HaSS final exams
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Roles of the Australian Constitution and the High Court
Interpreting the Constitution
Keeping the Constitution relevant
High court as an umpire
Protecting the rights of the Australian people
Resolving disputes
Interpreting the Constitution (2) + example
HC can hear and resolve disputes over meaning of constitution
only court in Australia with the power to interpret meaning of words and phrases
example: R vs. Brislan, had to interpret whether “postal telegraphic and telephonic” services included power to make laws about radio and broadcasting”
Keeping the constitution relevant (3)
drafts kept CW’s lawmaking powers in broad/general terms so CW could make laws in areas that were not in existence at the time
use of broad terms caused disputes, which HC has been asked to resolve
allow for new technologies to be included in the CW law-making powers
High Court as an “umpire”
Acts as an independent and impartial umpire to check that the CW does not make any laws that exceed its constitutional law making power
Protecting the rights of the Australian people + example
HC can interpret the Constitution and imply that various rights of the Australian people exist, even if not explicit
Resolving disputes (3)
Called upon to resolve disputes about whether or not a state or CW law has been made in breach of existing law
Has also resolved issues around international human right treaties and conventions
declared contravening laws (laws that breach the constitution) invalid.
United Nations. What is it? Why was it created? How many members? (4)
international org created in 1945
formed after WW2 in hopes that it would prevent war and horrors such as holocaust from happening again
seeks to promote international cooperation
193 members
4 Commitments of the UN
International peace and security in the world
Creating friendship between nations
Help nations work together to assist poor, alleviate hunger and disease, promote literacy, promote respect for peoples rights and freedoms
central points where nations can come together to achieve above mentioned goals
Australia’s role as a member of the UN
one of the first 51 counties
membership of UN allows us to have a voice in international affairs, play a role in promoting stability, help protect its own economic and security interests
Australia’s international role and responsibilities (4)
Foreign aid (role)
Peacekeeping (role)
Protecting the environment (responsibility)
Uphold human rights (responsibility)
What is foreign aid? Why is it given? Countries in immediate region who are recipients of foreign aid? (3)
assistance in the form of money, skills or other resources transferred from one country to another, mainly for humanitarian reasons. given to alleviate poverty assist community by developing standard of living. East Timor, Cambodia, Solomon Islands
Millennium Development Goals (4)
Eight UN goals
wiping out poverty
universal primary education
stopping spread of infectious disease
providing foreign aid equal to 0.7% of a countries income. (AUS needs to double it’s aid in contribution to meet this goal)
Australia’s peacekeeping responsibilities. What is peacekeeping? How does it achieve it’s goal?
assists countries who have been torn by conflict to achieve lasting peace
does this by
maintaining peace
protecting civilians
overseeing elections
disarming those involved in fighting
protecting HR
restoring rule of law
three basic principles that guide UN peacekeeping. Why?
consent of parties
impartiality
use of force as a last resort
because peacekeepers are told by the UN to use all necessary means to protect civilians, assist authorities and deter use of force that disrupts political process
Australia’s responsibility to protect the environment
most important area of environmental protection is climate change
(inter)national responsibillity to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
UN brings countries together to agree on targets to reduce
e.g 2008, Aus became a full member of the Kyoto protocol, where binding emissions- reduction goals were set. Aus then set emission reduction targets for 2020+
Australia’s responsibility to uphold human rights. What are human rights? What are some examples?
entitlements that all human beings possess regardless of gender, ethnicity, nationality or any other status
Universal Dec. of Human Rights created in 1945 and basis of international human rights law.
all people born free and equal
right to life
equal before the law
no one should be subject to torture or slavery
Australia is party to seven international human rights agreements. what are two of the agreements that elaborate on the principles established by the Universal Declaration and are legally enforceable?
International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural rights
What is a treaty?
international obligations that are written down in documents that Australia is compelled to or bound to observe
can be called convention, covenant
Bilateral treaties
a treaty between Australia and one other country
Multilateral treaty (2)
a treaty between Australia and two or more countries
developed and overseen by an international organisation such as UN or ILO
Who has the power to enter into treaties and contribute to international negotiations? Who makes the final decision to ratify? what does signing a treaty mean?
Commonwealth Government.
