Respiratory Anti-Virals
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
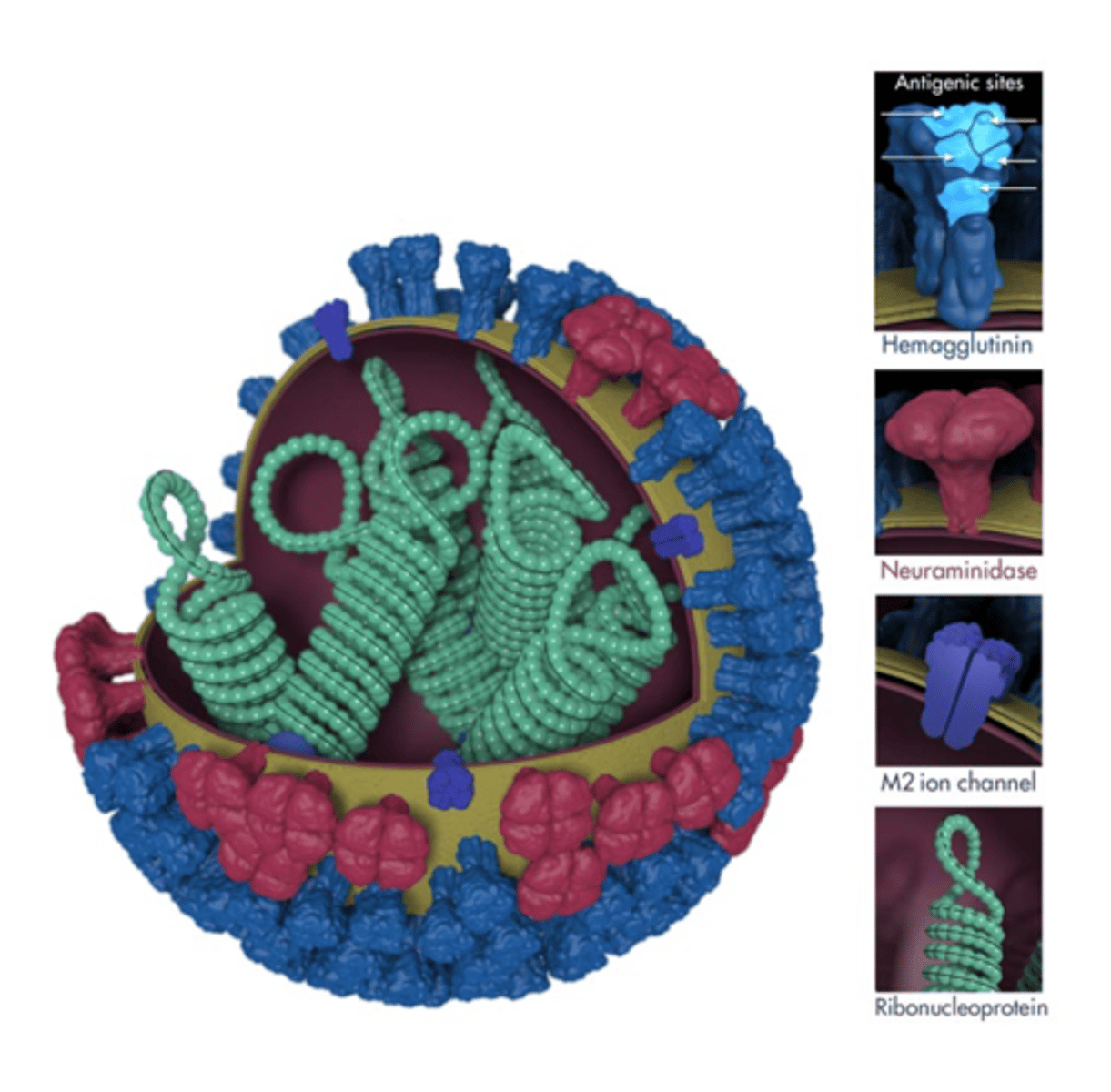
Influenza Virus
Hemagglutinin (16) and neuraminidase (9) are the target for the flu vaccine.
Neuraminidase promote viral spreading and infection:
• Enable release of virions
• Cleave sialic acid residues from mucus
M2 proton ion channel: allow the acidification of the interior of the virion in influenza A (NB in influenza B).
Neuraminidase Inhibitors - Drugs
• Oseltamivir (oral)
• Zanamivir (inhaled)
• Peramivir (IV)
Oseltamivir, Zanamivir, Peramivir - Mechanism of Action
• Inhibit the enzyme neuraminidase in influenza A and B virus.
• Blocks release of progeny virion.
Neuraminidase Inhibitors
Oseltamivir, Zanamivir, Peramivir - Therapeutic Use
Seasonal influenza who have been symptomatic for NO more than 48 hours.
For 2024-2025, the CDC recommends use of oseltamivir (oral), zanamivir (inhaled), peramivir (IV) or baloxavir (oral) for treatment of outpatients with acute uncomplicated influenza.
Neuraminidase Inhibitors
Oseltamivir, Zanamivir, Peramivir - Side Effects & Toxicity
• Oseltamivir: nausea, vomiting, and headache.
• Zanamivir: cough, bronchospasm.
• Peramivir: diarrhea, although serious rare skin or hypersensitivity reactions.
*All neuraminidase inhibitors increase the risk of hallucinations, delirium, and abnormal behavior.
