Genetics, Seedless Plants, Gymnosperms
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Female & Male Corn Flowers
males: tall, narrow and pointy; sperm is haploid (1n)
females: long, hair-like strands; egg is haploid (1n); zygote (fertilized egg) is diploid (2n)

Phenotype vs Genotype
pheno: observable traits (ex: corn kernel smooth, wrinkled, purple, yellow)
geno: the set of genes (homozygous dominant: PP; homozygous recessive: pp; heterozygous: Pp)
Corn Documentary
main idea was geneticist believed teosinte plant was an ancestor of modern corn; F2 generation form crossbreeding teosinte and maize proved his hypothesis was correct
Corn Model
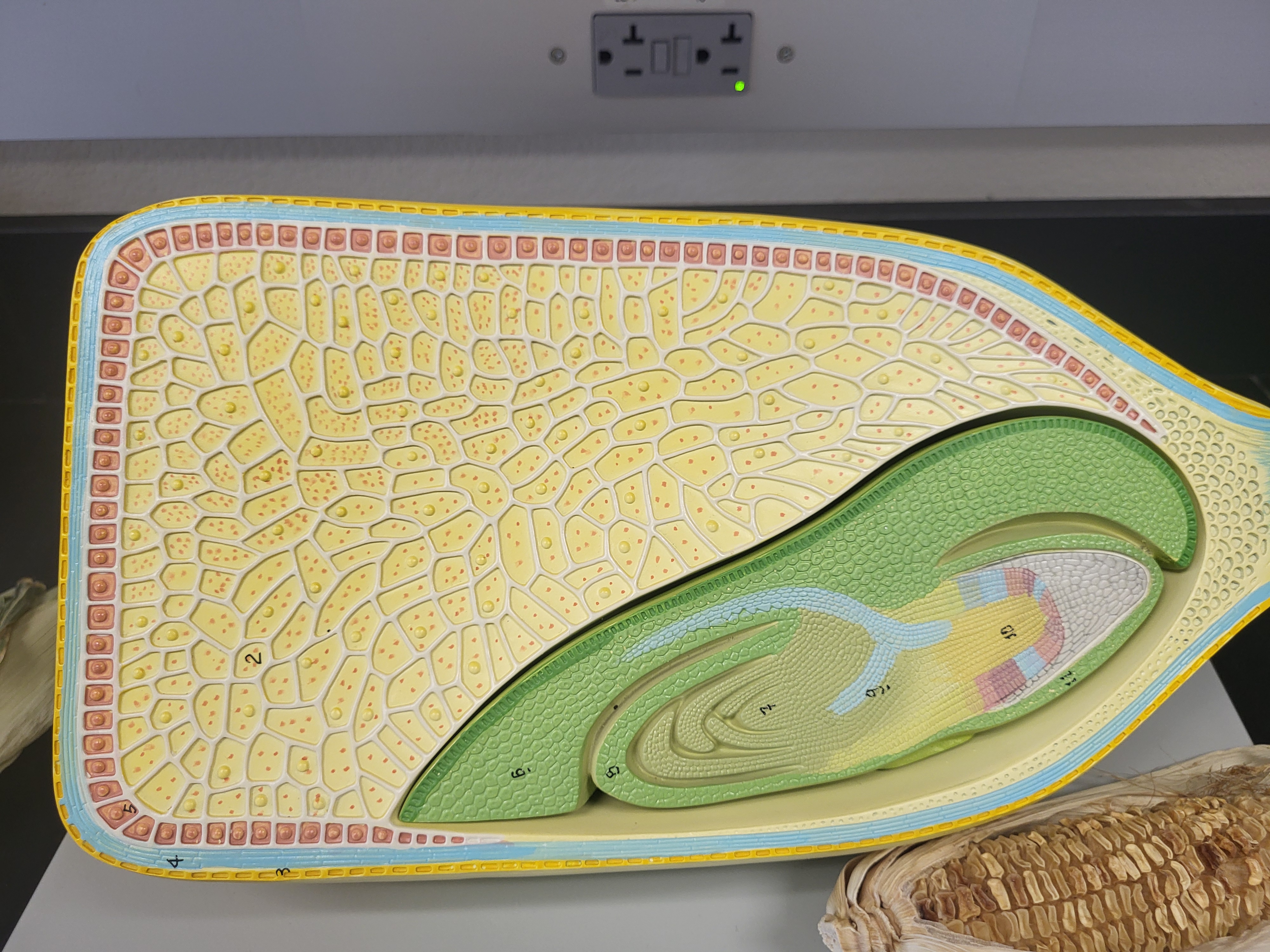
1: embryo
2: endosperm: nutritive part for seedling
3: pericarp- outer layer or kernel
4: seed coat- layer between pericarp and aleurone
5: aleurone- inner layer around endosperm
Punnett Squares
practice monohybrid using F1 of SS and ss; find F2 by crossing two offspring from F1 (Ss and Ss);
practice dihybrid cross- Punnett square that looks at two characteristics: use PPSS and ppss; use foil method to find genotype for F2 from F1 offspring
look at corn lab for help
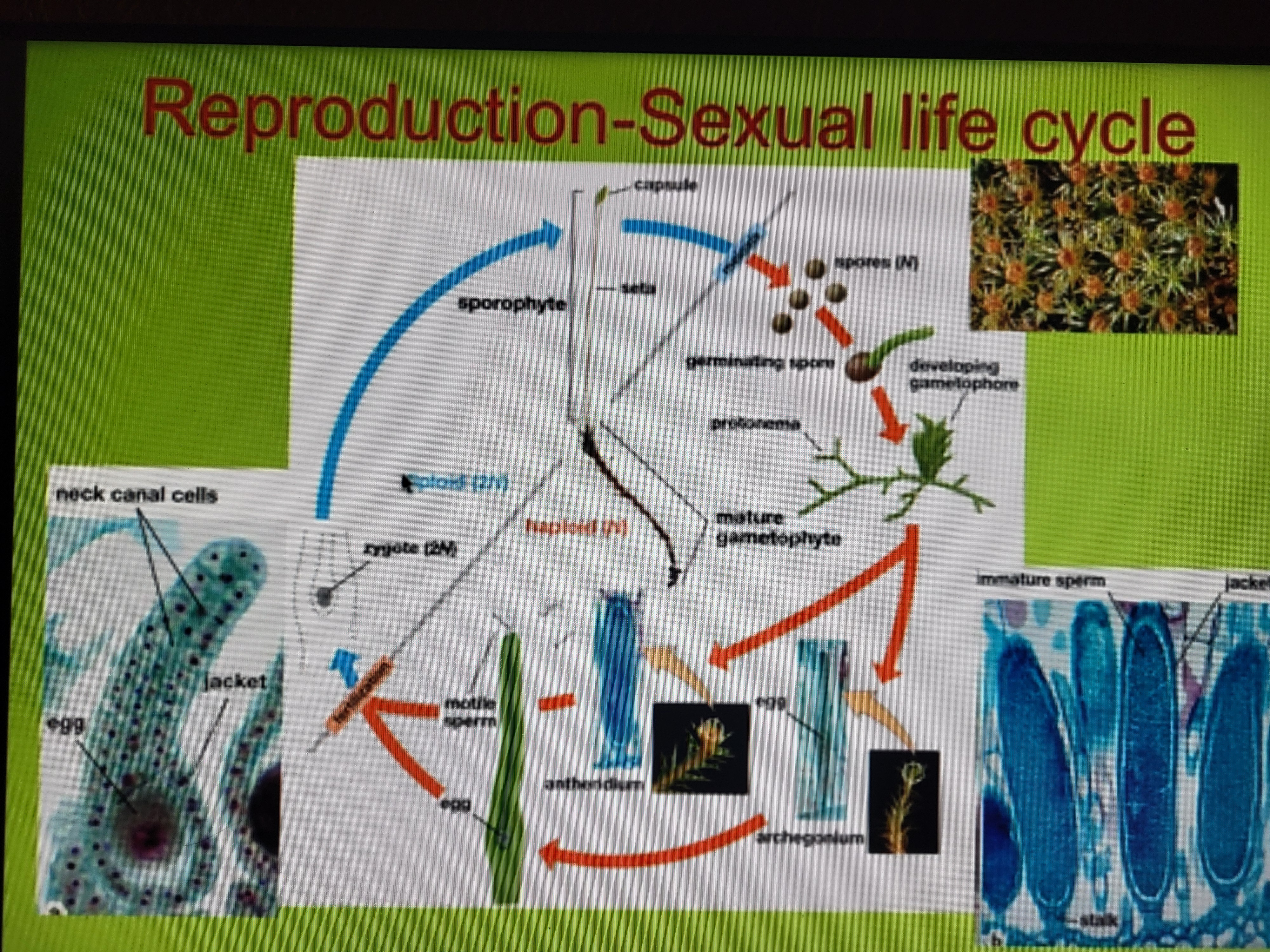