Minister/Cabinet makes final decision to sign and ratify a multilateral treaty
Signing a multilateral treaty indicates that Australia is bound by the treaty at a later date, but there’s an obligation to refrain from any acts that would defeat the purpose of the treaty
Ratification
process that legally binds Australia to implement the treaty
Parliaments role in treaties (3)
examines treaties that Aus enters, apart from those considered urgent/sensitive
passes legislation to ensure the provisions of treaty become law
not always necessary to pass new laws, because existing legislation may be sufficient
Examples of 2 treaties and the Australian law that reflects the principles of it
Convention on the rights of the child
children are treated with respect and are not abused
Children and Community Services Act 2004 (WA only)
a child must be protected or moved to a safe place by an authorised officer if they are in danger of being harmed
Convention for the Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage
protect heritage around the world to have value and to be preserved for future gens
World Heritage Properties Conservation Act 1983
An attempt to destroy a world heritage site through mining is unlawful
What is policy making? Example where Australia worked closely with other countries and implemented policies with other countries
Involves the government taking action in a certain area to achieve a desired outcome
protecting ozone layer through legal obligations of the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.
Failure to live up to international obligations results in what? What role does the UN play in this?
international pressure to change policy. UN monitors how well Australia is performing.
Australia and the UN: REPORT CARD recently gave Australia what scores in climate change and refugee and asylum seekers? What does this do?
CLIMATE CHANGE: D+, rely too heavily on fossil fuels and needs to set stronger targets for reductions
REFUGEES AND ASYLUM SEEERS: F, increased hostility, questioned whether current policy fulfills international legal obligations.
Shining a light on these areas for improvement may influnce policy change
What is GDP?
A measure of the total value of all goods and services produced in Australia over a year
what is economic growth?
An increase in the amount of goods and services produced per person within a specific period of time
Components of GDP
GDP = C + I + G + (X-M)
C= consumption, I = investment G= government spending (X-M) net exports
factors that impact GDP and causes of economic growth
Increased in the components of GDP
decreased savings, taxation and imports indirectly cause growth by allowing more consumption expenditure
target for economic growth
3%
What is the importance of Economic growth? (3)
increased collection of tax revenue
more employment and wages
better living standards
lower unemployment results
higher average incomes
increased consumption of G/s
improved material welfare
decline in poverty
Why is increased collection of tax revenue good? (4)
lower gov debt
improved public G/S
improved economic infrastructure
improved public health
Costs of economic growth (5)
structural and frictional unemployment
inflation
higher interest rates
increased imports
environmental damage
How can governments manage economic growth
Fiscal and Monetary policy
Fiscal policy
government budgets
surplus budgets and causing leakages when economy is gorwing
deficit budget resulting in increased injections when economy is too slow
injections through investment in infrastructure and educations
Monetary policy
Central/Reserve bank and interest rates
growing too slow lowering the cash rate target to stimulate economic growth
raising the cash rate (growing too fast)
What if economic growth falls (3)
decline in G/S produced
decline in employment and wages
decline in standard of living
Real GDP and Real GDP per capita
Real GDP GDP - Inflation
REAL GDP per capita - Real GDP shared between an economy’s population
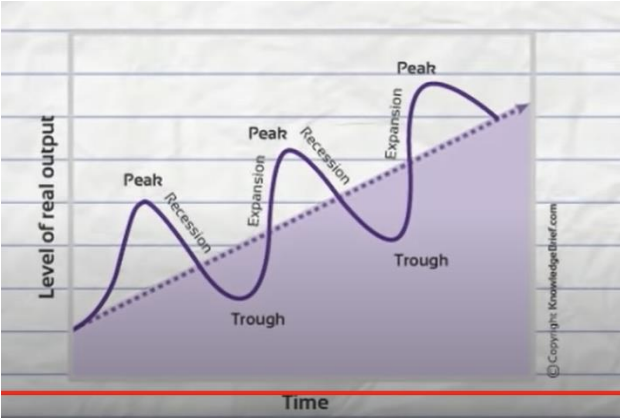
recession, and what leads to a depression (2)
where economic growth falls for two or more quarters in a row
depression: recession lasting 2+ years
What type of variable is economic growth? What does this mean?