Neuraminidase Inhibitors
Polymerase Acid Endonuclease Inhibitor - Drugs
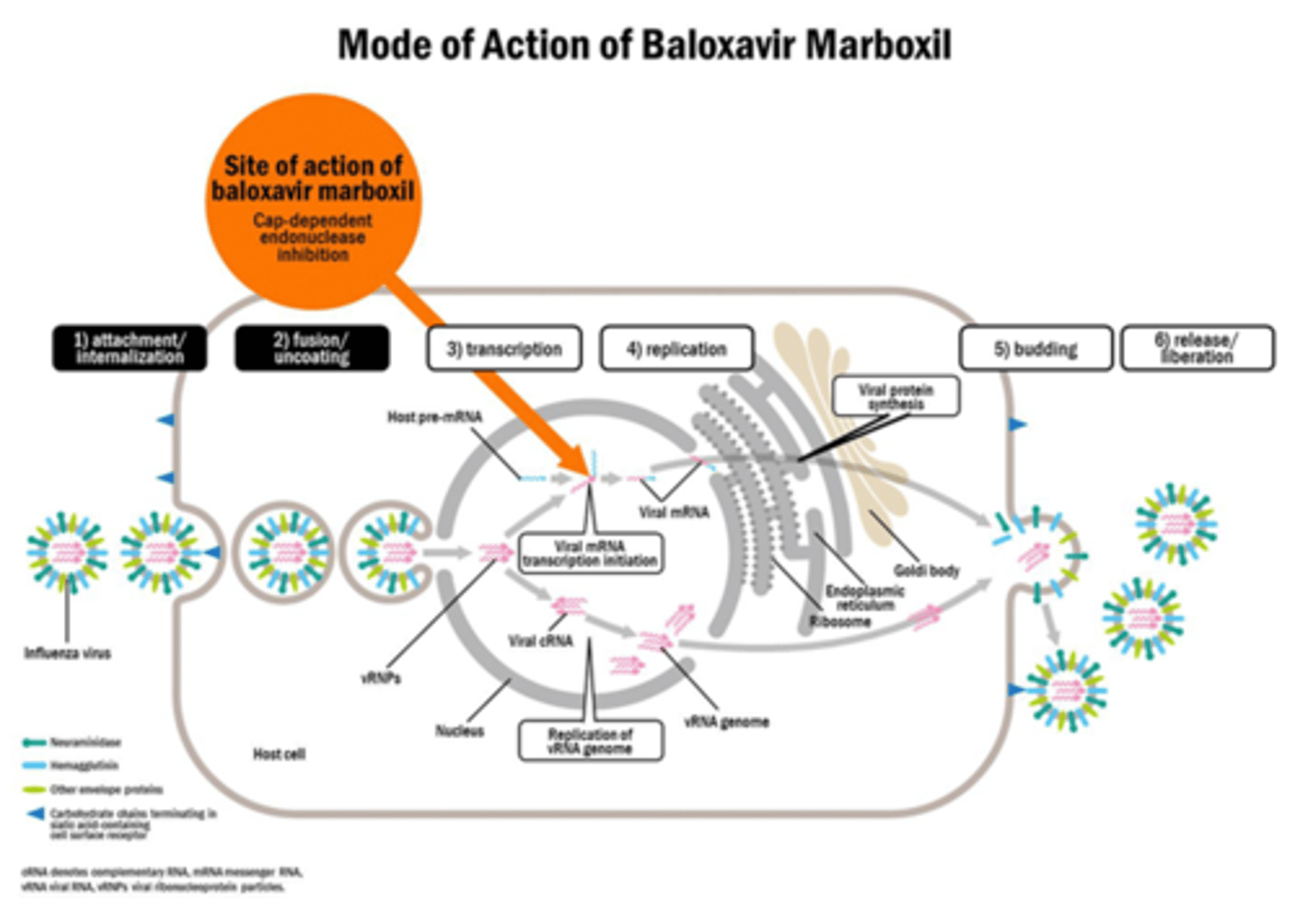
Baloxavir marboxil (single pill oral)
Baloxavir marboxil - Mechanism of Action
Cap-Dependent Endonuclease (CEN) Inhibitor
Polymerase Acid Endonuclease Inhibitor
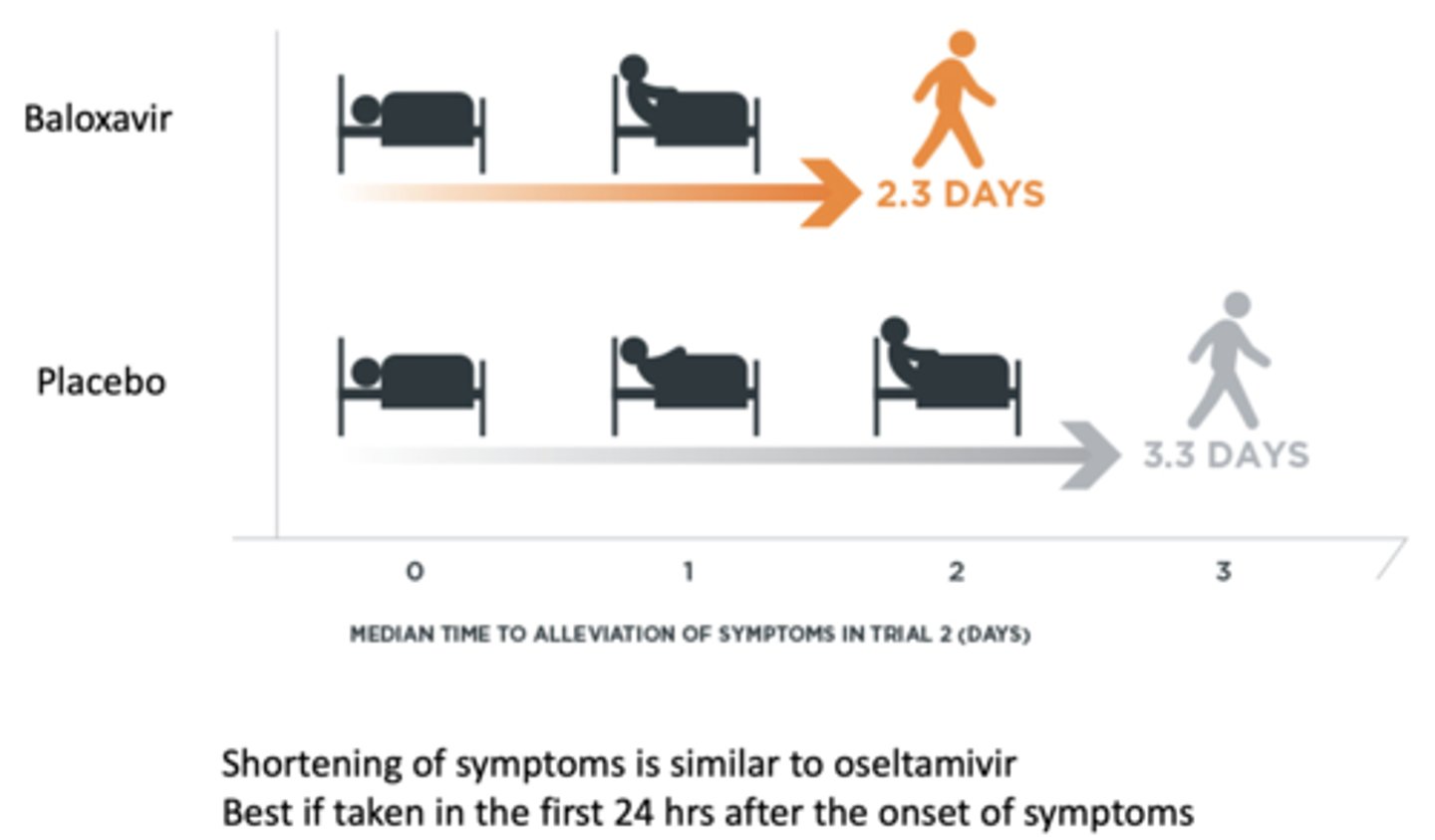
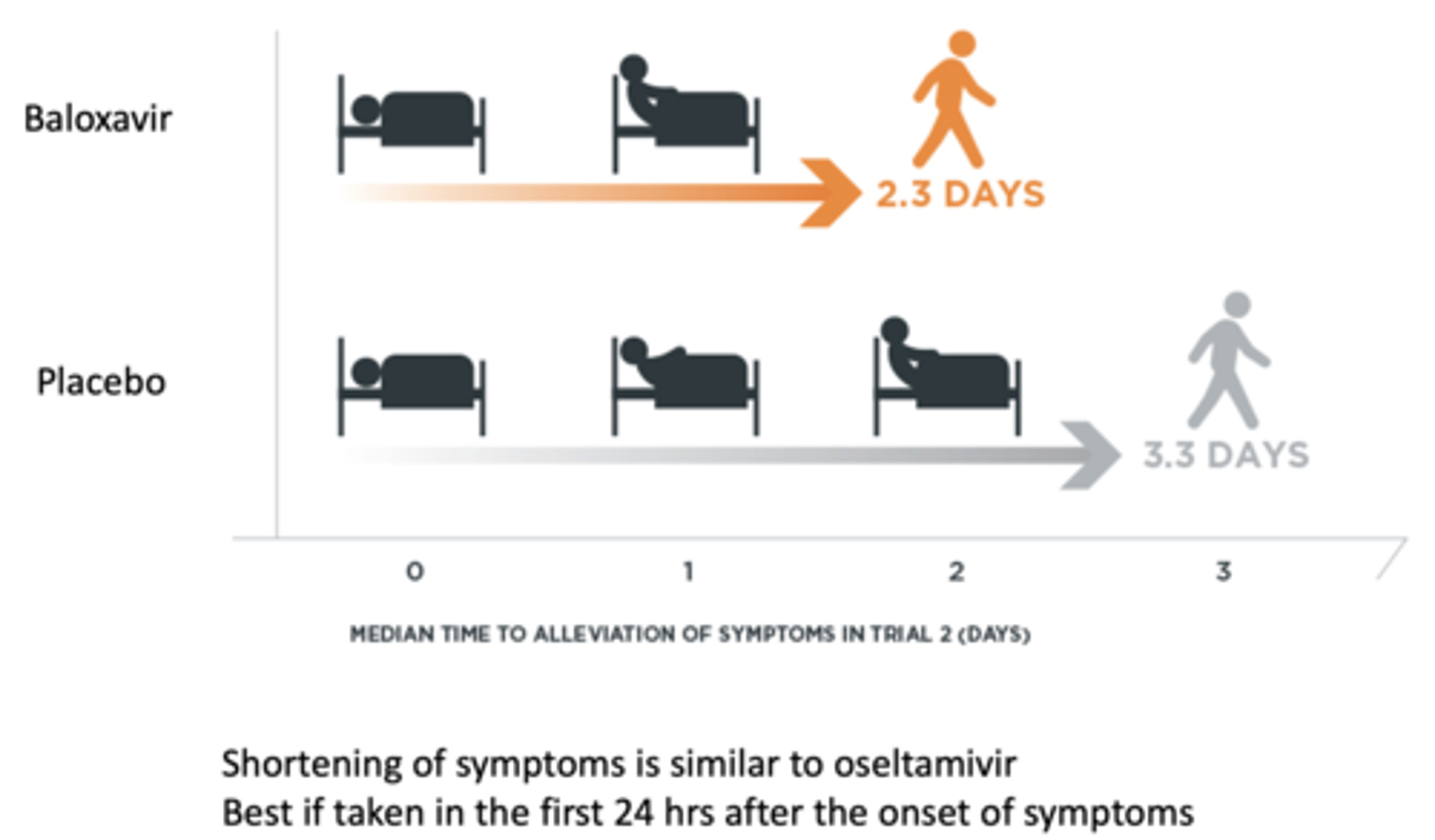
Baloxavir marboxil - Therapeutic Use
• Single dose oral treatment of acute uncomplicated flu
• Active against influenza A and B.
Polymerase Acid Endonuclease Inhibitor
Baloxavir marboxil - Side Effects & Toxicity
Well tolerated, none more common than placebo in clinical trials.
*Less side effects than oseltamivir.
