Cellular Respiration: Chapter 7
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Catabolic pathways yield energy by _.
Oxidizing (Loss of electrons) organic fuels
Releasing energy

Fuel molecules (complex organic molecules) have what?
High potential energy

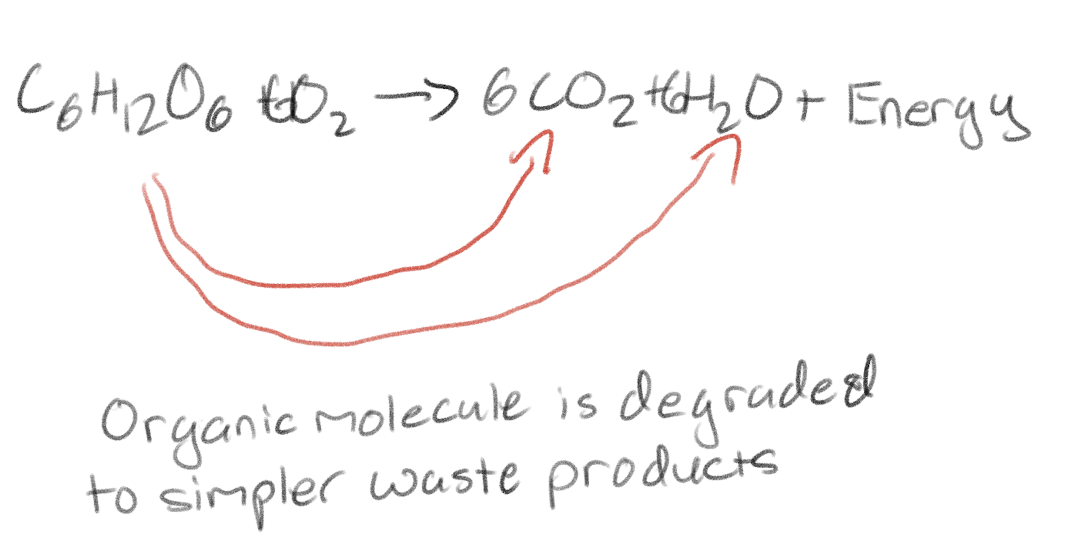
The complex organic molecules are degraded to what?
Simpler waste products
What are the 3 different catabolic pathways.
Aerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration
Fermentation
Briefly describe aerobic respiration
(Cellular respiration)
More complete degradation of sugars; final electron acceptors is O2
Briefly describe anaerobic respiration
(typically) more complete degradation of sugars; final electron acceptors is not O2
Briefly describe fermentation
Partial degradation of sugars; final electron acceptors is organic
Are anaerobic respiration and fermentation the same thing?
No they are not the same thing
Anaerobic respiration is not fermentation
Fermentation is anaerobic but is not the process anaerobic respiration (according to this class)
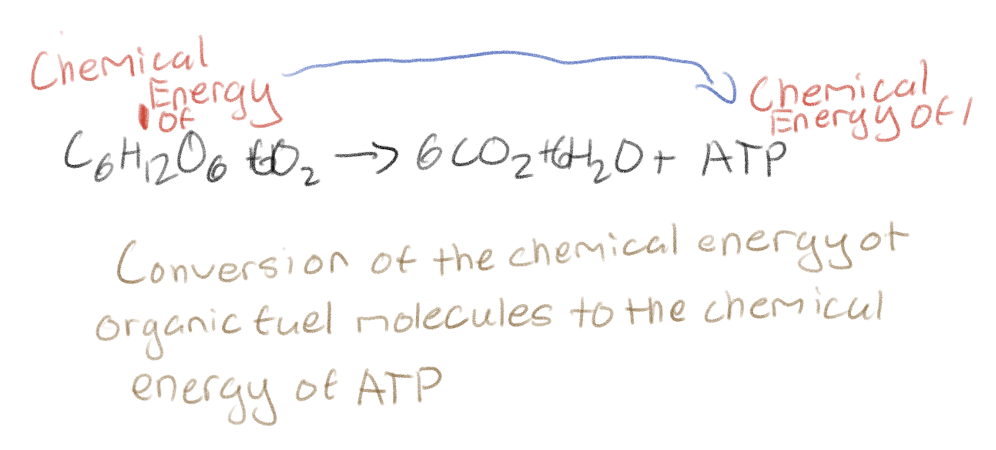
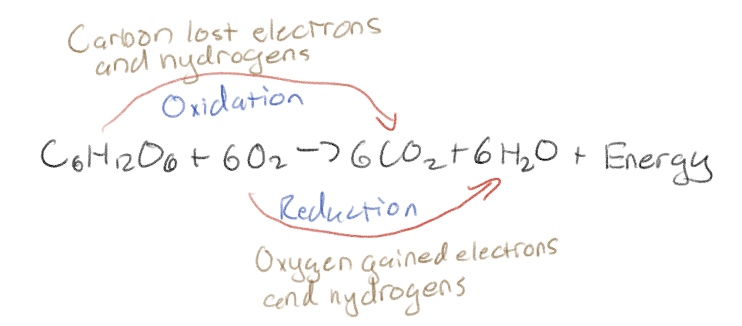
What is the formula of cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
∆G = -686 kcal/mol
Energy in cellular respiration = _ +
ATP; Heat

Cellular respiration is the conversion of what?
