Test: We the People - Units 1, 2, & 3
1/129
Earn XP
Description and Tags
130 terms all about the constitution.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

130 Terms
Great Compromise
An agreement reached during the Constitutional Convention that established a two-house legislature, balancing the interests of both large and small states by creating the House of Representatives and the Senate.

Senate
The upper house of the U.S. Congress, consisting of two representatives from each state.

House of Representatives
The lower house of the U.S. Congress, consisting of representatives based on state population.

Abolish
To formally put an end to something.

Slave Trade
The buying and selling of humans for forced labor, primarily associated with the buying of people in Africa and selling them to landowners in the American South.
Three-fifths Clause
A constitutional provision that counted each enslaved person as three-fifths of a person for representation and taxation purposes.

The American Civil War
A conflict between Northern states and Southern states from 1861 to 1865, primarily over issues of slavery and states' rights. It resulted in the preservation of the Union between North and South as well as the abolition of slavery.

Fair
Impartial and just, without favoritism or discrimination.

Equal
Being the same in quantity, size, degree, or value.

Constitutional Convention
Another name for the Philadelphia Convention given by modern-day historians. It was the gathering of delegates in 1787 to draft the Constitution of the United States.

Interests
A specified common concern of a person or group of people.

Federal
In the United States, relating to the national government.

Preamble
The introductory statement of the Constitution that outlines its purposes and guiding principles.

Articles of the Constitution
The sections of the Constitution that detail the framework of government, including the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.

Constitutional Amendments
Changes or additions to the U.S. Constitution that modify its original text or laws.

Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution, which guarantee individual liberties and protect citizens from tyranny.

Roger Sherman
Founder and architect of the Great Compromise, which helped shape the legislative branch of the U.S. government.

George Washington
1st President of the United States and commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution.

Taxes
Required payments to a government.

Tyranny
Cruel and oppressive government rule.

Slave
A person who is the legal property of another person and is forced to obey them against their will.

Natural Rights
The idea that all humans are born with rights, which include the right to life, liberty, and property.

Consent to be Governed
The idea that government derives its authority from the people it governs.

Social Contract
An agreement between the people and their government signifying their consent to be governed.

Direct Democracy
A form of government in which citizens rule directly and participate in all aspects of government.

Representative Democracy
A system of government in which citizens elect representatives to make decisions and laws for all people.

Constitution
A set of rules and laws that explain how a government is organized and how it will run.

Limit
A point beyond which something cannot go.

Shay’s Rebellion
An armed protest in November 1786 by more than 1000 angry farmers against the state of Massachusetts. It showed the weakness of the Articles of Confederation.

Northwest Ordinance of 1787
A plan for adding new states to the United States. Allowed people in the Northwest Territories to organize their own governments.
Philadelphia Convention
A meeting in 1787 where delegates from twelve U.S. states convened to address the problems of the Articles of Confederation, ultimately leading to the drafting of the U.S. Constitution.

James Madison
A key Framer and the fourth President of the United States, known as the "Father of the Constitution" for his role in drafting the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights.

Benjamin Franklin
An influential Founder, Framer, inventor, and diplomat. Key in securing French support during the American Revolutionary War and a signer of the Declaration of Independence.

Articles of Confederation
The first plan for government in the United States. Set up a loose union of states with equal powers and a weak national government.

Confederation
A union of sovereign statesthat work together for common goals while maintaining their independence.

Delegate
An individual chosen or elected to represent a group at a convention or conference.
Framer
A delegate involved in drafting the Constitution of the United States at the Philadelphia Convention.

Inalienable
Something, like a person’s natural rights, that cannot be taken away or removed.

Congress
The legislative body of the United States government, consisting of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives.

Revolutionary War
A conflict from 1775 to 1783 in which the Thirteen Colonies fought for independence from British rule.

Blessings of Liberty
Gifts of freedom provided by the Constitution.

Common Defense
The protection of a whole country against foreign attack.

Domestic Tranquility
Maintaining peace within a nation.

Establish
To set up or create something.

General Welfare
The common good or what is good for all people in a nation.
Justice
The enforcement of laws and rules in a country.

Ordain
To establish by law.

Preamble
The introduction to the Constitution.