Polymerase Acid Endonuclease Inhibitor
Synthetic Guanosine Analogue - Drugs
Ribavirin
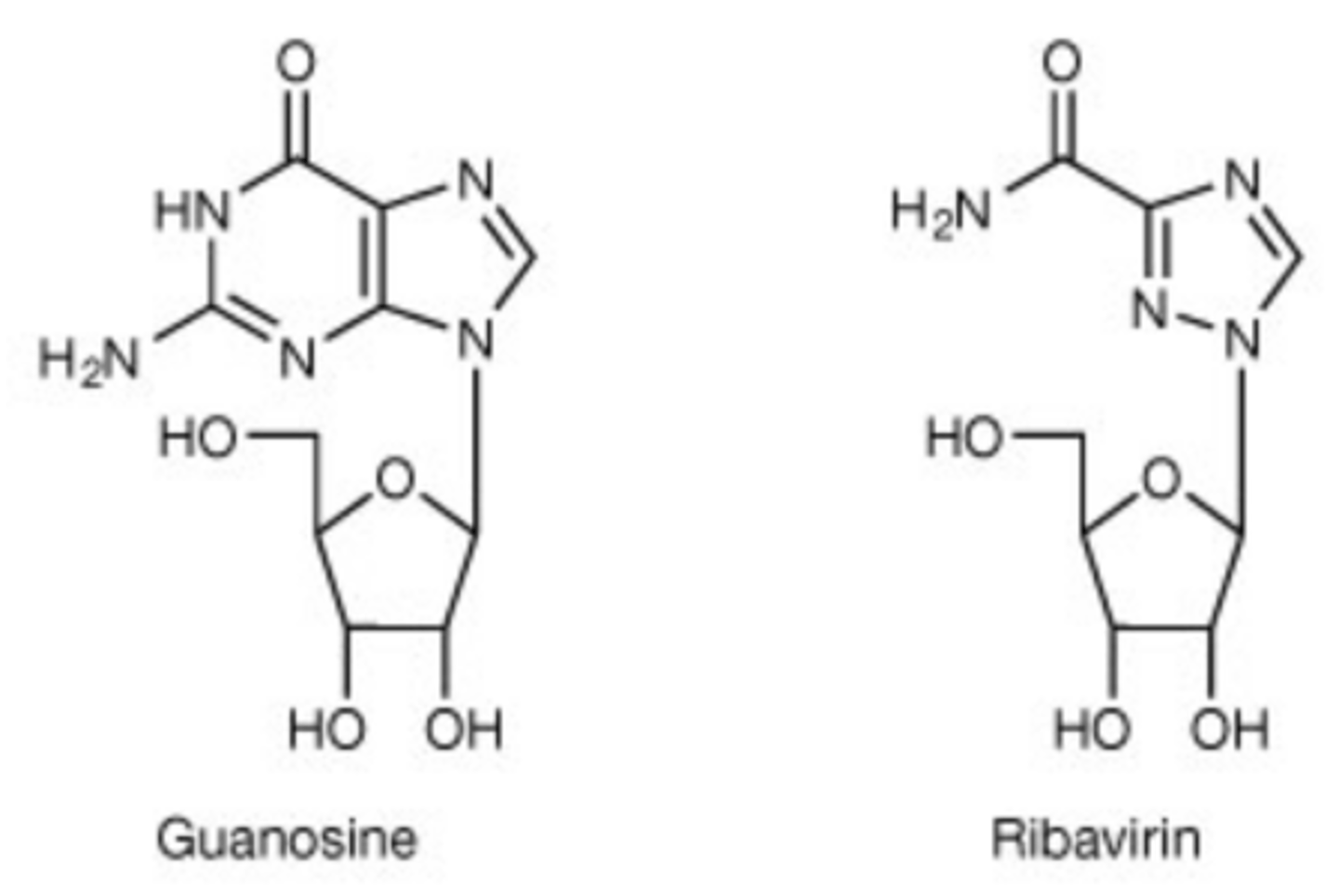
Ribavirin - Mechanism of Action
Inhibits replication of RNA and DNA viruses by inhibiting the formation of guanosine triphosphate → blocks RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
Synthetic Guanosine Analogue
Ribavirin - Therapeutic Use
• Treatment of infections with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), hepatitis C, Lassa virus.
• Also used for the treatment of flu (not currently recommended by CDC).
Synthetic Guanosine Analogue
Ribavirin - Side Effects & Toxicity
Dose dependent transient anemia, elevated bilirubin.
Synthetic Guanosine Analogue
Adamantanes - Drugs
• Amantadine
• Rimantadine
Many strain of influenza are now resistant, and they are NOT recommended any more by the CDC. This could change in the future based on future re-emergence of susceptible virus.
Adamantanes
Amantadine, Rimantadine - Mechanism of Action
Block the M2 proton ion channel and block replication
active against influenza A ONLY (not influenza B, M2 is absent and replaced by NB).
Adamantanes
Amantadine, Rimantadine - Therapeutic Use
• Prevention and treatment of influenza.
• Amantadine: Parkinson disease (increase in dopamine release?)
Adamantanes
Amantadine, Rimantadine - Side Effects & Toxicity
• Gastrointestinal: nausea, anorexia
• Central nervous system: nervousness, difficulty in concentrating, insomnia, light-headedness
• Serious: marked behavioral changes
- Delirium, hallucinations, agitation, and seizures (alteration of dopamine?)
