Biology IGCSE - Plant Nutrition
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
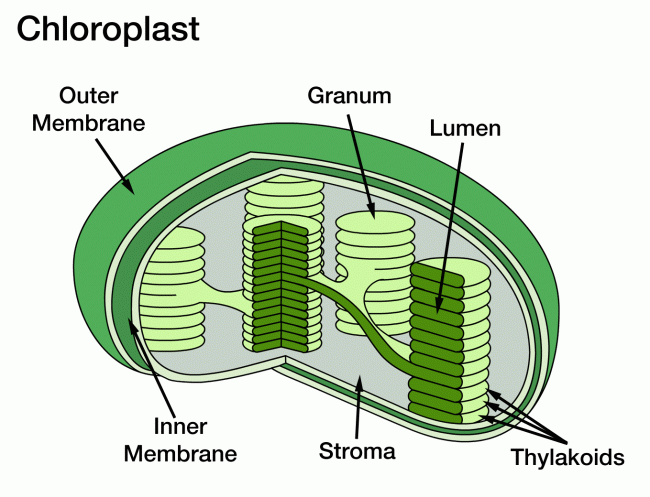
Chloroplast
Organelle found in cells of green parts of plants (leaves and stems) which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll where photosynthesis occurs
Chlorophyll
a green pigment that is found in chloroplasts
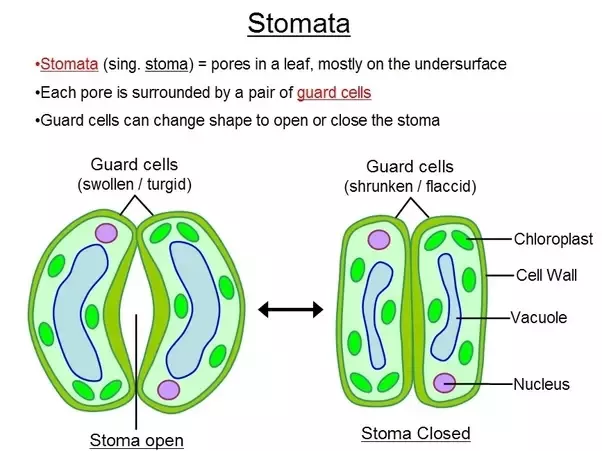
Stomata
Controls gas exchange in the leaf.
Stomata open
In light → guard cells absorb water by osmosis → become turgid (swollen) → stoma opens
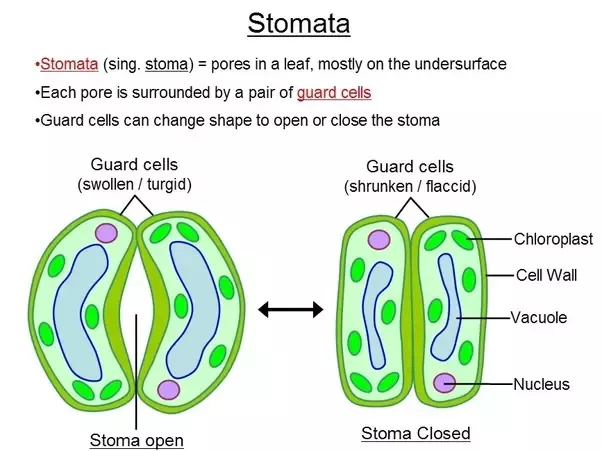
Stomata closed
In dark → guard cells lose water → become flaccid (shrunken) → stoma closes.
Photosynthesis
the process which plants manufacture carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light
Word equation for photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen (in the presence of light and chlorophyll)
Balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Need for chlorophyll in photosynthesis
Chlorophyll is vital for absorbing light energy → transfers into energy in chemicals → to synthesis carbohydrates
Need for light in photosynthesis
absorbed by chlorophyll → requires light energy to make carbon dioxide and water react to produce glucose and oxygen.
Need for carbon dioxide in photosynthesis
carbon dioxide is transformed into energy (sugars in the form of glucose) → used to synthesis glucose
Different uses and storage of glucose made in photosynthesis:
(a) starch as an energy store
(b) cellulose to build cell walls
(c) used in respiration for energy
(d) sucrose for transport in the phloem
(e) nectar to attract insects for pollination
Importance of nitrate ions for making amino acids
Use in plants: | Importance: | Symptoms of deficiency: |
making amino acids | needed to make protein → healthy growth | yellow leaves, weak growth |
Importance of magnesium ions for making chlorophyll
Use in plants: | Importance: | Symptoms of deficiency: |
making chlorophyll | forms central ion in chlorophyll molecule | yellow leaves between veins of leaves |
Limiting factor
something present in the environment in such short supply that it restricts photosynthesis from going faster. Light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration and temperature → limiting factors of photosynthesis.
