DNA Structure & Replication
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
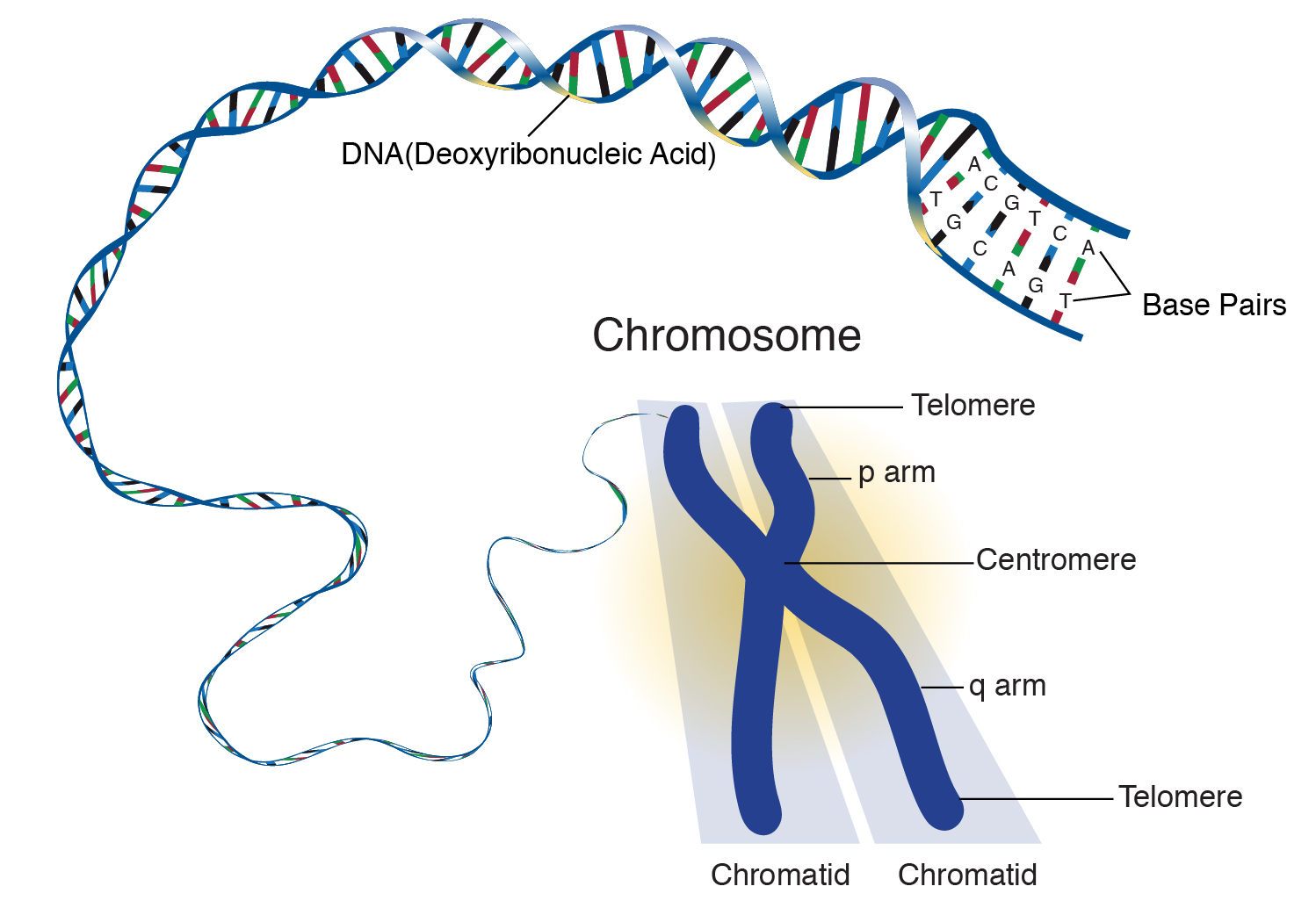
Chromosomes
Composed of 60% protein and 40% nucleotide.
Long tangled molecules of DNA wound around protein.
Hard to distinguish individual chromosomes → Collectively called chromatin.
Each chromosome (46 per human cell) contains 100s to 1000s of genes.
Gene: a segment of DNA that encodes the sequence of a particular protein.
