Comprehensive Pediatric Growth, Development, and Play Strategies for Infants to Adolescents
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What are the age ranges for newborns and infants?
Newborns are defined as less than 28 days old, and infants are from 1 to 12 months.
What are the key developmental theories to consider across age groups?
Psychosocial, cognitive, psychosexual, and moral development.
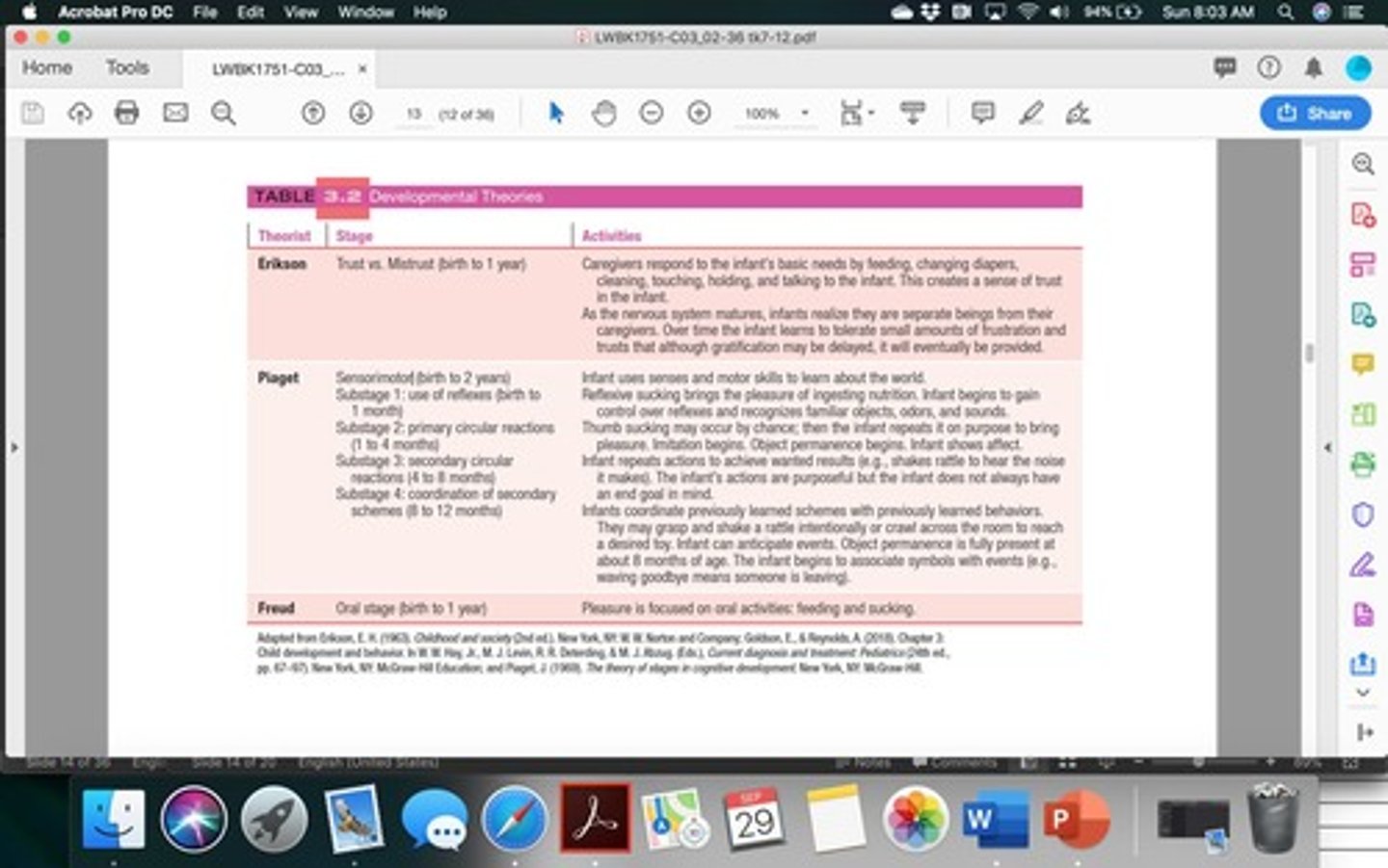
What are some infant care considerations regarding health and safety?
