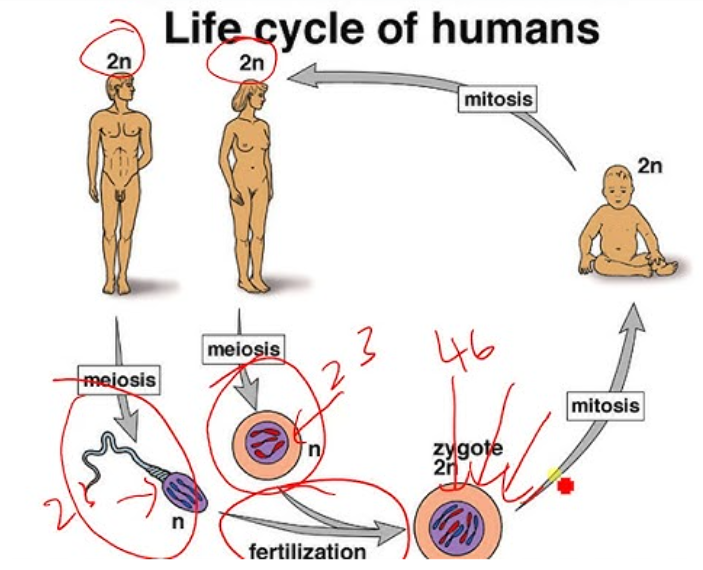
Meiosis
a process that creates haploid gametes cells in sexually reproducing diploid organisms
results in daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell
ex. humans have a diploid, 2n=46→meiosis produces sperm and eggs that are haploid n=23
involves two rounds of division
meiosis I and meiosis II
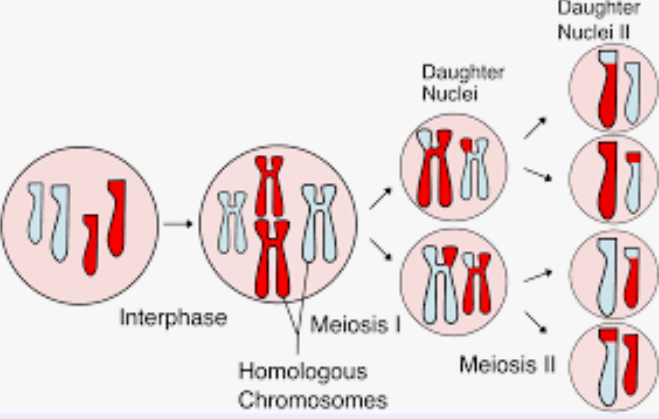
Mitosis vs Meiosis
Mitosis- occurs in somatic cells, 1 division, results in 2 diploid daughter cells, daughter cells are genetically identical
Meiosis- forms gametes(sperm/egg), 2 divisions, results in 4 haploid daughter cells, each daughter cells is genetically unique
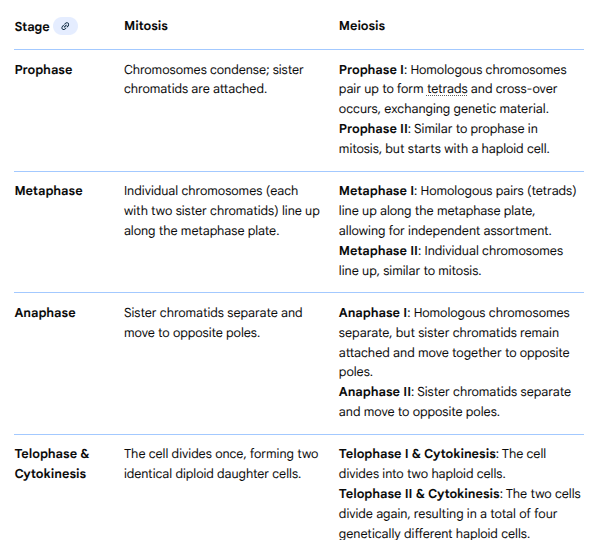
Key events in meiosis
3 key events in meiosis that are unique
Prophase I- synapsis and crossing over
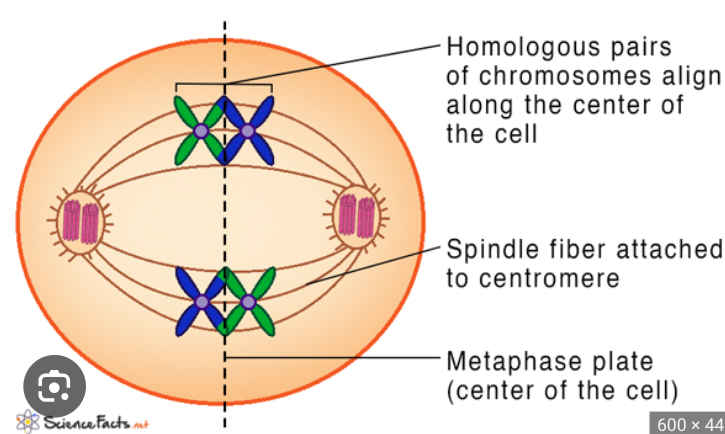
Metaphase I- tetrads (homologous pairs) line up at the metaphase plate
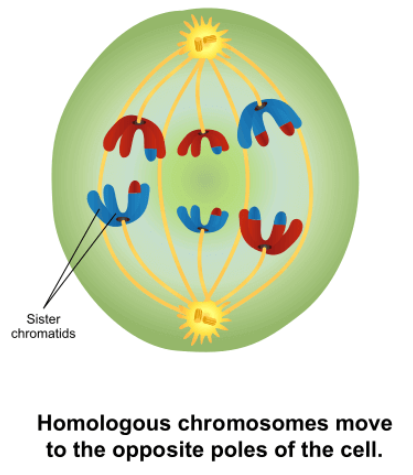
Anaphase I- homologous pairs separate
Meiosis I
Interphase→Prophase I→Metaphase I→Anaphase I→Telophase I and Cytokinesis
