CHEM 241 Chapter 4 Nomenclature of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all memory babyy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
bicyclic compounds (bicycloalkane)
two rings are fused on bridgehead carbons
example was pentalkane and hexalkane in a 3D-like structure
Recipe
mark bridgeheads
start with bridgeheads that substituents still get lowest number
(substituents first if necessary)bicyclo[# of C in longest chain ∙ # of C for second longest chain ∙ # of C for shortest path](# of C in bicycloalkane as parent chain)-ane
depends on substituents
-ane</mark></p><ul><li><p>depends on substituents</p></li></ul></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/723feb4e-a99b-4eca-9708-3d7ff655129d.jpg)
bridgehead carbons
two carbon atoms where two rings are fused together
Newman projection
visualization of the conformation of a chemial bond from front to back
look at chemical from certain orientation (eyeball)
take ALL atoms into account
draw front and back
noting that wedges are in front and dashes are behind page
dihedral angle (torsional angle)
the degree of angle separation between atoms that may be altered as the C-C bond rotates
staggered conformation
lowest energy conformation
most stable conformation
degenerate
the term for when staggered or eclipsed conformations have the same amount of energy
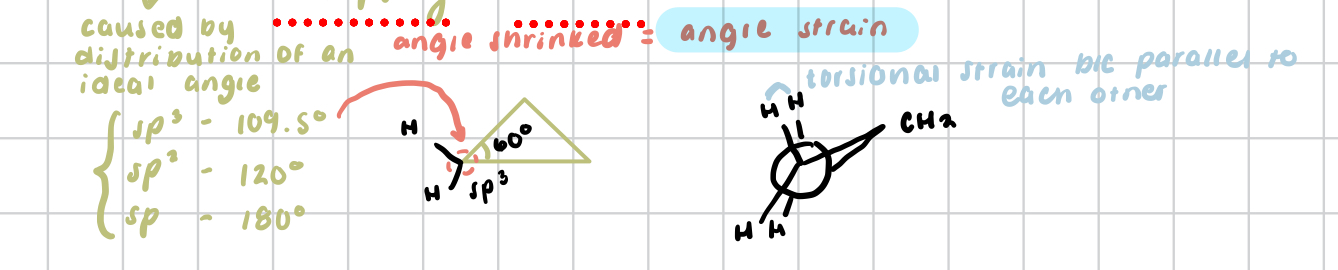
torsional strain/angle strain
the difference in energy (kJ/mol) between staggered and eclipsed conformations of ethane