The conversion of the chemical energy of organic fuel molecules (glucose) to the chemical energy of ATP
Oxidation-reduction reactions
Electron transferred from one substance to another
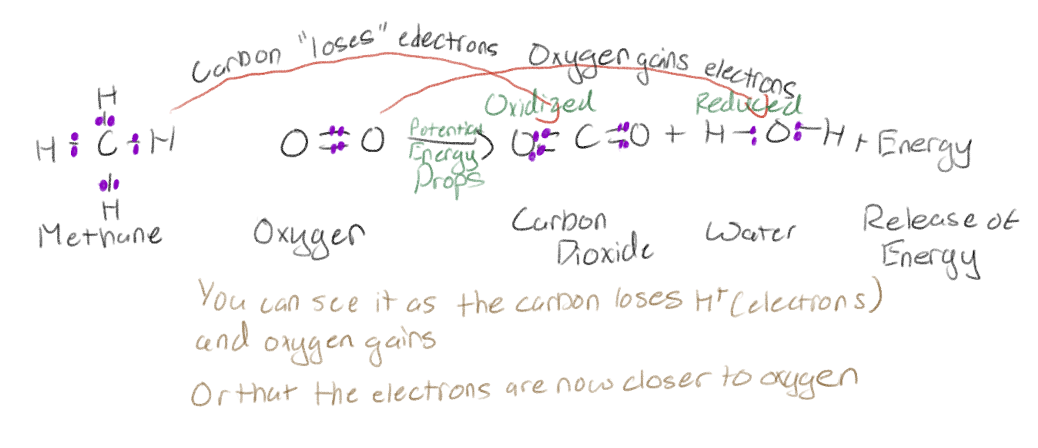
Oxidation
Loss of electrons

Reduction
Gain of electrons
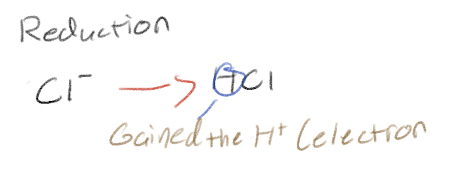
Classify a oxidation-reduction reaction of cellular respiration
(Say which one is oxidation and which one is reduction)
Cellular respiration is the oxidation of what?
Organic fuel molecules (sugar)
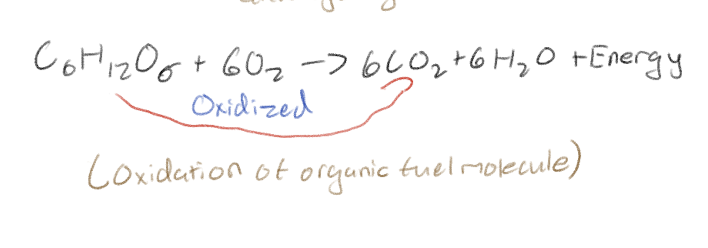
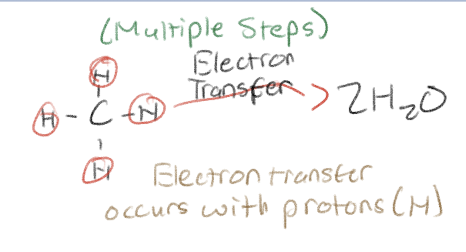
What does electron transfer occur with?
Occurs with proton (as a H atom)
Many series of steps
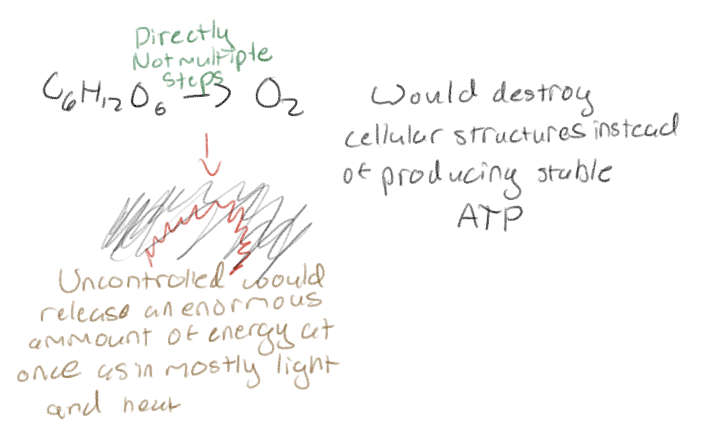
What would happen if electrons were transferred directly from glucose to oxygen in one step?
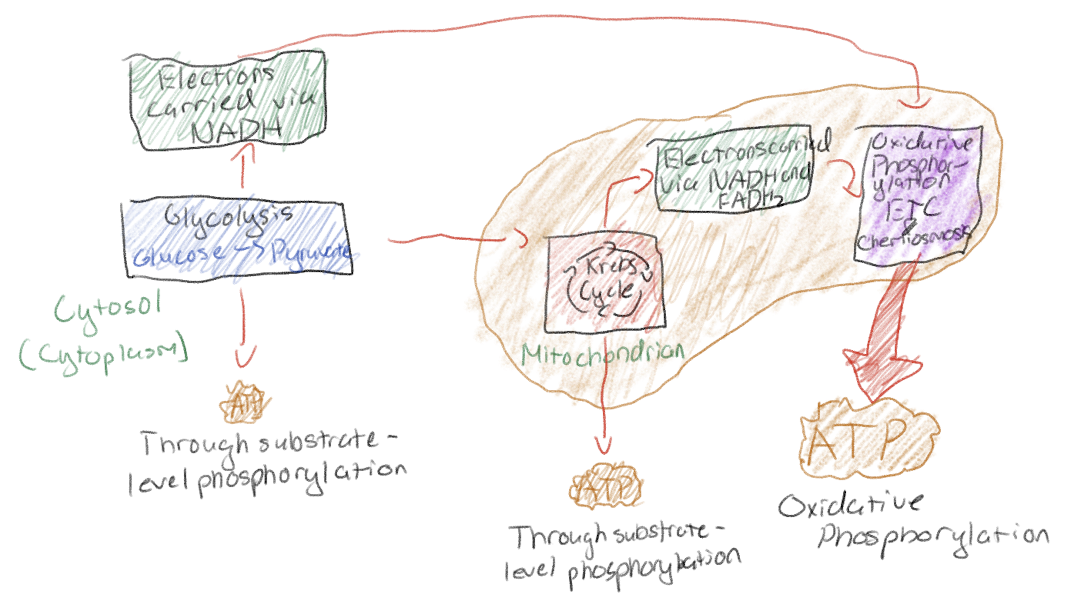
Cellular respiration has three major steps and briefly describe them.
Glycolysis - Catabolic pathway occurring in cytosol
The Citric Acid Cycle - Catabolic pathway occurring in mitochondria
Oxidative Phosphorylation (Includes both the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis) - harvest of energy from electrons from steps 1 and 2; occurs in mitochondria
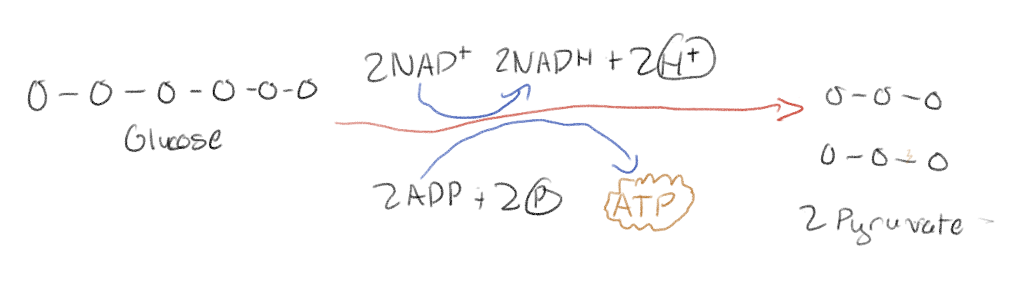
By what does glycolysis harvest chemical energy?
