Chemistry: Polar and Nonpolar Bonds and Molecules Review
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Polar Bond
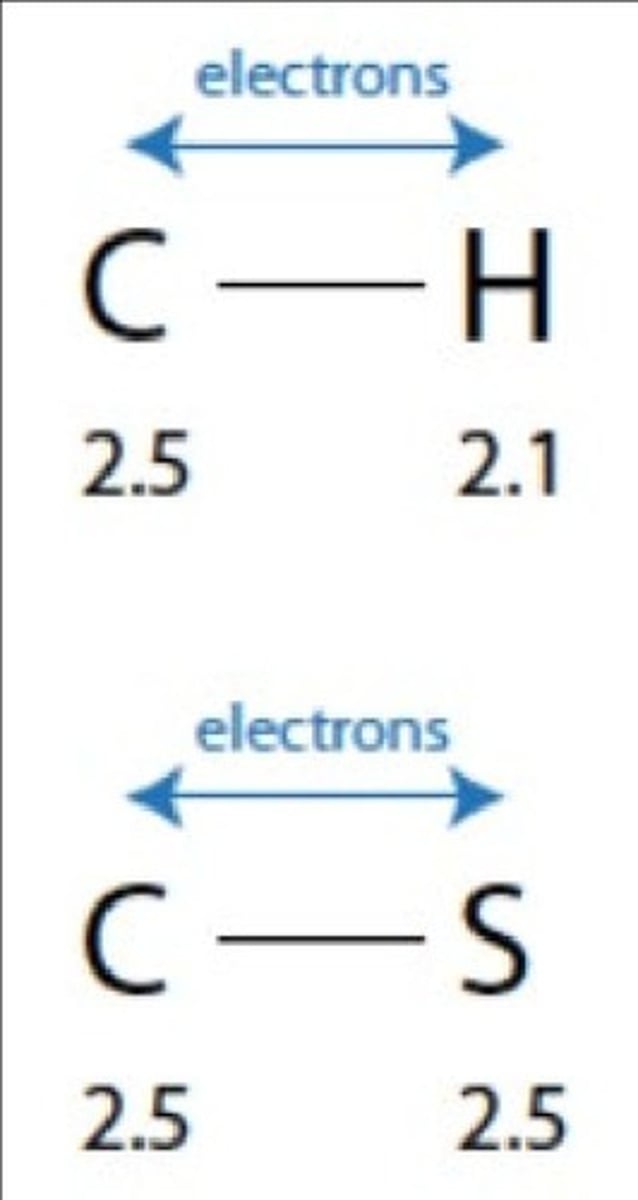
A bond between two atoms is polar if the atoms have significantly different electronegativities (>0.4).
Dipole Moment
Polar bonds do not share electrons equally, causing a dipole moment - one end of the bond is positive, and the other end is negative.
Non-polar Bond
A bond between two atoms is non-polar if the atoms have the same electronegativity or a small difference in electronegativities (<0.4).
Nonpolar Molecule
A molecule is nonpolar if all the bonds are nonpolar or if polar bonds are evenly (or symmetrically) distributed, causing the bond dipoles to cancel.
Polar Molecule
A molecule is polar if the distribution of polar bonds is asymmetrical, and bond dipoles do not cancel out.