for cycloalkanes, an increase in energy associated with a bond angle that has deviated from the preferred angle of 109.5°
therefore, 5-membered rings should contain almost no angle strain (in comparison to 4-membered 90° rings or 3-membered 60° rings)
cyclopropane
according to Bayer, the angle strain in this compound is severe
some strain may be alleviated if orbitals bend outward, but may have increase in energy associated w/ inefficient overlap of orbitals
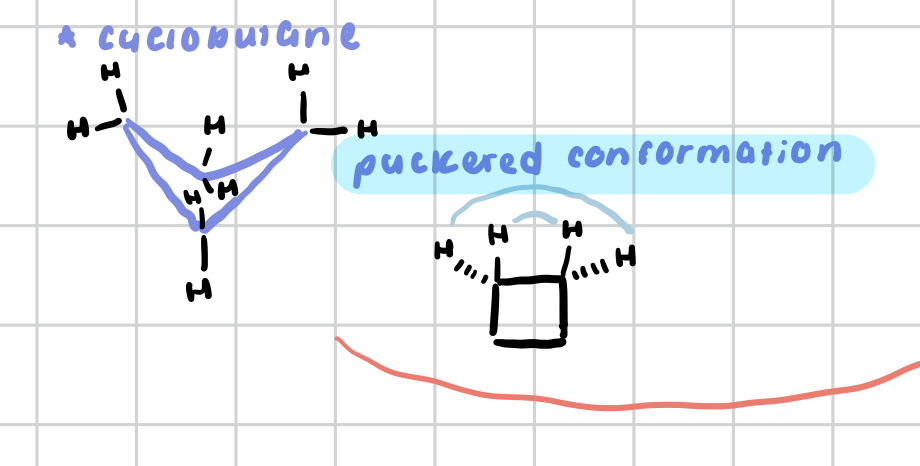
cyclobutane
has less angle strain than cyclopropane, but has more torsional strain due to 4 sets of eclipsing H’s
to alleviate torsional strain, can adopt a slightly puckered conformation w/o gaining too much angle strain
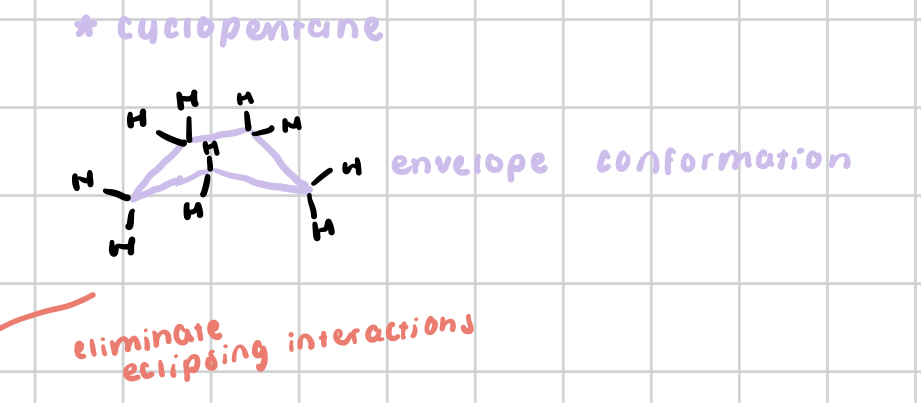
cyclopentane
has an envelope conformation as well as less angle strain than cyclobutane or cyclopropane
reduces much of its torsional strain by adopting envelope conformation
still experiences some strain, but has less total strain than cyclopropane or cyclobutane
cyclohexane
the most important conformation that can adopt 2 types of conformation:
chair conformation = most stable conformation, all substituents would be staggered
boat conformation = still may experience torsional strain due to flagpole interactions (which may lead to twist boat conformation)
bond angles fairly close to 109.5° and possess little angle strain
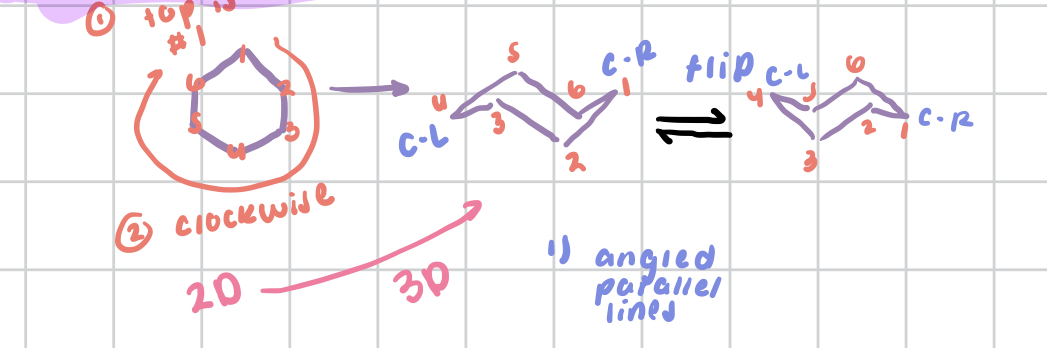
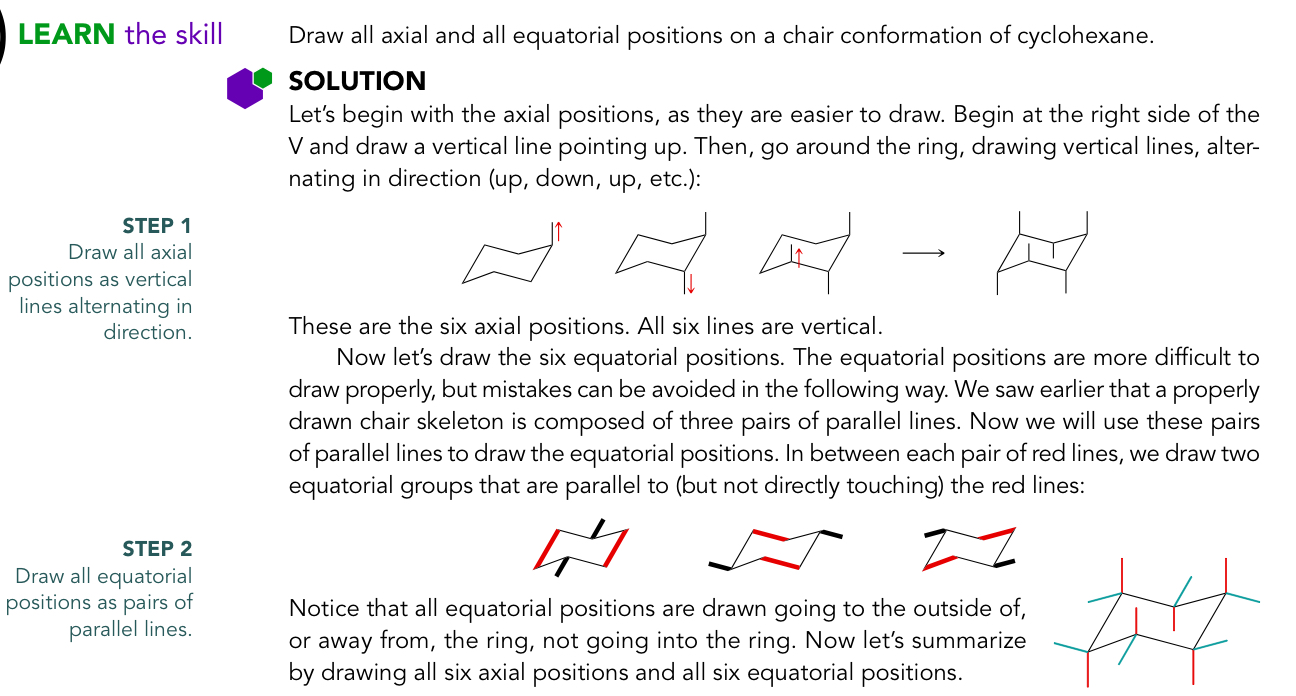
drawing both chair conformations at once, draw the double line “V’s” and the spikes