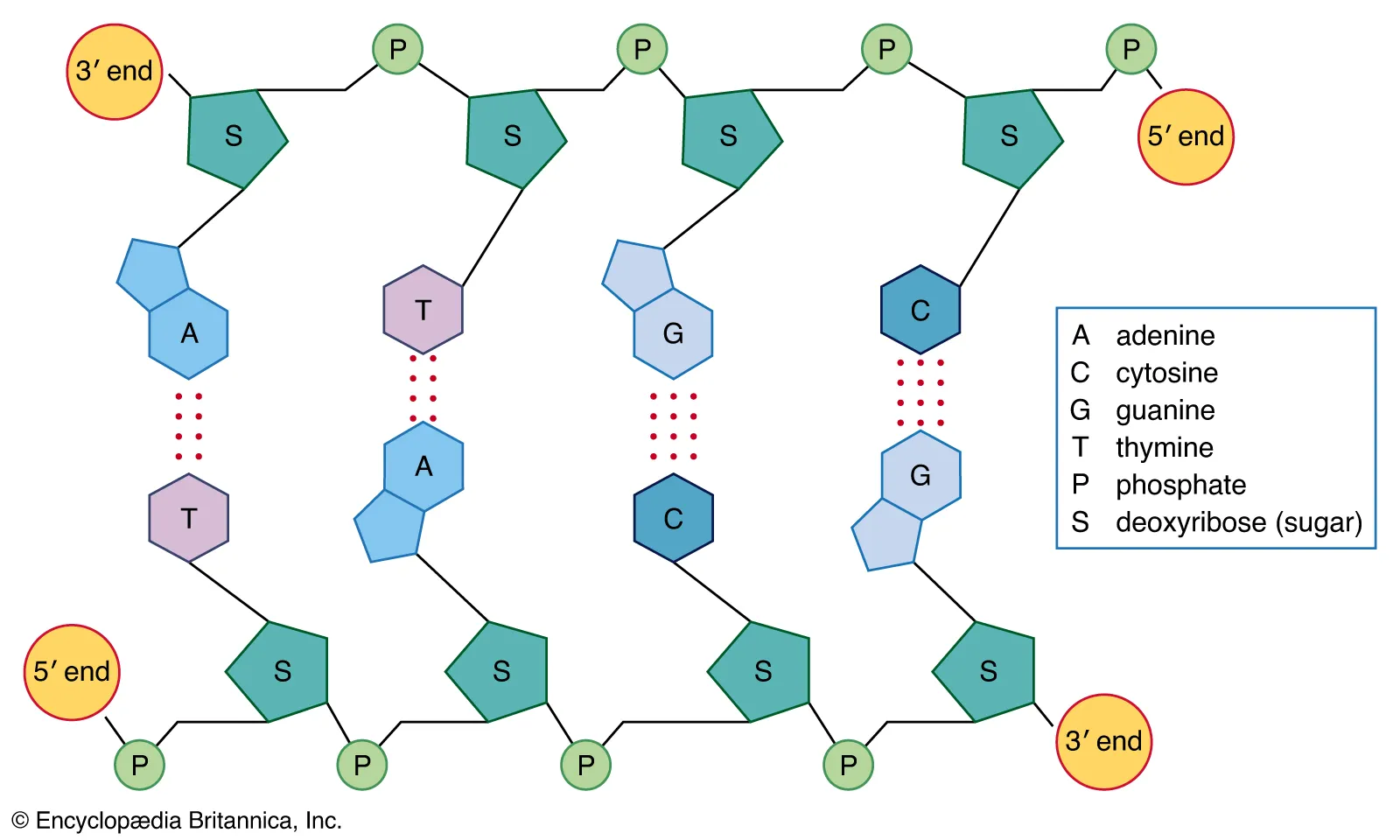
DNA Structure
Has a shape called a double helix, which resembles a twisted ladder.
Monomer is the nucleotide.
Polymer is the nucleic acid.
DNA is formed by two polymers attached in the middle by H-bonds.
There are 4 possible bases in DNA, and therefore, there are 4 different nucleotides.
Pyrimidines (1 ring): thymine & cytosine.
Purines (2 rings): adenine & guanine
Only pyrimidine pairs up with purine → A ratio of 1 pyrimidine: 1 purine.
→ DNA is always “3 rings” across.Interactions between the different nucleotides cause the twisting of the ladder.