Bryophyte Lifecycle
diploid stage: fertilization produces zygote; becomes sporophyte with capsule and seta attached to haploid mature gametophyte
haploid stage: meiosis produces spores; spores germinate; motile sperm from antheridium swim down neck canal of archegonium
rewatch lifecycles from week 12 lecture
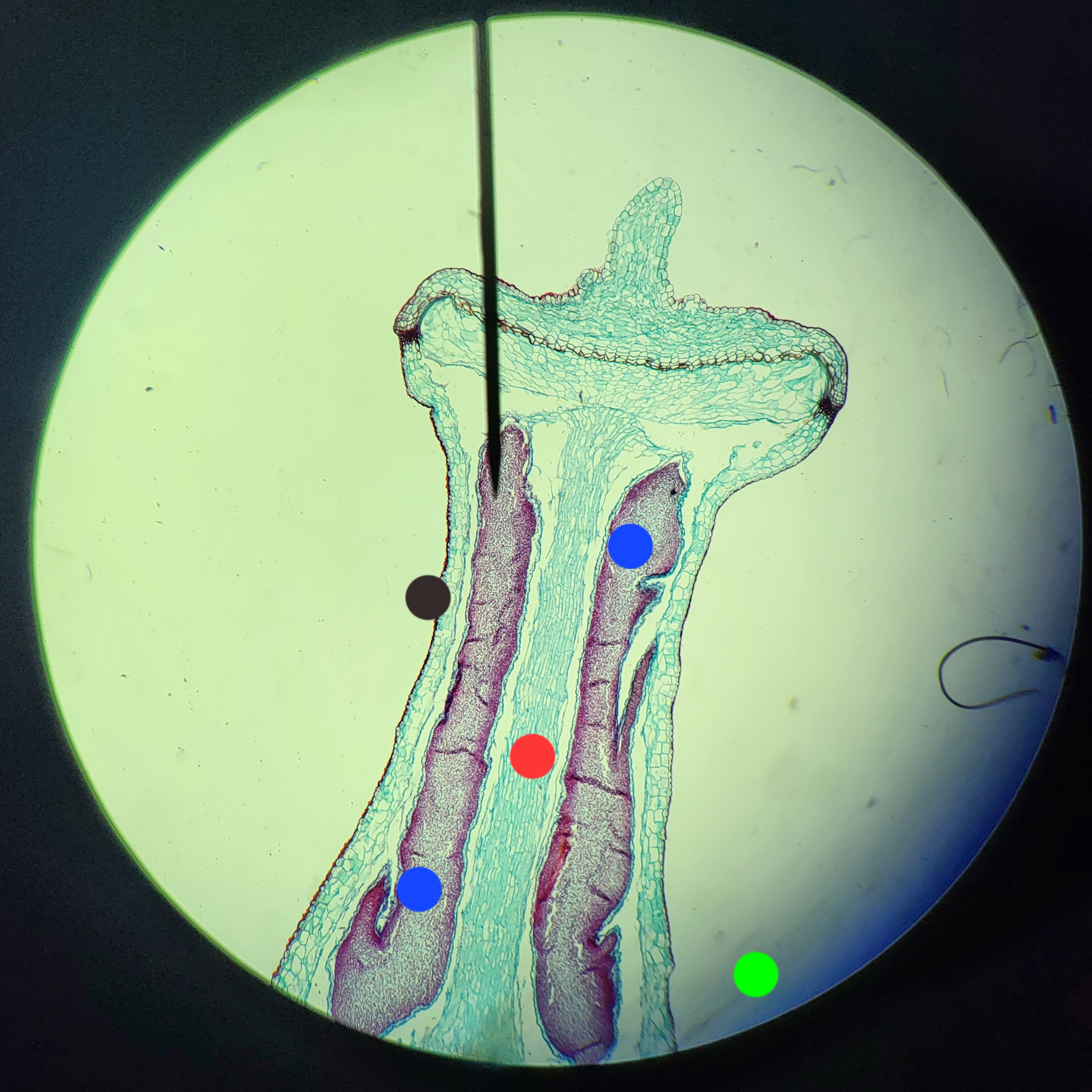
Polytrichum Capsule
black: epidermis (outermost layer)
red: columella
blue: spores
green: photosynthetic tissue is out of FOV but is above the seta near the bulge-y part
diploid
Marchantia Sporophyte
Lunularia (Liverwort)
