General Chemistry 2 ACS Final Review
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the 4 types of intermolecular forces listed from weakest to strongest?
London dispersion, dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding, ion-dipole
What effect does IMFs have on surface tension?
surface tension increases as strength of IMF increase
What effect does IMFs have on viscosity?
viscosity increases as strength of IMFs increase
What effect does IMFs have on boiling point?
boiling point increases as strength of IMFs increase
Which are miscible in water: polar or nonpolar compounds/liquids?
polar
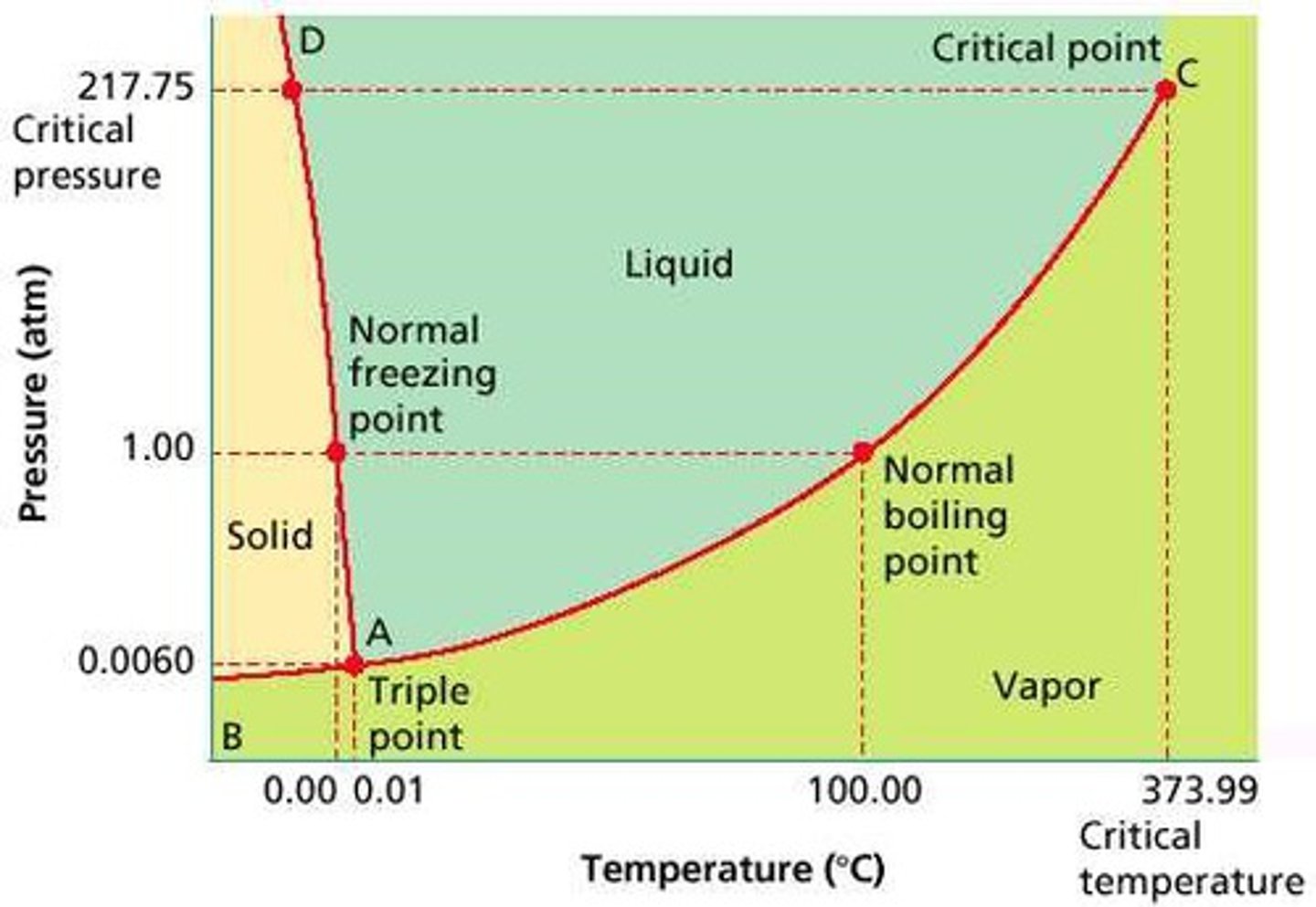
Draw a general phase diagram. Determine where the solid, liquid and gas phases reside. What are the "lines" called and what is the name of the other two significant points.
Solubility generally increases or decreases with increased temperature?
increases
What is dynamic equilibrium of a solution?
when rate of dissolution = rate of recrystallization
What factors effect the solubility of a gas?
temperature ( when temp increases, solubility decreases)
pressures (when pressure increases, solubility decreases)
what is molarity?
measurement of concentration
moles of solute/liters of solutuion
Which of the following are strong or weak acids?
1. HCl
2. HF
3. HBr
4. HCHO2
5. HNO3
1. strong
2. weak
3. strong
4. weak.
5. strong
Which of the following are strong or weak acids?
1. H2SO3
2. H2CO3
3. HI
4. HClO4
5. H2SO4
1. weak
2. weak
3. strong
4. strong
5. strong
what are the 6 most commonly found "strong" acids?
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4
Which of the following are strong or weak bases?
1. LiOH
2. NH3
3. CO3^2-
4. KOH
5. Sr(OH)2
1. strong
2. weak
3. weak
4. strong
5. strong
Which of the following are strong or weak bases?
1. HCO3^-
2. Ca(OH)2
3. NaOH
4. Ba(OH)2
5. C5H5N
1. weak
2. strong
3. strong
4. strong
5. weak
what are the 6 most commonly found "strong" bases?
LiOH, KOH, NaOH, Sr(OH)2, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2
what is mole fraction?
mol solute/mole solute+mole solvent
what is molality?
mol solute/kg solvent
what are 4 colligative properties
freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, vapor pressure lowering, osmotic pressure
what are factors that affect the rate of a reaction?
concentration of reactant particles, temperature, structure and orientation of particles
T/F the rate of a reaction can be predicted from just a balanced equation?
F
What does it mean if a rate reaction is zero order, first order or second order?
zero order: rate is independent on [reactants]
first order: rate proportional to [reactants]
second order: rate proportion to [reactants}^2
What is the 1/2 life equation for zero order rxn?
[Ao]/(2k)
What is the 1/2 life equation for first order rxn?
0.693/k
What is the 1/2 life equation for second order rxn?
1/(k [Ao])