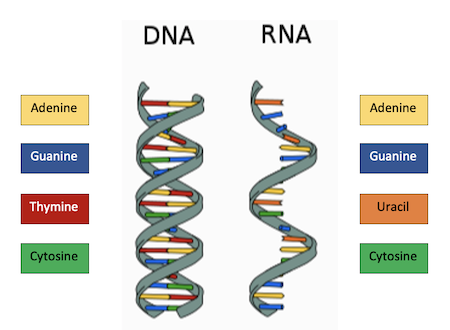
Comparison between DNA and RNA
Name
DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA: ribonucleic acid
Sugar
DNA: deoxyribose
RNA: ribose
Location in cell
DNA: nucleus and mitochondria
RNA: nucleus, nucleolus, cytoplasm, and ER (ribosomes)
Shape
DNA: double helix
RNA: single strand
Bases
DNA: A, T, C, G
RNA: A, U, C, G ( U = uracil is also a pyrimidine)
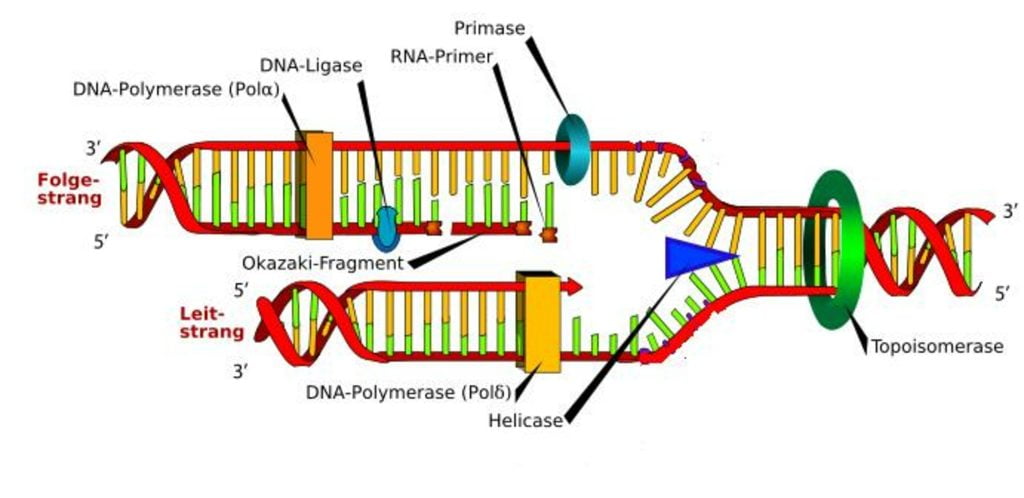
DNA replication
Mitosis: DNA must be precisely copied so that daughter cells are identical to parent cells.
Due to the complementary base pair, each DNA strand can be used as a template to build the opposite complementary strand.
Semi-conservative replication occurs because half of the new DNA molecule is new and half is conserved (saved) from the original molecule.
DNA replication has 3 major steps:
Unzipping
Complementary base pairing
Joining adjacent nucleotides
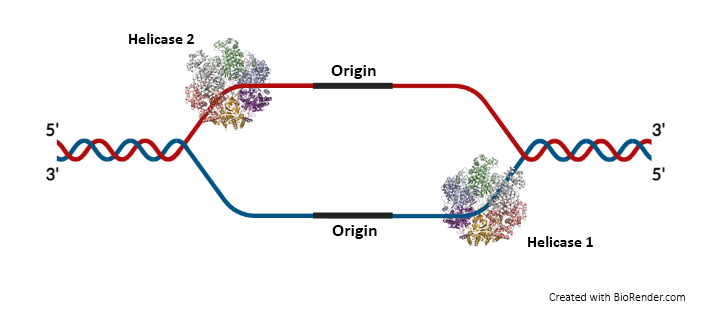
Unzipping
An enzyme called DNA helicase “unwinds” the DNA by disrupting the H-bonds between the paired nucleotides.
Proteins at the “knot” prevent the “rezipping.”
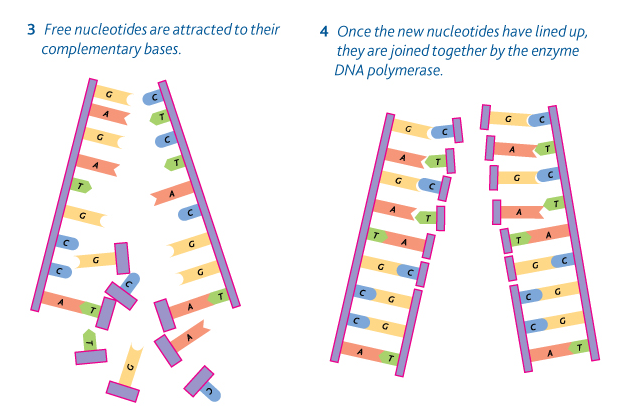
Complementary base pairing
“Free” nucleotides in the cytoplasm form H-bonds to the newly exposed bases.