By oxidizing glucose to pyruvate
Is glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic? And where does it occur?
Anaerobic (without oxygen); Occurs in the cytoplast
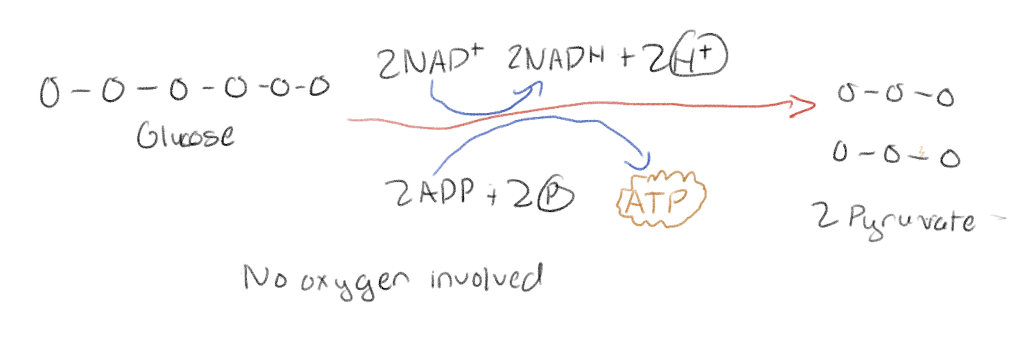
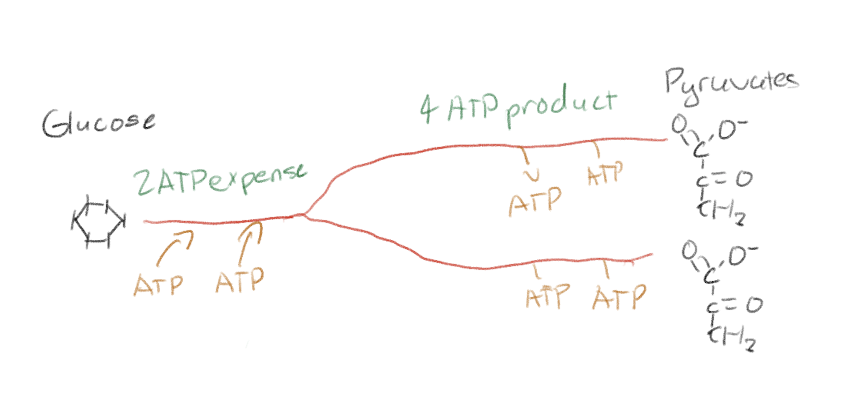
What is the net product of glycolysis using glucose?
2 pyruvate molecules + 2NADH + 2 ATP
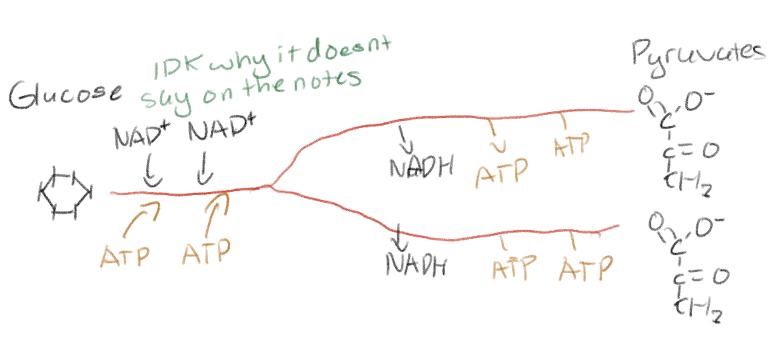
There are 2 big phases of glycolysis. Tell me what you use and/or what the products are for each phase per glucose.
The first half requires energy (2 ATP) and glucose (investment phase)
The second half requires whatever you got from the first half and the products are 2 NADH, 4 ATP, and 2 pyruvate molecules
Net yield is 2 ATP making glycolysis spontaneous
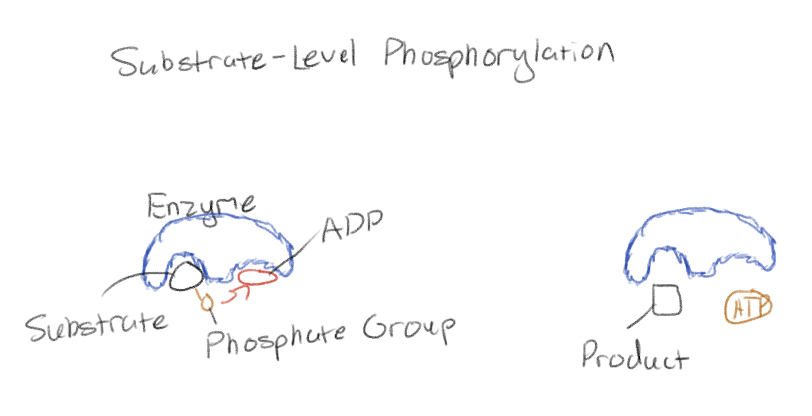
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
The way ATP is generated during glycolysis
Enzyme transfers phosphate group from a substrate to ADP, yielding ATP
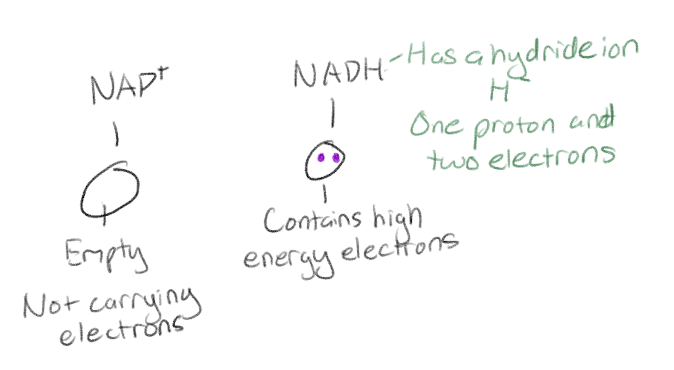
What does NAD+ acts like in cellular respiration?
