unit 3: development and learning
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
developmental psychology
focuses on how people grow and change throughout their lives
continuous development
refers to development that is gradual and smooth

discontinuous development
refers to development that occurs in distinct stages or steps
prenatal
the period of development that occurs before birth. typically includes the nine months of pregnancy, beginning from fertilization and ending with childbirth
teratogens
substances that can cause birth defects or developmental problems in a developing fetus
example: alcohol, tobacco, drugs, or environment toxins
fetal alcohol syndrome
conditions that occur from consuming alcohol during pregnancy, which can cause physical, behavioral, and cognitive problems for the baby
rooting reflex
an infant reflex where a baby’s cheek is gently stroked near their mouth, they turn in that direction, opening their mouths
imprinting
when a newborn animal forms an attachment to the first moving object they see, normally its mother
puberty
when an individual reaches sexual maturity, meaning they can now reproduce
menarche
the first menstrual period in females
spermarche
the first time males ejaculate
menopause
typically occurring in middle age, when a woman’s menstrual cycle ends
gender roles
social expectations about how males and females should think, act, and feel
sensorimotor stage
from birth to around 2 years old, when infants learn through their senses and motor actions
preoperational stage
occurs from about 2 to 7 years old, when children begin to represent the world with words, images and symbols
concrete operational Ssage
occurs from around 7 to 11 years old, when children think more logical and can perform more mental operations
formal operational stage
age 12 and continues through adulthood, when people can think abstractly, use logic in more advanced ways, etc
conservation
the understanding that something stays the same amount even if its shape changes
example: pouring water from one glass to another
reversibility
being able to mentally reverse an action
example: knowing that 2+2=4 but struggling with 2-4=2
animism
when human-like qualities are given to non-living things
example: a child believing that their toy bear can feel sad or happy
egocentrism
the inability for a person (mainly child) to understand that others have different perspectives and feelings
object permanence
the understanding that objects continue to exist even when they are out of sight
zone of proximal development
the gap between what a child can do alone and what they can do with help
example: a child can’t do a puzzle alone but can finish it with a parent’s help
phonemes
the first sounds an infant makes
example: the “buh” sound in bat
morphemes
the smallest unit of meaning in a language
example: "cat" (animal) and "s" (means more than one)
semantics
the meaning behind words and sentences
example: knowing that “child” and “kid” mean the same thing shows understanding of _______
one-word stage
third stage in language development, around 12-18 months, when children communicate using single words to represent entire thoughts or requests
example: mom, dad, or ball
telegraphic speech stage
18-24 months, when a child can start to connect two or three word phrases together
example: “i want cookie”
holophrases
when words will refer to different objects, people, or individual needs
example: a toddler saying “milk” to mean “I want milk”
ecological systems theory
explains how a person’s development is affected by different layers of their environment
microsystem (ecological systems theory)
includes other people and groups that an individual has direct interactions with
example: family, friends, teachers
mesosystem (ecological systems theory)
