Alcohols
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
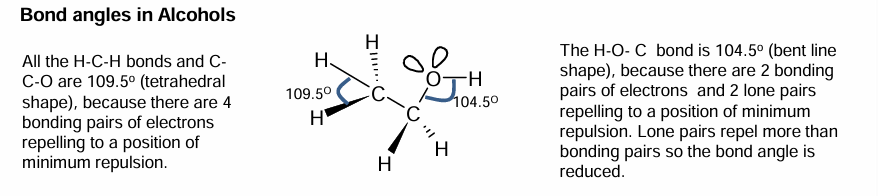
Bond angles in Alcohols

Boiling points of Alcohols
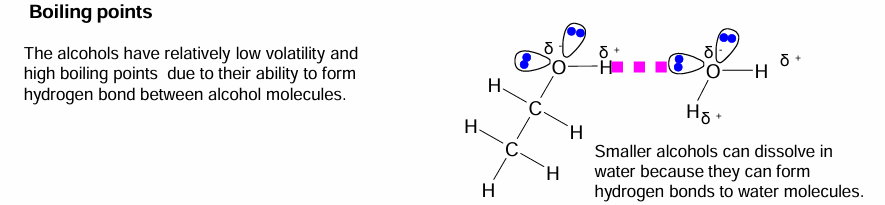
The smaller alcohols are soluble because a larger proportion of the molecule is polar whereas the larger the molecule is, the longer the hydrocarbon chain, which is non-polar.

