animal cell structure
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
including some plant cell info too!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what is a cell?
smallest building block in an organism and are capable of carrying out specific functions
how are cells able to carry out different functions?
differentiation
what is ultrastructure?
the internal structure of a cell as not visible on a light microscope
what are the three domains of all living things?
archaea
bacteria
eukaryota
what is a cell made of (main groups)?
proteins
polysaccharides
lipids
nucleic acids
what is the significance of the proteins w/in a cell?
enzymes in the cytoplasm and inside organelles
associated w/ the membrane
associated w/ DNA in the nucleus
associated w/ RNA in ribosomes
cytoskeleton
what is the significance of the polysaccharides w/ in a cell?
associated w/ the membrane
makes up cell walls
stored for energy reserve
what is the significance of the lipids w/in a cell?
stored for energy reserve
phospholipids make up cell membranes
cholesterol associated w/ membrane and controls fluidity
where are the nucleic acids w/in the cell found?
DNA: associated w/ proteins in the nucleus
RNA: mRNA, rRNA, tRNA - different types found in nucleus or cytoplasm or associated w/ proteins in ribosomes
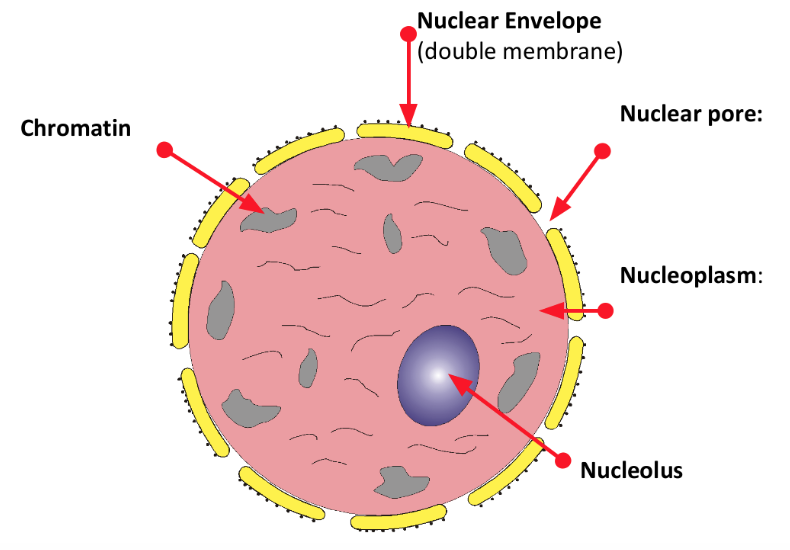
what is the function of the nucleus?
contains DNA instructions for protein synthesis
produces mRNA and tRNA needed for protein synthesis
nucleolus manufactures rRNA and ribosomes
what is the structure of the nucleus?
nuclear envelope: double membrane that surrounds the nucleus (membrane bound)
nuclear pores: allow large molecules out of the nucleus e.g. mRNA
nucleoplasm: granular, jelly-like material
nucleolus: small sphere w/in nucleus
chromosomes: linear DNA that is bound to histone proteins
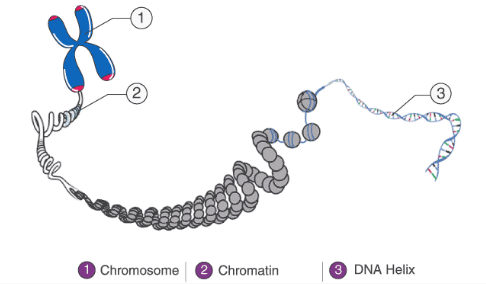
what is the difference between chromosomes and chromatin?
chromosomes:
linear molecule of DNA tightly wrapped around histone proteins
DNA is only in this form during cell division
chromatin:
DNA more loosely associated w/ histones
enclosed in the nucleus
what are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)?
what is the structure of the RER?