Procyclical - when cycle increases, economic growth also increases
what happens in a depression? (4)
economic growth falls
decrease in available credit
significant increase in unemployemnt
little consumer confidence
Limitations of GDP. what does it not take into consideration (4 things)
does not assess true performance. producing more G/S may have undesirable environmental and social consequences.
enough leisure time
spending time with family
good health
rewarding job
What is inflation?
an increase in the general level of prices paid for goods and services over a sertain period of time, measured on a yearly basis
rising prices in inflation means that
consumer must pay more for goods and services if they want to continue to consume the same amount to maintain their standard of living
When is inflation thought to be sufficiently low?
If it does not exceed target of 2-3% per year
reasons for inflation (2)
stronger demand in the economy for goods and services, leading to shortages of goods and services with companies unable to keep up with demand for their products so prices increase
Increased spending might be due to (5)
consumers feel confident about their income and employment
businesses feel confident about the future (expand operations, employ people, invest in better equipment)
trading partners performing well and demanding exports
low interest rates, encouraging businesses to borrow more
lower taxes and increased gov expenditure
why else might inflation occur? What does higher tax and higher interest rates on money borrowed result in?
increasing costs (wages increase, extra cost passed onto consumers through higher prices).
higher tax and higher interest rates on money borrowed result in increased costs businesses must bear
Who are the winners of inflation? (3)
High income earners - jobs whose incomes increase at same rate / faster than inflation
Borrowers - rising prices = better to borrow with fixed interest rate + make purchase now
Importers - price of imported goods cheaper than goods from AU
Inflation losers
Low to middle income earners - people on incomes that do not increase as fast in inflation (unemployed, part-time, pensioners
Bank savers - money sitting in bank may not buy as much as it did before
Exporters - exported goods become more expensive, demand from overseas will fall
How is inflation measured? What does it do?
Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Measures the price change of a typical basket of goods and services purchased by AU households every quarter.
What is unemployment?
A person aged 15 and over who is actively looking for work and has not worked for at least one hour a week
What is unemployment rate? what does the labour force include?
The percentage of people in the labour force who are unemployed. the labour force includes those who are employed and unemployed
What happens when total unemployment rate in Australia is high?
The government collects less revenue in taxes and must pay more to assist the unemployed in social benefits and welfare programs.
What are the social consequences of high unemployment rate
reduced standard of living
loss of skills from the workforce
possible psychological effects of not working (depression)
Causes of unemployment
GDP weak/spending decreased. businesses hire less and cut back on staff to save money
increased competition from overseas
businesses take operations offshore or close down.
labour saving tech introduced, leading to unemployment
What is the unemployment rate formula?
unemployed/labour force x 100
Goals for unemployment
5% - 6% unemployment (frictional, seasonal and structural)
2-3% to help achieve full employment
limitations of unemployment rate (3)
hidden unemployment - people dropping out of the labour force
disguised unemployment - people with jobs but want more hours
blunt instrument - little account of hours worked, income earned, length of time unemployed
Youth unemployment
disproportionately face higher unemployment rates because it is harder to get stable job as graduate vs someone with experience
types of part-time and casual jobs are more vulnerable
types of unemployment
frictional
structural
seasonal
cyclical
frictional unemployment
people are between jobs, usually short term and during expansions (because people feel comfortable finding a new job)
structural unemployment
occurs when worker skills and experience do not match employer requirements (e.g when new technology arrives or when jobs are outsourced)
seasonal unemployment
occurs because demand for certain types of workers changes according to the season (fruit pickers, shearers, ski operators)
Cyclical unemployment
unemployment that arises due to a lack of demand for G + S in the economy because the economy is contracting, can be long term.
Unemployment changes though the economic cycle
Cyclical - recession, counter cyclical
Structural unemployment - expansion (new technology makes jobs redundant)
frictional unemployment - occurs expansion and peak phases
material living standards, and how they’re assessed?
access to goods and services. measured by GDP
assisted by higher employment and better access to goods and services
Non-material living standards and examples
intangible but affect our enjoyment
freedom of speech
free elections
low levels of crime
OECD Better Life Index
Organisation for Economic Co-operation
more holistic picture of living standards of 40 different countries
criteria of jobs, income, health, education, environment.