Food safety, monitoring wet diapers per day, growth and development, oral health, SIDS prevention, stranger fear, and separation anxiety.
What developmental challenges are common in toddlers?
Growth and development regression, negativism, and tantrums.
What is a significant aspect of preschooler development?
Imaginary playmates, sexual curiosity, and Erikson's stage of initiative versus guilt.
What are the key health promotion topics for adolescents?
Sequence of sexual maturation in males, dysmenorrhea, caloric intake balance, body piercing, tattooing, and sleep.
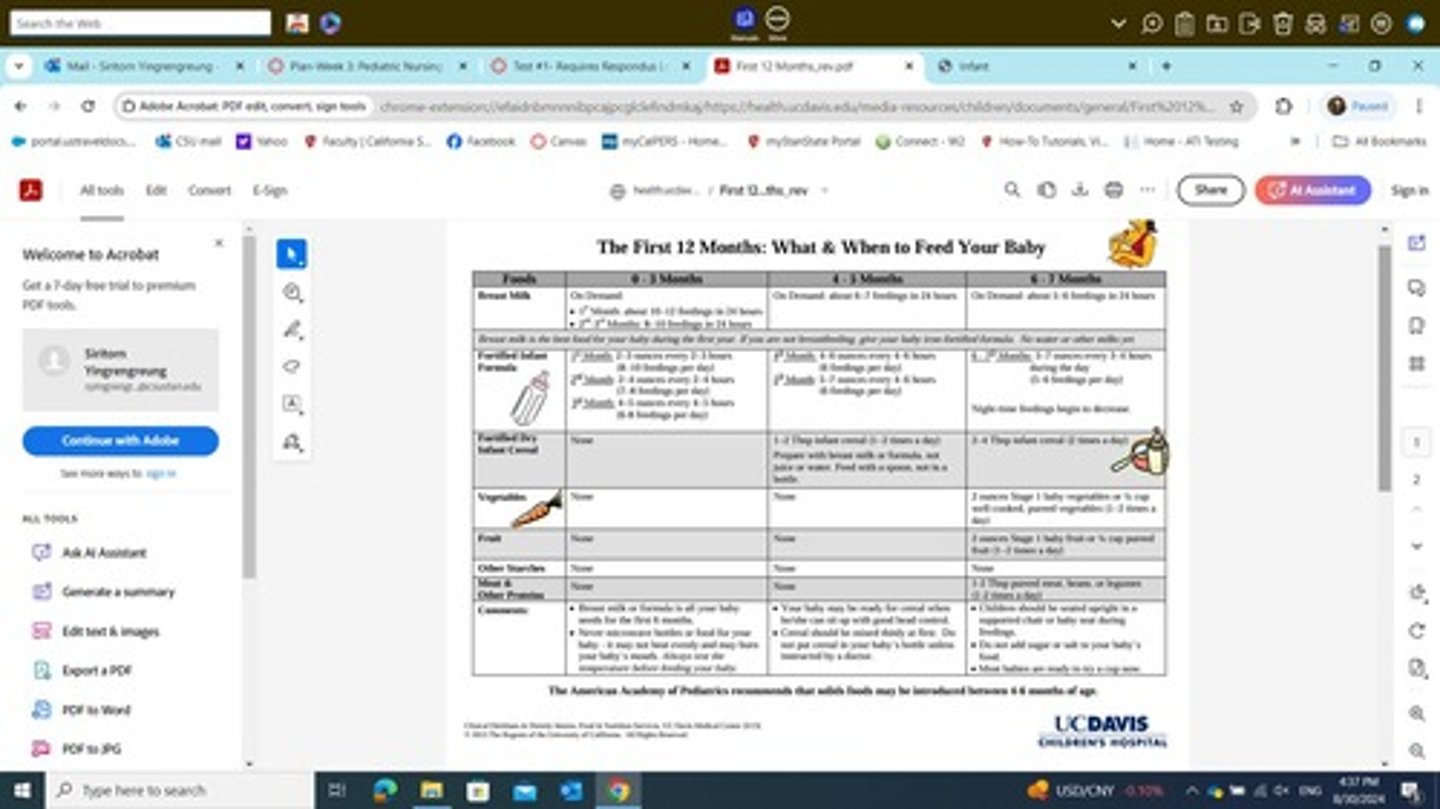
What is the growth pattern for infants in terms of weight?