continuous w/ the nuclear membrane, membrane bound
has ribosomes on cisternae
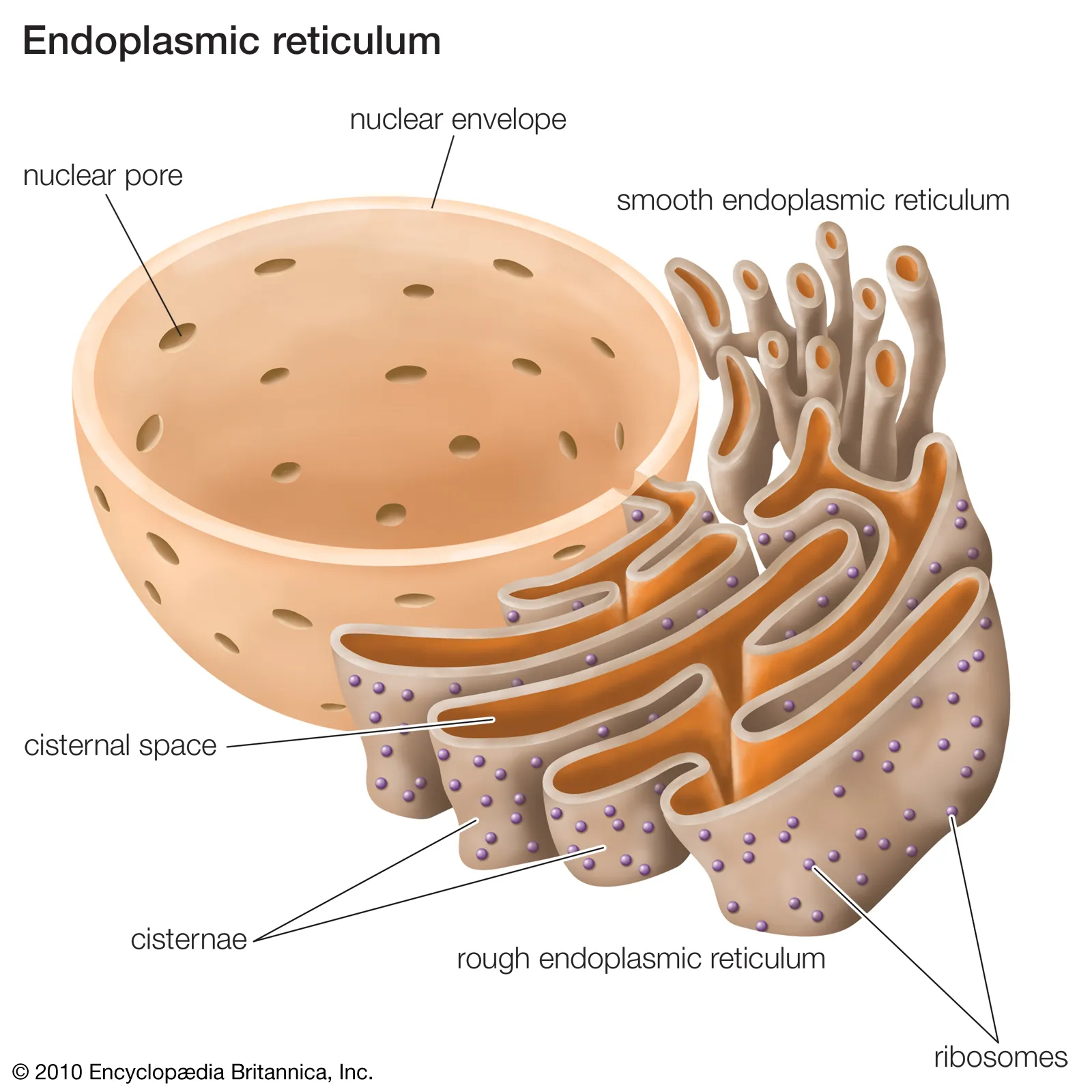
what is the function of the RER?
cisternae provide large SA for protein synthesis
protein collects inside RER and transported throughout cell
what is the structure of the SER?