• Teratogenic
Adamantanes
C) within 48 hours after the onset of the fever
Several colleagues of a 26-year-old medical student living on campus have developed a flu. This student has become sick with fever and muscle ache. You advise this student that the best time to initiate a treatment including oseltamivir is:
A) 48 hours before the onset of the symptom
B) within 48 hours after he/she returns from break
C) within 48 hours after the onset of the fever
D) after a minimum of 48 hours of coughing and/or fever
E) useless if he/she has been vaccinated this year against the flu
F) immediately
COVID-19 – SARS-CoV-2
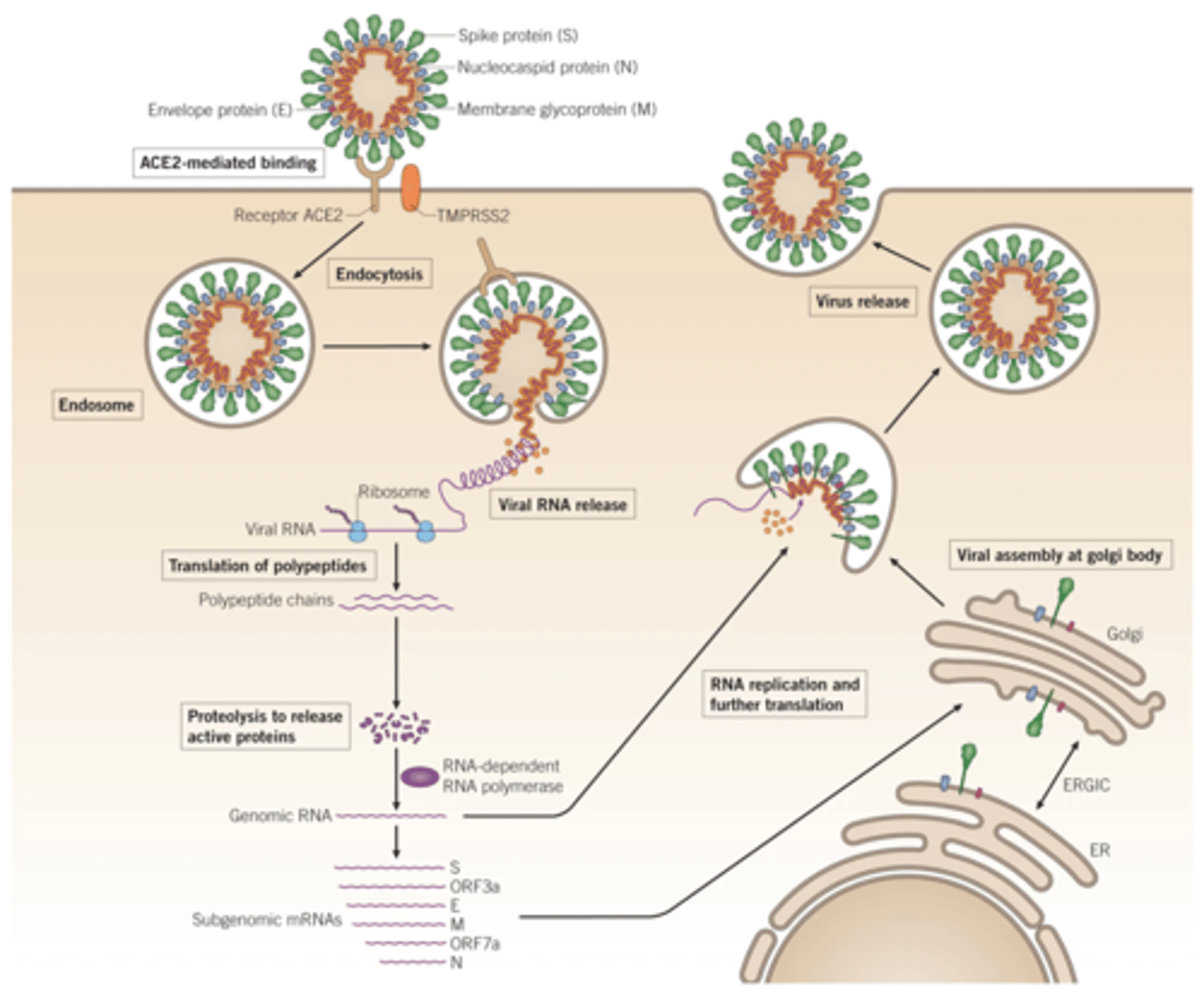
Protease Inhibitor - Drugs
Ritonavir-Boosted Nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) (oral)
Ritonavir-Boosted Nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) - Mechanism of Action
Nirmatrelvir
- 3C-like protease (3CLPRO) inhibitor → inhibit viral replication.
Ritonavir
- A potent inhibitor of cytochrome P450 CYP3A4.
Protease Inhibitor
Ritonavir-Boosted Nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) - Therapeutic Use
Mild-to-moderate COVID-19 (>12yo) who are at risk of severe illness.
Protease Inhibitor
Ritonavir-Boosted Nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) - Side Effects & Toxicity
• Dysgeusia (taste disorder that causes an altered sense of taste, where foods taste metallic, sour, bitter, or sweet)
• Diarrhea, hypertension, and myalgia.
• Anaphylaxis, hepatotoxicity
Protease Inhibitor
Ritonavir-Boosted Nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid) - Drug Interaction
Interaction with the CYP3A4 inhibition and metabolism.
- CYP3A4 inducers decrease efficacy of paxlovid.
- CYP3A4 inhibitors increase the risk of toxicity of paxlovid.
- Drugs dependent on CYP3A4 for clearance can accumulate and become toxic.
Protease Inhibitor

Adenosine Triphosphate Analog
Remdesivir (IV)
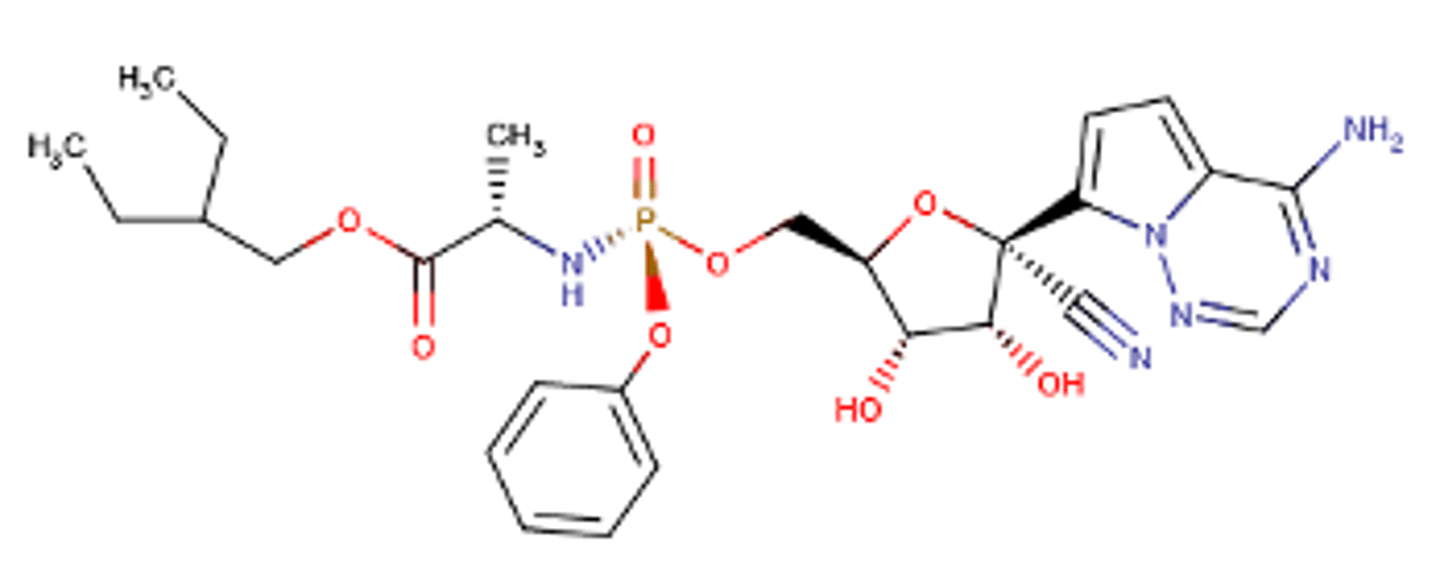
Remdesivir - Mechanism of Action
Inhibit of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase → termination of RNA transcription.