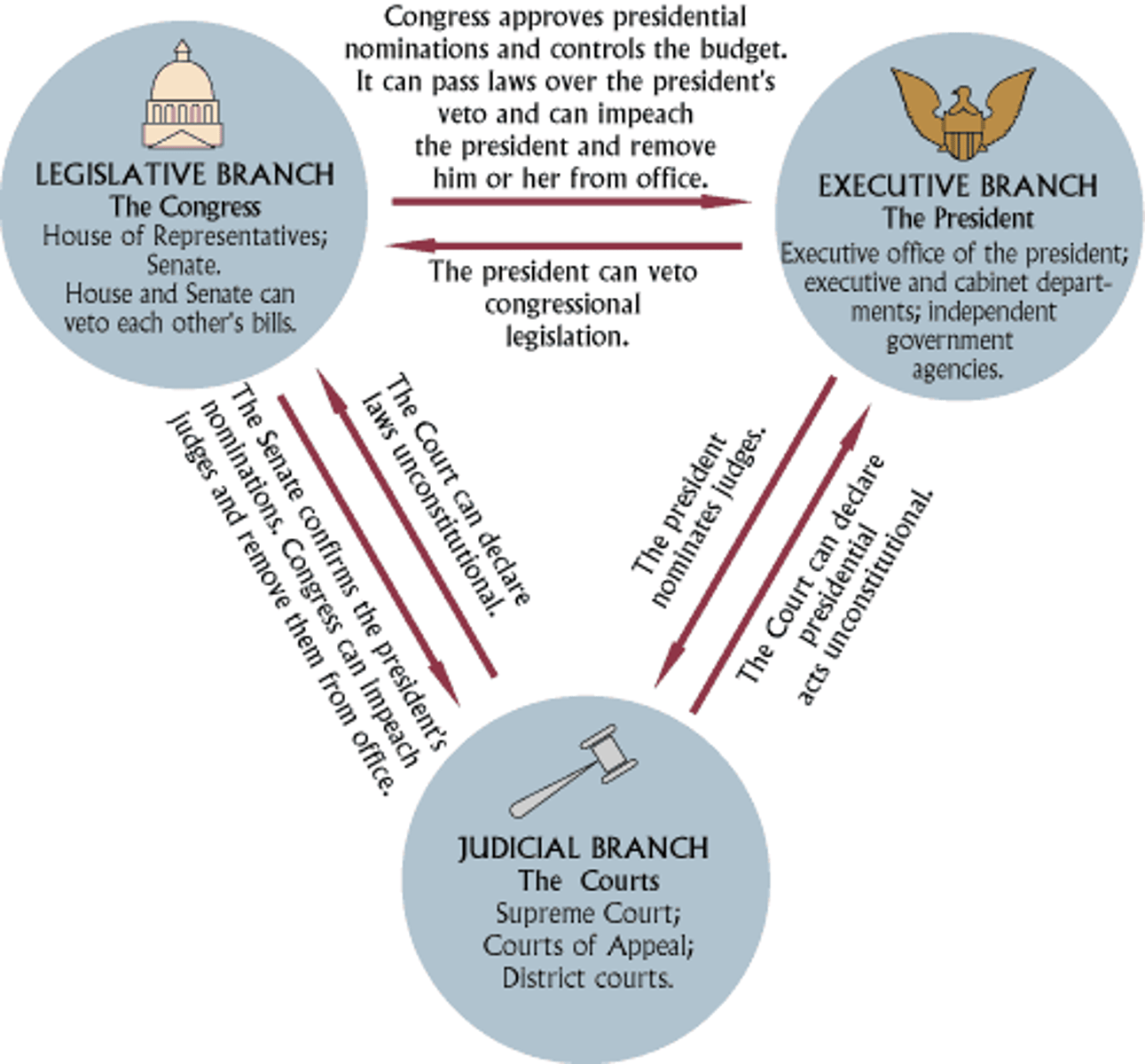
Balancing Powers
No one branch of government is given so much power that it can completely control the other branches

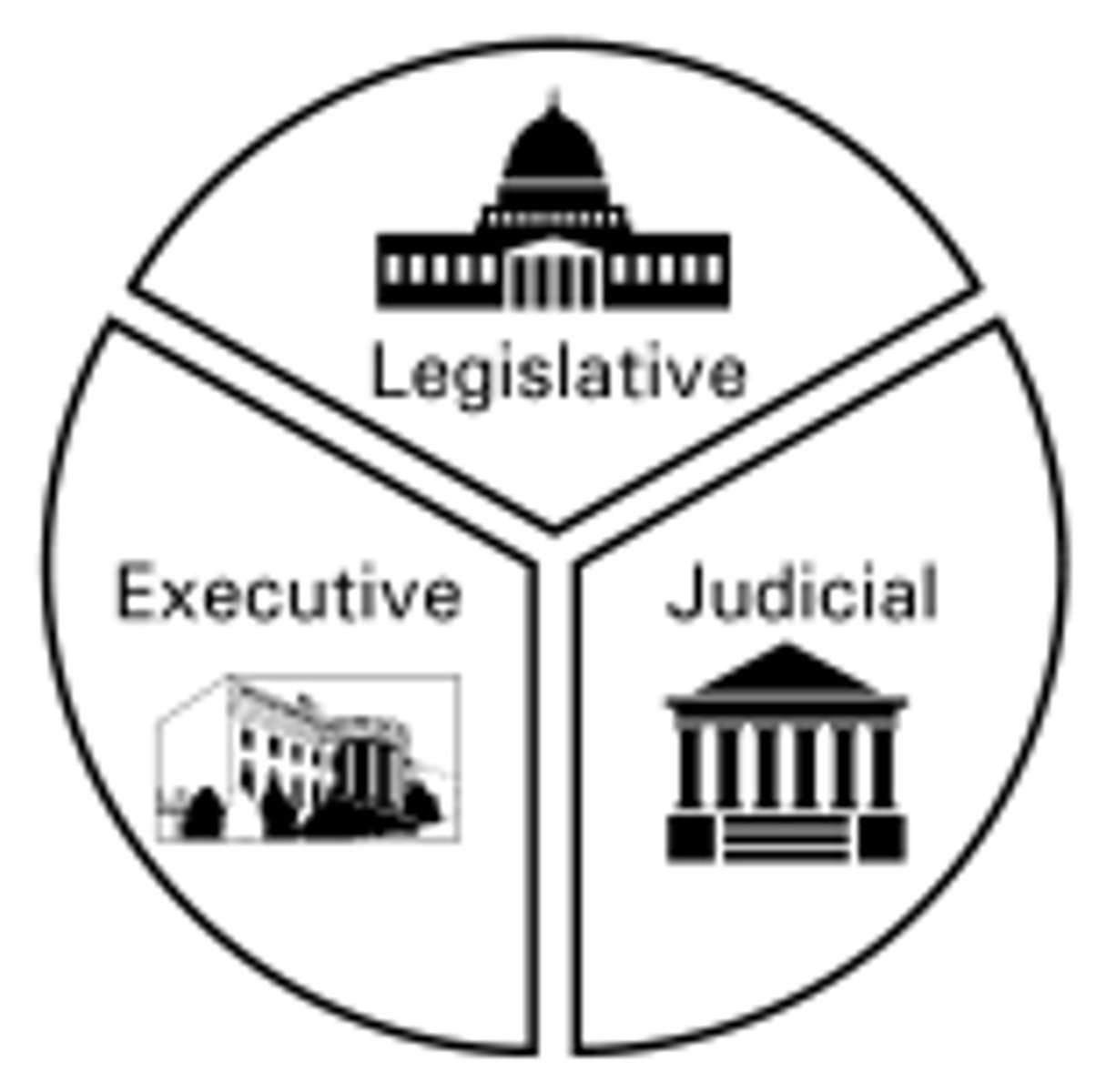
Three Branches of Government
Legislative, Executive, and Judicial; created to prevent one person from gaining complete control of the government.