Like an electron shuttle
What are dehydrogenases?
Enzymes that remove a pair of hydrogen atoms from a substrate and deliver two electrons and one proton to NAD+
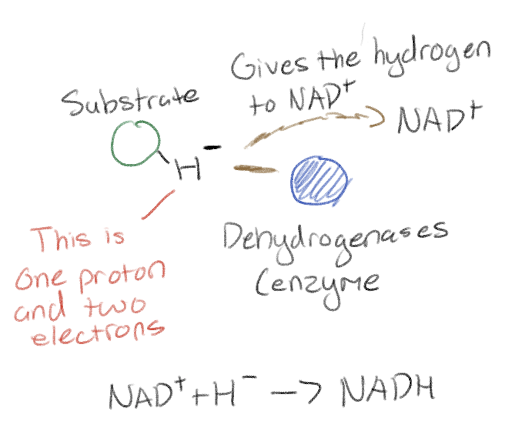
Make an analogy for NAD+ and NADH
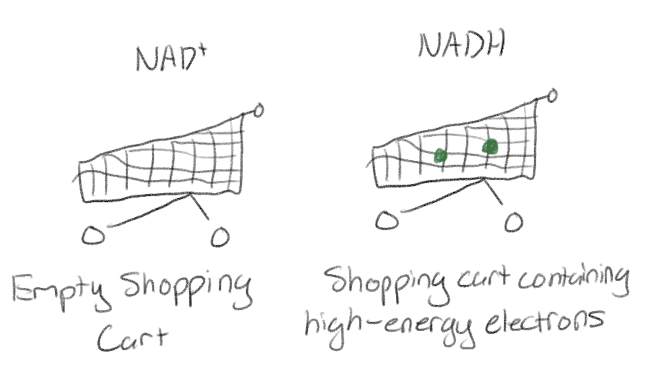
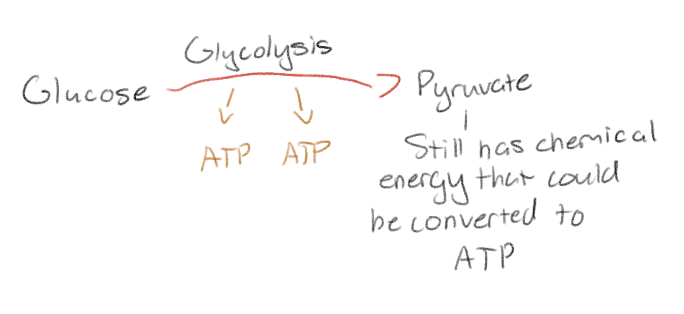
Glycolysis releases a _ of glucose’s chemical energy.
Fraction
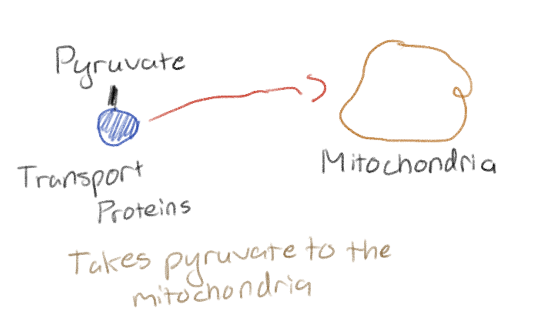
By what is pyruvate transferred into the mitochondria in the Krebs cycle
By transport proteins
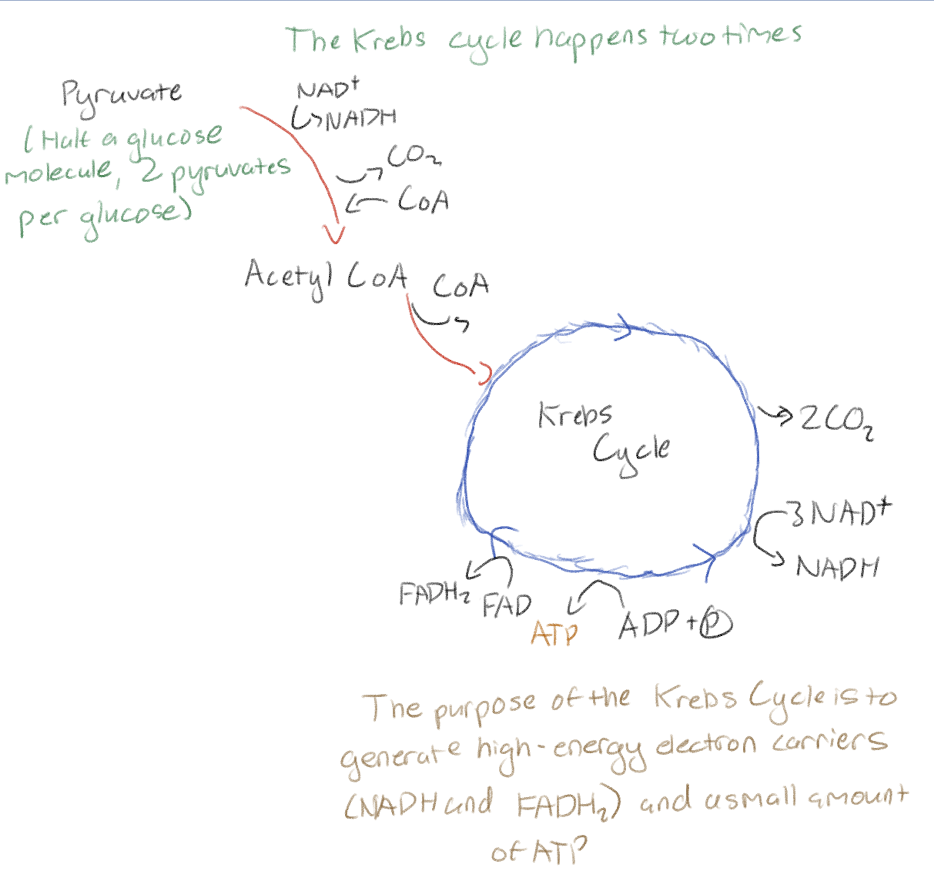
Pyruvate is converted to what in the Krebs cycle
Acetyl CoA

In the Krebs cycle 2x per glucose molecule what are the products that come out?