Infants gain 680 g (1.5 lb.) per month for the first 5 months, double their birth weight by 6 months, and triple it by 12 months.
What is the height growth pattern for infants?
Infants grow 1 inch per month for the first 6 months and increase by 50% of their birth height by 12 months.
When do infants typically get their first teeth?
First teeth erupt at 6-8 months.
How should an infant's gums be cared for?
Clean the gums after feeding with a damp washcloth; after the first tooth erupts, use a soft bristle toothbrush with water until 18 months.
What are some methods to manage teething pain in infants?
Use a frozen teething ring or ice cube wrapped in a washcloth; administer Tylenol or Advil (for ages > 6 months) for no more than 3 days.
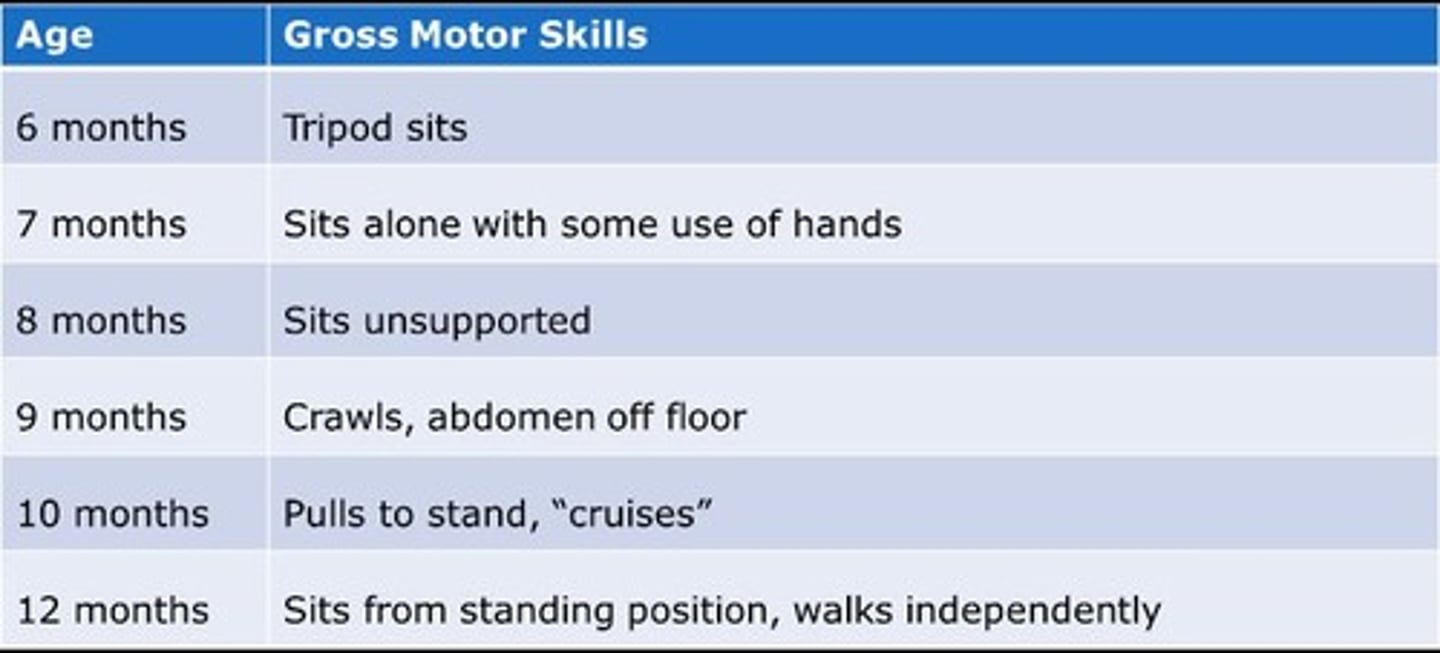
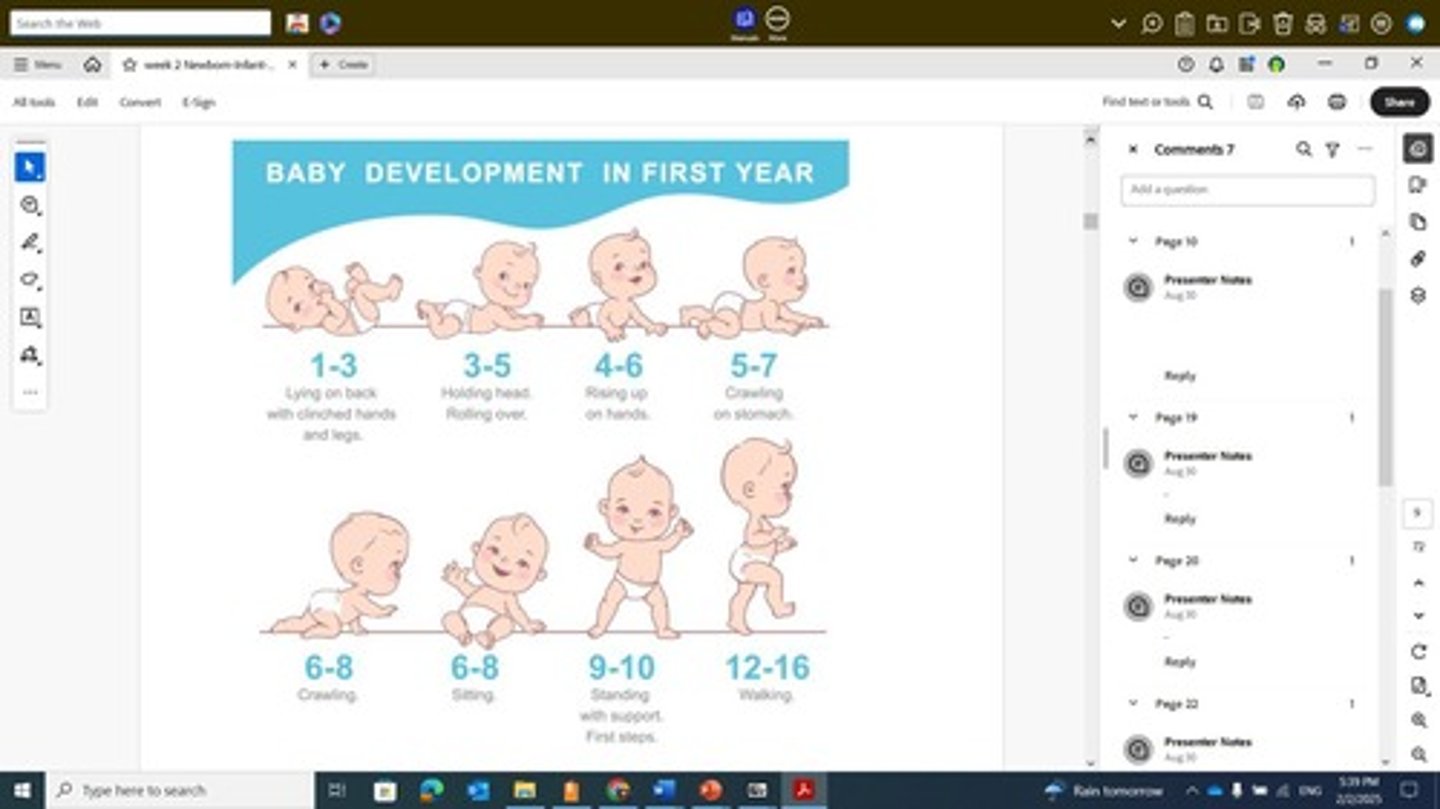
What are the gross motor skill milestones for a toddler at 15 months?
Walks alone with a wide gait and creeps up stairs.
At what age can toddlers typically run but fall easily?
18 months.
What fine motor skill can a 15-month-old perform?
Build towers of 2 cubes and hold them in one hand.
What language skills are expected from a 10-12 month old infant?
Says 3-5 words like 'mama' and 'dada', responds to simple directions, and uses hand movements to communicate needs.
What is the vocabulary expectation for a 2-year-old?
Uses 2-3 word sentences and has a vocabulary of about 300 words.
What is a characteristic of speech development in children aged 3 to 4?
They use three or four-word sentences, often termed 'telegraphic' speech.
At what age do children typically understand all parts of speech?
By age 6.
What is the expected vocabulary size for a 5-year-old?
More than 2100 words.
What is a common communication skill development activity for young children?
Reading books together, storytelling, and engaging in interactive adult-child conversations.
What is the significance of Erikson's stage of initiative versus guilt in preschoolers?