Checking Powers
Each branch can stop the other branches from making final decisions or from taking certain actions.
Executive Powers
Powers given to the Executive Branch to carry out and enforce the laws made by Congress

Judicial Powers
Powers given to the courts to settle disagreements about what the laws mean.

Legislative Powers
Powers given to Congress to make the laws for the whole nation.

United States Supreme Court
The highest court in the United States.

Article 1 of the Constitution
The first article of the Constitution. It lists the powers of Congress.

Bill
A proposed law.

Unconstitutional
Not allowed under the constitution.

Veto
Executive power to reject a bill passed by Congress.

Appoint
To choose for an office or position.

Article II of the Constitution
Second article of the Constitution that establishes the executive branch and lists the duties and powers of the president.

Budget
A plan for making and spending money.

Commander in Chief
A term for the president as commander of the nation's armed. forces

Impeach
To formally charge a public official with misconduct in office.

Treaty
A formal agreement between two or more nations.

Appeal
Apply to a higher court for a reversal of the decision of a lower court.

Article III of the Constitution
Third article of the Constitution. It describes the responsibilities and powers of the judicial branch.

Associate
To join with others as a partner, member, or friend.

Federal Courts
The courts that deal with problems between states; they also handle cases that deal with the Constitution and the laws made by Congress.

Judicial Review
Judicial power that allows the court to determine the constitutionality of laws.

Sugar Act of 1764
An act that raised tax revenue in the colonies for the British monarchy. It also increased the tax on foreign sugar imported to the Americas.

Colonies
Lands that are controlled by another nation
Patriot
An American colonist who favored American independence.

George Washington
1st President of the United States and commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution.

Marquis de Lafayette
French aristocrat and soldier who served under George Washington in the American Revolution.

Mutiny
Open rebellion against authority.

Loyalist
American colonists who remained loyal to Britain and opposed the war for independence.

Aristocrat
A member of a rich and powerful family.

Treaties
Formal agreements between nations.

Treaty of Paris
Agreement signed by British and American leaders that stated the United States of America was a free and independent country.

Charles Cornwallis
British general who surrendered at Yorktown ending the American Revolution.

King George III
King of England during the American Revolution.

Taxes
Required payments to a government.

Tyranny
Cruel and oppressive government rule.

Boycott
A refusal to buy or use goods and services.