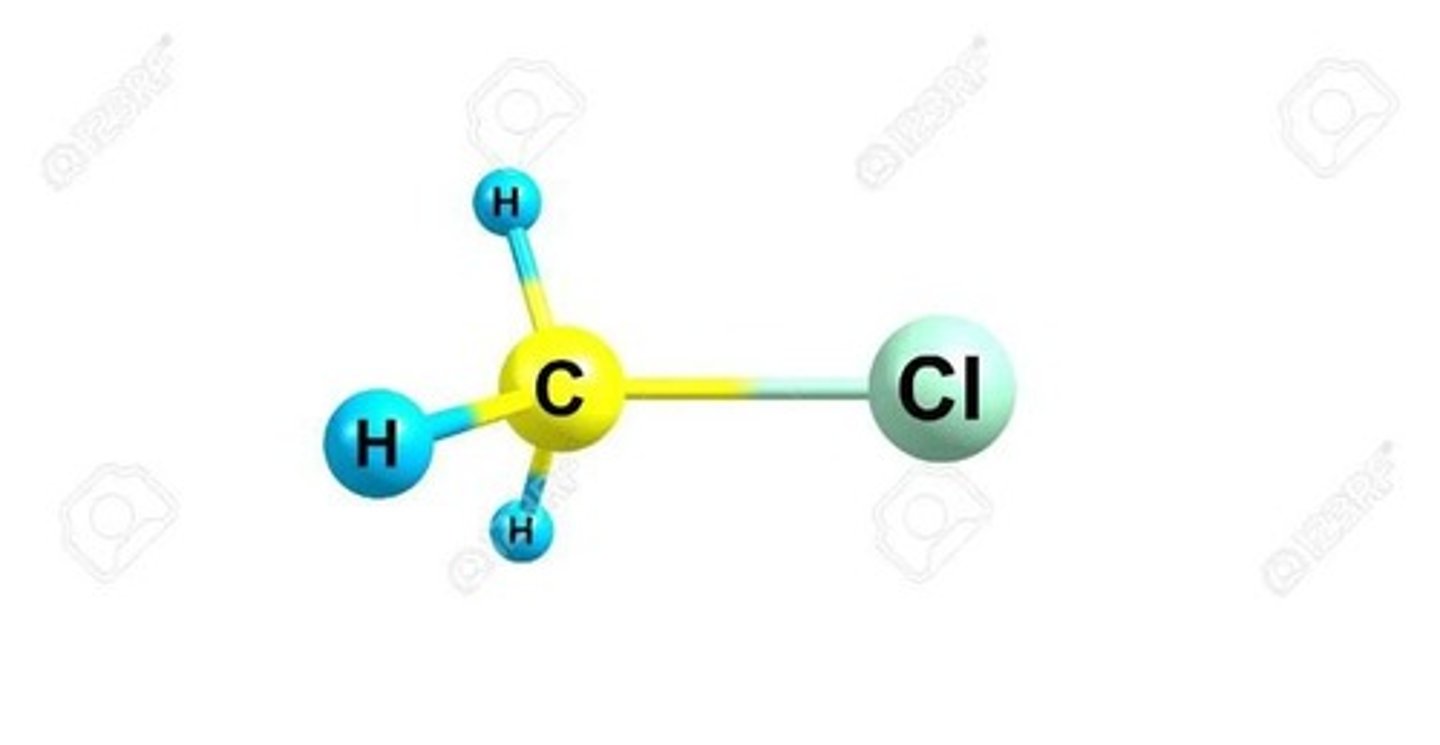
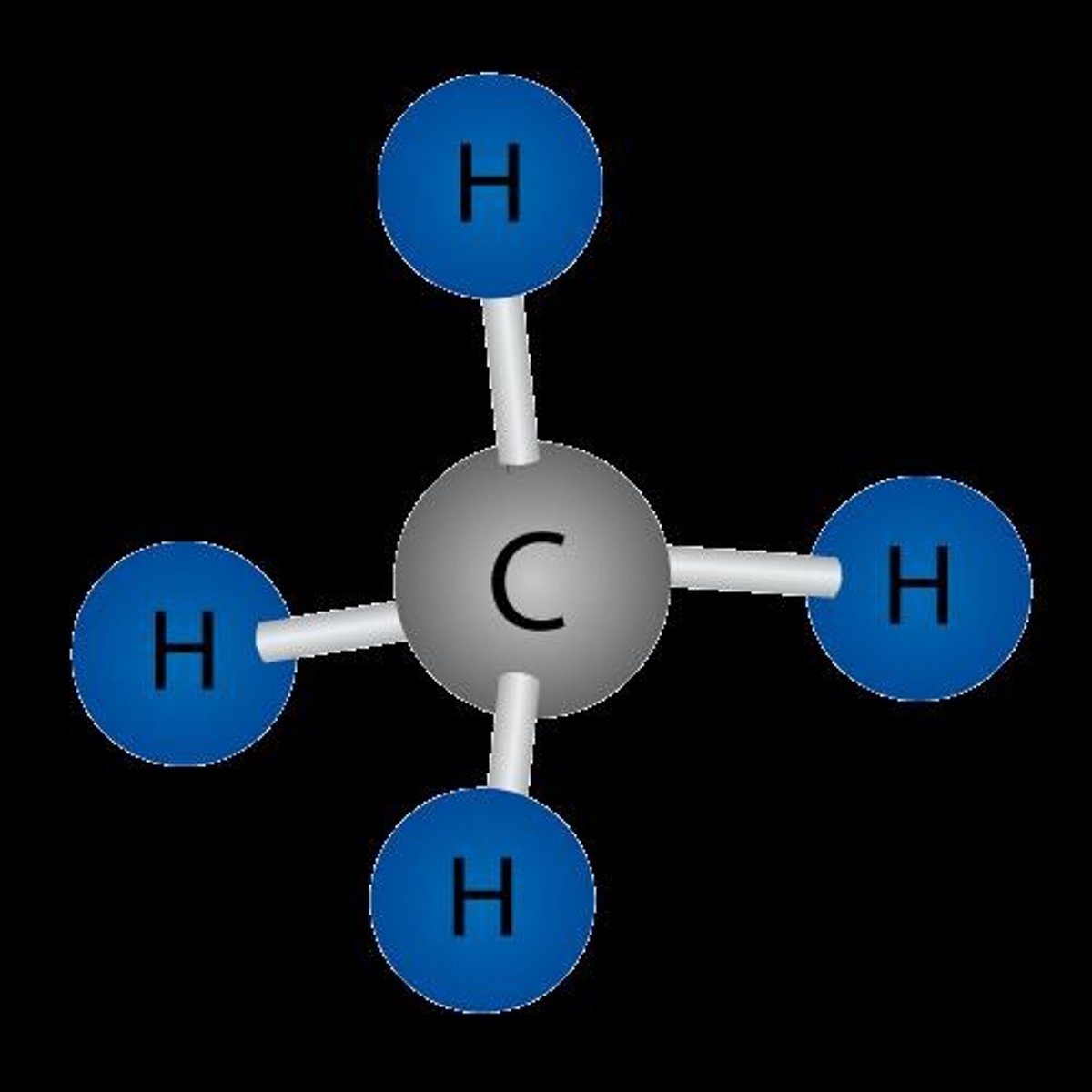
Determining Polar or Nonpolar for Organic Molecules
For organic molecules (contain C), it is non-polar if it contains only C and H, and most likely polar if it contains a heteroatom (an atom other than C and H like O, N, S, P, Cl, F, Br...).
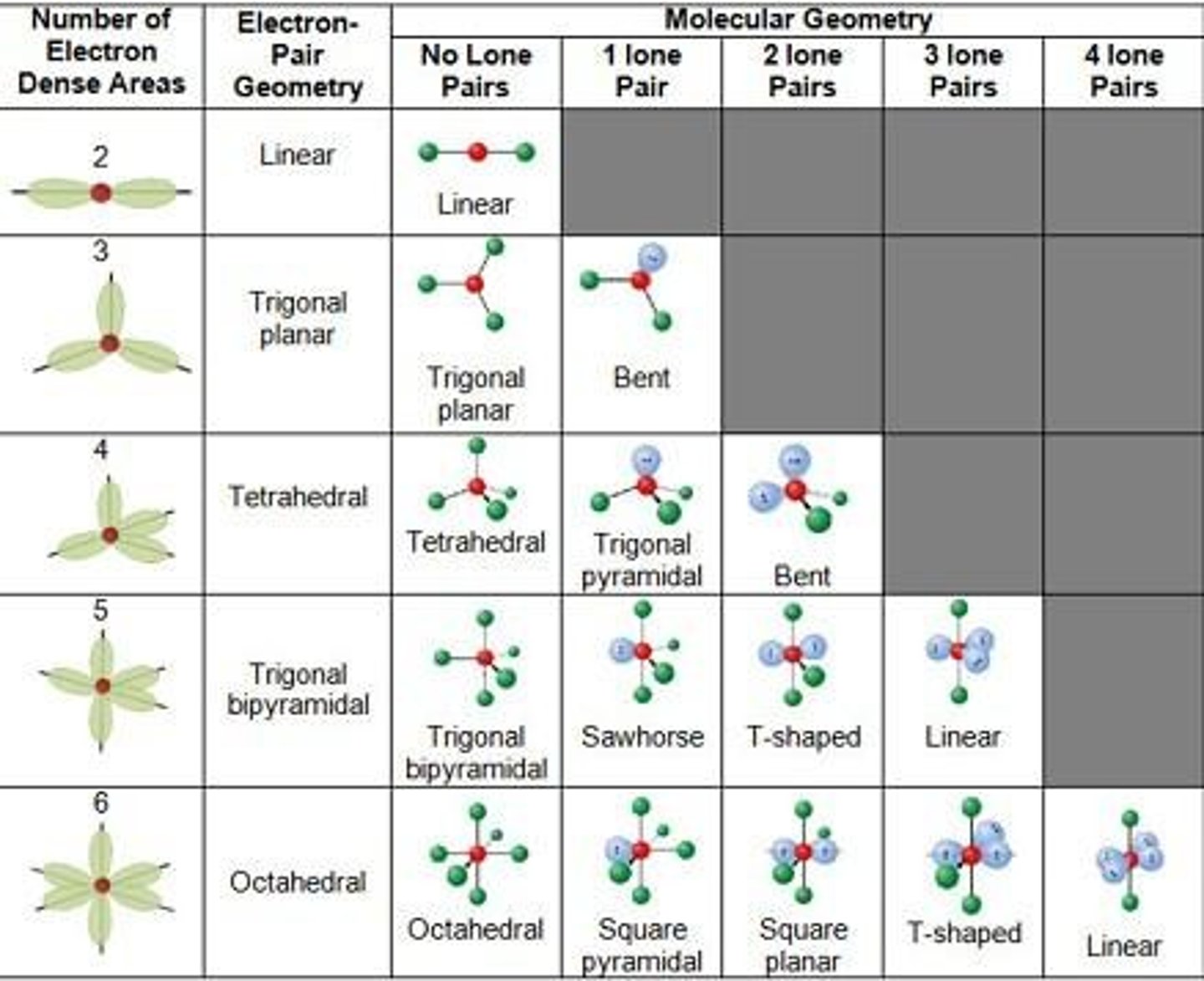
Determining Polar or Nonpolar for Inorganic Molecules
For inorganic molecules (no C), it is non-polar if completely symmetric. Shape = linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramid, octahedral or square planar and all bonds are the same. It is polar if not symmetric.
Symmetric Shapes
Symmetric shapes include linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramid, octahedral, or square planar.
