Sedimentary processes (quiz 1)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the principle of original horizontality?
Sediments accumulate in essentially horizontal layers.
What is the principle of superposition?
Sedimentary layers are deposited in sequence, and unless the entire sequence has been turned over by tectonic processes, the layers at the bottom are older than those at the top.
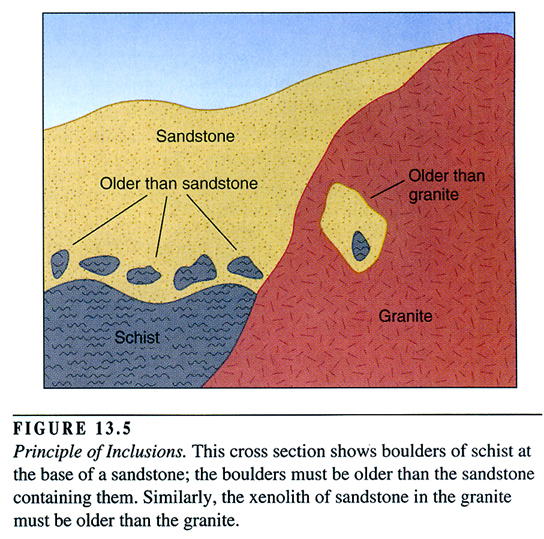
What is the principle of inclusions?
Any rock fragments in the sedimentary layer must be older than the layer.
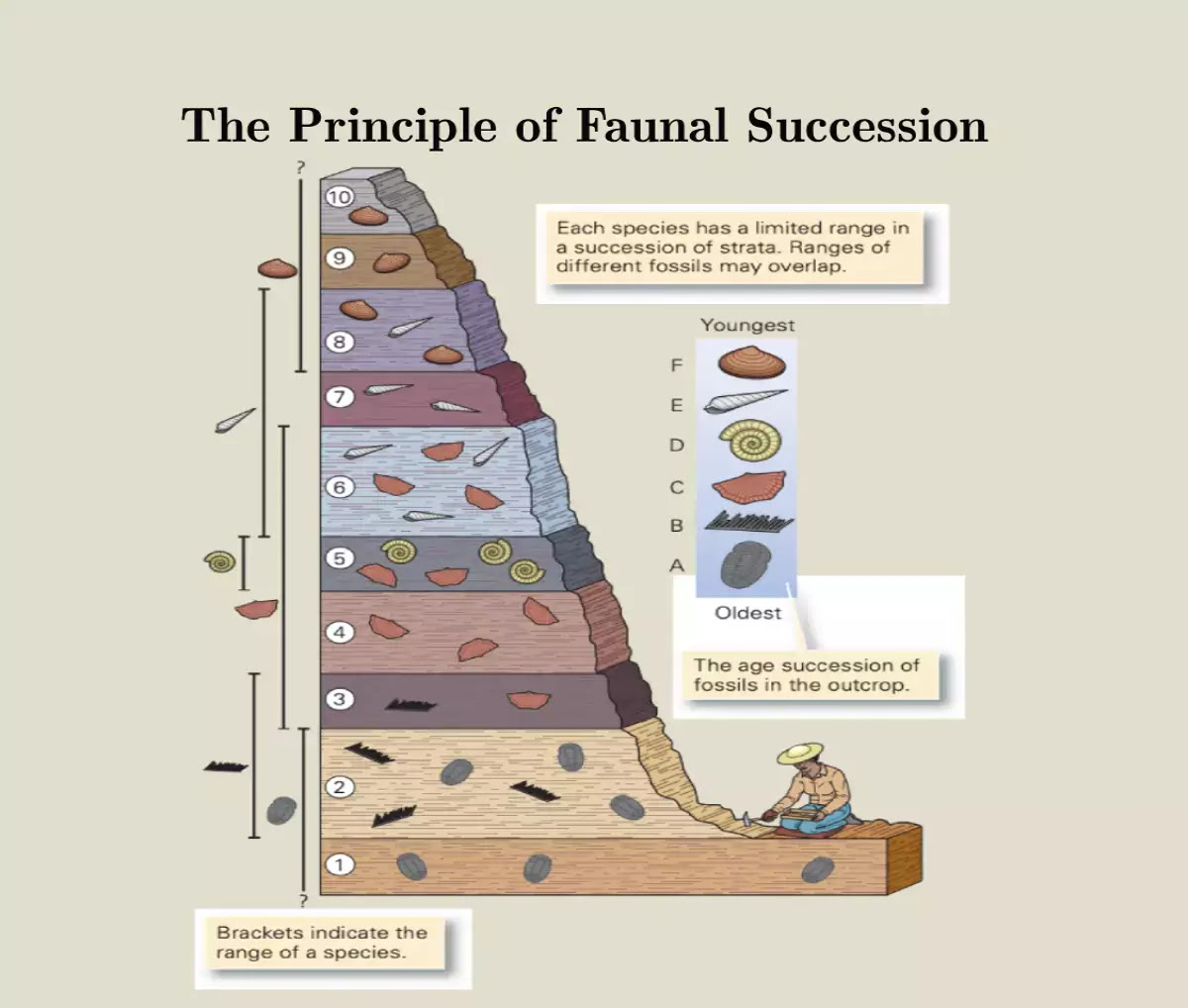
What is the principle of faunal succession?
The identification of specific fossils in a rock can be used to determine its age.
What is bedding?
