BUAD304 CH10: Managing Conflicts and Negotiations
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definition of vocabs and concepts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Conflict
Energy created by the perceived gap between what we want and what we’re experiencing
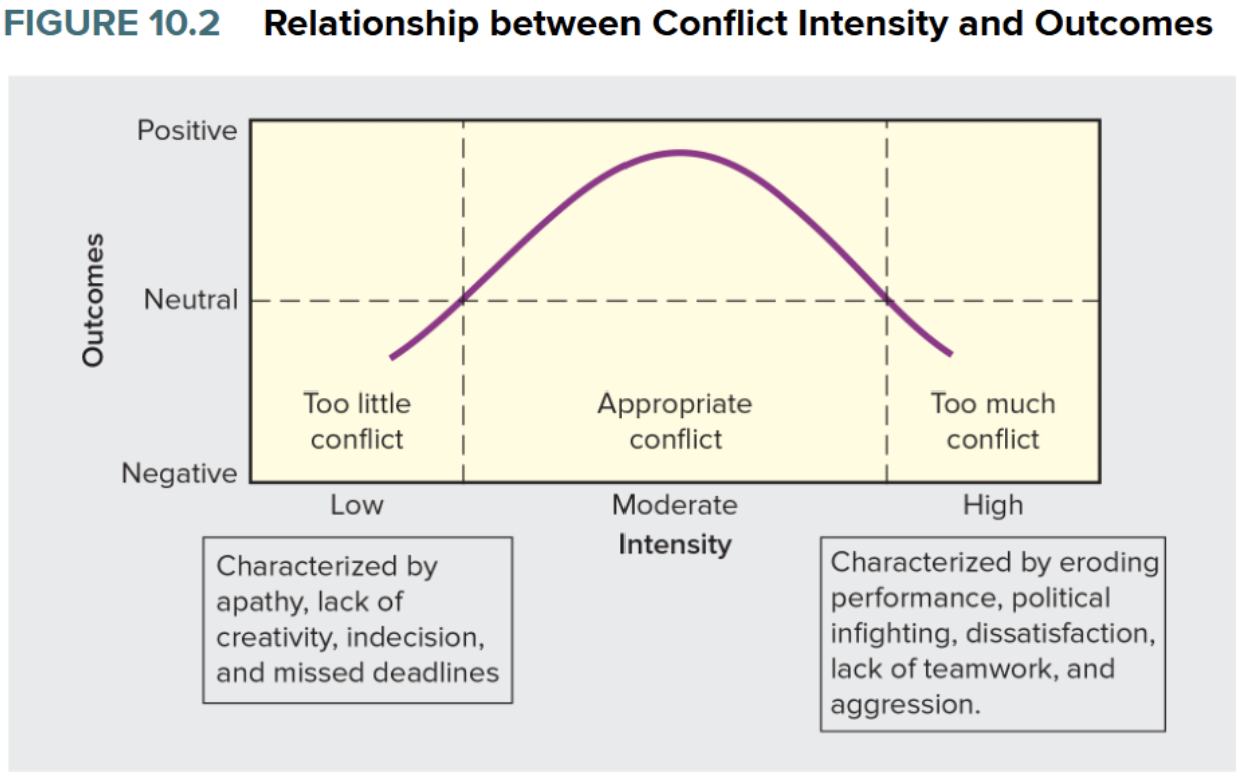
Functional Conflict (aka Constructive/cooperative conflict)
Characterized by consultative interactions, a focus on the issues, mutual respect, and useful give-and-take
Dysfunctional Conflict
Disagreements that threaten or diminish an organization’s interest
Cost: Absenteeism, Turnover, Unionization, Litigation - legal remedies
Warning Signs of Conflict Escalation
Tactics change - persuasion to powerplays/violence
Number of issues grows
Issues move from specific to general
Number of parties grows
Goals change - “doing well” to winning
Personality Conflict
Interpersonal opposition based on personal dislike or disagreement
Intergroup Conflict
Conflict among work groups, teams, departments, and organizations
Contact Hypothesis
The more members of different groups interact, the less intergroup conflict they will experience
Psychological Safety Climate
Shared belief among team members that it is safe to engage in risky behaviors, such as questioning current practices without retribution or negative consequences
Work-Life Conflict
Perception that expectations and demands between work and nonwork roles are mutually incompatible (both ways)
Flex Space (employer responsibility)
Ex. Telecommuting, occurs when policies enable employees to do their work from different locations besides the office (coffee shop, home, or the beach)
Flextime (employer responsibility)
Flexible scheduling, covering either the time when work must be completed (deadlines) or the limits of the workday (9-5, 10-4, or any time today)
Incivility
Any form of socially harmful behavior
Bullying
Unwelcome behavior that occurs over a period of time and is meant to harm someone who feels powerless to respond
Evident to others, affects even those not bullied, group-level implications
Cyber Bullying
Targets are harmed both by direct assault or event, and the fear of future mistreatment
Harassment
Discrimination based on a protected class (race, gender, religion, pregnancy, age, disability), that becomes illegal when it threatens your employment or is considered intimidating, hostile, or abusive