3 CO2 (1 from link)
4 NADH (1 from link)
1 FADH2
1 ATP (by substrate level phosphorylation
What is the electron transport chain
Molecules (mostly proteins) in mitochondrial inner membrane
Passage of electrons between molecules (redox reactions); each molecule in chain is more electronegative than the last
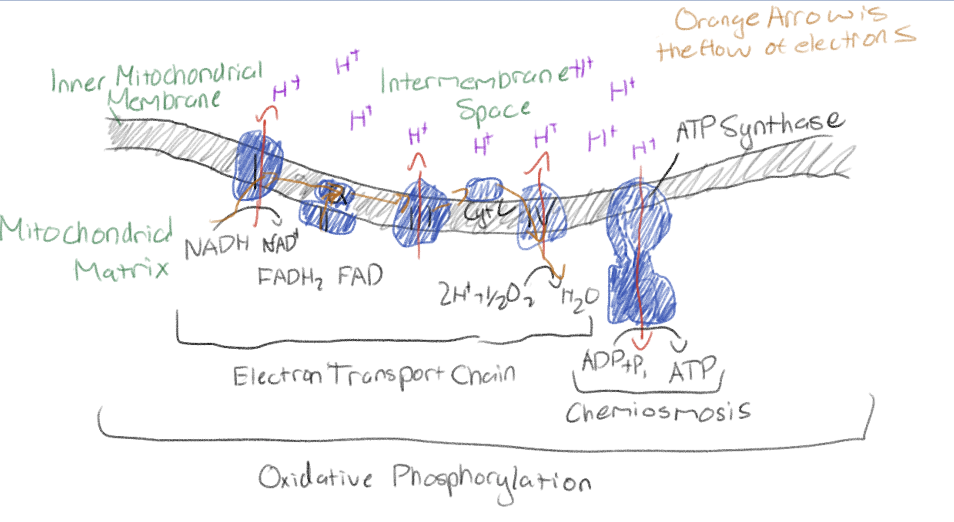
How is the energy of high-energy electrons harvested from NADH (and FADH?2)
“Falling” down steps: electron transport chain
Series of redox reactions
Each member of electron chain is more electronegative than the last
Oxygen at the “Botton” pulling electrons along
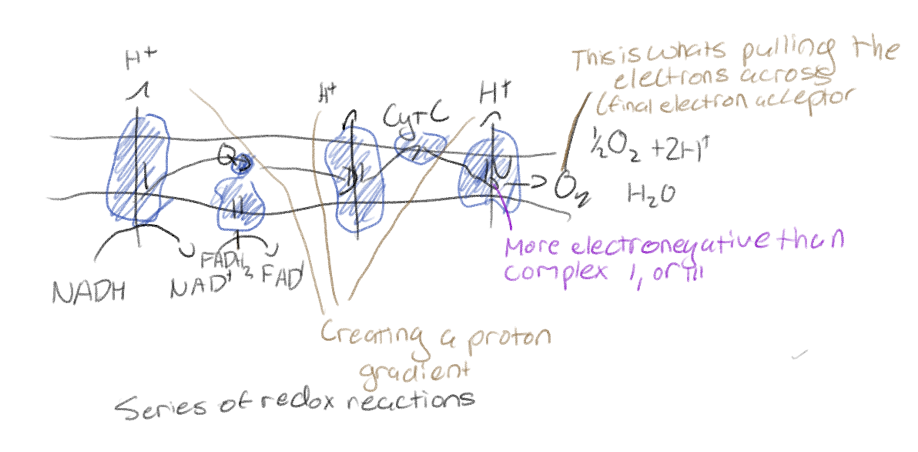
What is oxygen in the ETC (electron transport chain)?
The final electron acceptor
How does the electron transport chain work?
The energy released as electrons are passed down ETC is used to pump H+ across the inner mitochondrial membrane (active transport), resulting in proton-motive force
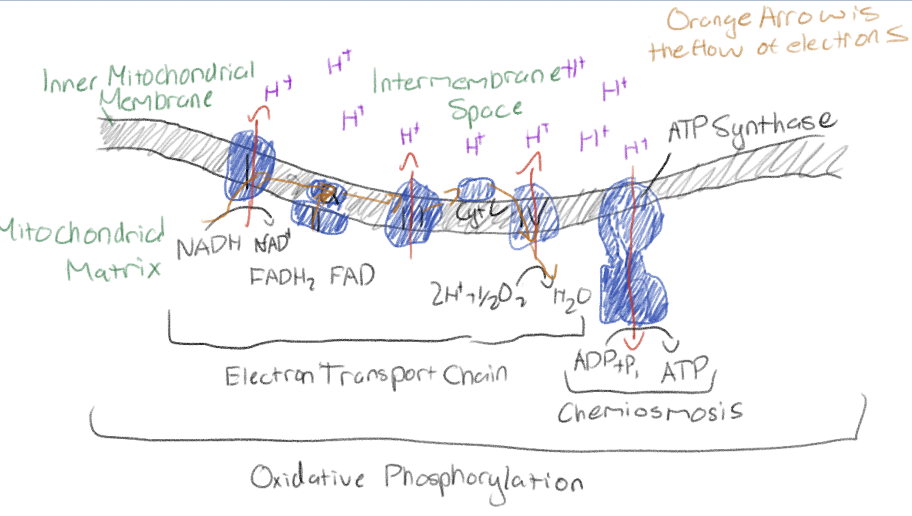
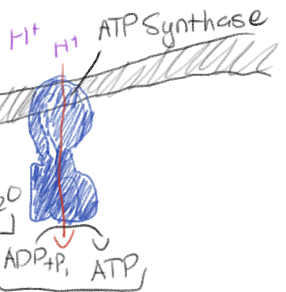
What is chemiosmosis?
H+ diffuses back through ATP synthase (facilitated diffusion), generating ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
Most ATP in cellular respiration is generated by what and approximately how much?
Oxidative phosphorylation; approximately. 26-34
What is approximately the total ATP produced by cellular respiration of 1 glucose molecule?
Approx. 30-38
Why is it difficult to determine the exact number of ATP generated per glucose?
The ration of NADH to ATP is not a whole number
ATP yield varies depending on type of shuttle used to transport electrons into mitochondria
Power of proton-motive force can power other work
Approximately how much % of energy in glucose is transferred to ATP?
<40%
What is DNP?
DNP would make the mitochondrian membrane more leaky allowing H+ to diffuse through the cell membrane
This will make oxidative phosphorylation less efficient as there would not be as much gradient for the H+ to defuse through ATP synthase.