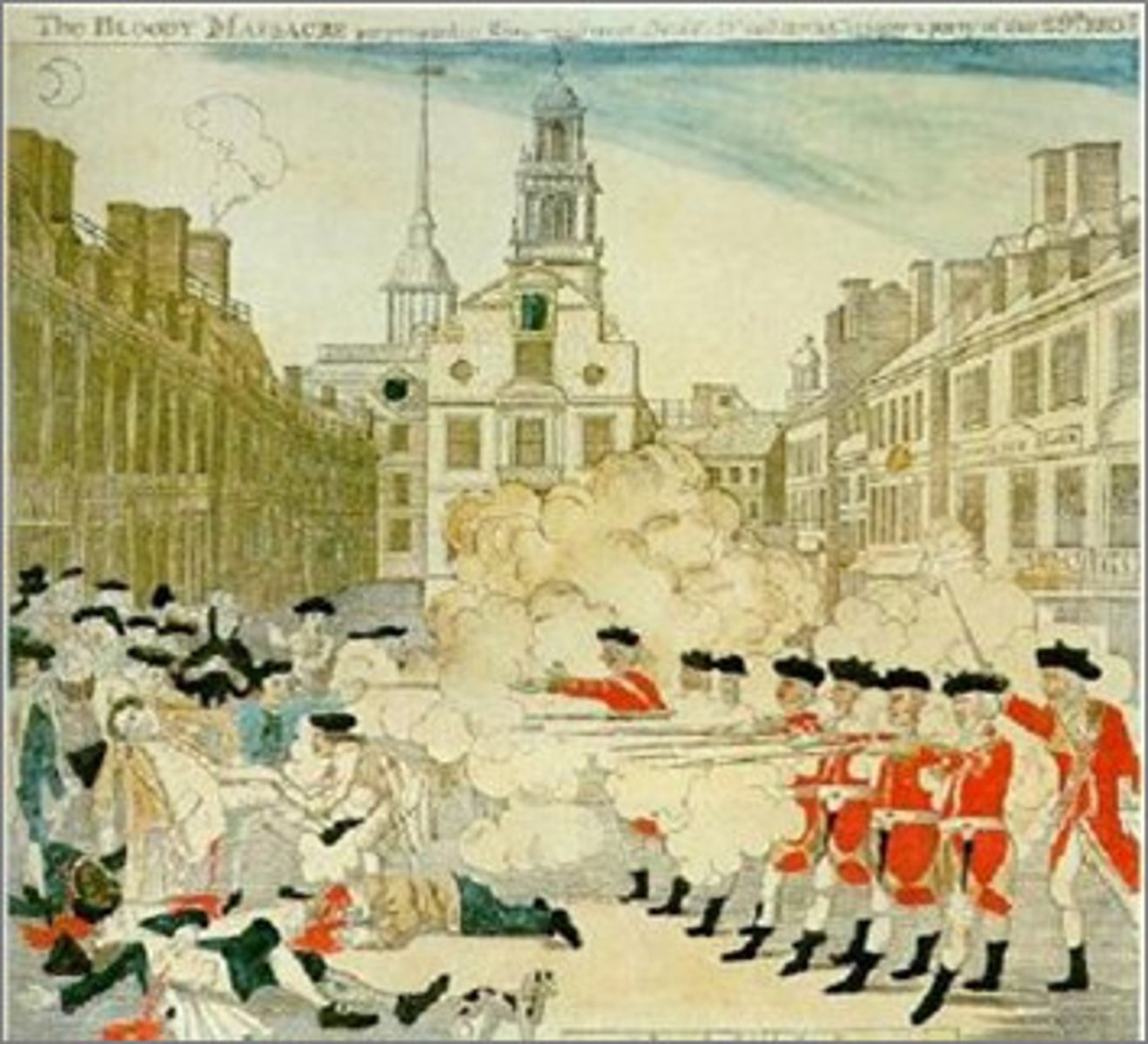
Boston Massacre
An incident in 1770 in which British troops fired on and killed American colonists.