thallus is fleshy green area
rhizoids are delicate root-hair-like structure that function in anchorage and absorption
moon-shaped cups that contain gemmae
gemma is a small outgrowth of tissue that becomes detached from the parent body and is capable of developing into a complete new plant or other organism

Gemmae Cup Dissection

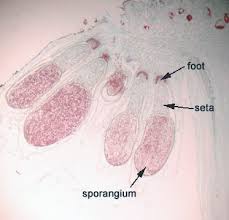
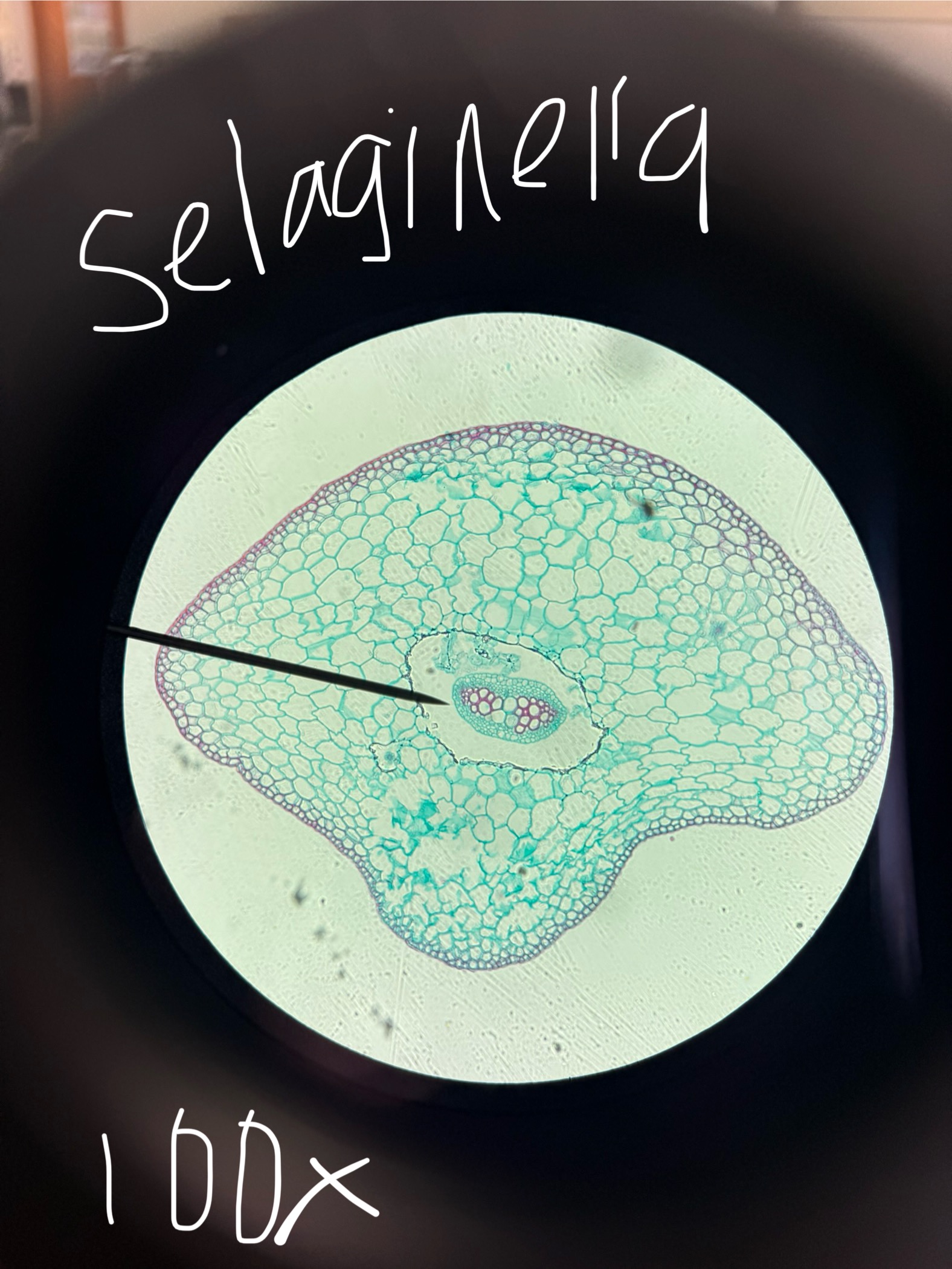
Selanginella Stem
Strobilus (Lycophyte Cone)
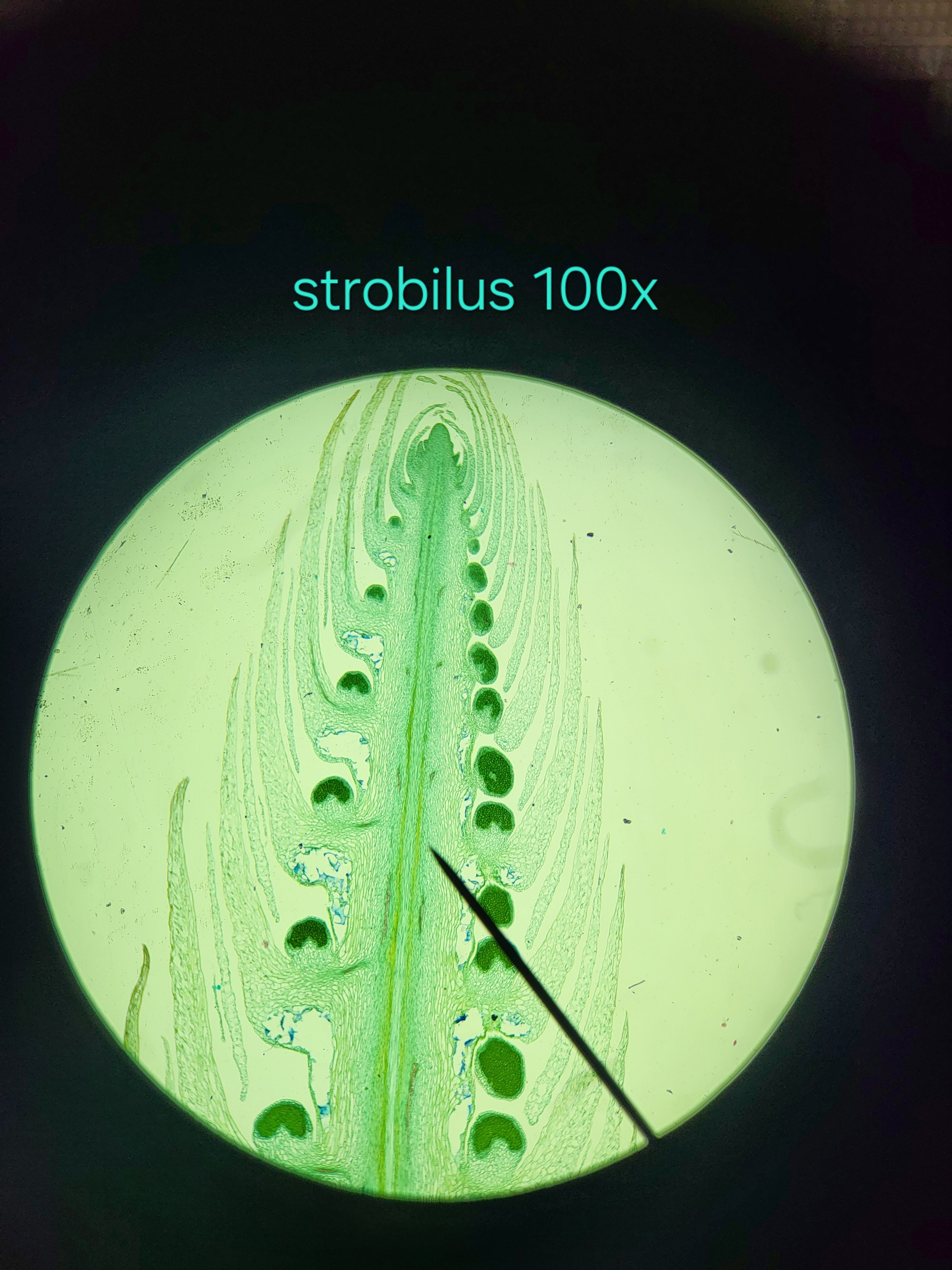
sporangium: contain spores; the darker green splotches
sporophyll: sporangium-bearing modified leaf