the connections between different parts of a person’s life
example: the relationship between your parents and your friends
exosystem (ecological systems theory)
the environment that affects a person indirectly, even if they aren't directly involved
example: a parent’s stressful job affecting how they treat their child at home
macrosystem (ecological systems theory)
the “big picture”, larger cultural values, laws, and customs that influence a person’s life
example: growing up in a society that values education shapes how much a child values school
chronosystem (ecological systems theory)
how life events and changes over time affect a person’s development
example: parents getting divorced, moving to a new city, covid
authoritarian parenting style
characterized by strict rules, little warmth, and often consists of punishment to enforce rules
example: a parent enforces rules without explaining why and expects obedience
authoritative parenting style
parenting style that is balanced, with clear rules, support, and open communication
example: a parent who sets rules but also explains the reasons behind them, and listens to their child’s feelings
permissive parenting style
involves few rules, high warmth, lots of freedom, and parents avoiding setting limits
example: a parent who lets their child stay up as late as they want
negligent parenting style
parents who are completely uninvolved in their children’s lives, playing little to no role in the life of the child
example: a parent who doesn’t know where their child is or who they’re with
secure attachment
when a child feels safe with their caregiver and explores freely
example: a child playing confidently while their parent is nearby
avoidant (insecure attachment)
the child tends to avoid or ignore their caregiver, showing little emotion when their parent leaves or returns to them
anxious (insecure attachment)
child is overly dependent on their caregiver and show extreme distress when seperated
disorganized (insecure attachment)
when a child shows confusing or fearful behavior toward their caregiver
temperament
a child’s personality traits
example: if they are easy going, shy, or if they get angry easily
separation anxiety
when a child feels nervous, upset, or fearful about being away from their caregiver
parallel play
when children play together side by side but don’t directly interact
pretend play
when a child uses their imagination to act of different scenarios with toys, objects, and other children
imaginary audience
a belief that one is constantly being watched a judged, resulting for an individual to become self-conscious
stages of development (erik erikson)
says that individuals go through psychosocial conflicts at each stage of life
social clock
societal expectations about when major life events should happen
example: feeling pressure to get married by 30
primary sex characteristics
characteristics that are developed and present at birth
example: sexual organs such as the penis, testes, uterus, and ovaries
secondary sex characteristics
physical traits that develop during puberty
example: breast development in females, facial hair in males
adverse childhood experiences (ACE)
stressful or traumatic events that occur during a person’s childhood that can impact long-term health and well-being
example: abuse or neglect
achievement (identity process)
when a person has explored options and committed to an identity
example: a teen who explored careers and chose to become a teacher
diffusion (identity process)
when a person has not yet explored or committed to any identity, leading to a poorly defined sense of self
foreclosure (identity process)
when a person commits to an identity without exploring other options
example: a teen deciding to become a doctor just because their parents expect it