Interphase
cell goes through G1, S(DNA is copied), and G2
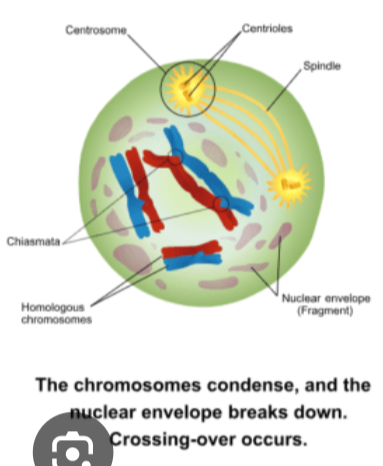
Prophase I
homologous chromosomes condense and pair up in a process known as synapsis
the homologous pairs (tetrads) are held together by a protein framework called the synaptonemal complex
meiotic spindle begins to form
centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
nuclear envelope breaks down
crossing over (recombination): DNA is exchange between the non-sister chromatids
-physical X-shaped connections where sites of recombination/crossing over occurred are called chiasmata
-produces recombinant chromatids, every chromatid that is produced by a unique combinations of DNA
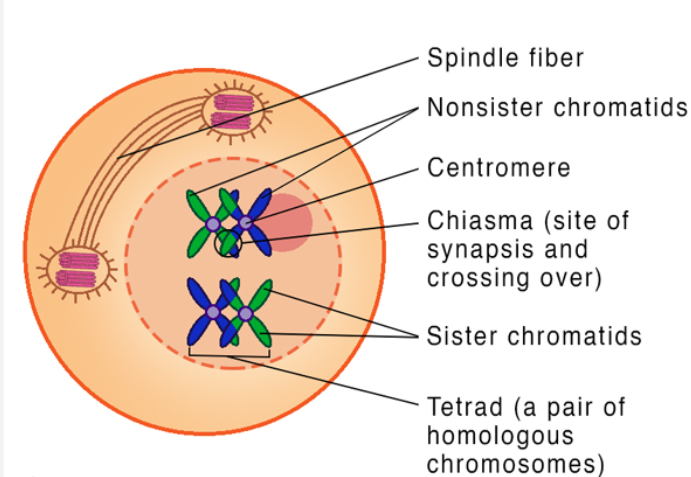
Metaphase I
independent orientation- meiotic spindle fibers align tetrads at the metaphase plate
chromosomes can independently orient themselves in 8 million different ways here
Anaphase I
pairs of homologous chromosomes separate as meiotic spindle fibers pull them towards poles