Adenosine Triphosphate Analog
Remdesivir - Therapeutic Use
• Remdesivir was originally investigated as a treatment for Ebola virus but has potential to treat a variety of RNA viruses including SARS-CoV-2.
• Should be started within 7 days of symptoms onset.
Adenosine Triphosphate Analog
Remdesivir - Side Effects & Toxicity
• Nausea, elevated transaminase
• Anaphylaxis
74% eliminated in the urine and 18% eliminated in the feces.
Adenosine Triphosphate Analog
Nucleotide Analogue - Drugs
Molnupiravir (oral)
Molnupiravir - Mechanism of Action
Prodrug hydrolyzed in N4-hydroxycytidine
→ phosphorylated in tissue to the active 5’-triphosphate form.
→ incorporated into the genome of new virions.
→ accumulation of inactivating mutations (viral error catastrophe).
Nucleotide Analogue
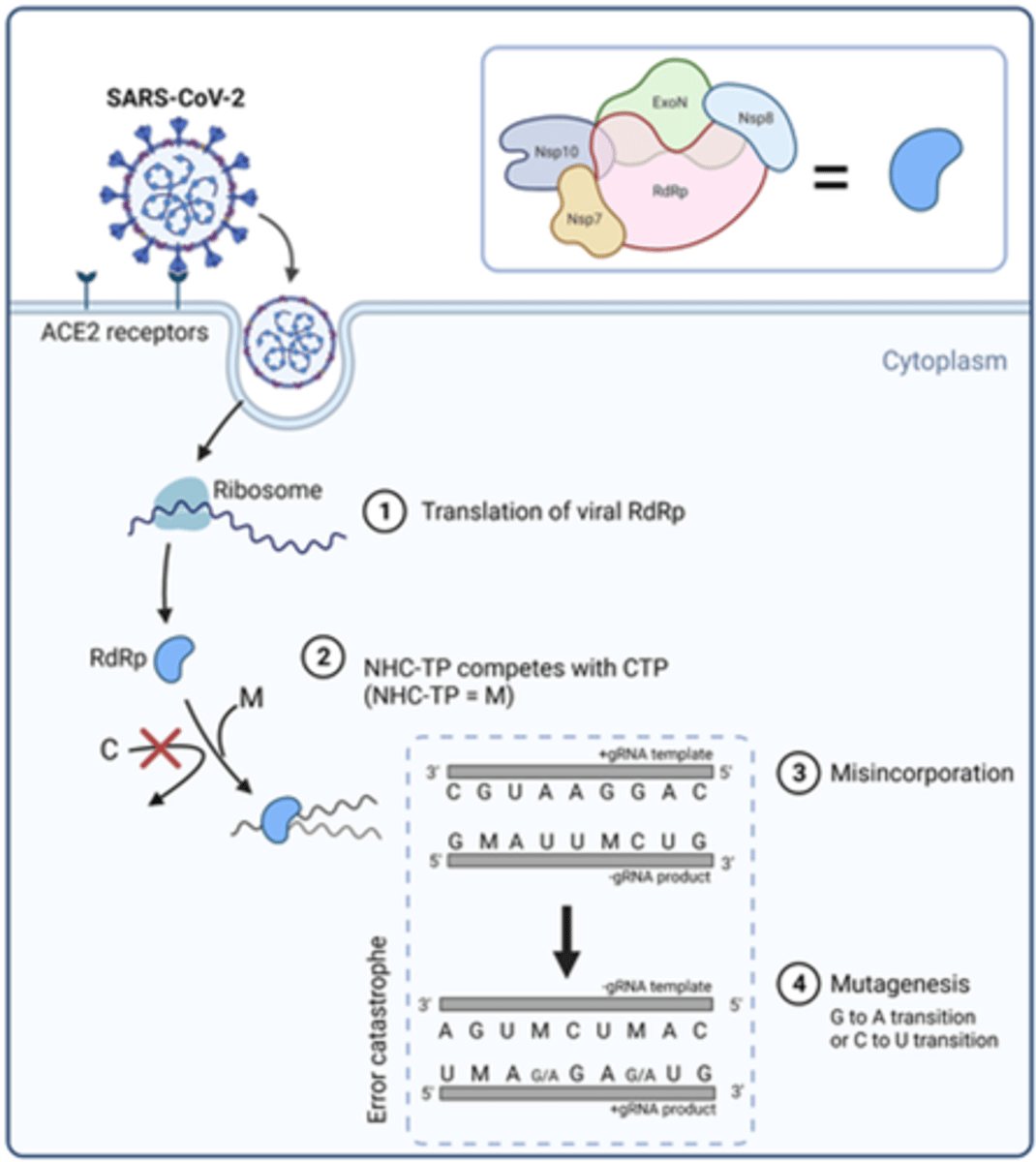
Molnupiravir - Therapeutic Use
• Activity against influenza, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2
• High-risk adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Nucleotide Analogue
Molnupiravir - Side Effects
• Diarrhea, nausea, dizziness
• Skin rash, anaphylaxis
Nucleotide Analogue
Monoclonal Antibody - Drugs
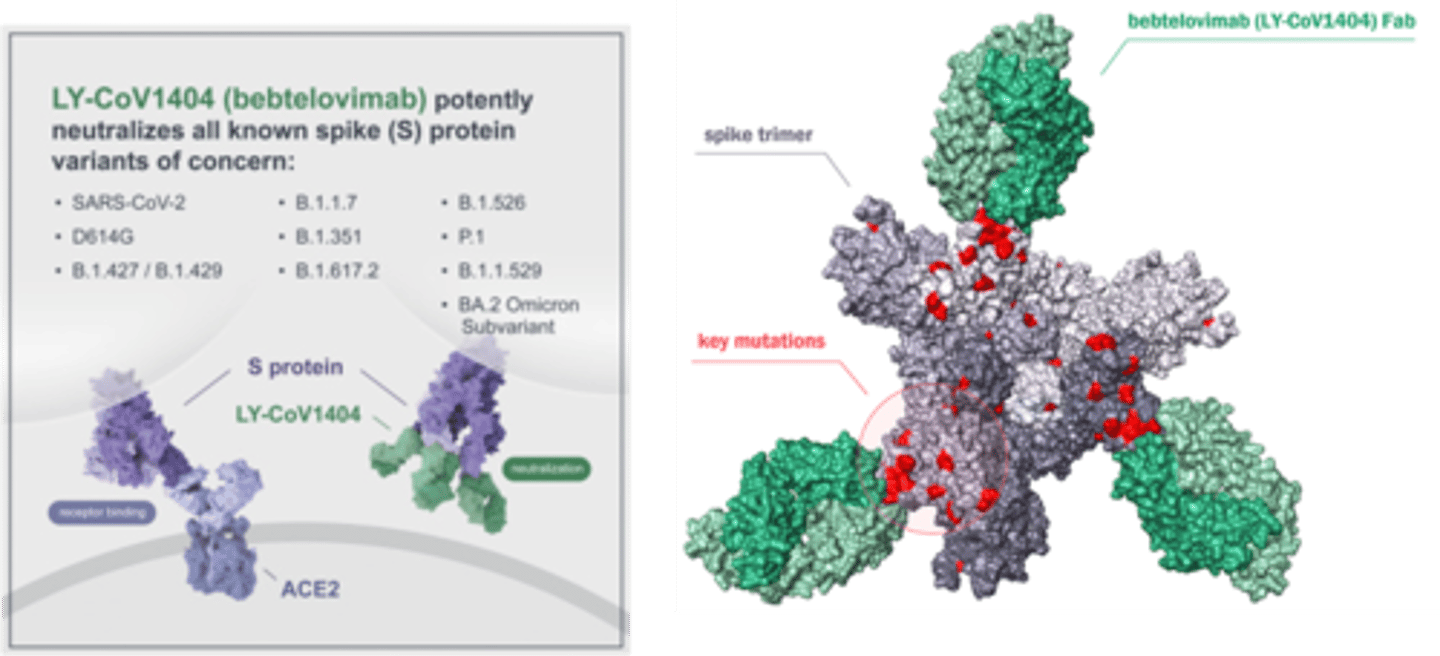
Bebtelovimab
(NOT IN USE ANYMORE)
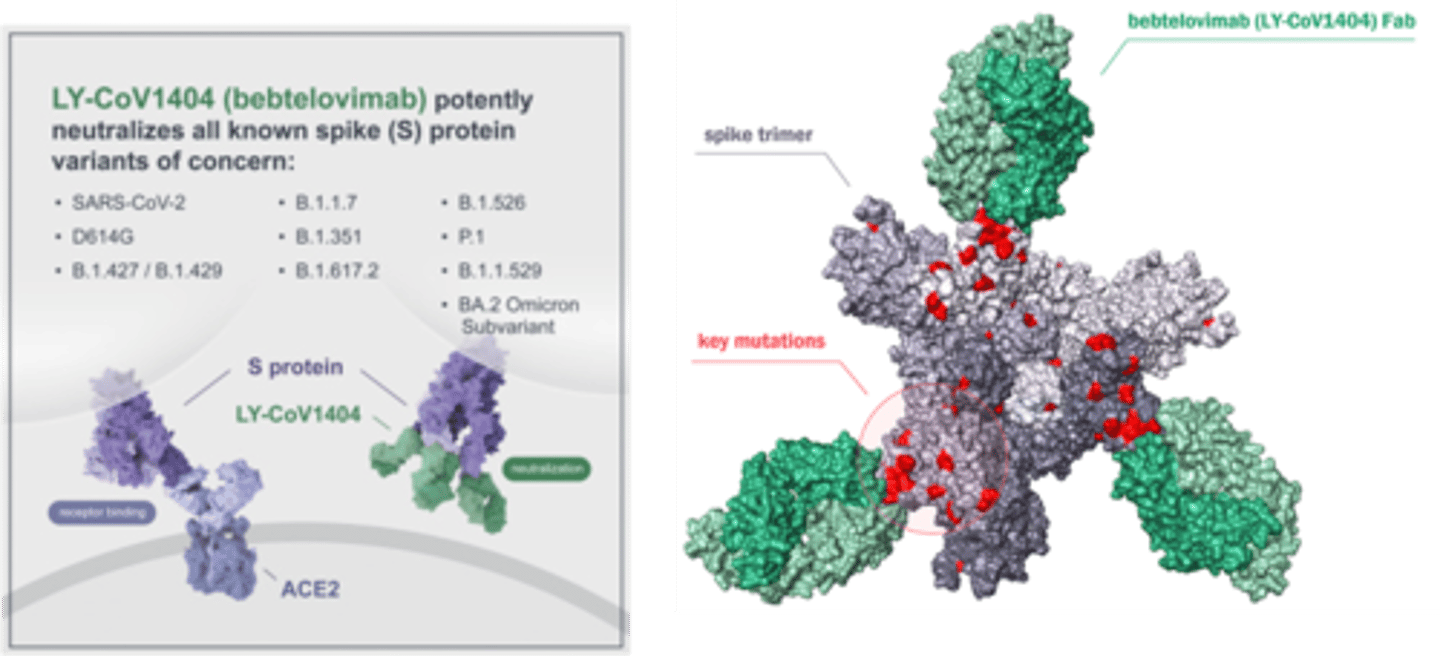
Bebtelovimab - Mechanism of Action
Neutralizing human mAb that binds to the spike protein.