It reflects their developing sense of initiative and ability to take action versus feelings of guilt when they overstep boundaries.
What are the signs of gross motor skill development in infants by 4 months?
No head lag, indicating improved head control.
What are the fine motor skill milestones for a 2.5-year-old?
Build towers of 8 cubes and draw circles.
What behavioral signs indicate stranger anxiety in infants aged 6-8 months?
Behaviors such as clinging to the parent, crying, and turning away from the stranger.
How can parents help infants adjust to new people?
By having close friends or relatives visit often.
What is the significance of object permanence in infants, and when does it typically develop?
It develops around 6-8 months, indicating that infants become distressed when a parent leaves or is no longer in sight.
What are the characteristics of the Stage of Despair in separation anxiety?
Refusal to eat or drink, withdrawal, sadness, lack of interest in the environment, uncommunicative behavior, and regression to earlier behaviors.
Describe the Stage of Detachment/Denial in separation anxiety.
A superficial adjustment to loss, showing increased interest in surroundings, interaction with strangers, forming new but superficial relationships, and appearing happy.
What behaviors might be observed during the Stage of Protest in separation anxiety?
Crying, screaming, searching for the parent, clinging to the parent, and rejecting contact with strangers.
What are some aggressive behaviors toddlers may exhibit towards strangers during separation anxiety?
Verbally attacking strangers, physically attacking them (kicking, biting, hitting, pinching), and attempting to escape to find the parent.
What strategies can help manage separation anxiety in children?
Maintain a calm environment, provide familiar items, offer choices, follow home routines, and encourage caregiver presence.
What are the three developmental tasks of infants according to Piaget?
Separation from others, object permanence, and mental representation.
At what age does object permanence typically develop in infants?
Around 9-10 months.
What cognitive abilities are associated with intuitive thought in children aged 4-7 years?
Understanding concepts of left and right, time in relation to events, and developing magical thinking.
What is magical thinking in children aged 2-7 years?
The belief that thoughts are powerful and can cause events to happen.
How can magical thinking lead to feelings of guilt in children?
Children may feel responsible for negative events if they had 'bad' thoughts about them.
What is the role of play in children's cognitive development?
Play helps children understand, adjust to, and work through life's experiences.
What is the implication of magical thinking for parents and caregivers?
It is essential to clarify that thoughts do not make things happen and that children are not responsible for negative outcomes.
What is the typical age range for the onset of separation anxiety in infants?
4-8 months.
What is the relationship between magical thinking and egocentrism in children?
Children's egocentrism leads them to believe their thoughts can influence events, making them feel guilty for negative thoughts.
How can caregivers support a child experiencing separation anxiety?
By validating their feelings, providing comfort, and using coping strategies like music and relaxation techniques.
What are some common regression behaviors in children experiencing separation anxiety?
Thumb sucking, bedwetting, and reverting to the use of a pacifier or bottle.
What is the significance of maintaining a safe distance from an infant during separation anxiety?
It helps avoid sudden, intrusive gestures that may increase anxiety.
What cognitive development occurs towards the end of the sensorimotor period?
Children begin to use language and engage in representational thought.
How does the concept of causality develop in children?
Children start to understand causality, but may struggle to logically reason the cause and effect of illness or injury.
What is the recommended approach for talking to children about their feelings during separation anxiety?
Talk softly and meet the child at eye level to appear less intimidating.
What type of messages should be used to communicate feelings without blaming?
Use 'I' messages rather than 'you' messages.
What is the difference between separation and individuation in toddler development?
Separation is the child's emergence from symbiotic fusion with the mother, while individuation is the expression of individual characteristics in the environment.
What is rapprochement in child development?
A phase where a child experiences conflict between wanting independence and fearing abandonment, returning to the mother for reassurance.
What are transitional objects and why are they important?
Transitional objects, like a favorite blanket or toy, minimize fear, loneliness, and stress during separations.
What type of play is typical for infants?
Solitary play, where infants have short attention spans and do not interact with other children.
List some toys and activities that stimulate infant development.
Rattles, soft stuffed toys, teething toys, reading books, and mirrors.
What types of play should toddlers engage in?
Imitation play, locomotive skills, fine motor skills, creative/imaginative play, linguistic abilities, and tactile play.
What are some examples of toys that promote imitation play for toddlers?