is the separation of sediments into layers that either differ from one another in texture, composition, colour, or weathering characteristics.
What is partings?
narrow gaps/beds that many be due to seasonal differences, changes in climate, changes in locations of rivers or deltas, or tectonic changes.
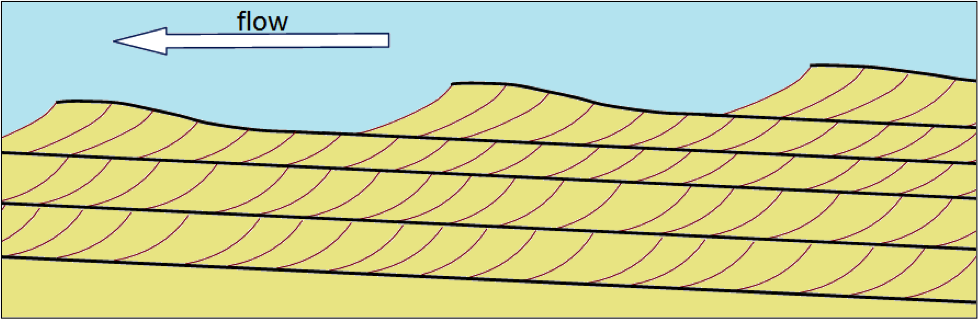
Describe cross-bedding
bedding that contains angled layers and forms when sediments are deposited by flowing water or wind.
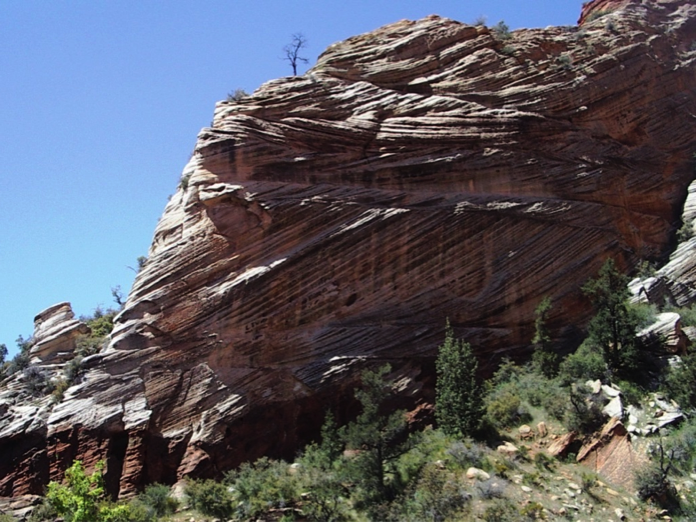

What are aeolian sediments?
They are wind deposited sediments.
Describe how to figure out which direction the current was flowing for cross-beds
Ripples/cross-section - the leading edge is the steep edge, which is where the sediments are being deposited.