Bryophyte Antheridia and Archegonia
Gymnosperm Overview
produce seeds that are “naked” i.e. not protected by fruit
woody trees, shrubs, or lianas (woody vines)
members: conifers, gnetophytes, cycads, and gingko
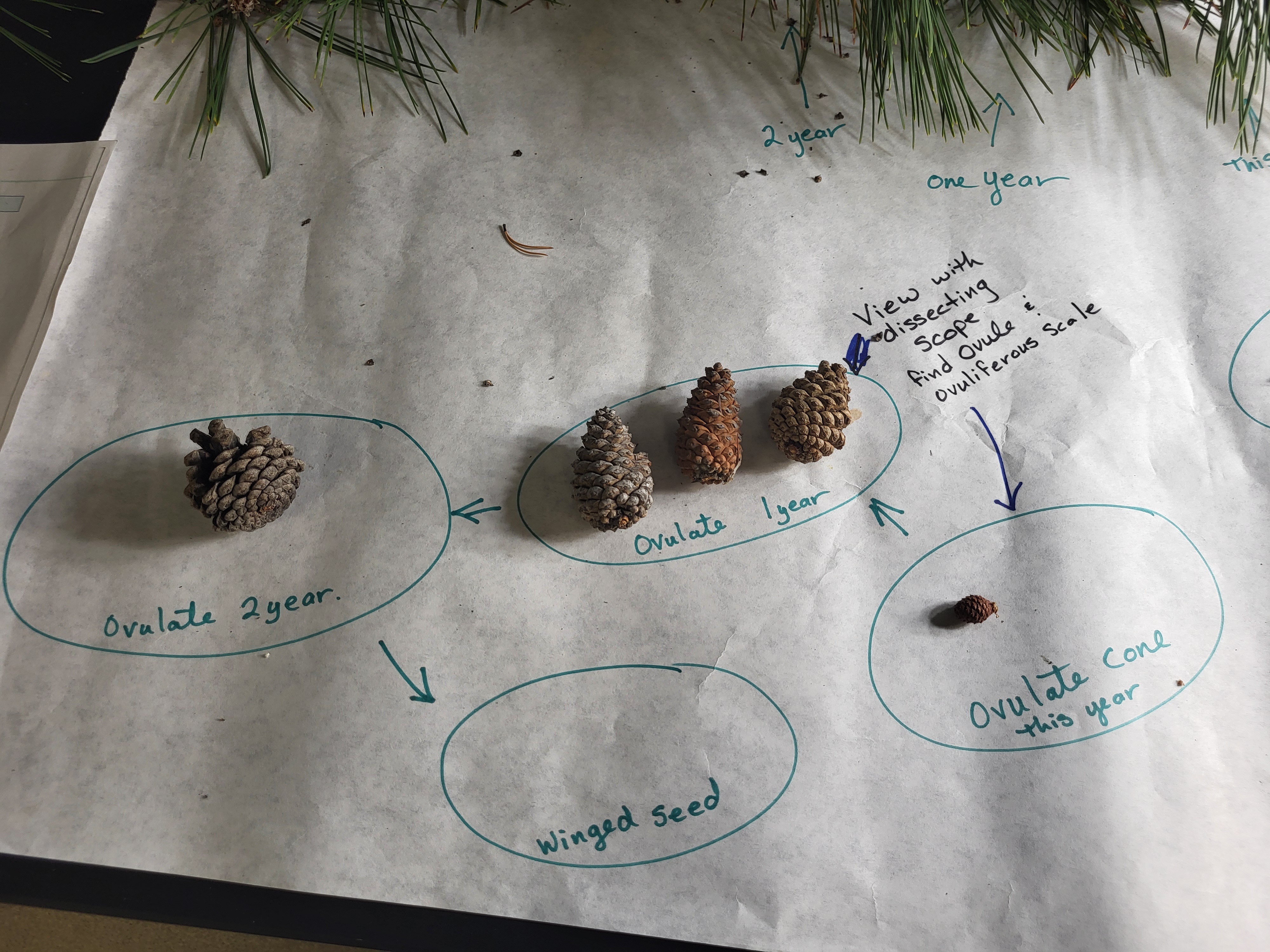
Pine Ovulate (Female) Cone 1 Year
label/define megasporocyte, ovule, ovuliferous scale

Ovulate Cone Dissection Scope
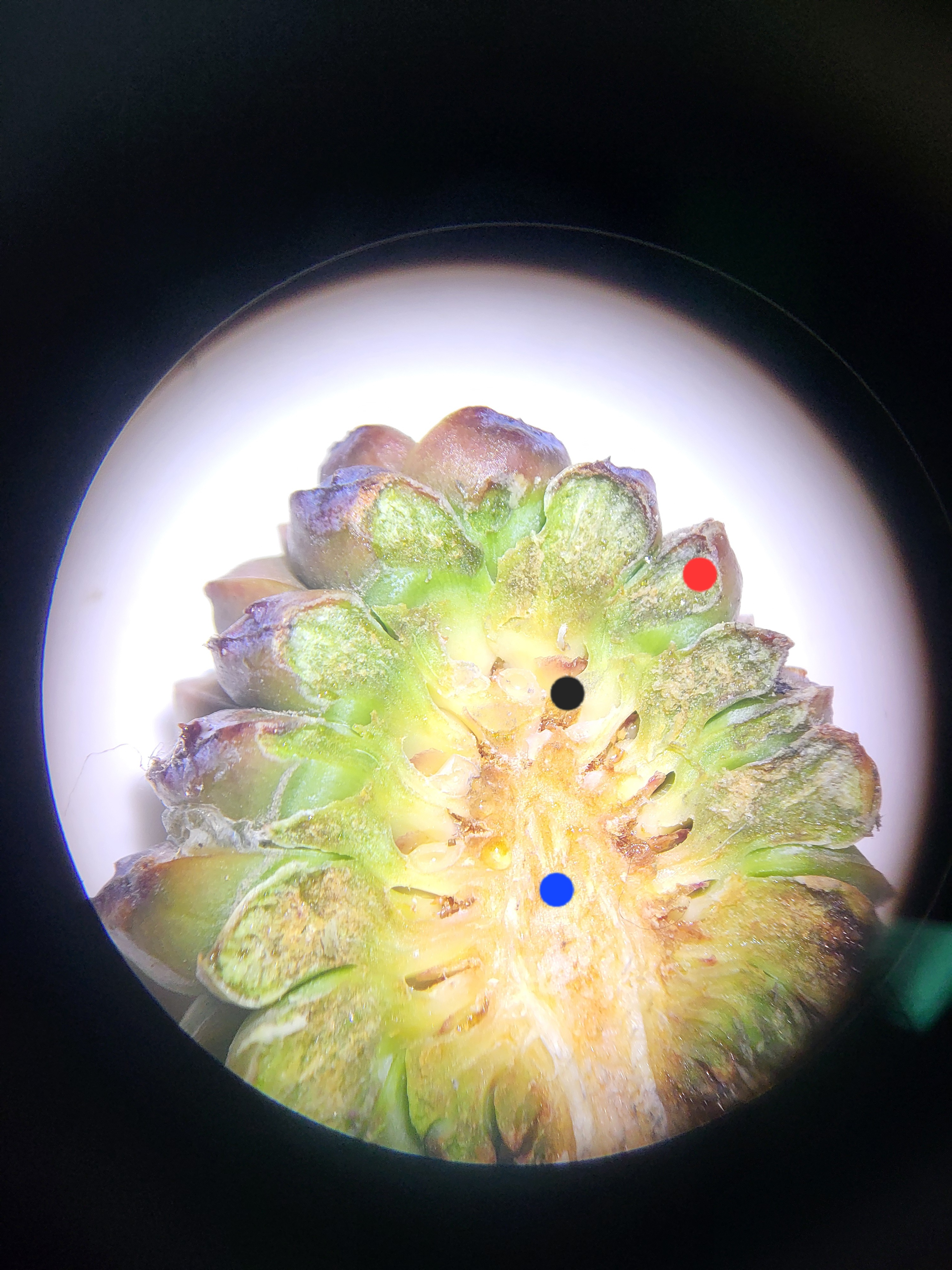

blue: cone axis
red: ovuliferous scale
black: ovule
Cones at Different Years

Pine Staminate (Male) Cone
label/define microsporangium and microspores
what do microsporangia develop into?