For weight loss, but does kill people
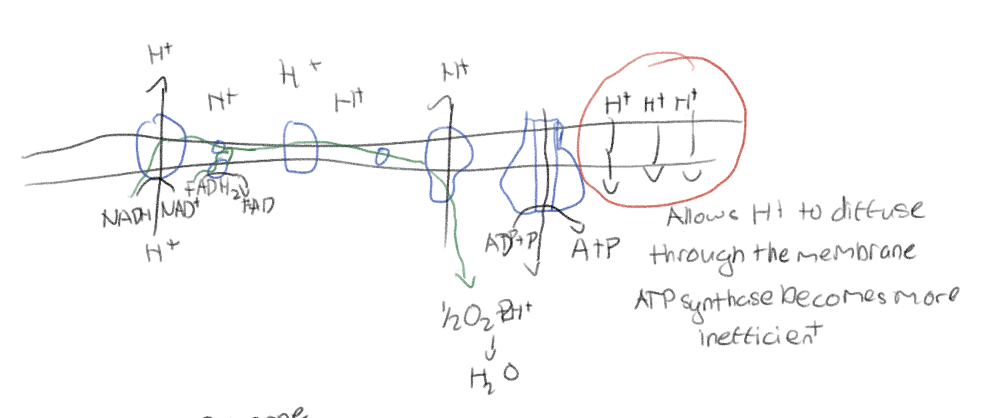
Rotenone in cellular respiration
Blocks cellular respiration by inhibiting complex 1
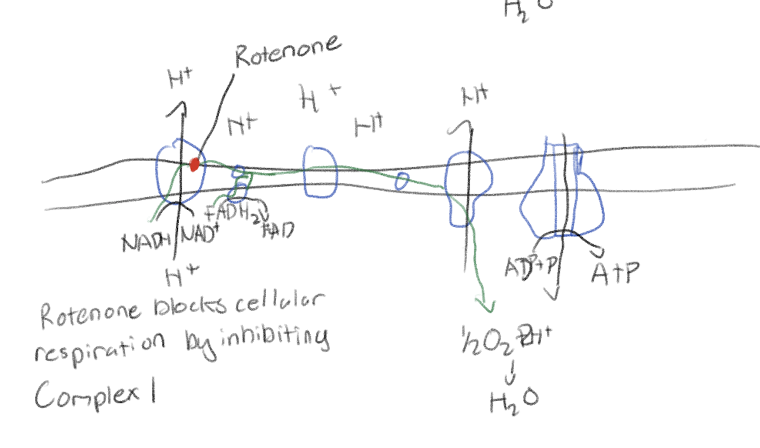
Cyanide and carbon monoxide in cellular respiration
Blocks cellular respiration by inhibiting complex 4
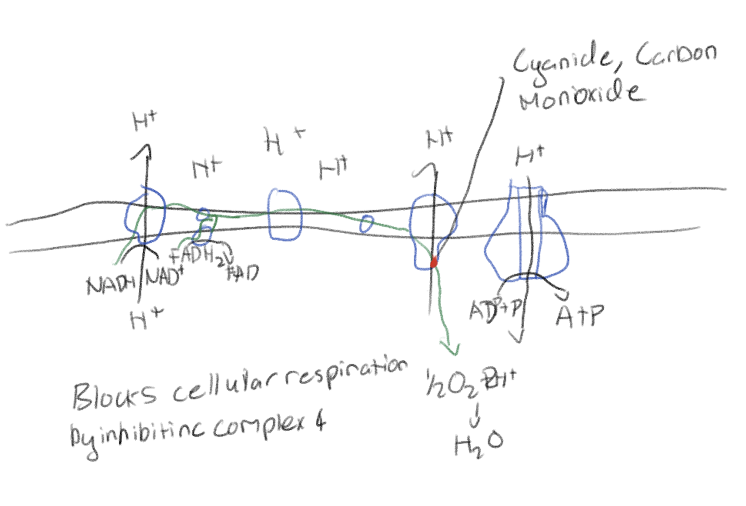
Oligomycin in cellular respiration
Blocks cellular respiration by inhibiting ATP synthase
Fermentation
Can occur under anaerobic conditions (without oxygen)
Food molecules are oxidized by NAD+
It contains glycolysis
The ATP is produce by substrate level phosphorylation
What are the two types of fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation
Alcohol fermentation
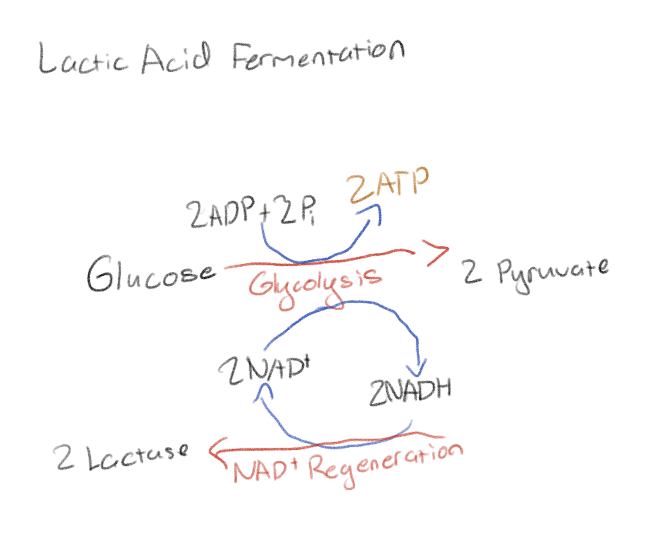
What is lactic acid fermentation?
It has the first step same as cellular respiration (glycolysis) then converts the pyruvate to lactic acid
Lactic acid fermentation can be used by humans as a backup when we don’t have enough oxygen to support the entire body such as when we are doing cardio heavy exercises
What is alcohol fermentation?