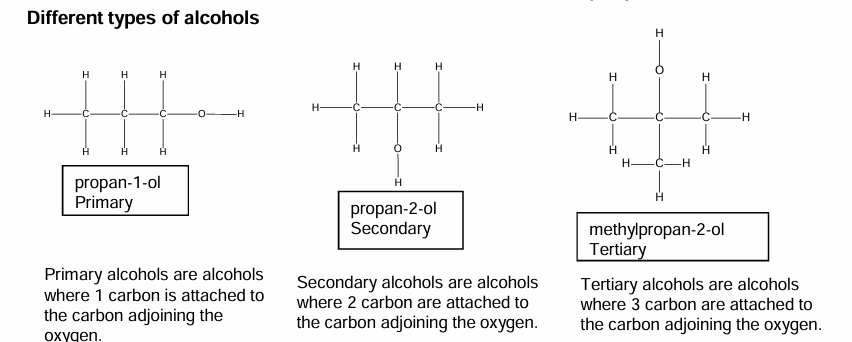
Different types of alcohols

Oxidation of alcohols overview
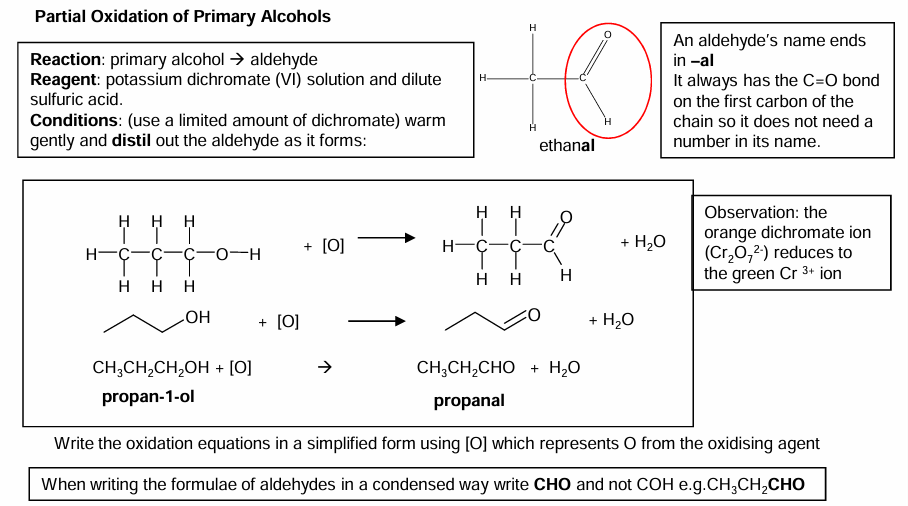
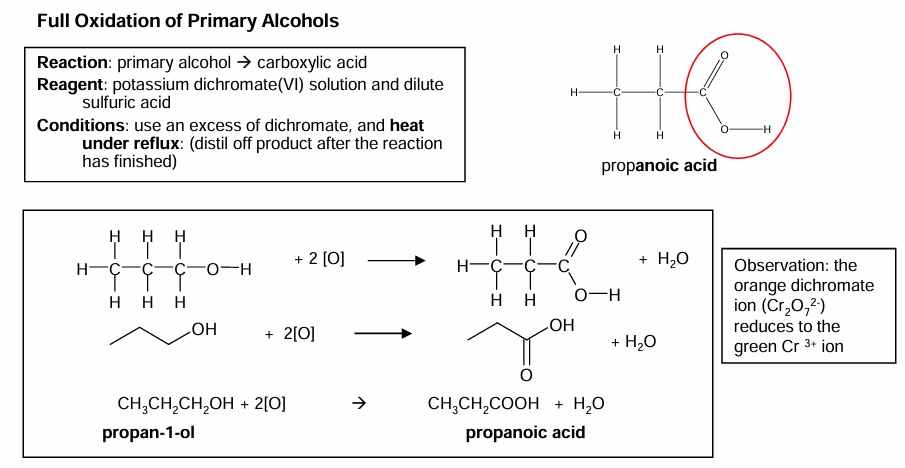
Primary → oxidise to form aldehydes → carboxylic acids or can skip aldehydes if conditions are harsh enough.
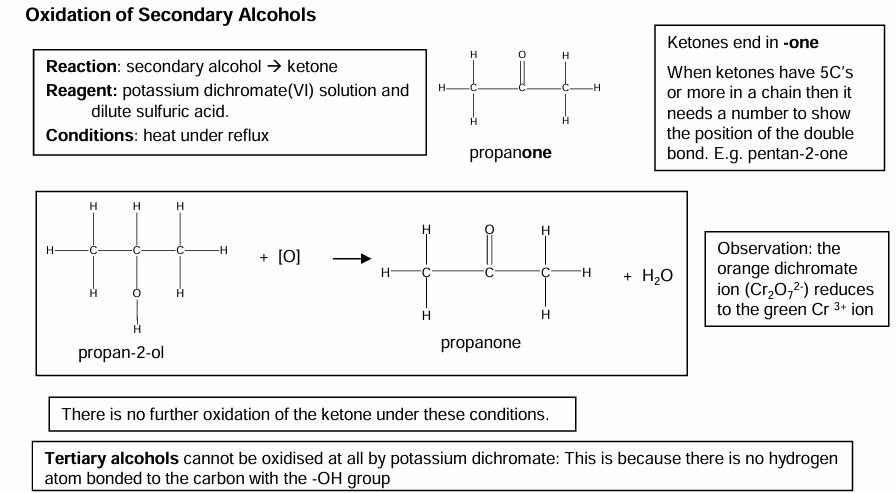
Secondary → oxidise to form ketones
Tertiary → Cannot easily be oxidised
Partial oxidation of primary alcohols