sister chromatids are still attached
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
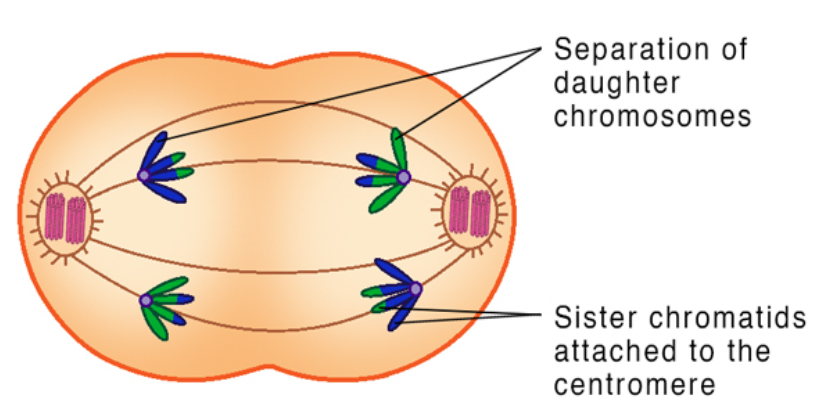
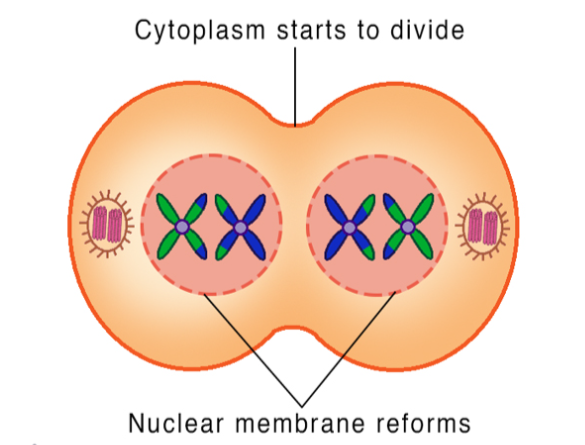
meiotic spindle breaks down
new nuclear envelope develops
cleavage furrow or cell plate forms
cytokinesis occurs
there is now a haploid set of chromosomes in each daughter cell
Meiosis II
prophase II→metaphase II→anaphase II→ telophase II and cytokinesis
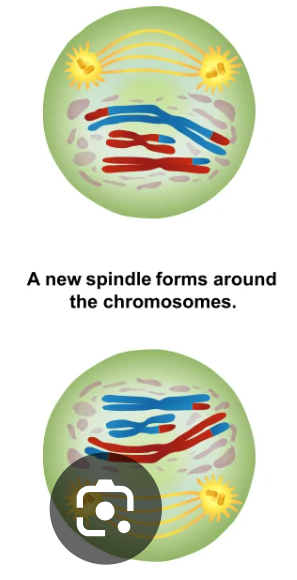
Prophase II
no crossing over
meiotic spindle forms
sister chromatids connected at the centromere attach to meiotic spindle
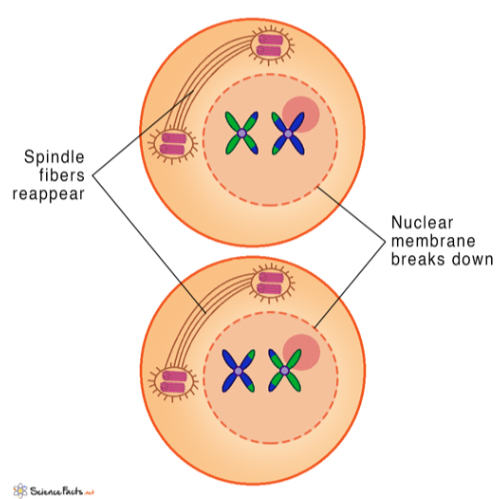
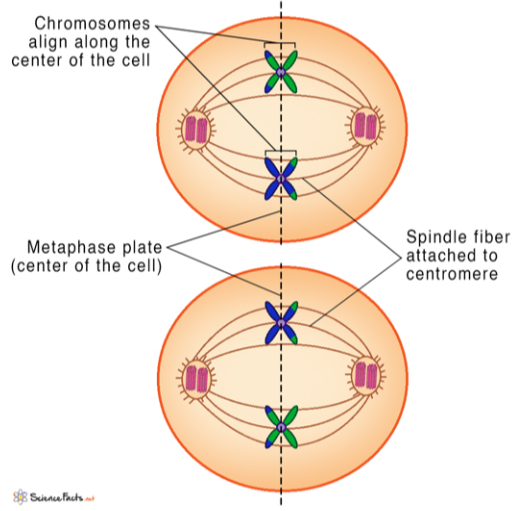
Metaphase II
chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate
because of crossing over in meiosis I, the chromatids are unique
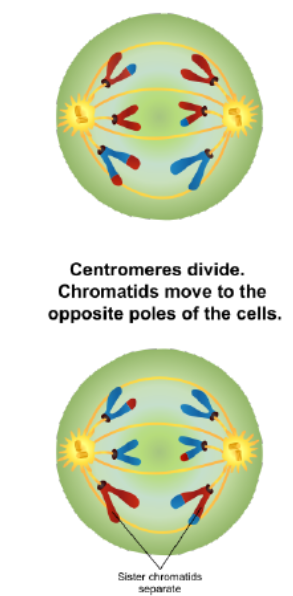
Anaphase II
proteins at the centromeres break down
sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles
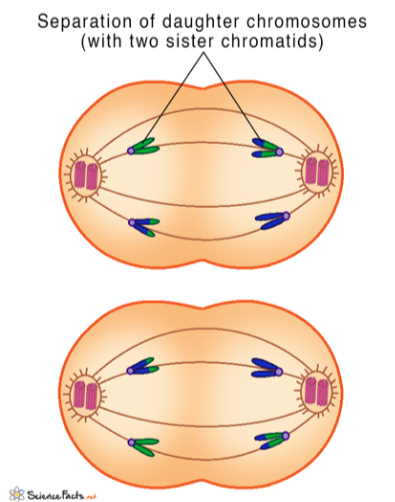
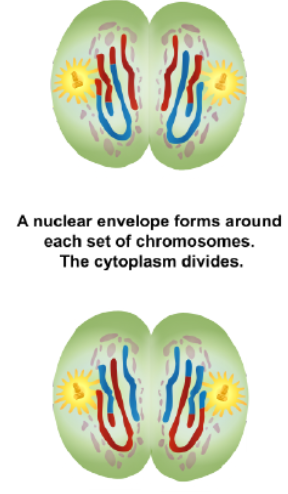