Understand and describe the effects of varying light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
Light energy required for photosynthesisn → chlorophyll traps light energy → transfers it into chemical energy. Increase light intensity → increasing rate of photosynthesis
Levels off → another factor limiting photosynthesis or all chlorophyll is being used at any one time and cannot trap anymore light.
Understand and describe the effects of varying carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis
CO2 is a reactant → requirement of photosynthesis Increasing carbon dioxide concentration → increase rate which carbon is incorporated into chemical reaction → rate of photosynthesis increases
Levels off → another factor limiting photosynthesis.
Understand and describe the effects of varying temperatures on the rate of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis → controlled by enzymes
Reactions speed up → more kinetic energy.
After optimum temp. → enzymes are denatured → less frequent successful collisions
Hydrogen carbonate indicator with more CO2
More yellow → more CO2 present
Respiration happening more than photosynthesis
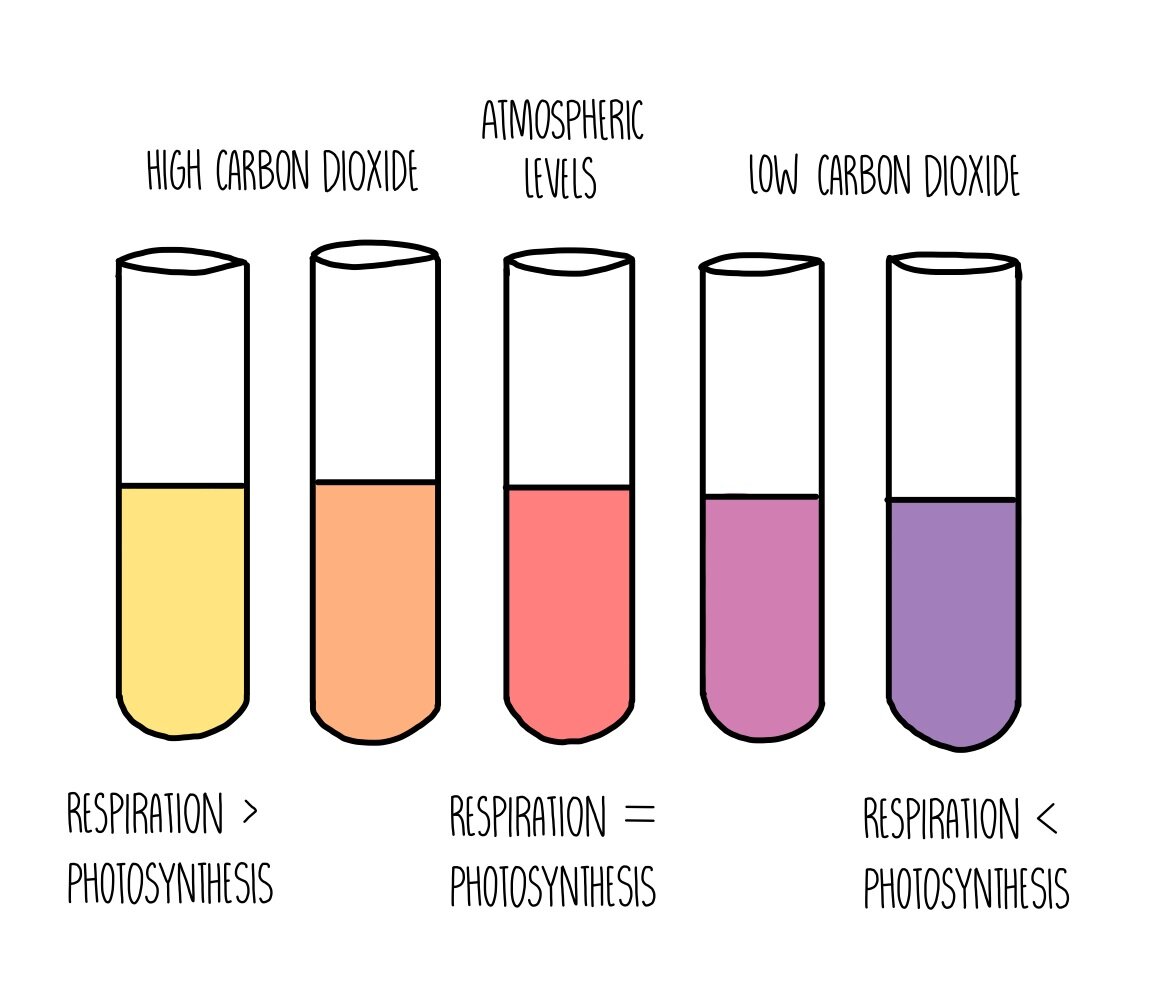
Hydrogen carbonate indicator with less CO2