Full oxidation of primary alcohols

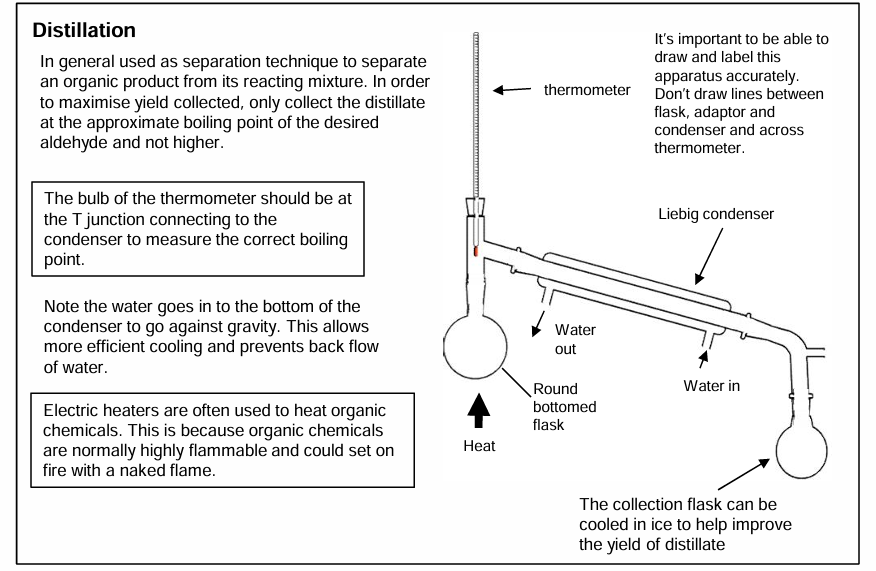
Distillation
Aldehydes have lower boiling points as it doesn’t have H-bonds but only v.d.w.s and permanent dipole-dipole interactions.

Reflux
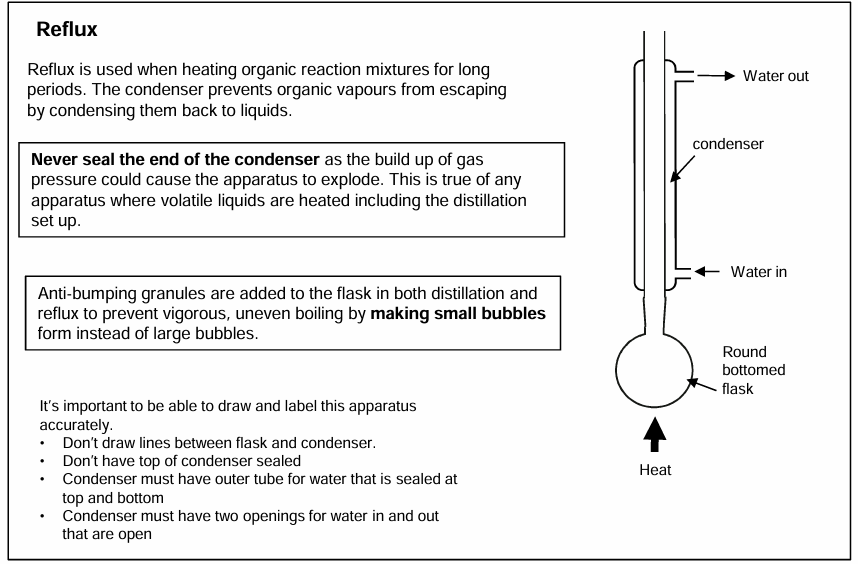
Allows you to carry out a reaction at the boiling point of the chemicals without losing any reactants or products.