microsporangia develop into pollen grains
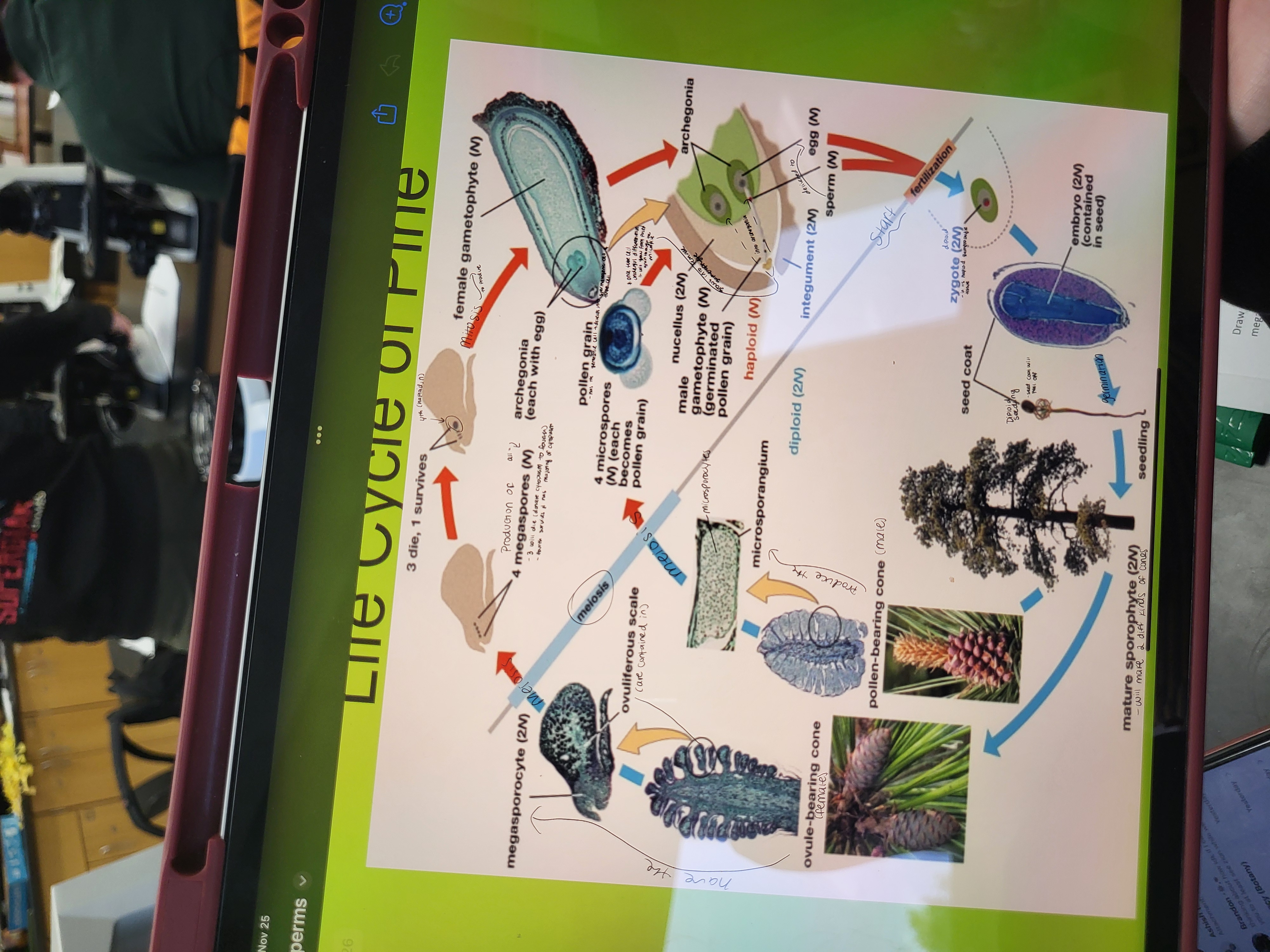
Pine Lifecycle
Pollen Grains
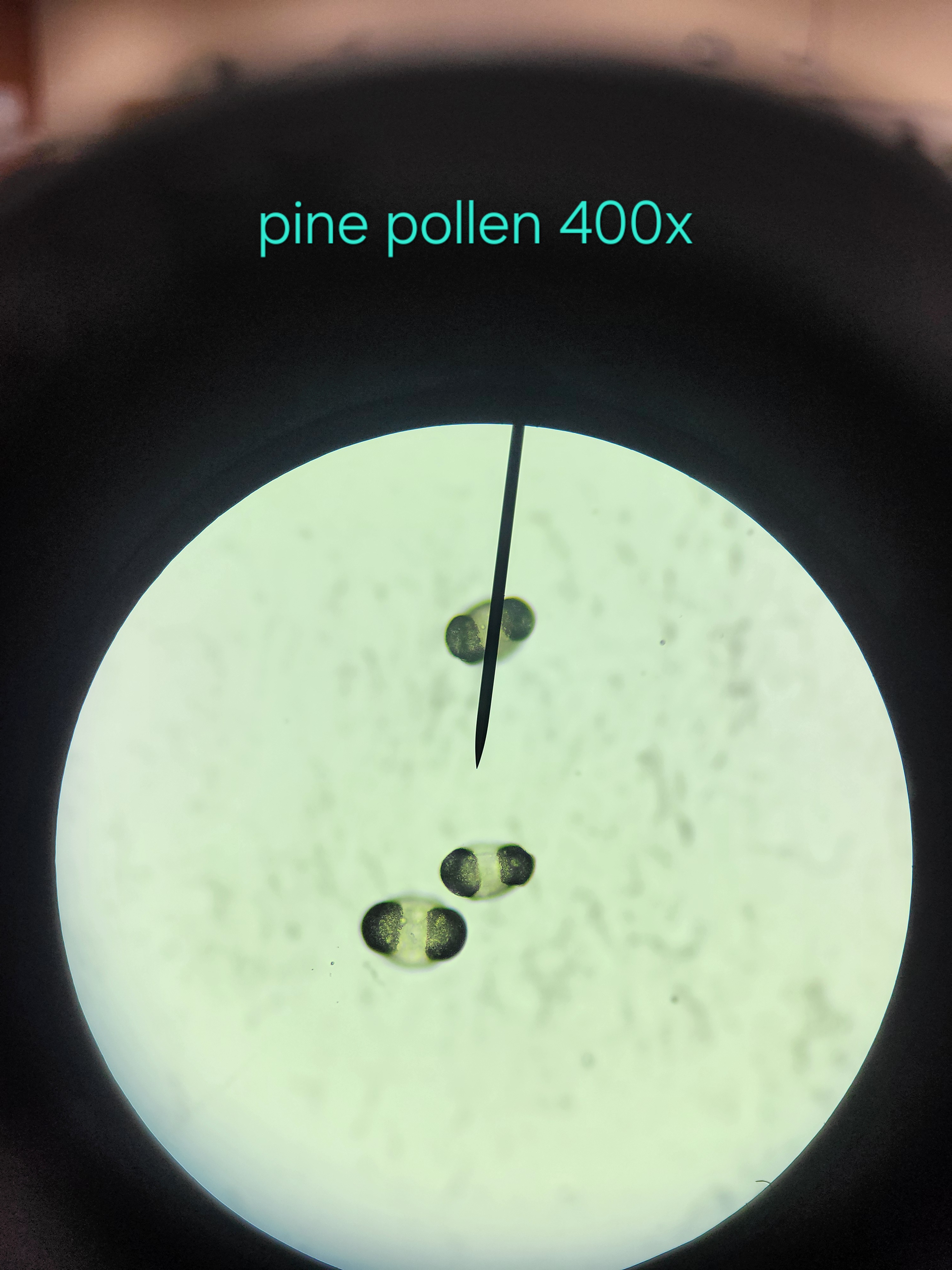

haploid
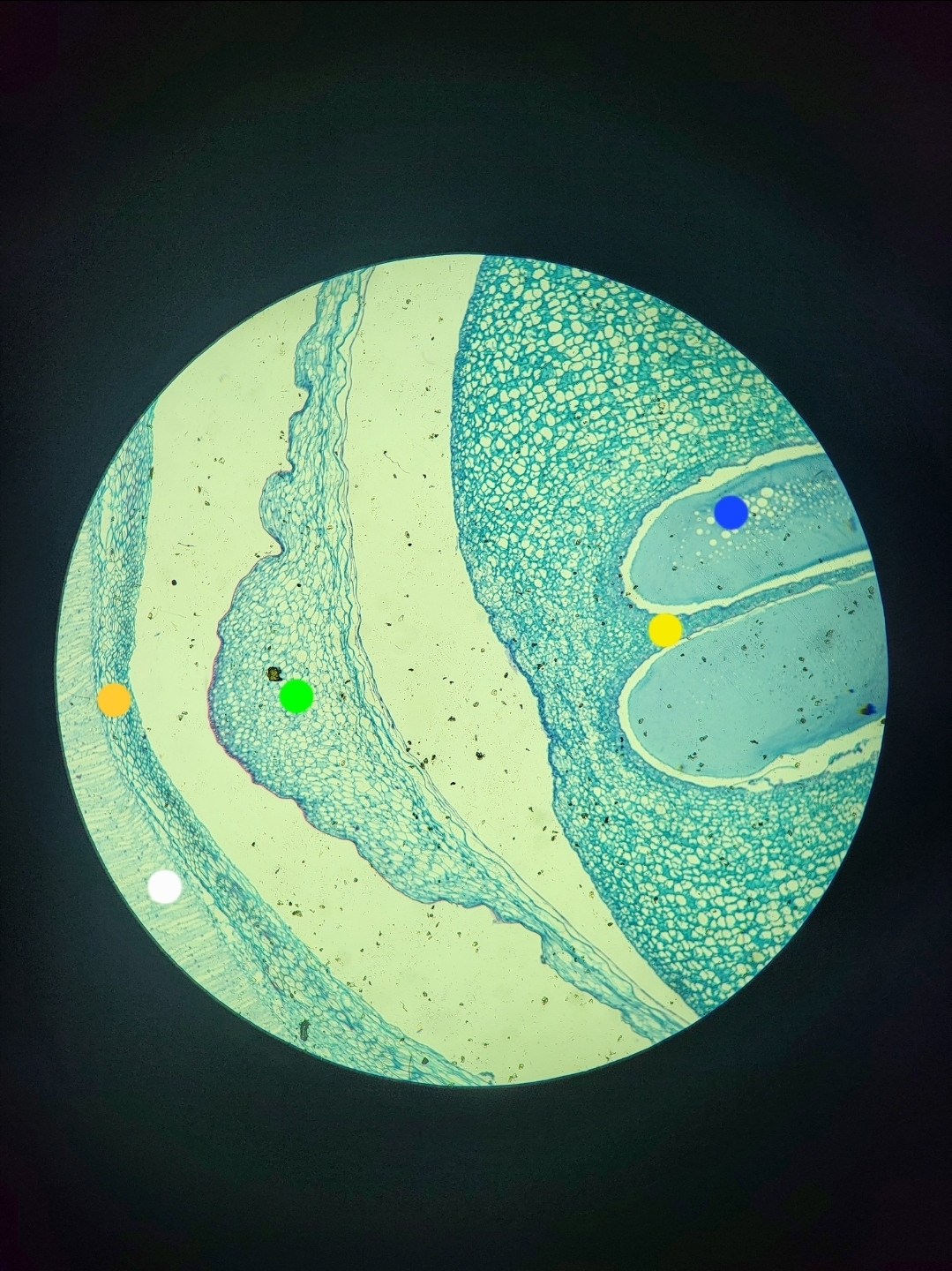
Zamia Ovule