More purple → less CO2 present
Photosynthesis happening more than respiration
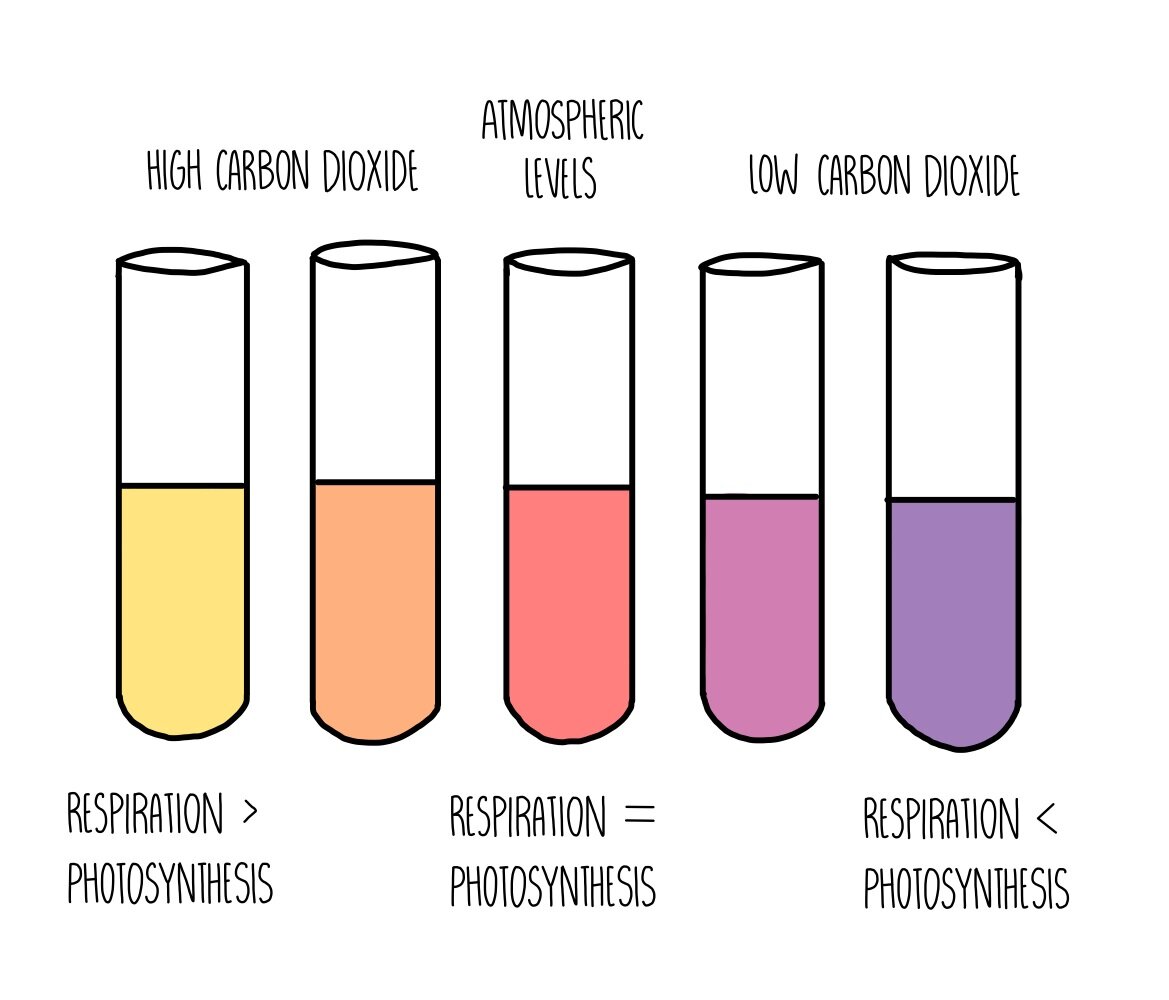
Understand and describe the effect of greater light intensity conditions on gas exchange in an aquatic plant using hydrogencarbonate indicator solution
Greater light intensity → greater rate of photosynthesis → carbon dioxide being used for photosynthesis → colour would be purple
Understand and describe the effect of lower light intensity conditions on gas exchange in an aquatic plant using hydrogencarbonate indicator solution
Lower light intensity → lower rate of photosynthesis → no light → respiration occuring → greater carbon dioxide concentrations → colour would be yellow
Most leaves have a large surface area and are thin
larger surface area → exposed to more light → maximise light absorption
thin → carbon dioxide + oxygen has shorter distance to diffuse → diffusion occurs at a faster rate
thin → light able to penetrate + reach all cells in the leaf
Structure of a leaf
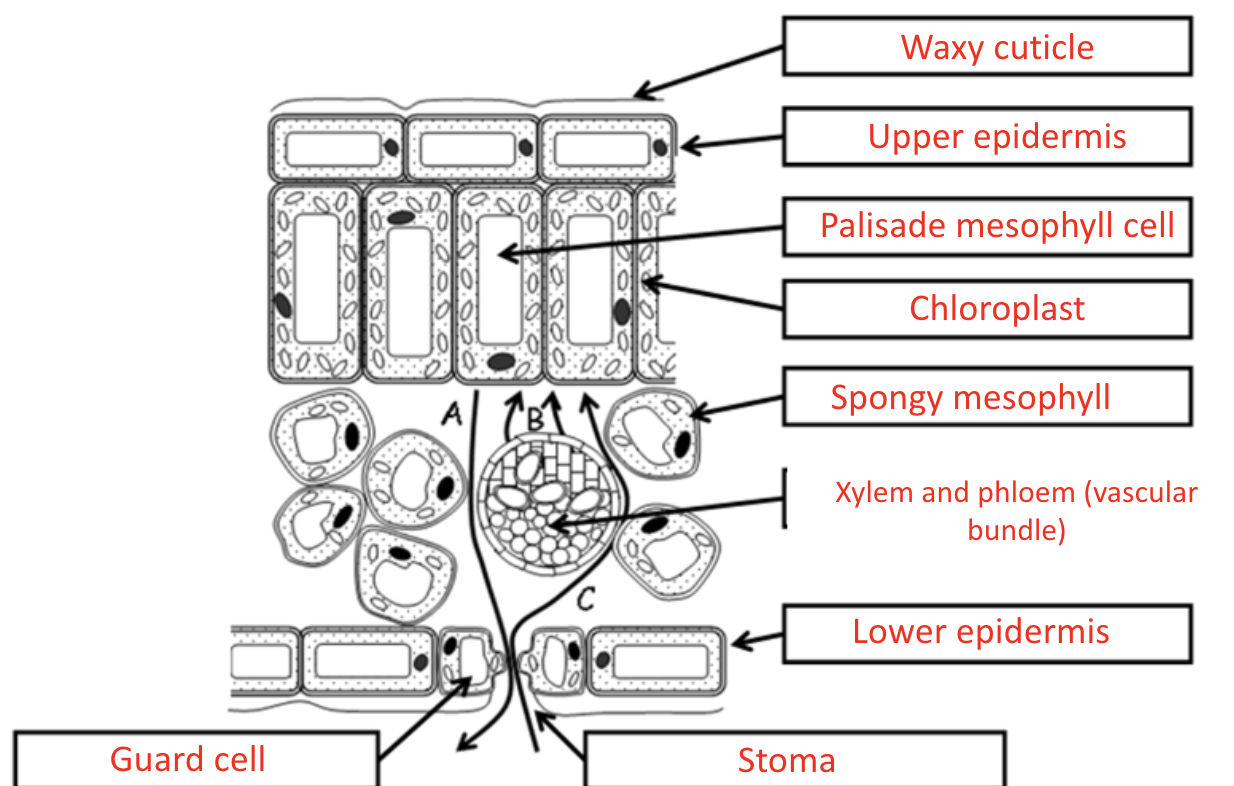
Waxy Cutcile
Features | Chloroplast | Function |
1. Transparent 2. Waxy | X | 1. Reduce water loss from upper surface of leaf 2. allow light to penetration |
Chloroplasts
Features | Function |
