the tissue level of organization
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Tissue
Collection of specialized cells and cell products working together to perform a limited number of functions
Histology
The study of tissues
Epithelial tissue
Covers exposed surfaces, intestinal passageways and forms glands
Connective tissue
Fills internal spaces, provides structural support, Transports material, and stores energy
Muscle tissue
Specialized for contraction; includes skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
Neural tissue
Carries electrical impulses throughout the body
Epithelia
Layers of cells that cover internal or external surfaces
Glands
Structures that produce fluid-like secretions; either are attached to or are derived from epithelia
Cellularity
Epithelial is composed almost entirely of cells
Polarity
Structural and functional differences between apical and basal surfaces
Attachment
Basal surfaces are attached to a basal lamina
Avascularity
Epithelia lack a blood supply
Regeneration
Cell division and replacement occurs at a faster rate than most other tissues
Functions of epithelial tissue
Provided physical protection
Control permeability
Provide sensation
Produces specialized secretions
Three types of cell junctions
Tight junctions
Gap junctions
Desmosomes
Tight junctions
The lipid portion of the plasma membranes fo two cells are tightly bound together by interlocking membrane proteins; so tight they prevent the passage of water and ions between cells
Gap junction
Composed of channel called connexons; form narrow passageways that allow small molecules and ions to pass from cell to cell
Desmosomes
Very strong connections made of CAM’s and proteoglycans that can resist stretching and twisting
Cell adhesion molecule (CAM)
Proteins that attach large areas of opposing plasma membranes
Three types of epithelial cell shapes
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Squamous
Thin and flat in appearance
Cuboidal
Appears as boxes or cubes
Columnar
Tall and relatively slender in appearance
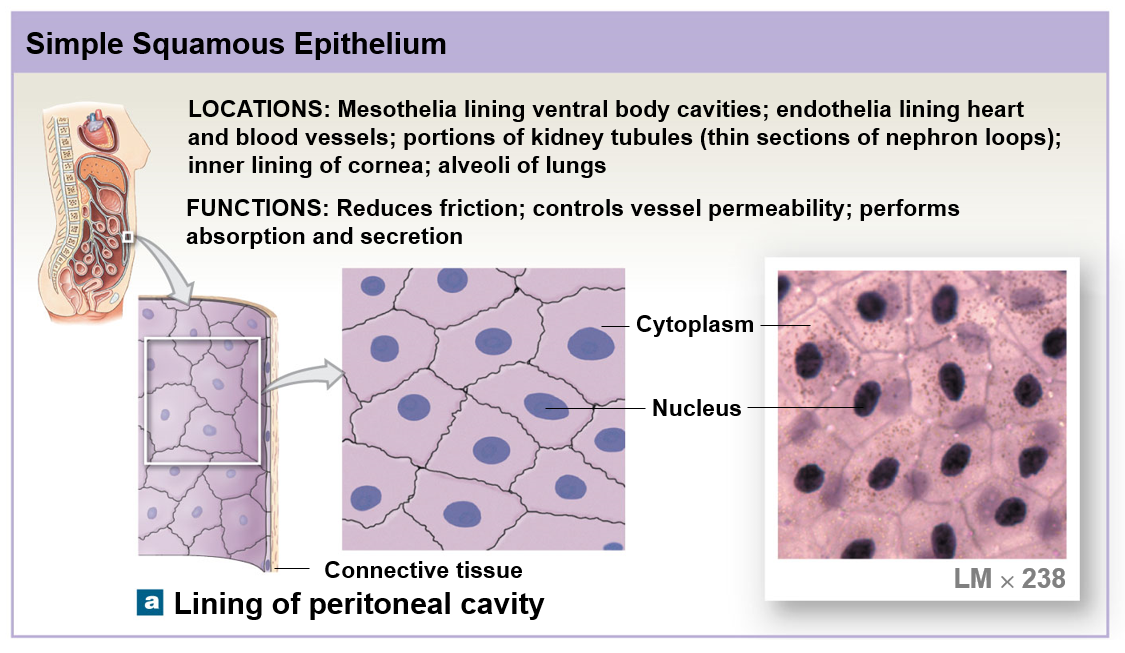
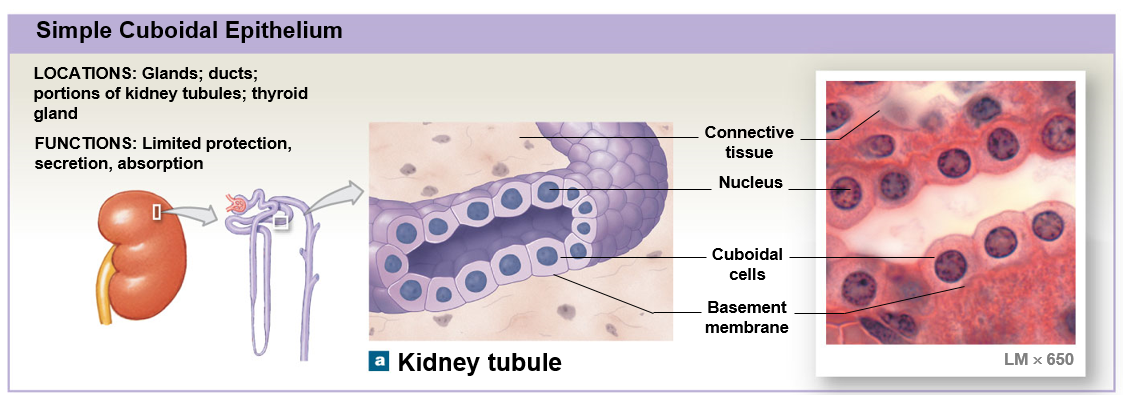
Simple epithelium