green: megasporangium; yellow: archegonia; blue: egg; pinkish: integument; orange: micropyle (check atlas for better pic of last two)
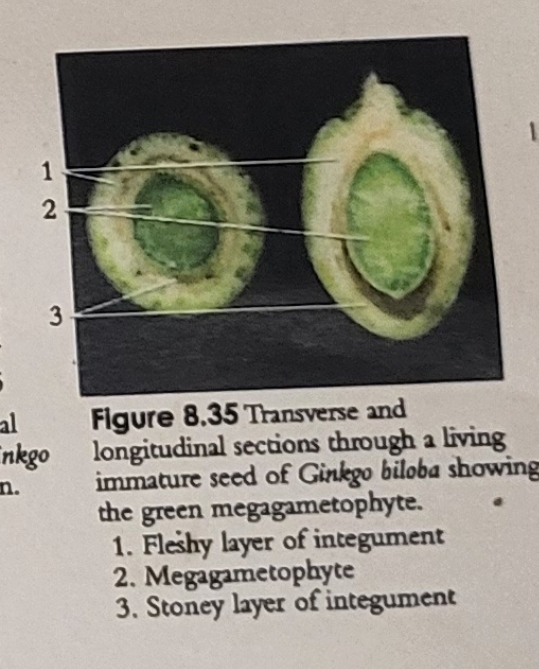
Ginkgo Catkins & Fruit
