Maths GCSE
4.3(3)
4.3(3)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
Cosine Rule (for finding a side)
a² = b² + c² - 2bc CosA
2
New cards
Cosine Rule (for finding a angle)
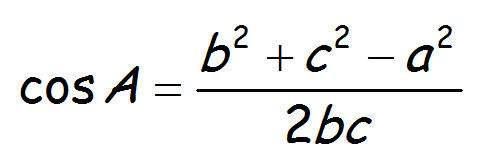
3
New cards
Sine Rule (for finding a side)
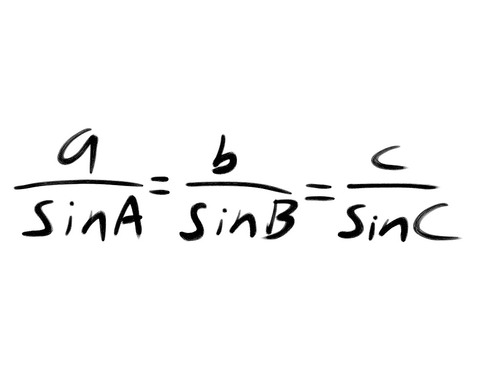
4
New cards
Sine Rule (for finding a angle)
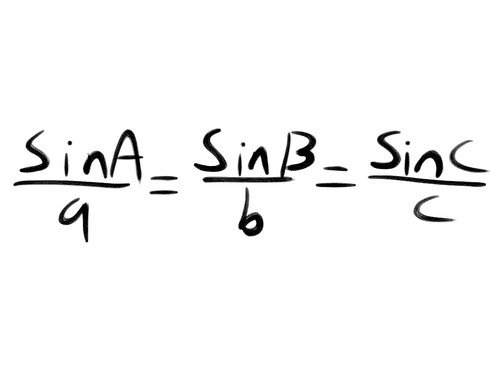
5
New cards
Pythagoras' Theorem
a² + b² = c²
6
New cards
Area Of a Triangle
½ ab SinC
7
New cards
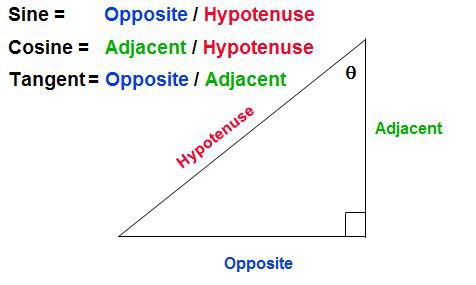
SOH CAH TOA
8
New cards
Area Of circle
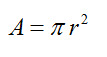
9
New cards
Volume Of Prism
area of cross section × length
10
New cards
Surds
A irrational number, a number which cannot be expressed as a fraction or as a terminating or recurring decimal. It is left as a square root. It can also be a non-cube number left in cube root form and so on.
11
New cards
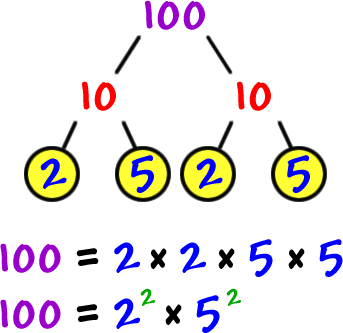
Prime Factors
12
New cards
Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)