Has glycolysis as well but the pyruvate is converted into ethanol instead
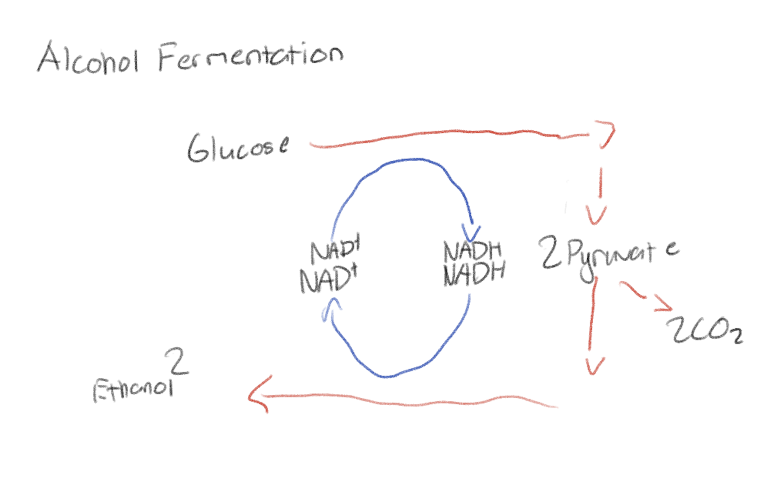
The second steps of lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation do not produce ATP, what is the point of them?
To convert the NADH back into the NADH so that they can recycle and use it again for glycolysis
What is aerobic respiration?
It is not fermentation
Is preformed by some microbes
It includes the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport chain and chemiosmosis); but no oxygen is involved
Uses a different final electron acceptor like nitrate
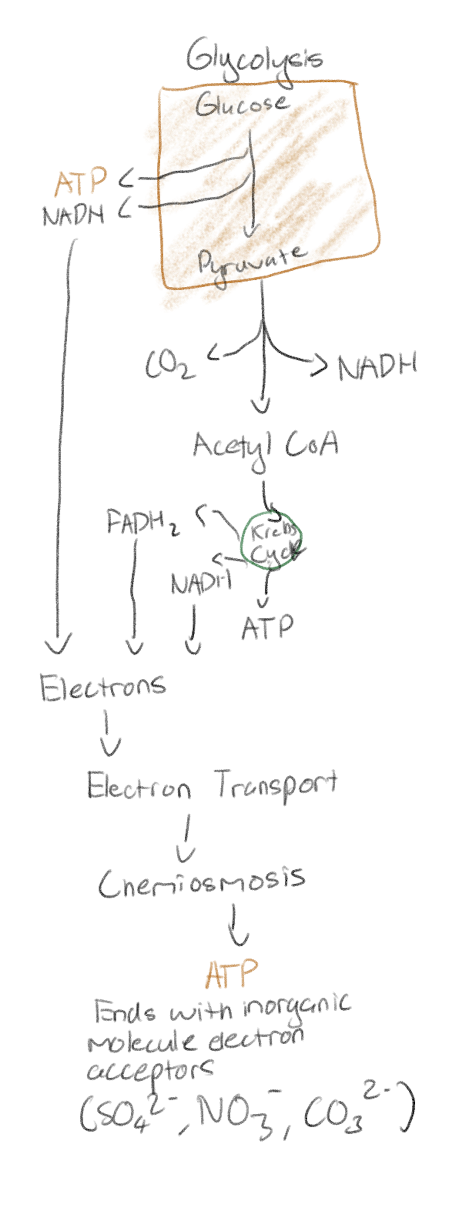
Do prokaryotes do anaerobic respiration?
Yes prokaryotes do anaerobic respiration even without a mitochondria; they do oxidative phosphorylation and the Krebs cycle in their cytoplasm and cell membrane
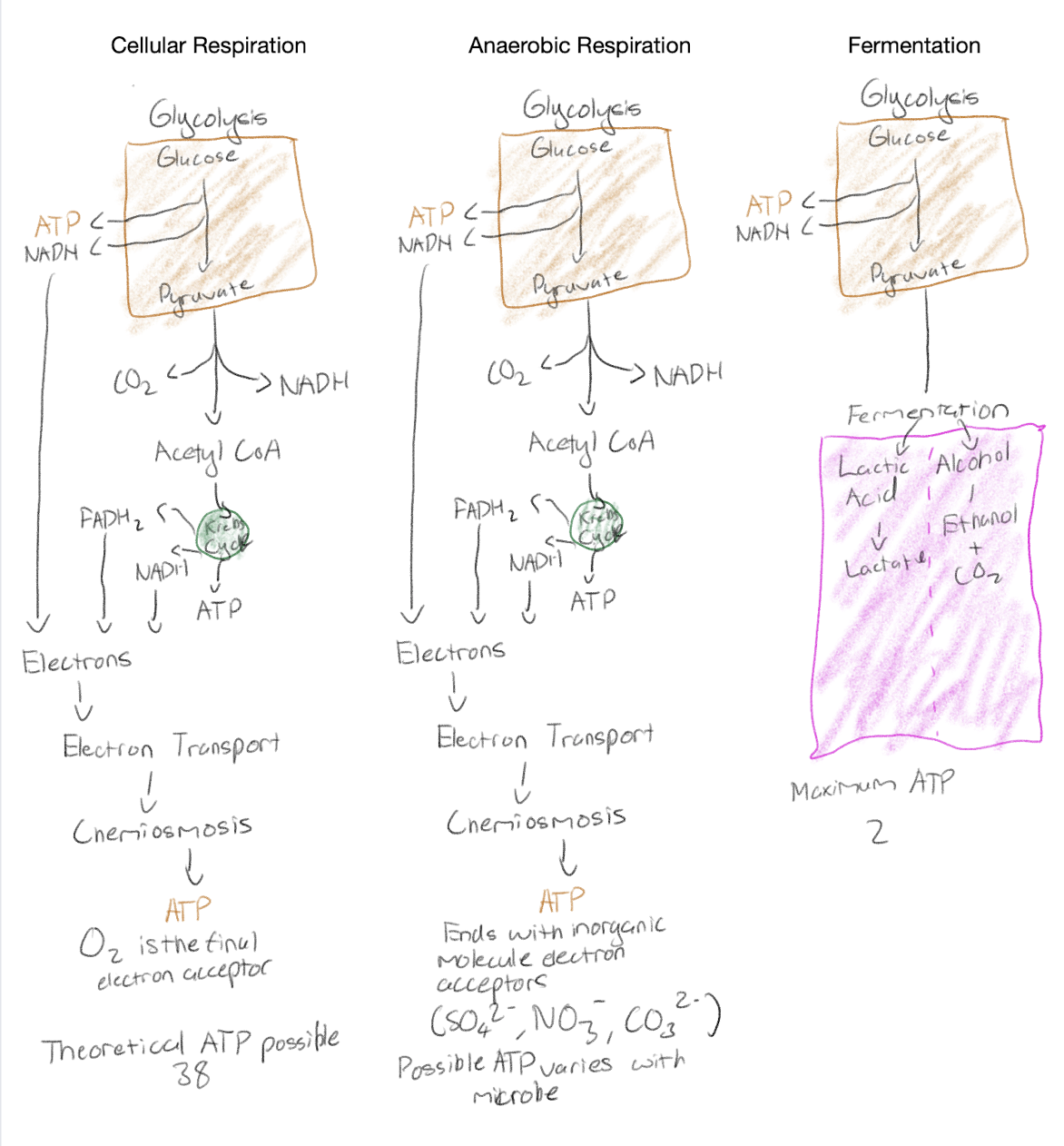
Make a diagram showing the differences between cellular respiration, anaerobic respiration and fermentation and the amount of ATP they produce
Not all fuel molecules are glucose. What are some molecules that could be a fuel molecule?