What is graded bedding? Describe normal versus inverse grading.
normal = course on bottom, fine on top
inverse = fine on bottom, course on top
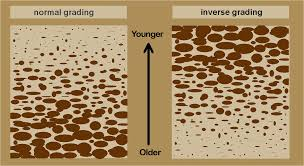
When does normal graded bedding occur?
When deposition of a sediment happens in a flow that was slowing down
When does inverse graded bedding occur?
When deposition of a sediment happens in a flow that was speeding up (avalanche)
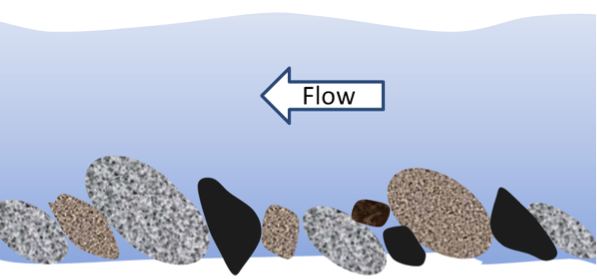
What does imbricated mean?
When boulders, cobbles, and pebbles become tilted in the same direction (upper end pointing downstream) where it is in its most stable position with respect to the stream flow.
Sedimentary particle greater than 2mm are collectively referred to as…
Gravel (collectively)
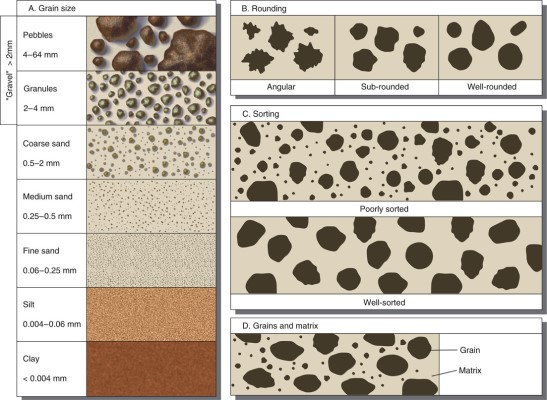

Very fine-grained sediments (less than 2 microns) are collectively referred to as…
Mud
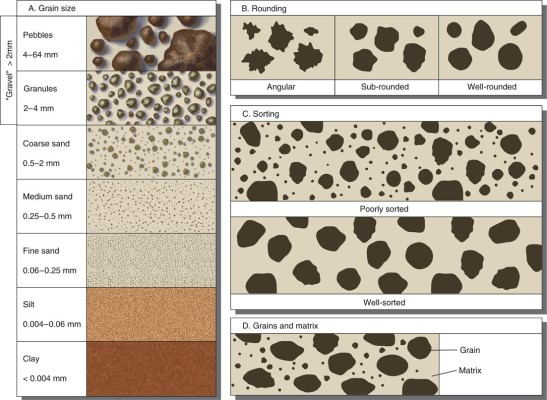

Over time, during the transport of sediments, sedimentary particles will tend to become…
more rounded, finer, well sorted.
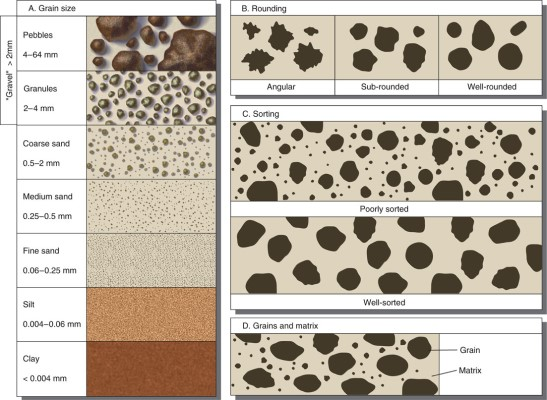

What would a sedimentary rock containing mud cracks represent?