Sexual Harassment
Two different forms:
Quid Pro Quo - literally demanding sex
Hostile work environment
Devil’s Advocacy (Programmed Conflict)
One individual is assigned the role of devil’s advocate and identifies any potential shortcomings in the proposal (should rotate)
Dialectic Method (Programmed Conflict)
Structured dialogue or debate of opposing viewpoints prior to making a decision
5 Common Conflict-Handling Styles
Integrating, dominating, compromising, obliging, avoiding
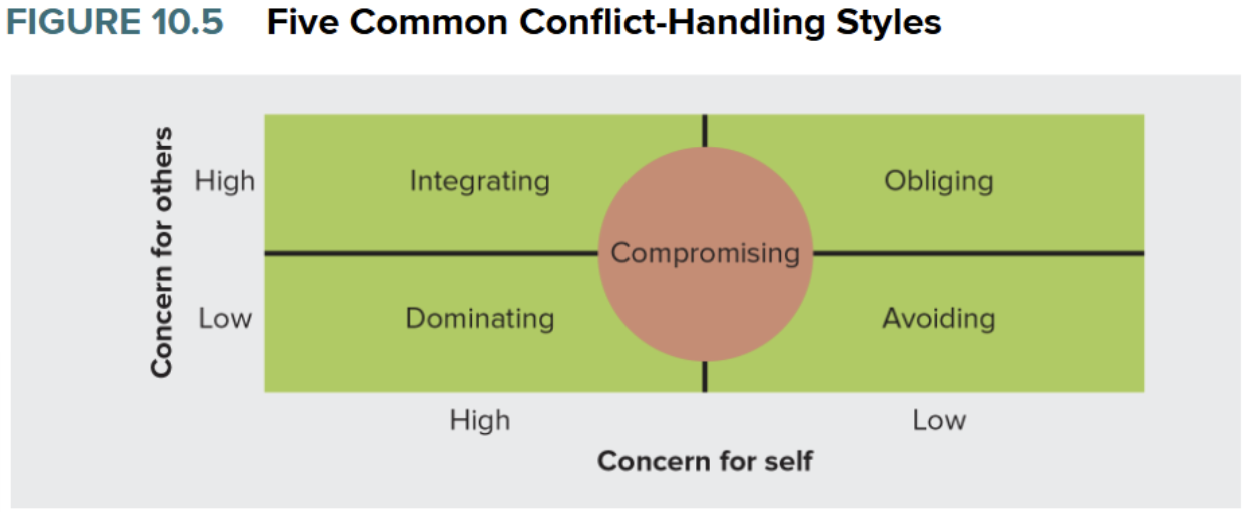
Integrating
Interested parties confront the issue and cooperatively identify it, generate and weight alternatives, and select a solution
Obliging
Minimize differences and highlight similarities to please the other party
Dominating (aka Forcing)
Often characterized by “I win, you lose” tactics. The other party’s needs are largely ignored. Often relies on formal authority to force compliance
Avoiding
Passive withdrawal from the problem and active suppression of the issue are common
Compromising
Is a give-and-take approach. Appropriate when parties have opposite goals and possess equal power
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)
A means of solving disputes using an independent third party and avoids the costs and problems associated with litigation or unilateral decision making
Forms of ADR
Facilitation (third party demand resolution)
Conciliation (third party act as communicator)
Peer review
Ombudsman (respected person hears both sides and attempts to give solution)
Mediation
Arbitration (agree ahead of time to accept decision of neutral arbitrator in formal court-like setting)
Negotiation
Give-and-take decision-making process between two or more parties with different preferences
Position-Based, Distributive Negotiation
Usually concerns a single issue–a “fixed pie”--in which one person gains at the expense of another
Interest-Based, Integrative Negotiation
Numerous interests are considered, resulting in an agreement that is satisfactory for both parties
Emotional Ambivalence
Not clearly positive or clearly negative–can be detrimental in position-based negotiation
Moral Character
Individual’s general tendency to think, feel, and behave in ways associated with ethical and unethical behavior
Lies of Omission
one fails to reveal relevant information, offering false information