moratorium (identity process)
when a person is actively exploring different identities but hasn’t committed yet
example: a college student trying different majors to find what they like
classical conditioning
learning by linking two stimuli so that one predicts the other
example: a dog salivating at the sound of a bell after it has been paired with food
unconditioned stimulus
a stimulus that naturally triggers a response
example: food makes a dog drool
unconditioned response
a natural response that happens without any learning
example: salivating when feed is presented
conditioned stimulus
something that used to be neutral but now causes a response after learning
example: the bell makes a dog drool after being paired with food
conditioned response
a learned reaction to something that was once neutral
example: salivating when hearing the bell, even without food
acquisition
the process of learning to associate a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus, leading to a conditioned response
example: pavlov’s dogs experiment
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance after a pause of an extinguished conditioned response
stimulus discrimination
when an organism learns to respond only to the original stimulus and not to similar ones
example: the dog salivates to the specific bell sound but not to other sounds
generalization
when a learned response happens to similar things
example: a dog trained to sit when it hears “sit” might also sit when it hears “sit down.”
higher(second)-order conditioning
when a new neutral stimulus is paired with an already conditioned stimulus to create a new conditioned response
example: if a light is paired with the bell (which already causes salivation), the dog will eventually salivate to the light alone
extinction
when the conditioned response gradually declines
example: the bell is rung no food. over time the dog will stop salivating
taste aversion
a learned avoidance of a certain food after it’s paired with a negative experience, like illness
example: if a person eats something and then gets sick, they may avoid that food in the future
operant conditioning
learning through reinforcement and punishment; behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on the consequences that follow them
example: a dog sits on command and gets a treat
positive reinforcement
(positive means adding) adding something desirable to increase the likelihood of a behavior occurring again
example: a child mows the lawn and gets rewarded 10 dollars, making it most likely for the child to mow the lawn again
negative reinforcement
(negative means removing) removes something unpleasant to increase the likelihood of a behavior
example: buckling your seatbelt so the annoying beeping stops
positive punishment
adding something unpleasant to decrease a certain behavior
example: getting extra chores after talking back
negative punishment
when something good is removed to decrease a behavior
example: losing phone privileges after missing curfew
reinforcement discrimination
occurs when an individual learns to respond only to specific stimuli
example: a dog gets a treat only when it hears “sit,” not when it hears other words
reinforcement generalization
when a behavior learned through reinforcement spreads to similar situations
example: a child praised for cleaning their room also starts cleaning the classroom to get praise
shaping
teaching a behavior by rewarding small steps toward the desired action
example: giving a dog a treat for sitting, then only for lying down, then only for rolling over, slowly shaping the full trick
instinctive drift
happens when an animals learned behaviors fade and natural instincts take over
example: a raccoon washing its food instead of eating it directly