That the rock was originally a sediment deposited on land
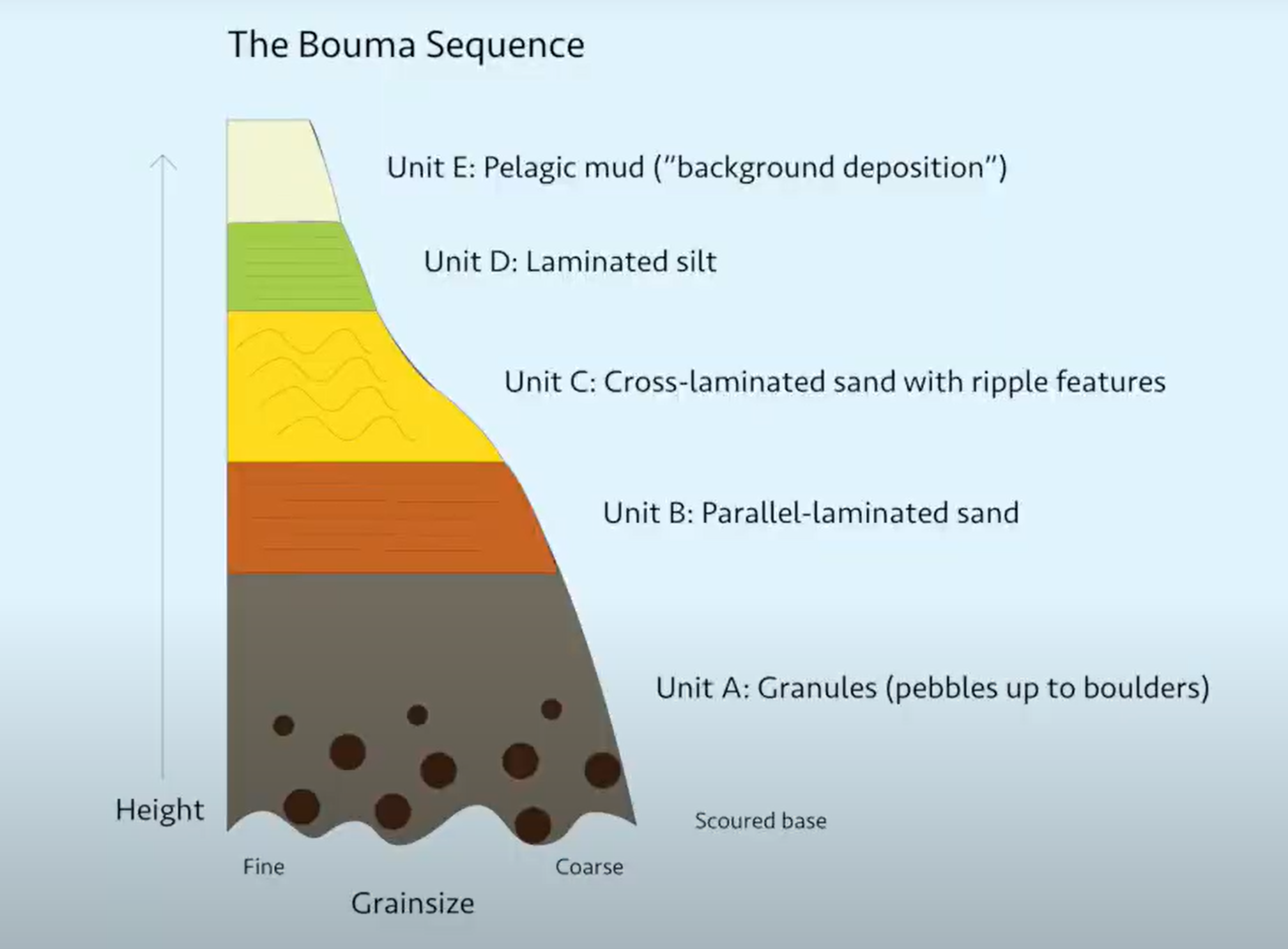
What are some characteristics of turbidites (3)?
water containing sediments that is denser than water (creation)
commonly composed of a variety of sizes of sedimentary particles
commonly arranged as course at the bottom and fine at the top.
What is a Bouma sequence (study diagram)?
A sequence that develops as a flow decreases in speed of over time.