Patrick Henry
An American leader from Virginia who spoke out against British rule of the American colonies; coined the phrase "Give me liberty or give me death."
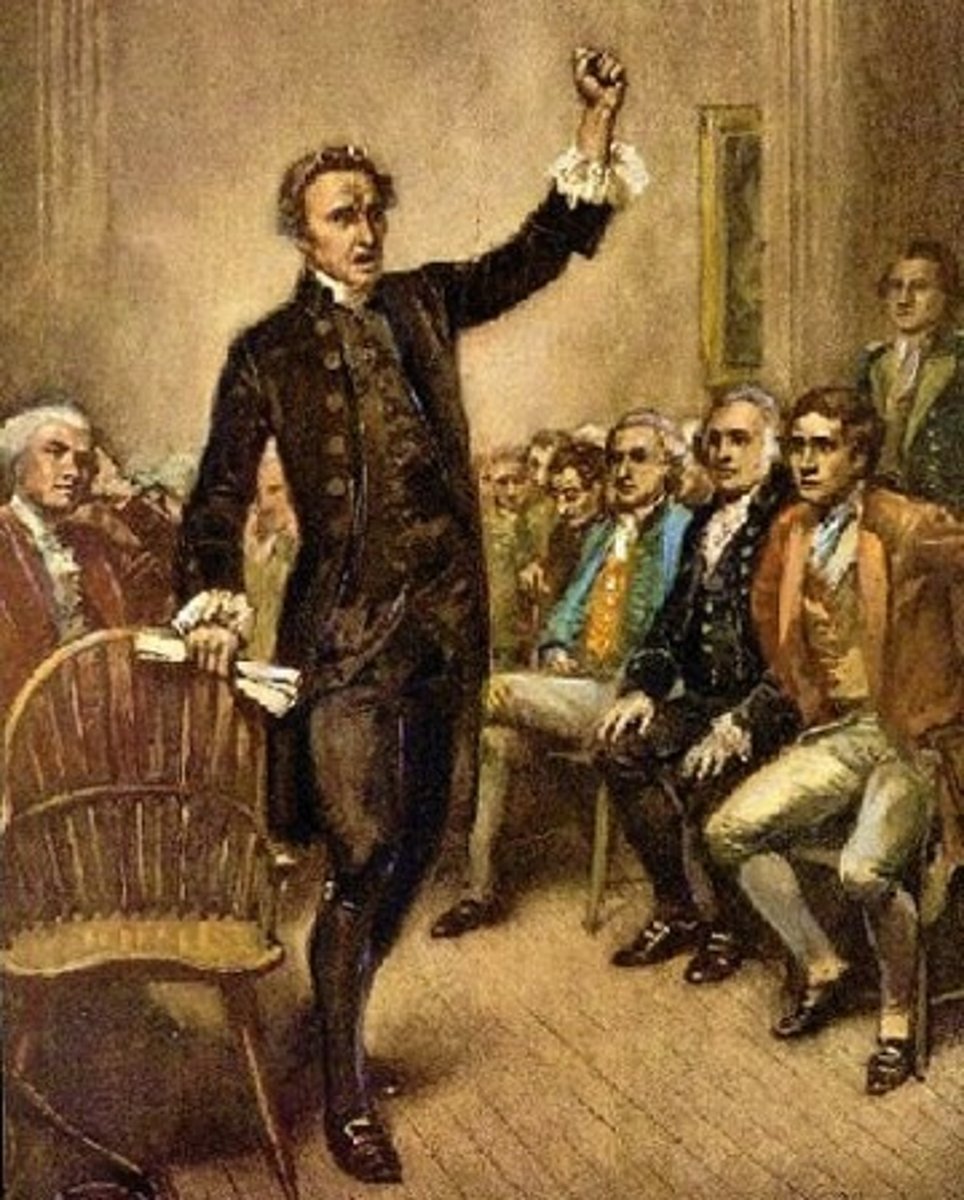
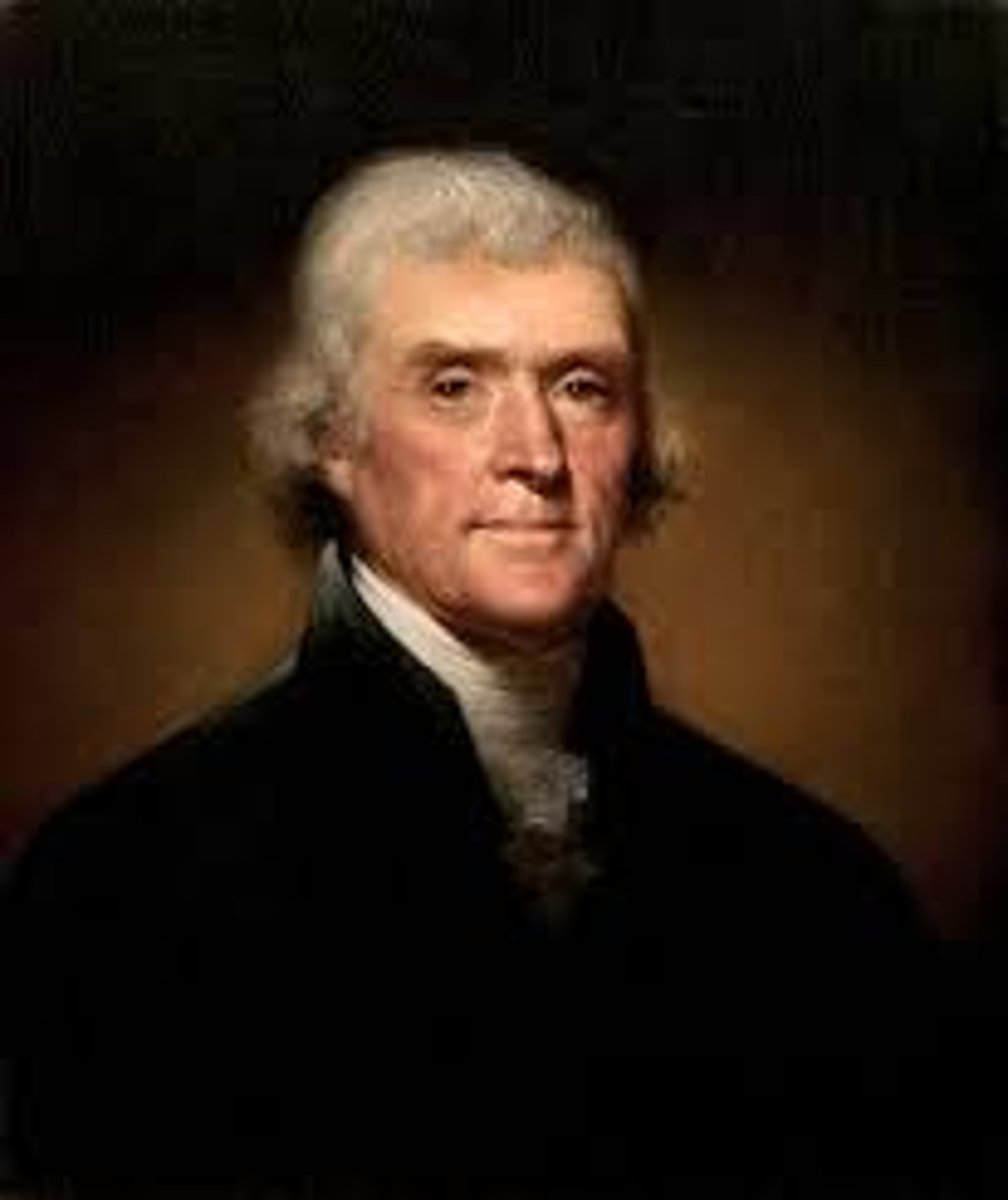
Thomas Jefferson
An American Patriot from Virginia and the author of the Declaration of Independence.