same rules apply when assigning locants to 2D structure
substituents get lowest locants
Number the chair conformations
starting at point on the right, go clockwise around the chair
using the 2D structure as a guide (wedge = up, dash = down) draw the substituents as axial or equatorial
pay attention to orientation of locant on chair
if asked for most stable chair conformation, will be structure with more equatorial substituents (less axial)
due to 1,3-diaxial interactions causing the chair conformation to be higher in energy when substituent is in the axial position
Recipe for drawing chair conformations
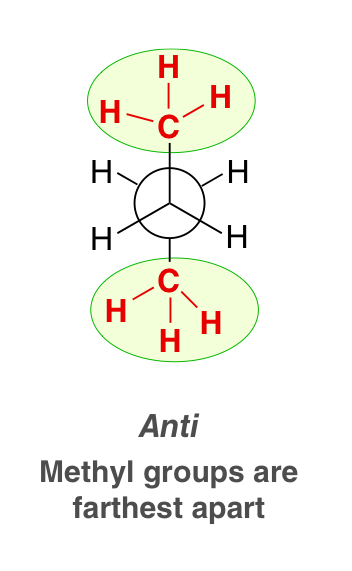
anti-conformation
the conformation with a dihedral angle of 180°
represents the lowest energy conformation
in butane, would be the conformation when the methyl groups are farthest apart
gauche interaction
an unfavorable energy conformation (steric interaction) where in butane, the methyl groups in staggered conformations are next to each other, repel each other, which cause an increase of energy

eclipsed conformation
highest energy conformation
most unstable conformation
axial position
substituents either straight up or down on chair conformation
equatorial position
substituents on sideway on chair conformation
equatorial
this is because substituents in the axial position may experience steric interactions called flagpole interactions
The most stable chair conformation will contain more substituents that are in the ____________position.