Telophase II and Cytokinesis
meiotic spindle breaks down
new nuclear envelope develops
cleavage furrow or cell plate forms
chromatids begin to decondense
cytokinesis occurs
4 genetically unique haploid cells
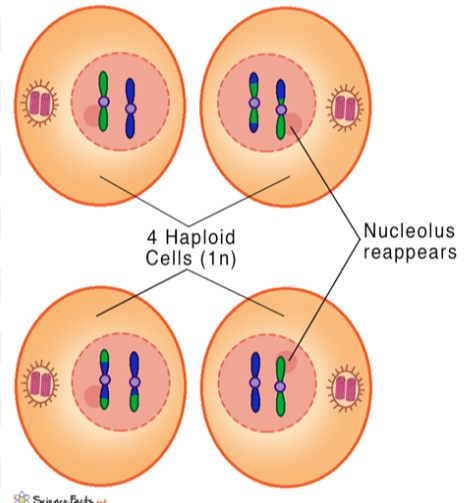
How does meiosis lead to genetic variation?
crossing over, independent assortment, random fertilization
Crossing over
happens in prophase I
produces recombinant chromosomes: they exchange genetic material
helps to create genetic variation
Independent assortment
chromosomes are randomly oriented along the metaphase plate during Metaphase I
each can orient with either the maternal or paternal chromosomes closer to a given pole
creates genetic variation
Random Fertilization
any sperm can fertilize any egg
creates genetic variation
Nondisjunction
when homologous chromosomes in meiosis I or sister chromatids in meiosis II separate incorrectly and the resulting gametes are not haploid
the gametes may carry an extra chromosome(n+1) r lack one altogether(n-1)
ex. down syndrome, 3 copies of chromosomes 21