Oxidation of secondary alcohols

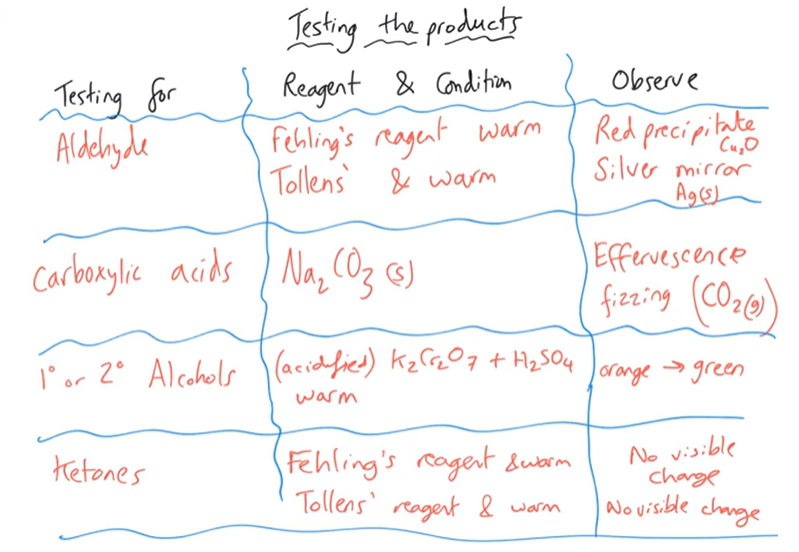
Testing the products of oxidation

Elimination/Dehydration of Alcohols

Primary alcohols e.g. propan-1-ol form propene and water whereas secondary alcohols e.g. butan-2-ol will form but-1-ene and but-2-ene (could exist as E/Z isomers).
Producing alkenes from alcohols provides alternative route to polymers without using alkenes derived from oil.
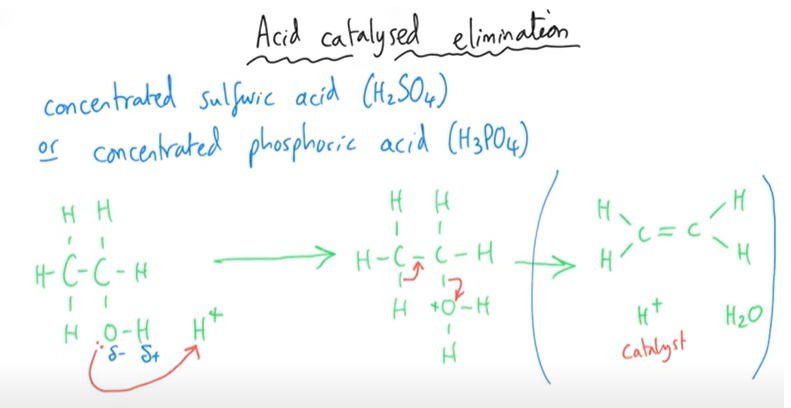
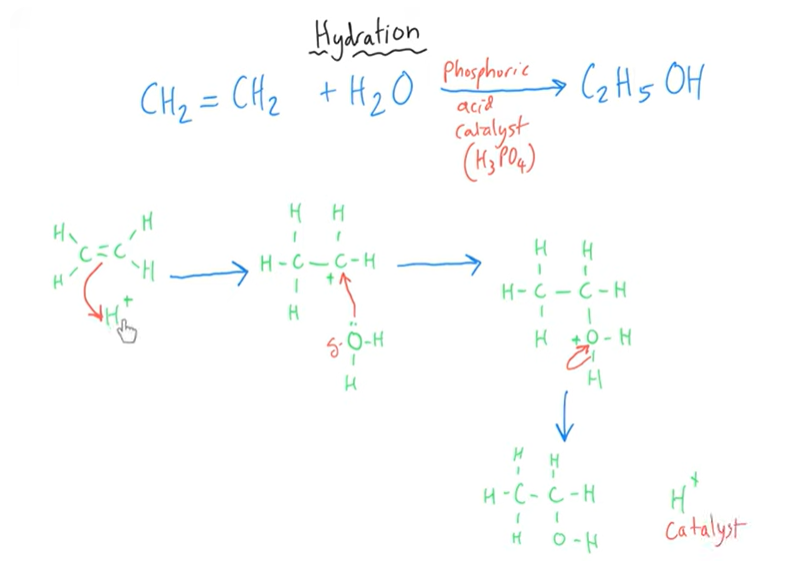
H+ comes from the acid.