Dolls, dollhouses, cooking utensils, and dress-up clothes.
What skills do push-pull toys and riding toys develop in toddlers?
Locomotive skills.
What is associative play in preschoolers?
Group play in similar activities without rigid organization or rules.
How do toys benefit children's development?
They help with cultural assimilation, muscle coordination, understanding rules and cooperation, creativity, and therapeutic stress reduction.
At what age do toddlers typically recognize sexual differences?
By age 2 years.
When do children develop gender identity?
By age 3 years.
How should parents react to toddlers' sexual curiosity?
Parents should not condone the behavior but teach that it is more acceptable to perform it in private.
What do temper tantrums indicate in toddlers?
They indicate the child's instability to control emotions.
Why are toddlers prone to tantrums?
They are frustrated due to a lack of motor and cognitive skills for mastery and autonomy.
What strategies can help manage temper tantrums?
Stay calm, ignore the behavior, ensure safety, and use positive reinforcement during calm periods.
What is an effective method for managing tantrums in public?
Immobilize the child with a hug and use a calm voice to soothe them.
What age is appropriate for using time-outs to manage tantrums?
At 18 months old.
What types of toys support fine motor skills in toddlers?
Finger paints, thick crayons, puzzles, and chalk.
What is the role of parental affection in a child's development of sexual and emotional relationships?
It is important for the child's capacity for future relationships.
What types of play should be encouraged to foster creativity in toddlers?
Creative/imaginative play with blocks, dolls, and clay.
What is the recommended total media time for children over 2 years old?
Less than 1 hour per day.
What are the criteria for abnormal temper tantrums in children over 5 years old?
Temper tantrums lasting more than 15 minutes or occurring more than 5 times a day.
What is negativism in toddlers?
A persistent negative response as an assertion of self-control, often answering 'no'. It can be mitigated by providing choices instead of asking questions.
What is regression in toddlers?
The retreat to past levels of behavior, such as increased dependency or refusal to use the potty, often triggered by threats to autonomy like illness or separation.
What is a common approach to handle regression in toddlers?
Ignoring the regression while praising appropriate behavior.
What are common fears in preschool children?
Fears of the dark, monsters, and night terrors.
How can animism affect a child's behavior?
A child may refuse to use the toilet after seeing it portrayed as a monster in media.
What is a recommended strategy for addressing children's fears?
Gradually expose children to the feared object in a safe situation.
How many times should a new food be offered to a baby?
At least 8-15 times, as a baby's taste may change over time.
What are the first signs of sexual maturation in girls?
Breast changes, rapid increase in height and weight, growth of pubic and axillary hair, and menstruation.
What indicates the beginning of puberty in boys?
Enlargement of the testicles.
What is gynecomastia and when does it occur?
Gynecomastia is breast tissue enlargement that occurs during midpuberty in boys.
What are Tanner stages?
Stages of secondary sex and genital development.
What is the ideal age for girls and boys to begin puberty?
Girls at age 10 and boys at age 12.
What is dysmenorrhea?
Pain shortly before or during menstruation, which can be primary (biological) or secondary (pathologic).
What is the difference between primary and secondary dysmenorrhea?
Primary dysmenorrhea is caused by prostaglandins, while secondary dysmenorrhea is due to underlying pathologic conditions.
What are some therapeutic management options for dysmenorrhea?
NSAIDs, oral contraceptives, heat, exercise, and comfort measures like massage.
What is the recommended timing for NSAID administration for dysmenorrhea?
At the first sign of symptoms or 1-2 days before the onset of menses.
What are some comfort measures for managing dysmenorrhea?
Heat application, exercise, massage, biofeedback, TENS, progressive relaxation, yoga, and acupuncture.
What are the key components of formal sex education?
Information on sexual maturity, reproduction, and answering questions at the child's level of understanding.
What physical examinations may be performed for dysmenorrhea?
Gynecologic examination, ultrasound, D&C, endometrial biopsy, or laparoscopy.
What factors should be assessed in a pain assessment for dysmenorrhea?
Onset, duration, type of pain, relationship to menstrual flow, age at menarche, family history, and previous treatments.
What is the role of comfort measures in dysmenorrhea management?
They help with muscle relaxation and minimizing uterine ischemia.
What is the significance of the age of 13½ to 14 years in boys?
Puberty changes might be delayed if scrotal changes have not occurred by this age.