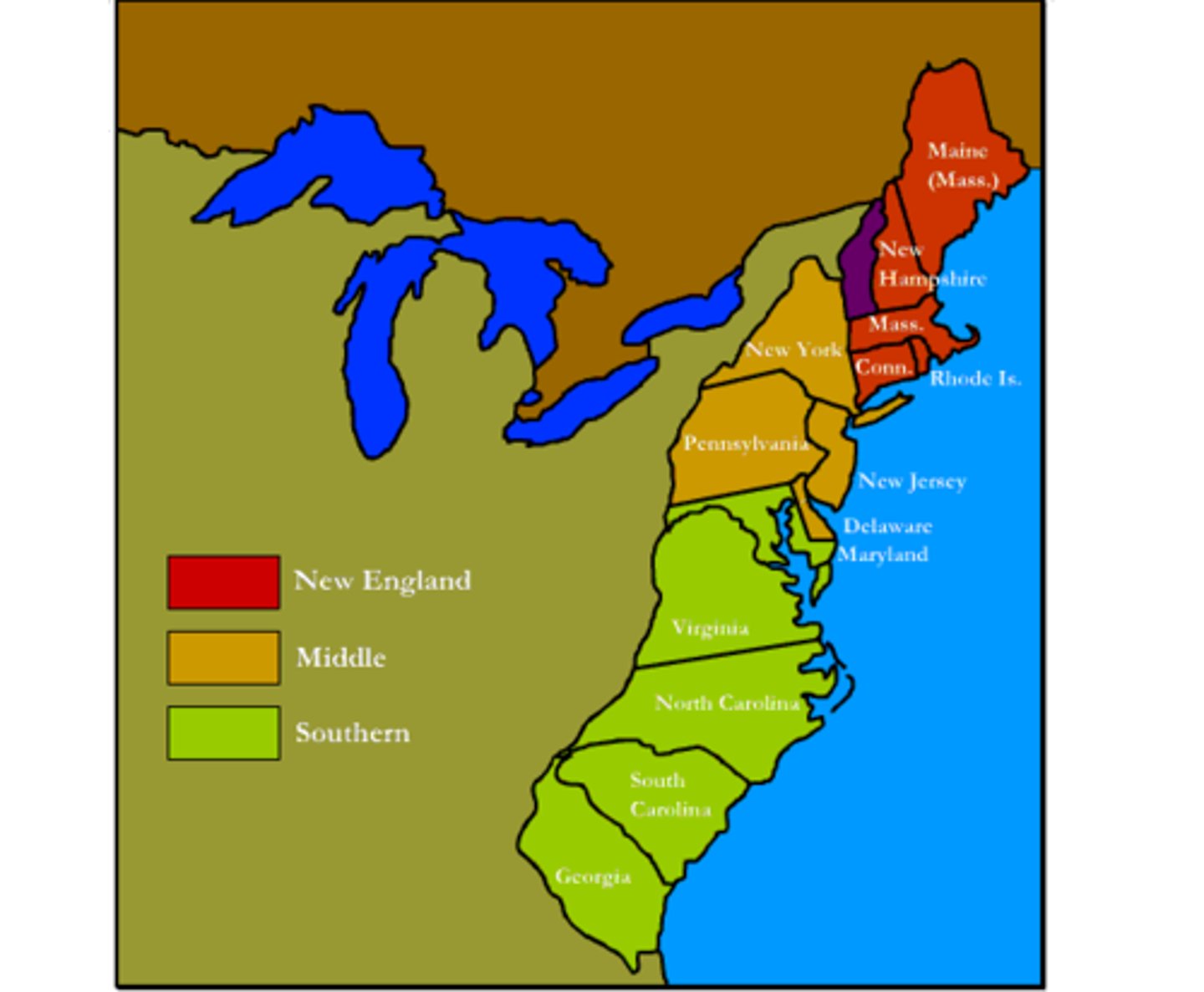
Colony
A group of people in one place who are ruled by a parent country elsewhere.
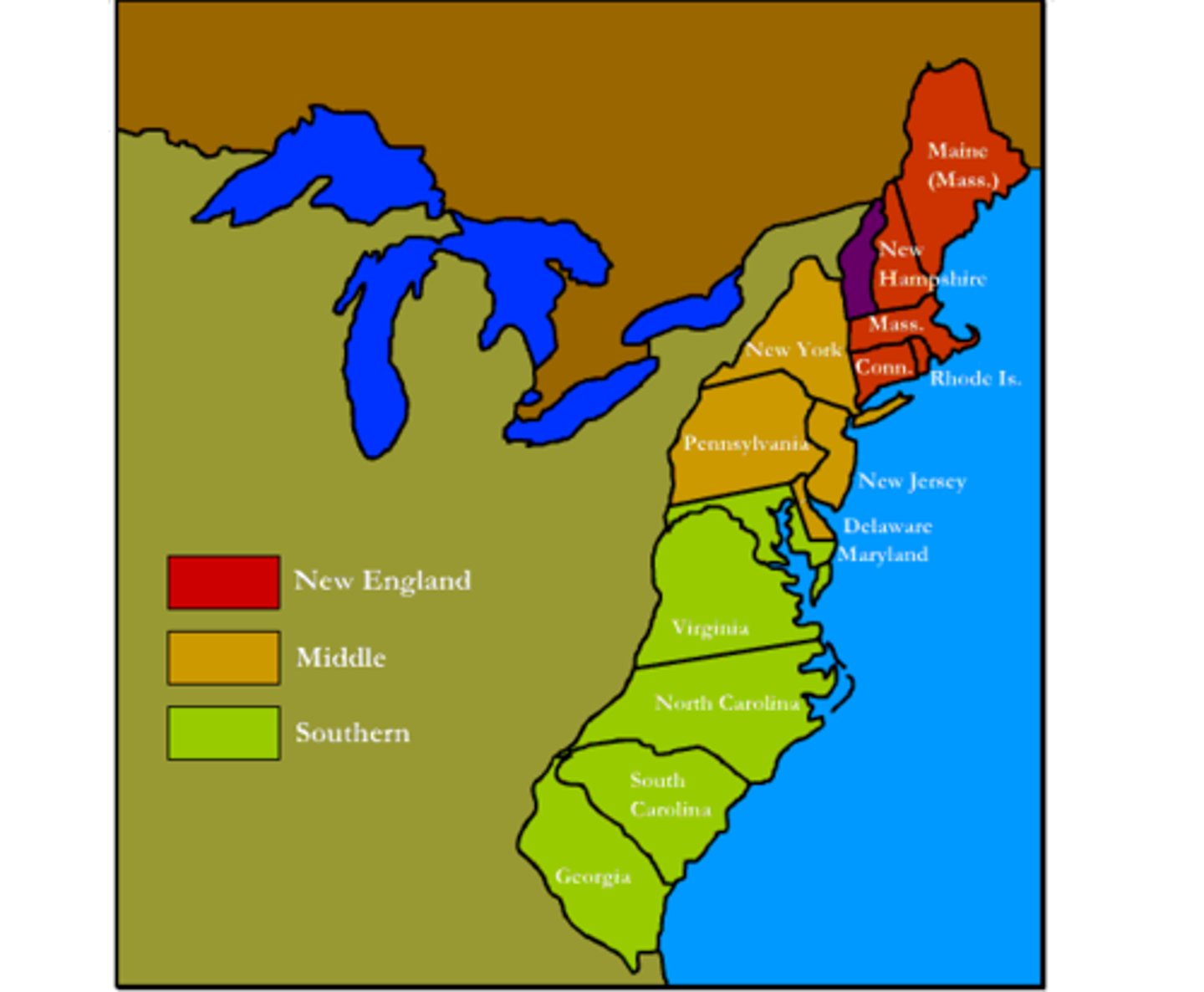
Diverse
Anything that has a great deal of variety, like ideas or people.