Asymmetric Shapes
Asymmetric shapes include bent, trigonal pyramid, see-saw, t-shape, square pyramid, or a symmetric shape with not all bonds the same.
Electron Sets
To determine the shape of a molecule, identify the number of electron sets, including bonding and nonbonding.
Electronegativity Difference
A significant difference in electronegativities (>0.4) indicates a polar bond.
Symmetrical Distribution
In a nonpolar molecule, the distribution of polar bonds is symmetrical, leading to cancellation of dipoles.
Asymmetrical Distribution
In a polar molecule, the distribution of polar bonds is asymmetrical, preventing cancellation of dipoles.
Heteroatom
An atom other than C and H, such as O, N, S, P, Cl, F, Br, that can influence the polarity of a molecule.
Linear Shape
A molecular shape where all atoms are arranged in a straight line, contributing to symmetry.
Trigonal Planar Shape
A molecular shape where three atoms are arranged around a central atom in a flat plane, contributing to symmetry.
Tetrahedral Shape
A molecular shape where four atoms are arranged around a central atom, contributing to symmetry.
Trigonal Bipyramid Shape
A molecular shape with five atoms around a central atom, contributing to symmetry.
Octahedral Shape
A molecular shape with six atoms around a central atom, contributing to symmetry.
Square Planar Shape
A molecular shape with four atoms in a plane around a central atom, contributing to symmetry.