alkanes
hydrocarbons that lack π-bonds
cycloalkanes
alkanes that contain a ring (if the longest C-chain is located as a ring)
substituents
simple or branched alkyl groups that will be apart from the parent chain
locant
the numbering of C along the parent chain to identify the “location” of each substituent
Id. the parent chain
choose the longest chain
choose the chain with the greater number of substituents
Id. and name the substituents
Number the parent chain and assign a locant to each substituent
give the 1st substituent with the lowest possible number, then where the second substituent has the lower number
Arrange the substituents alphabetically
place locants in front of each substituent
substituent prefixes are ignored when alphabetizing
ex. locant-substituent(-locant 2-substituent 2)parentname
Recipe for assigning alkane names
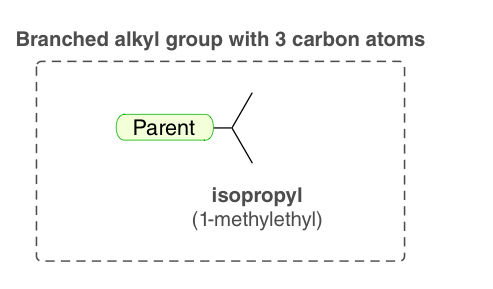
isopropyl (1-methylethyl)
an alkyl group bearing 3-C atoms that can only be branched one way
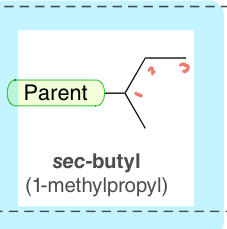
sec-butyl (1-methylpropyl)
4-C substituent with one bond to the parent chain and the C atoms are in a linear arrangement
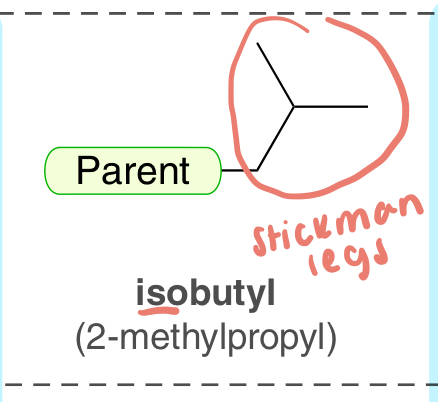
isobutyl (2-methylpropyl)
4-C substituent with a stickman legs
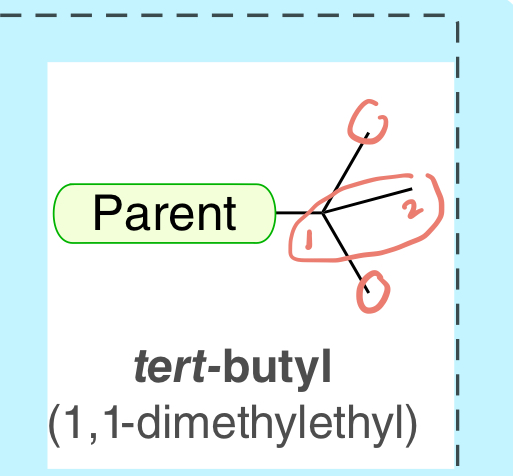
tert-butyl (1, 1-dimethylethyl)