Monoclonal Antibody (NOT IN USE ANYMORE)
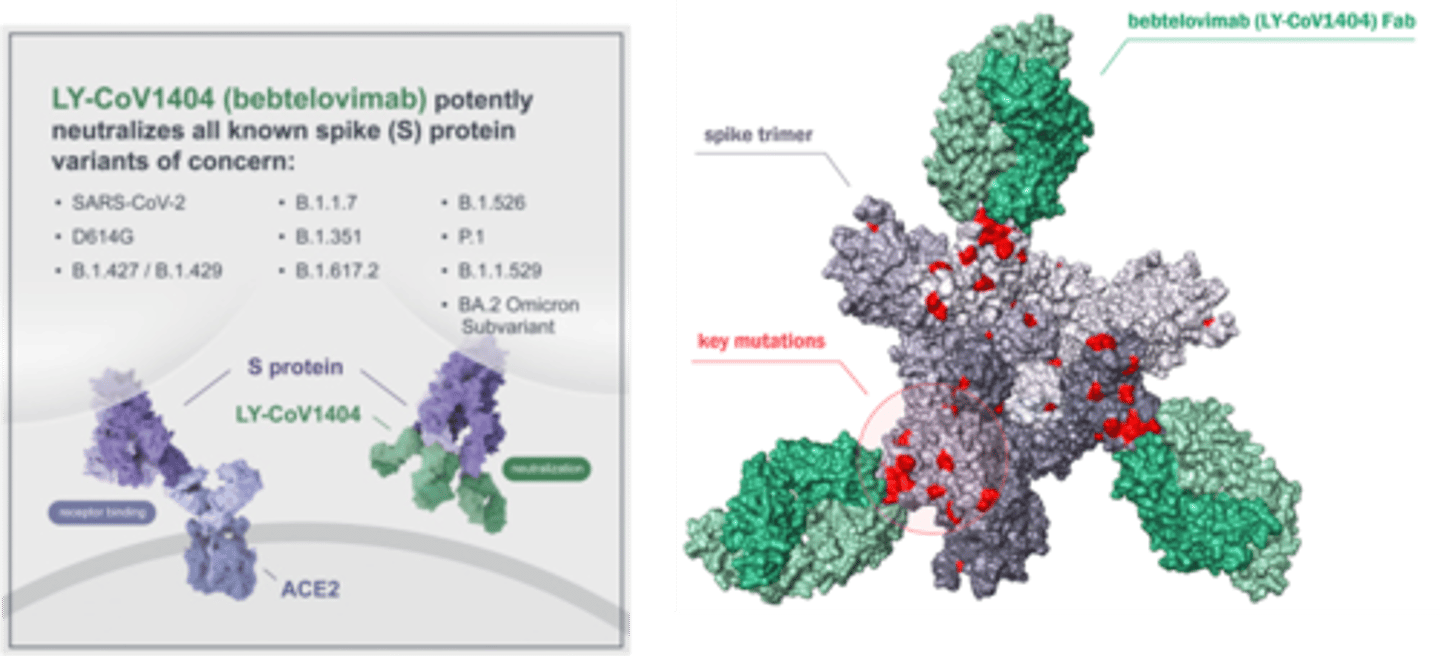
Bebtelovimab - Therapeutic Use
Mild to moderate COVID-19 in non-hospitalized adults and pediatric patients aged ≥12 years and weighing ≥40 kg who are at high risk of disease progression.
Monoclonal Antibody (NOT IN USE ANYMORE)
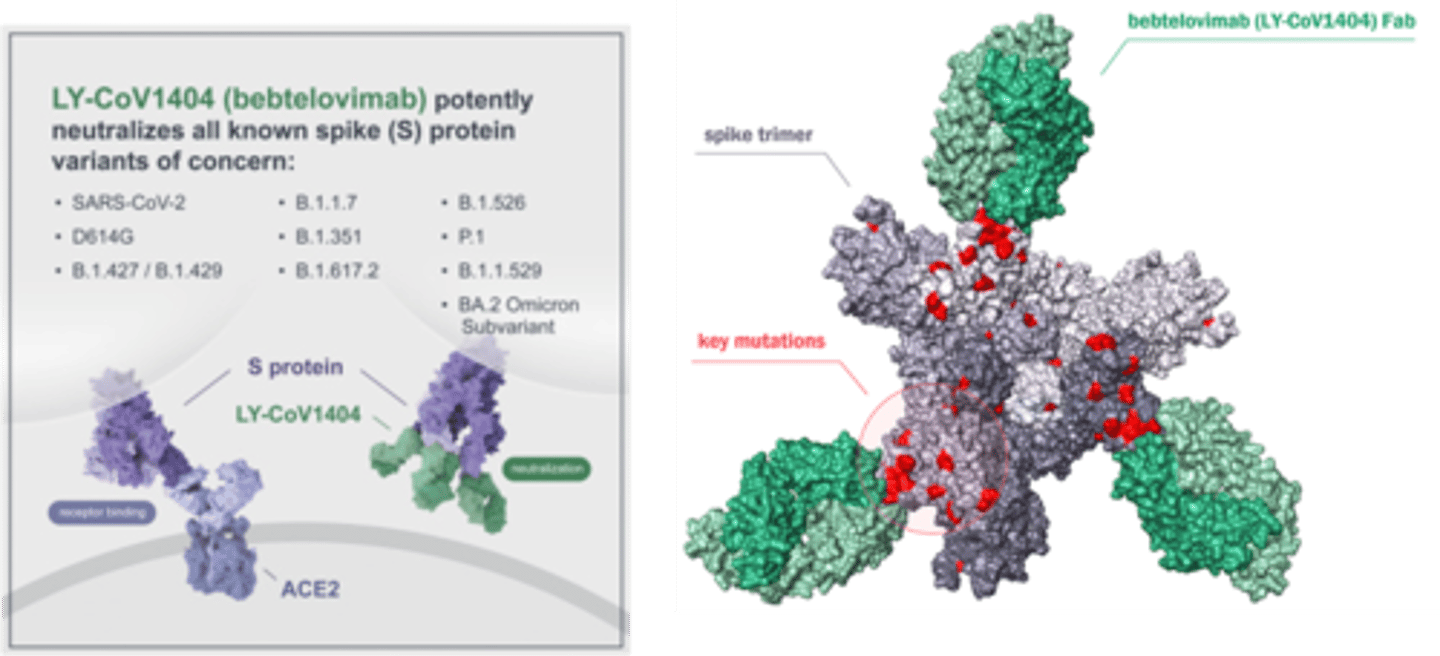
Bebtelovimab - Side Effects
Anaphylaxis
Monoclonal Antibody (NOT IN USE ANYMORE)