superstitious behavior
when someone believes their actions cause an unrelated outcome
example: a player wears the same socks every game because they believe it brings good luck, even though it's just a coincidence
learned helplessness
when an individual or animal stops trying because they believe their actions won’t change the outcome, even when the reality is they can
example: student repeatedly gets Fs, so they stop studying
partial reinforcement
when a behavior is rewarded only sometimes, not every time
example: slot machines or lottery games
fixed-interval schedule
when a behavior is reinforced after a set amount of time
example: getting paid every two weeks, regardless of how much work is done

variable-interval schedule
when reinforcement is given after an unpredictable amount of time
example: checking your phone for a message and getting one at random times
fixed-ratio schedule
when reinforcement is given after a specific number of behaviors
(blue line)
example: a worker gets paid after every 10 items produced
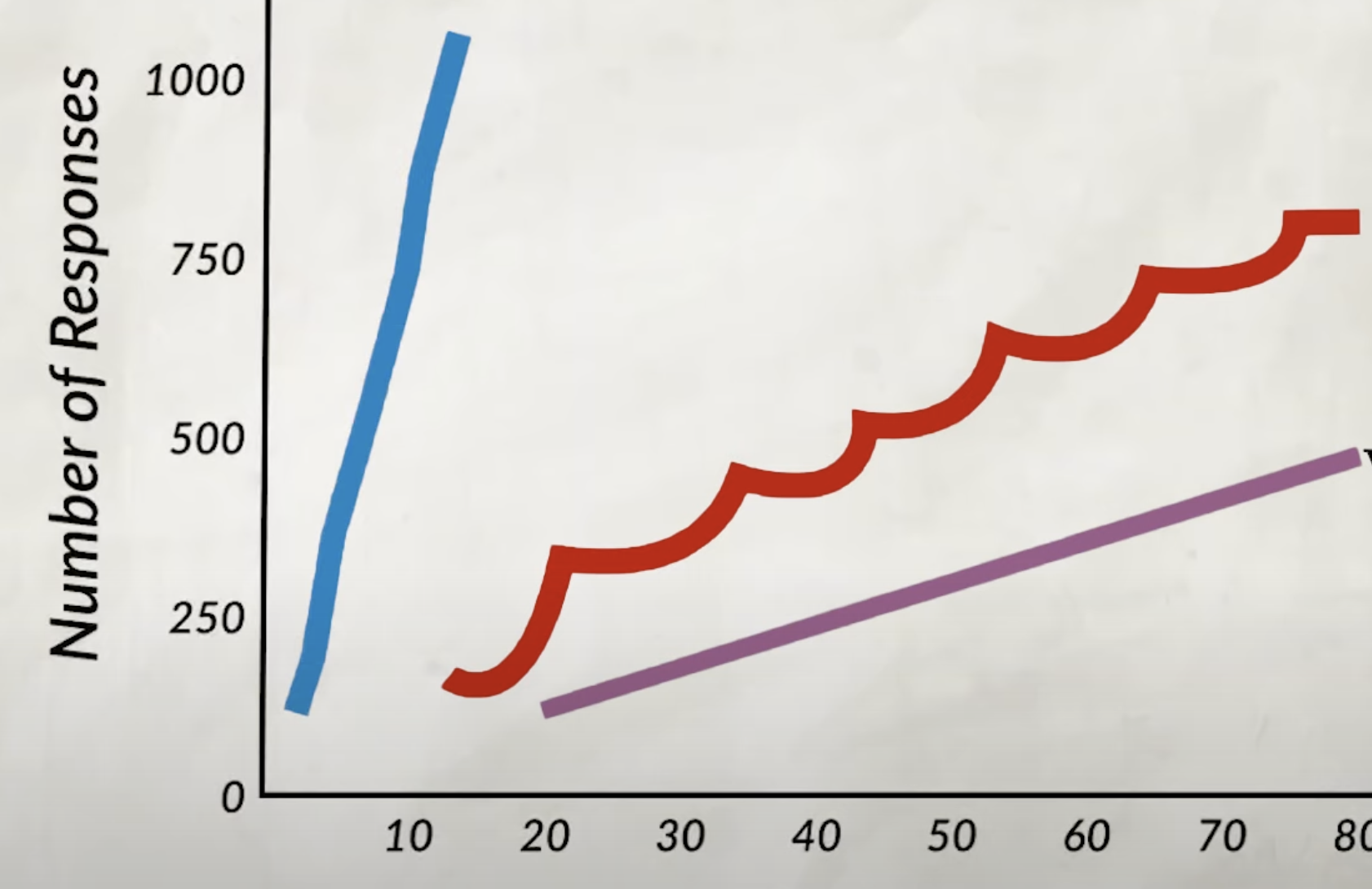
variable-ratio schedule
when a behavior is reinforced after a random number of correct behaviors, has the highest chance of extinction
example: slot machines in casinos, reward might be in 2 pulls or 50 pulls

law of effect
behaviors followed by positive outcomes are likely to be repeated, while those followed by negative outcomes are less likely to be repeated
social learning theory
suggests that people can learn new behaviors and information by watching and observing others
example: a child learns how to tie their shoes by watching a parent do it
vicarious conditioning
learning through the observation of others' experiences, especially their rewards or punishment
example: a child learns not to touch a hot stove after seeing another child get burned
insight learning
when there is a sudden solution or realization that pops into someone’s mind
example: a person trying to solve a riddle, and they suddenly figure out how to solve it
latent learning
when an individual learns new information or skills but does not realize it at the time
example: a child learns the route to school because of the bus, but only uses it when they need to walk alone
intrinsic motivation
doing something because you enjoy it or find it satisfying
example: reading a book because you love the story, not for a reward
extrinsic motivation
doing something for an external reward or to avoid a punishment
example: studying to get good grades or avoid a bad report card
cross-sectional study
involves studying different groups of people at different ages all at the same time
example: the fast food of research; quick, cheap, and gets the job done, but cant show relationships between variables or change over time
longitudinal study
involves studying the same group of people over a long period of time to observe changes and developments in their behavior
side effects: could be costly, may take too long, or may suffer from patient attrition
stability vs change
explores how certain characteristics of a person will remain constant (stable), while others evolve and change
nature vs nurture
the debate about whether who we are comes more from our genes or from our environment
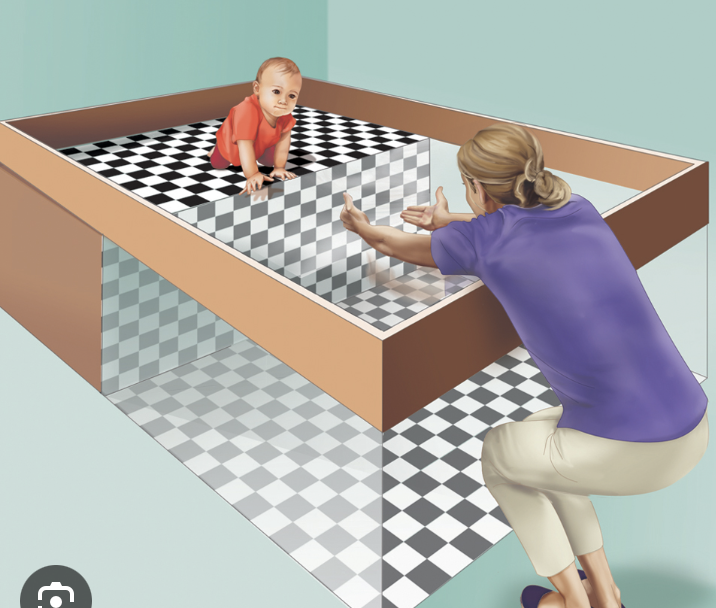
visual cliff experiments
provides insight into when an infant develops depth perception

theory of mind
second half of the preoperational stage where a child understands that people have thoughts, feelings, and perspectives that are different from their own
scaffolding
giving support to help someone learn a new skill, then slowly taking it away as they get better
cooing stage
the first stage in language development. when an infant makes soft repetitive vowel sounds like ooo and aaa