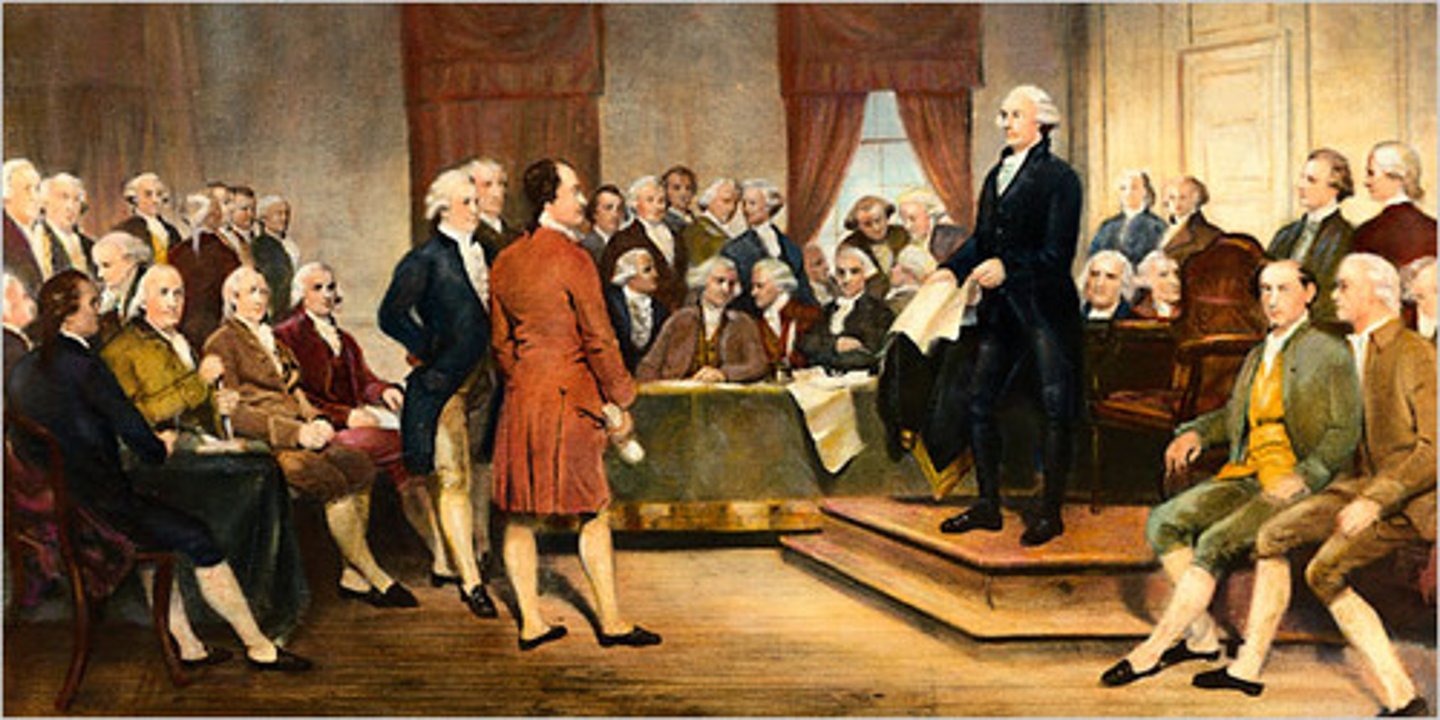
Founders
The people who were involved in establishing the United States via the Declaration of Independence.