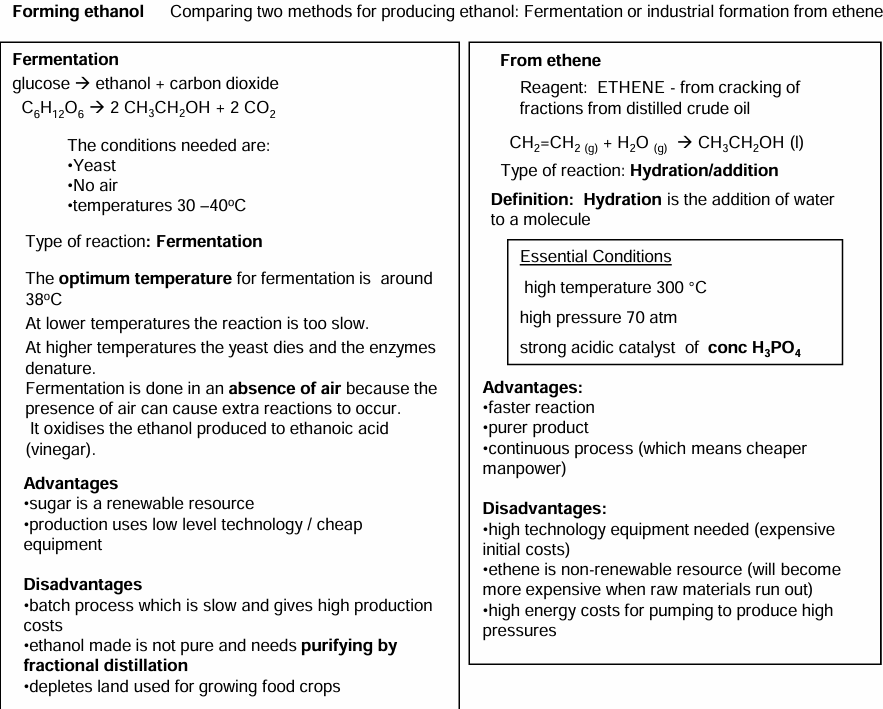
Fermentation vs hydration of ethene

Acid catalysed addition mechanism for hydration of ethene.

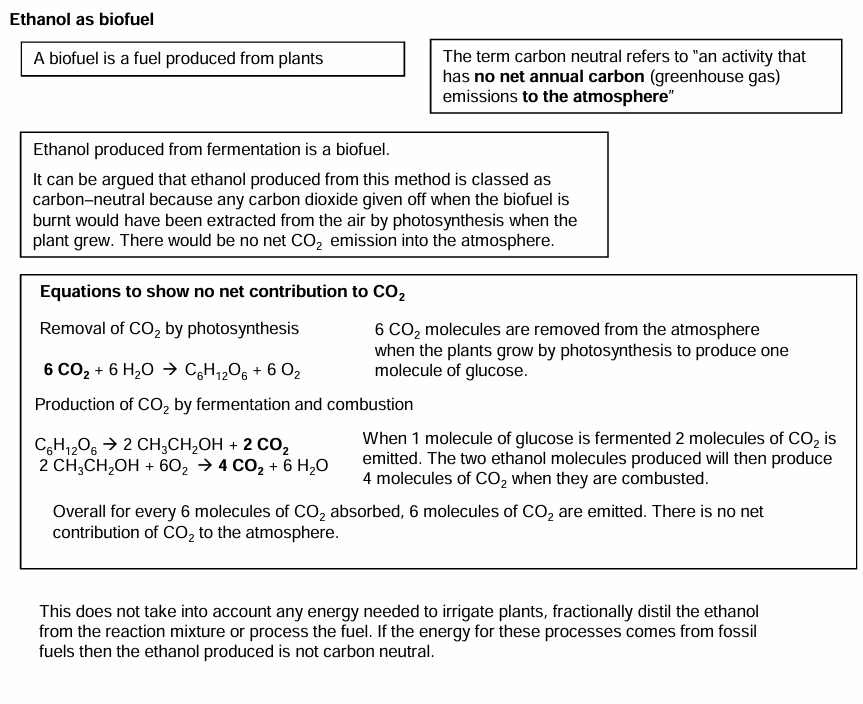
Ethanol as a carbon-neutral biofuel