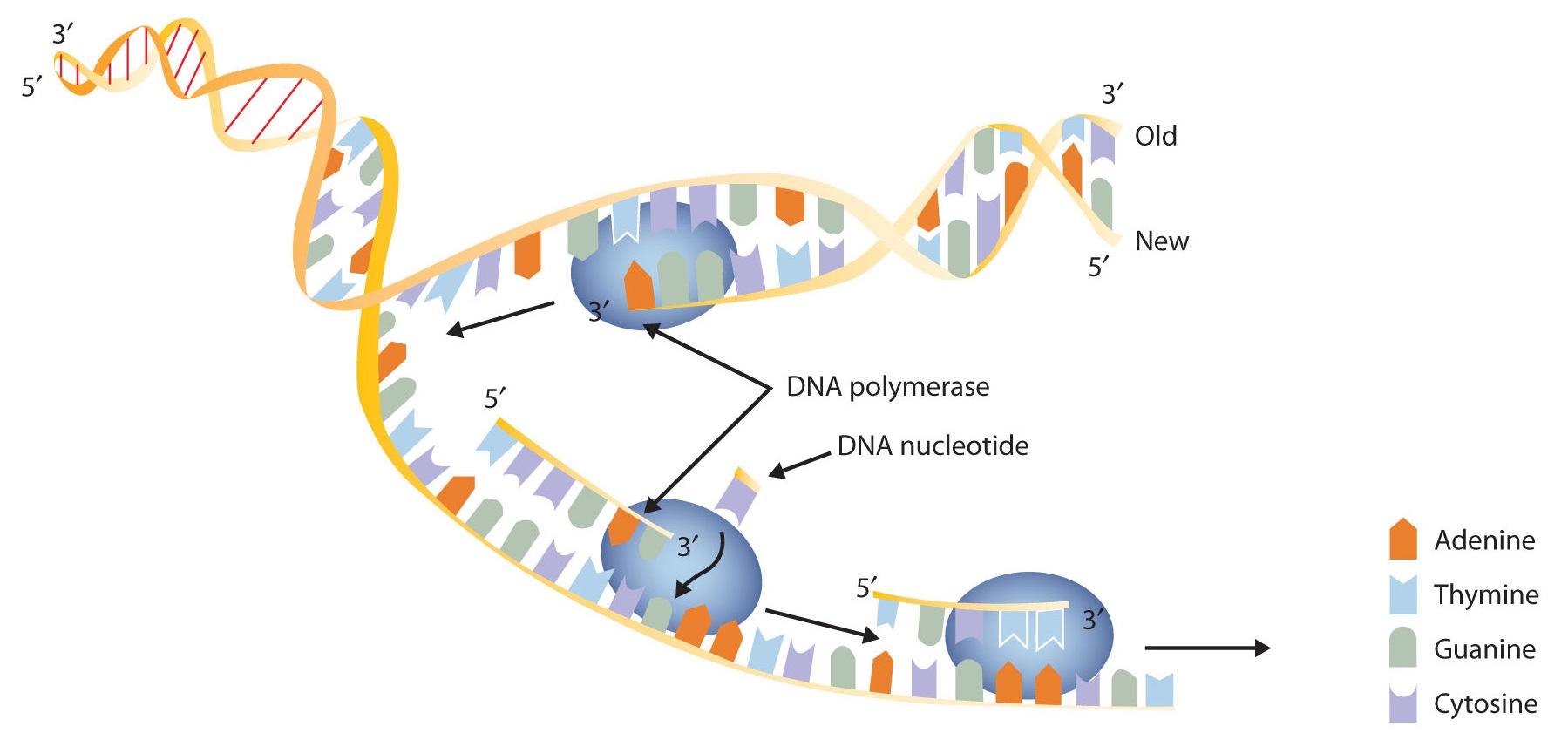
Joining adjacent (side by side) nucleotides
An enzyme called DNA polymerase attaches the sugar-phosphate backbone of the NEW strand of DNA.