identify female gametophyte, embryo, seed coat

Dissected Gingko Fruit

Parts of Ginkgo Fruit
Cycads
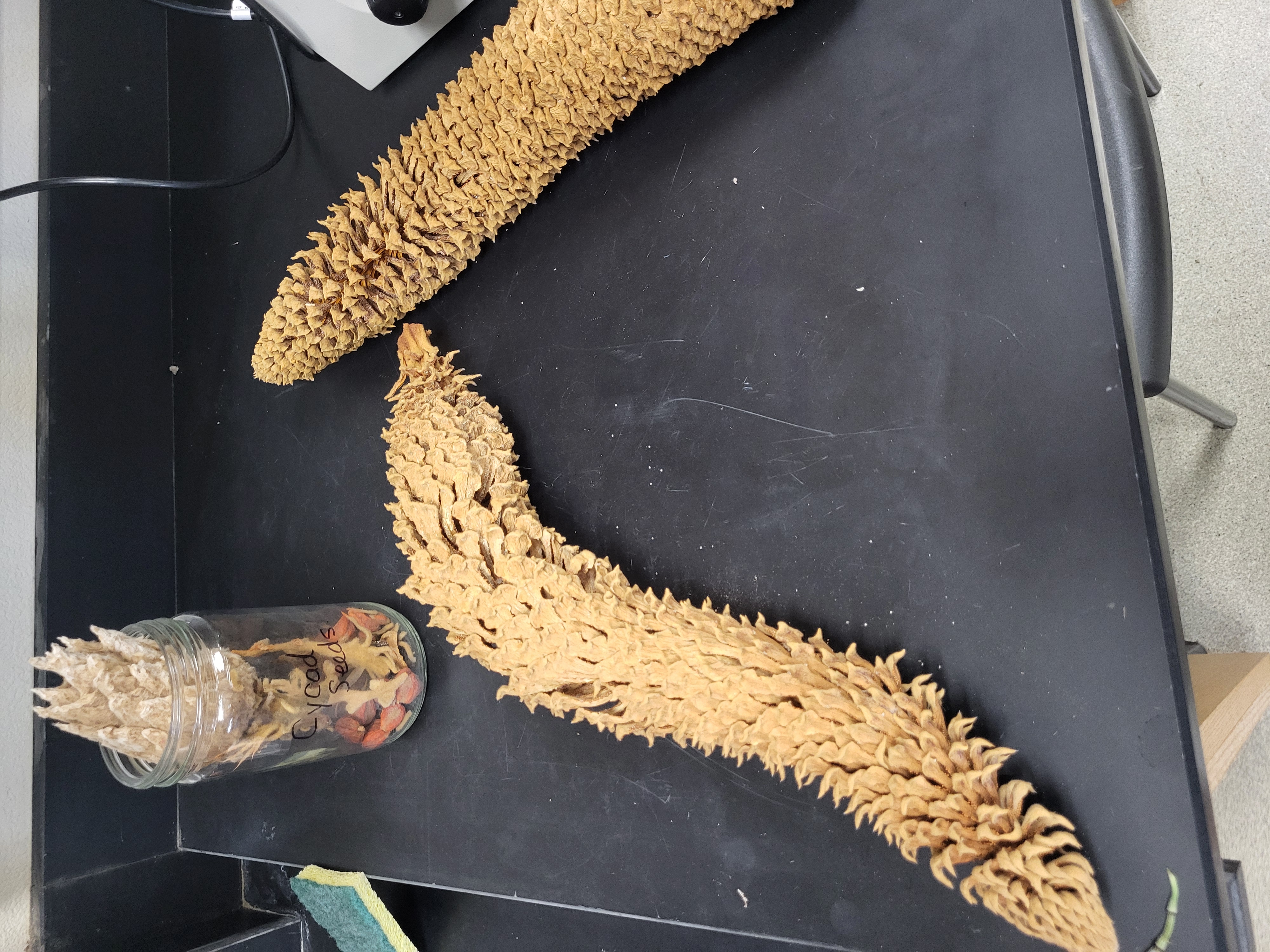

from one of those plants that look like palm trees but aren’t
Juniper Berries