Indentured Servants
Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a specific number of years.

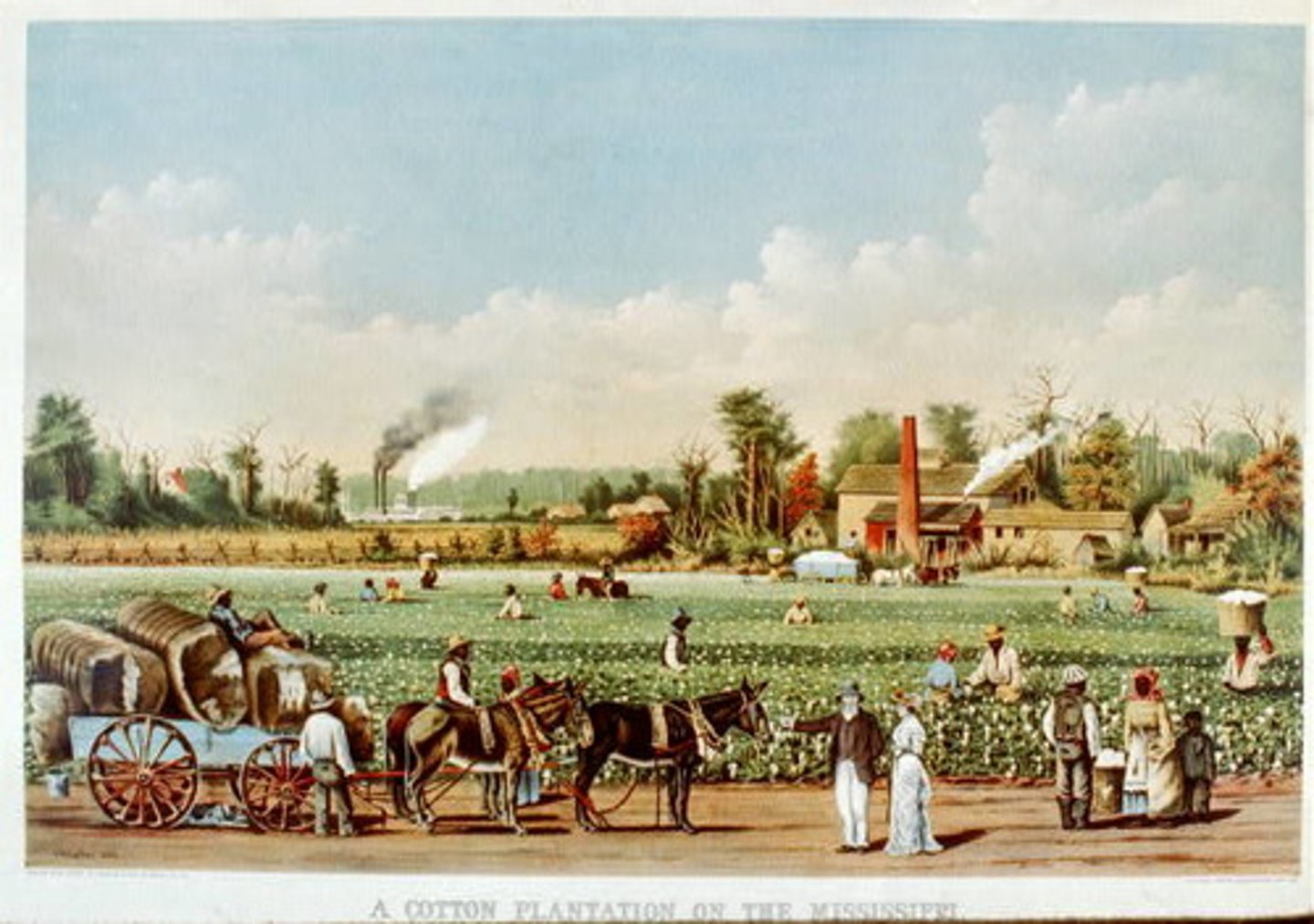
Plantation
A large estate farmed by many workers, typically in the American south.

Self-sufficient
Being able to produce enough for one's own needs.

Subject
Someone who owes allegiance to a government or ruler.

Slave
A person who is the legal property of another person and is forced to obey them against their will.

Natural Rights
The idea that all humans are born with rights, which include the right to life, liberty, and property.

Consent to be Governed
The idea that government derives its authority from the people it governs.

Social Contract
An agreement between the people and their government signifying their consent to be governed.

Civic Virtue
Willingness on the part of citizens to sacrifice their self-interests for the public good.