Other carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids (beta oxidation)
(normally the body prefers carbs but fat and proteins can also be used)
Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle also provide building blocks for catabolic or anabolic pathways?
Anabolic pathways
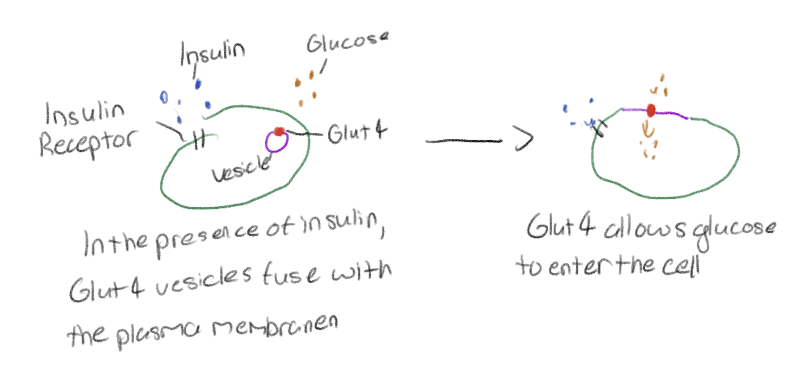
Control of cellular respiration
Controlling the amount of glucose entering a cell
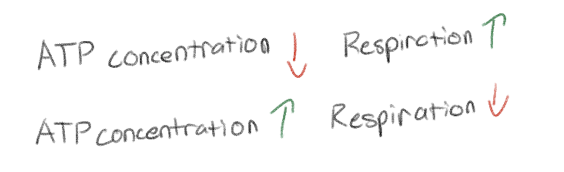
If ATP concentration drops, _.
If ATP builds up, _.
This is an example of what?
Respiration speeds up (more respiration to get more oxygen for more ATP)
Respiration slows down (less respiration to get less oxygen so less ATP)
This is an example of feedback inhibition (negative feedback)
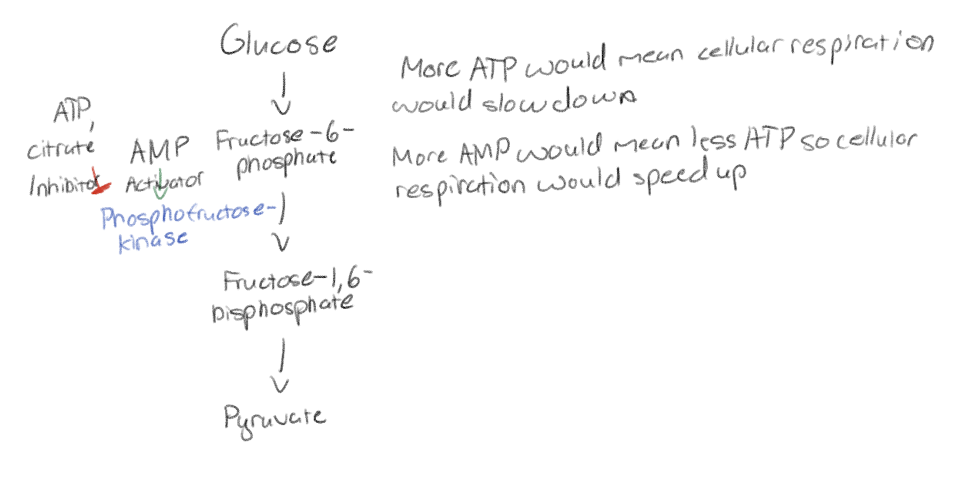
What is phosphofructokinase?
The pacemaker of respiration
Allosteric enzyme with inhibitions and activators
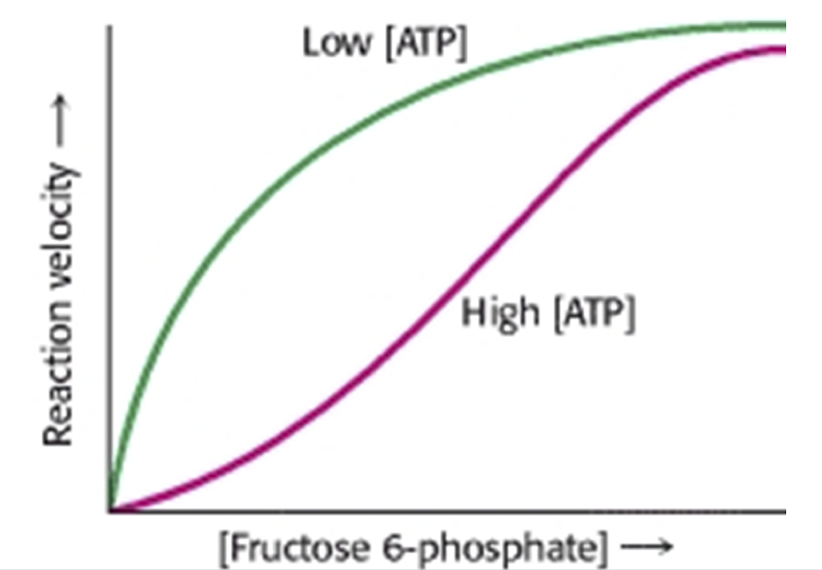
Explain this graph
A high level of ATP inhibits the phosphofructokinase so there would be less affinity for fructose 6-phosphate so less reaction velocity
A low lever of ATP meaning that there would be more AMP so it would activate the PFK so there would be more affinity for fructose 6-phosphate so more reaction velocity