4-C substituent with 3 tree branches
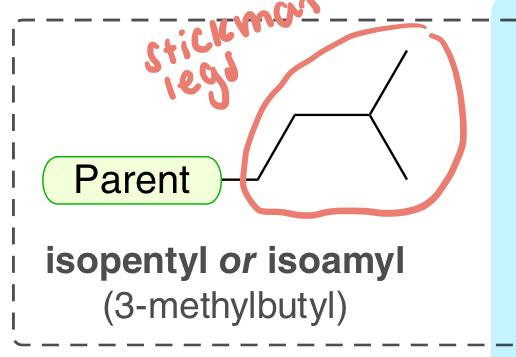
isopentyl (3-methylbutyl)
5-C substituent with stickman legs
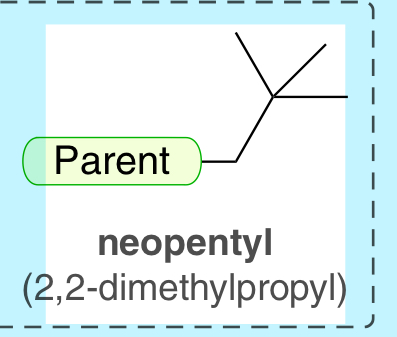
neopentyl (2,2-dimethylpropyl)
5-C substituent with 3 tree branches
cis
used to signify that the two groups (substituents) are on the same side of the ring
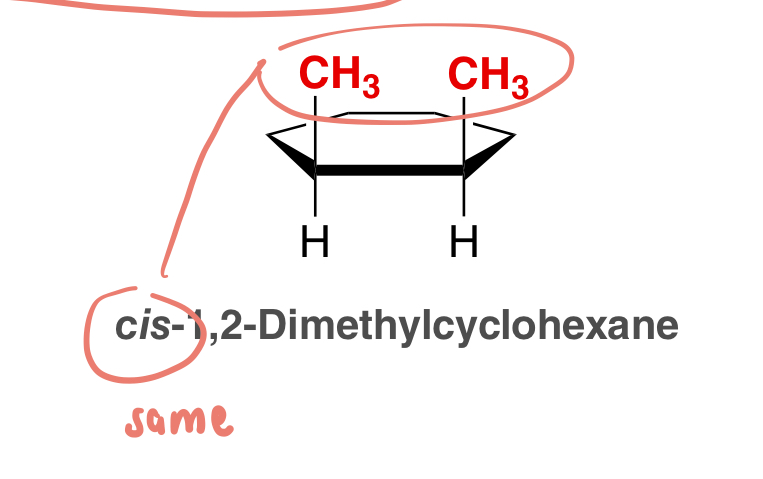
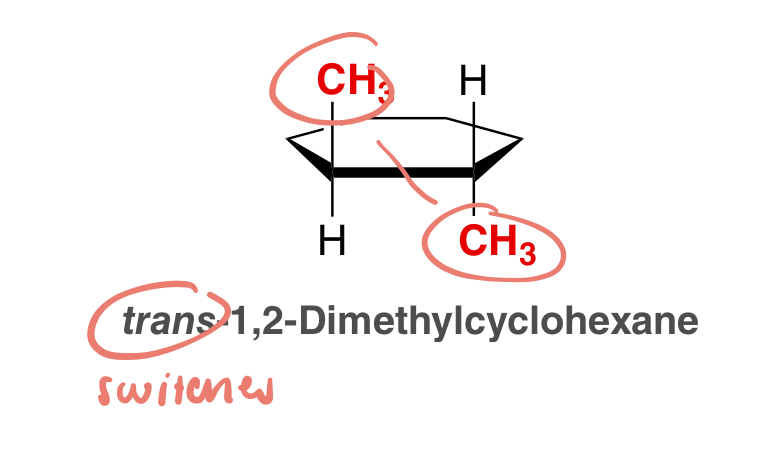
trans
used to signify that the two groups (substituents) are on opposite sides of the ring
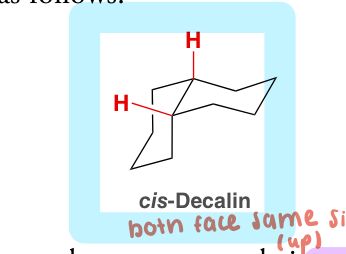
decalin
a bicyclic system composed of 2 fused 6-member rings
cis-decalin and trans-decalin are stereoisometric (different compounds with different physical properties
cis-decalin
both substituents face the same side (both up or both down)
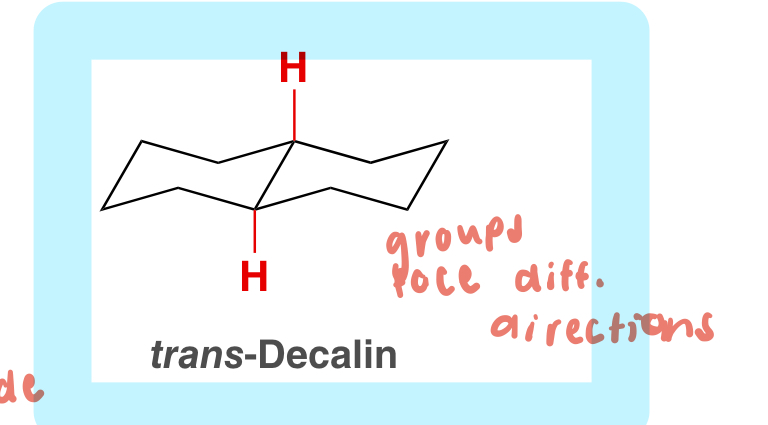
trans-decalin
both substituents face different directions (1 up and 1 down)
The less stable compound would be expected to have a larger heat of combustion. Straight chain alkanes would have greater heat given off during the reaction due to them being less stable (larger).
For heat of combustion, would a more stable or less stable compound be expected to have a larger heat of combustion?
branched alkanes are lower in energy (more stable) than straight chain alkanes