Of only one layer of cells covers the basements membrane
Are fragile and don’t provide mechanical protection
Line internal compartments and passageways such as the ventral body cavities, heart chambers, and blood vessels
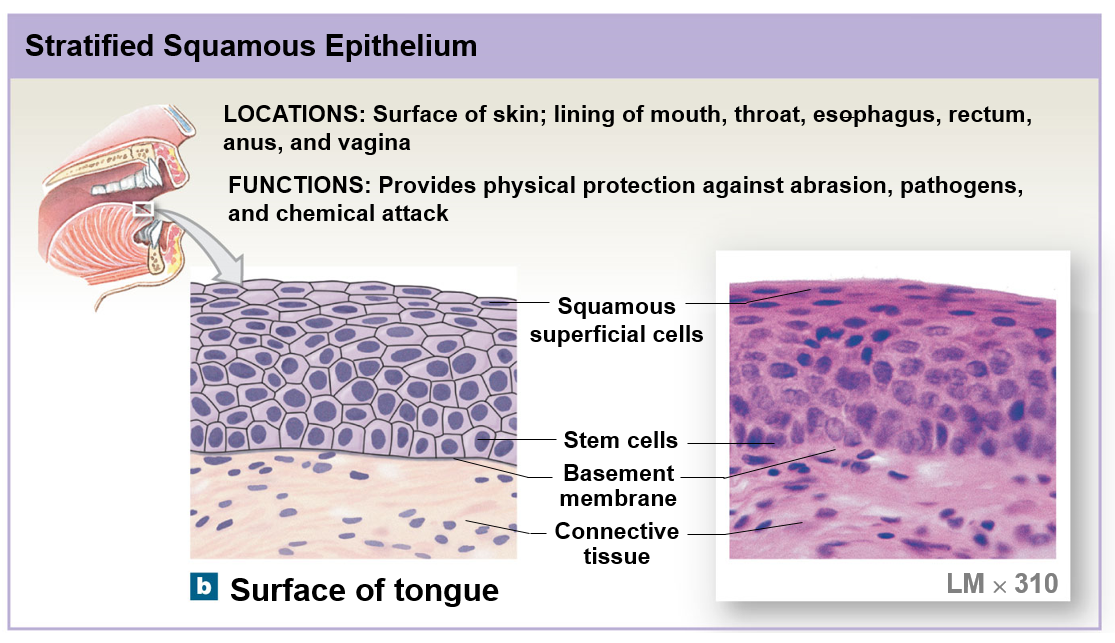
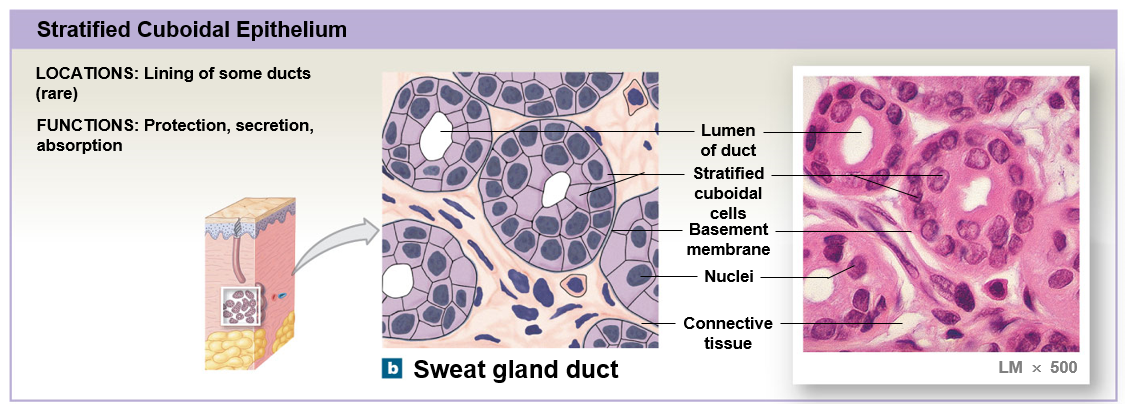
Stratified epithelium
Several layers of cells are present along the basements membrane membrane
Generally located in areas that are exposed to chemical and mechanical stresses such as the surface of the skin and linings of the mouth
Simple squamous epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium
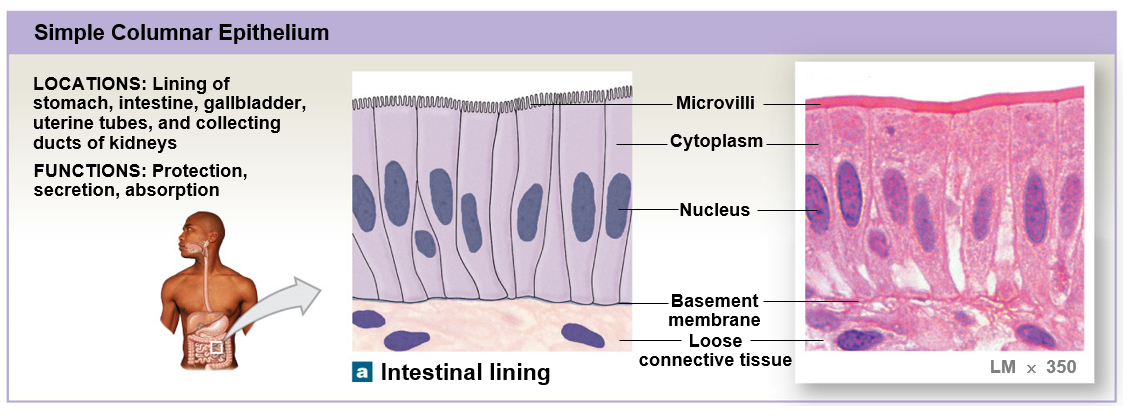
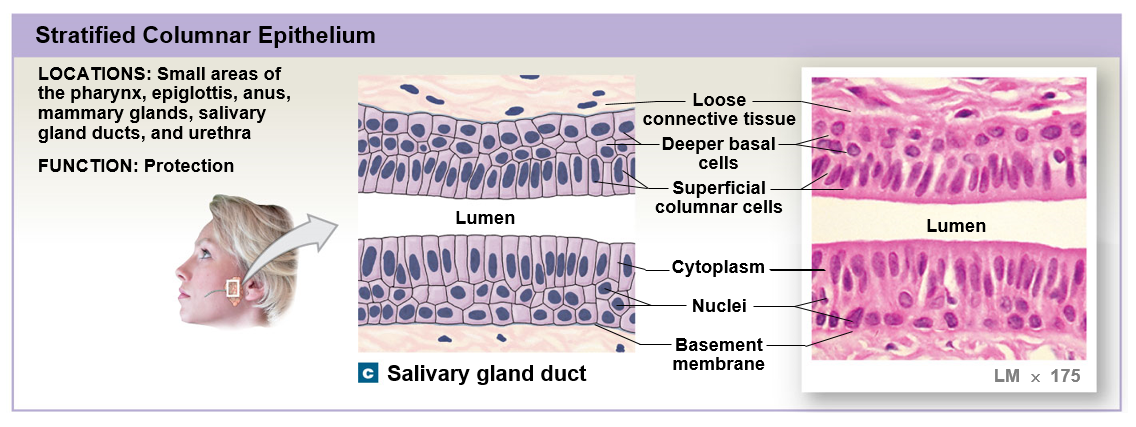
Stratified columnar epithelium
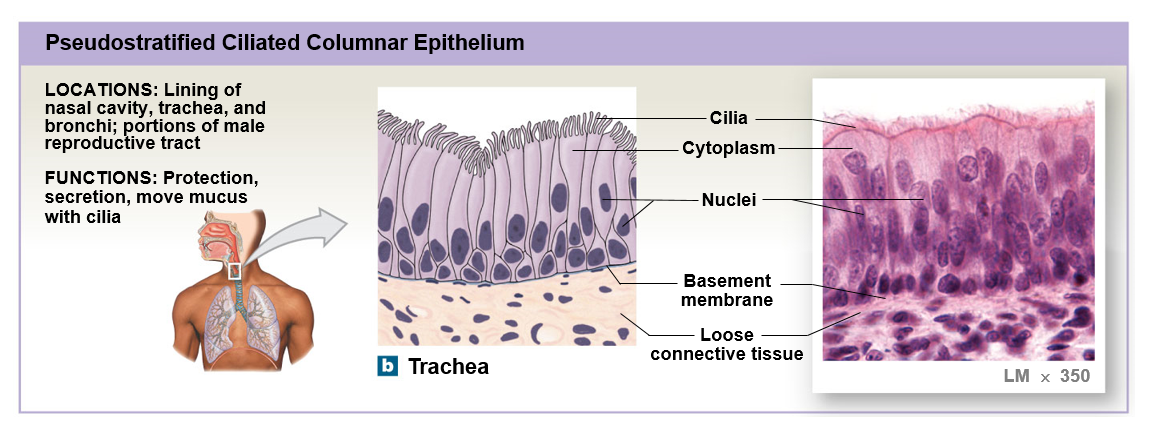
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
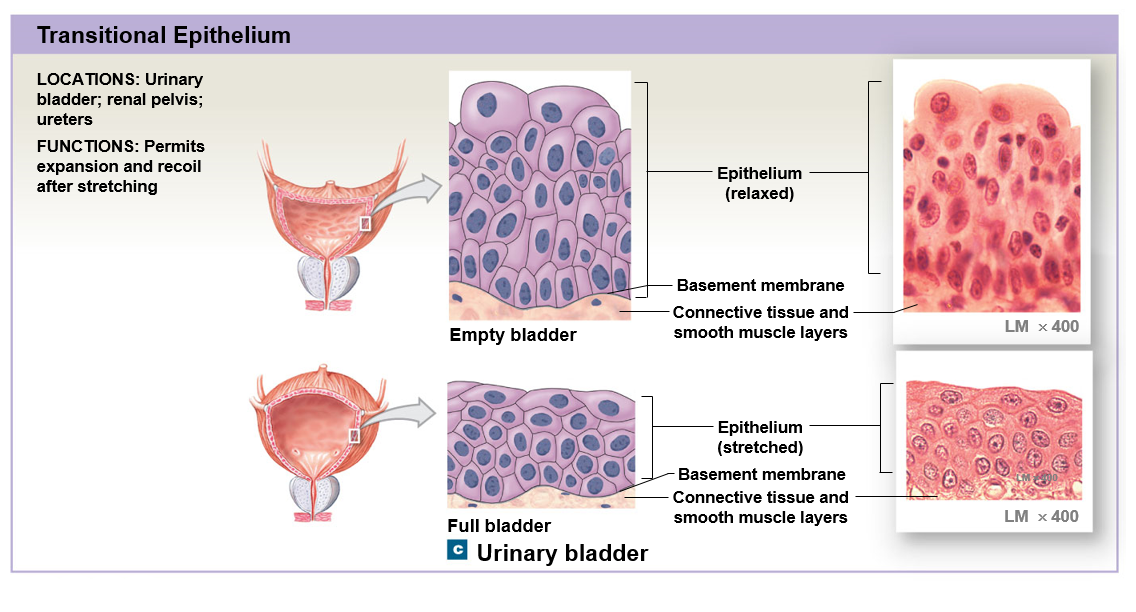
Transitional epithelium
Endocrine glands
Release secretions into interstitial fluid
Exocrine glands
Release secretions into passageways called ducts
Merocrine secretion: product is released by exocytosis
Apocrine secretion: involves the loss of cytoplasm as well as secretory product
Holocrine secretion: involves cell destruction during secretion
Serous glands
Secrete a watery secretion that contains enzymes; the parotid glands are examples
Mucous glands
Secrete mucin that hydrate to form mucous; the sub mucosal glands of the small interstice are examples
Mixed glands
Contain more than one type of gland cell; the submandibular glands are an example
Simple gland
Doesn’t have a branching duct
Compound gland
Has at least one branching duct
Connective tissue
Connects the epithelium to the rest of the body
Three basic components
Specialized cells
Extracellular protein fibers
Ground substance
Matrix
Extracellular fibers and ground substance combined; typically makes up the majority of a connective tissue
Connective tissue proper
Broad category divided into loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue based on the number of cell types present and the proportion of fiber and ground substance
Fluid connective tissue
Have distinct populations of cells suspended in a watery matrix; blood and lymph