1. contains chlorophyll | 1. absorbs light energy for photosynthesis |
Guard cells and stomata
Features | Chloroplast | Function |
1. Inner surface is very thick 2. contain few chloroplast | Few | 1. Allow gas exchange 2. reduce water loss (guard cells open and close stomata) |
Upper epidermis
Features | Chloroplast | Function |
1. transparent 2. closely - fitting | X | 1. allow light to penetrate 2. secrete waxy cuticle 3. Prevent the entry of bacteria and fungi |
Lower epidermis
Features | Chloroplast | Function |
1. transparent | X | 1. allow light to penetrate 2. secret waxy cuticle 3. Protect leaves from pathogens |
Palisade mesophyll
Features | Chloroplast | Function |
1. Near light - source 2. Closely packed 3. Contain many chloroplast | Many | Layers of cells packed closely together and contains chloroplast to photosynthesis |
Spongy mesophyll and air space
Features | Chloroplast | Function |
1. Loosely packed 2. Many air spaces 3. Contain few chloroplast | Few | 1. Gas exchange to occur inside the leaf 2. Photosynthesis |
Vascular bundle (phloem and xylem)
Features | Chloroplast | Function |
Upper: xylem - water + mineral ions Lower: phloem - sucrose + amino acids | X | 1. Supports the leaf 2. Transports water and organic substances to and from leaf |