13
New cards
Highest Common Factor (HCF)
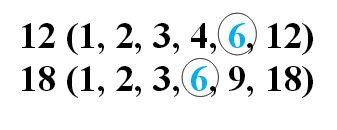
14
New cards
BIDMAS

15
New cards
Percentages

16
New cards
Standard Form
(+, −, ×, ÷)
17
New cards
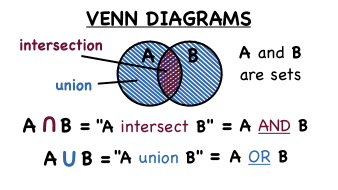
Venn Diagrams
18
New cards
Expanding Brackets
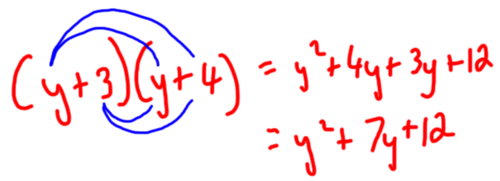
19
New cards
Expanding Brackets 2
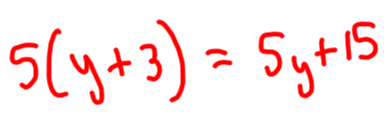
20
New cards
Factorising
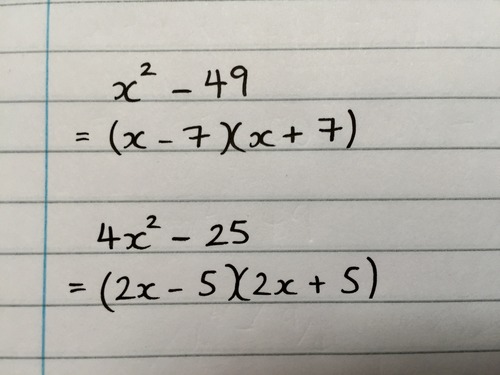
21
New cards
Inequalities
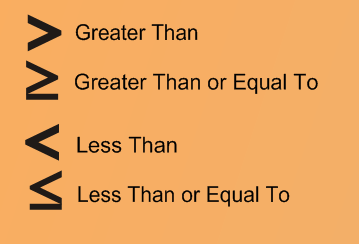
22
New cards
Quadratic Formula
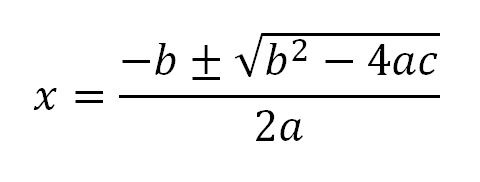
23
New cards
Polygons
24
New cards
Speed / Distance / Time
25
New cards
Tranformations
Rotation, Reflection, Translation and enlargement
26
New cards
Rotation
Rotational symmetry is where you can turn an object so that it looks exactly the same. The number of positions in which it looks exactly the same gives you its order of symmetry.
27
New cards
Reflection
When an object is transformed by a reflection the object and its image are always the same perpendicular distance from the mirror line.
Perpendicular means 'at right angles to'.
Examples:
Perpendicular means 'at right angles to'.
Examples:
28
New cards
Enlargement
When working out enlargements, you will need to know the scale factor and centre of enlargement.
The scale factor tells us by how much the object has been enlarged.
The centre of enlargement tells us where the enlargement is being measured from.
The scale factor tells us by how much the object has been enlarged.
The centre of enlargement tells us where the enlargement is being measured from.
29
New cards
Translation
If we translate an object, we move it up or down or from side to side. But we do not change its shape, size or direction.
30
New cards
Enlargement
31
New cards
Sector of circle
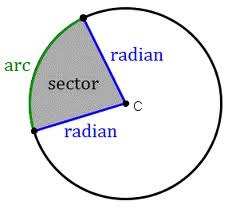
32
New cards
Circle Theorems
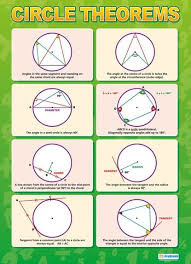
33
New cards
3D Shapes (Volumes)
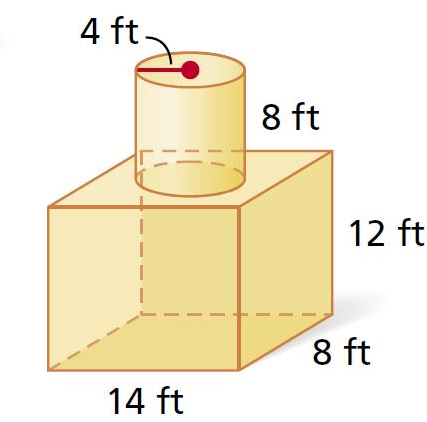
34
New cards
3D Shapes (Surface Area)
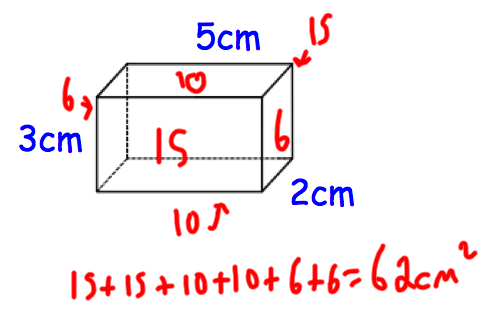
35
New cards
Mean
Is the average, add up all the numbers and divide by the number of numbers.
36
New cards
Median
Is the middle value, but them all in order and find the middle one.
37
New cards
Mode
Is the number that occurs the most frequently
38
New cards
Range
The difference between the lowest and the highest number
39
New cards
Tree Diagrams
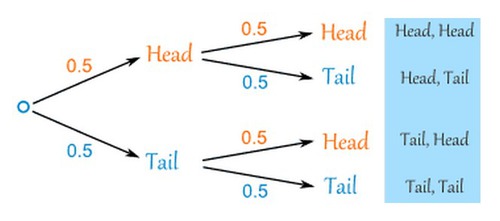
40
New cards
Histograms