membrane bound
no ribosomes (hence smooth)
more tubular than RER
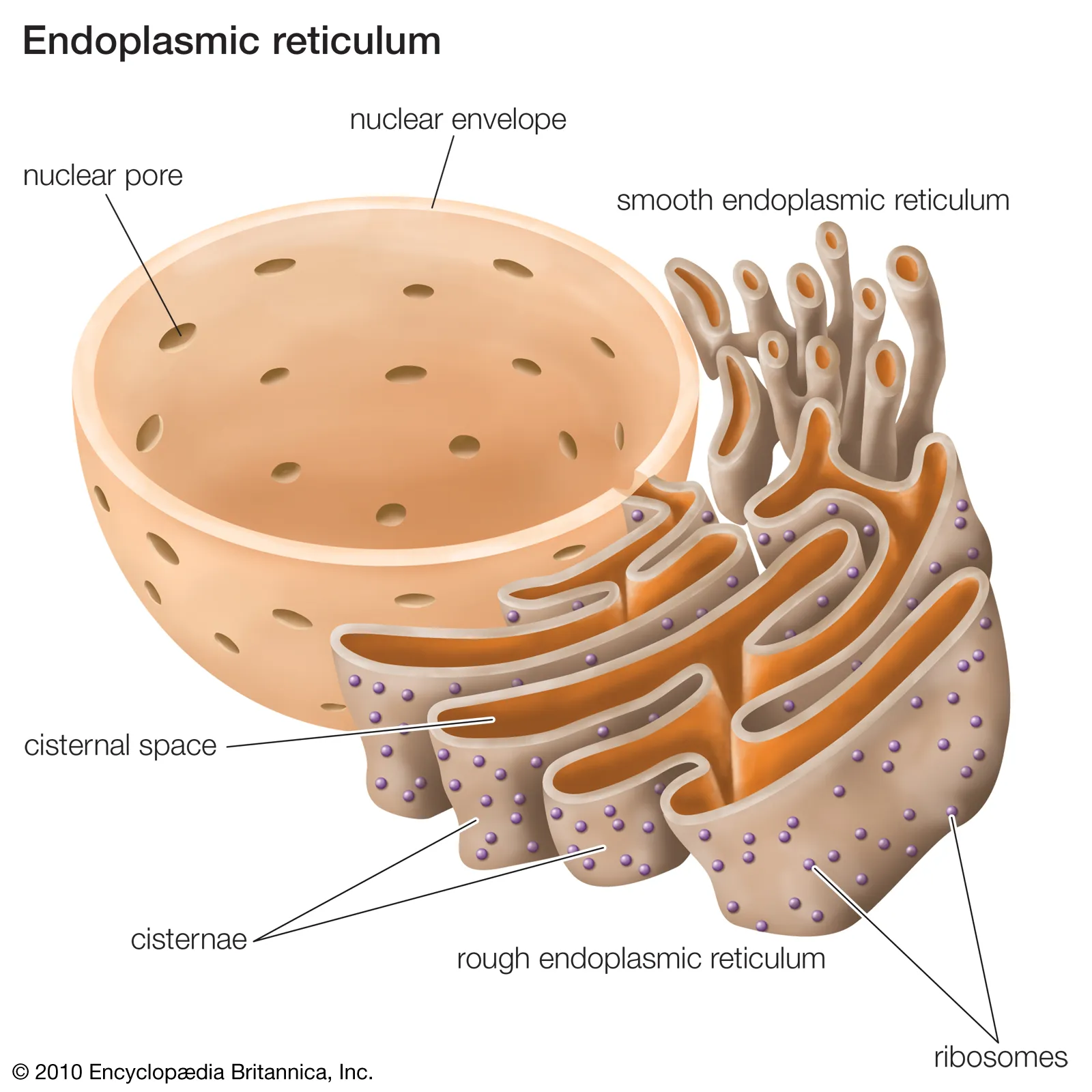
what is the function of the SER?
synthesises, stores and transports lipids, steroids and carbohydrates
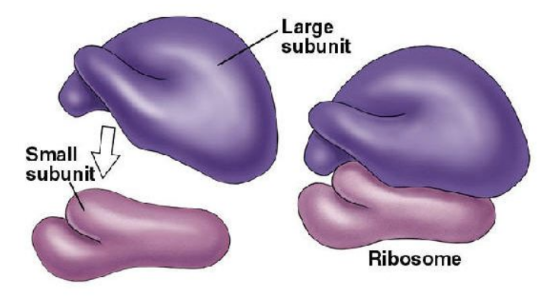
what is the function of the ribosomes?
site of protein synthesis
what is the structure of the ribosomes?
made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein
consists of a large and small subunit
two types: 80S (found in eukaryotic cells) and 70S (found in prokaryotic cells, mitochondria and chloroplasts)
what is the structure of the Golgi apparatus?
membrane bound
stacks of cisternae (flattened, membrane bound sacs)
vesicles are continuously pinched off from the ends
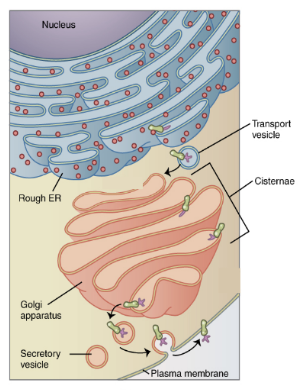
what is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
modifying/packaging/transporting proteins/glycoproteins
modifying/packaging/transporting lipids/glycolipids
form vesicles and lysosomes (as they are Golgi vesicles)
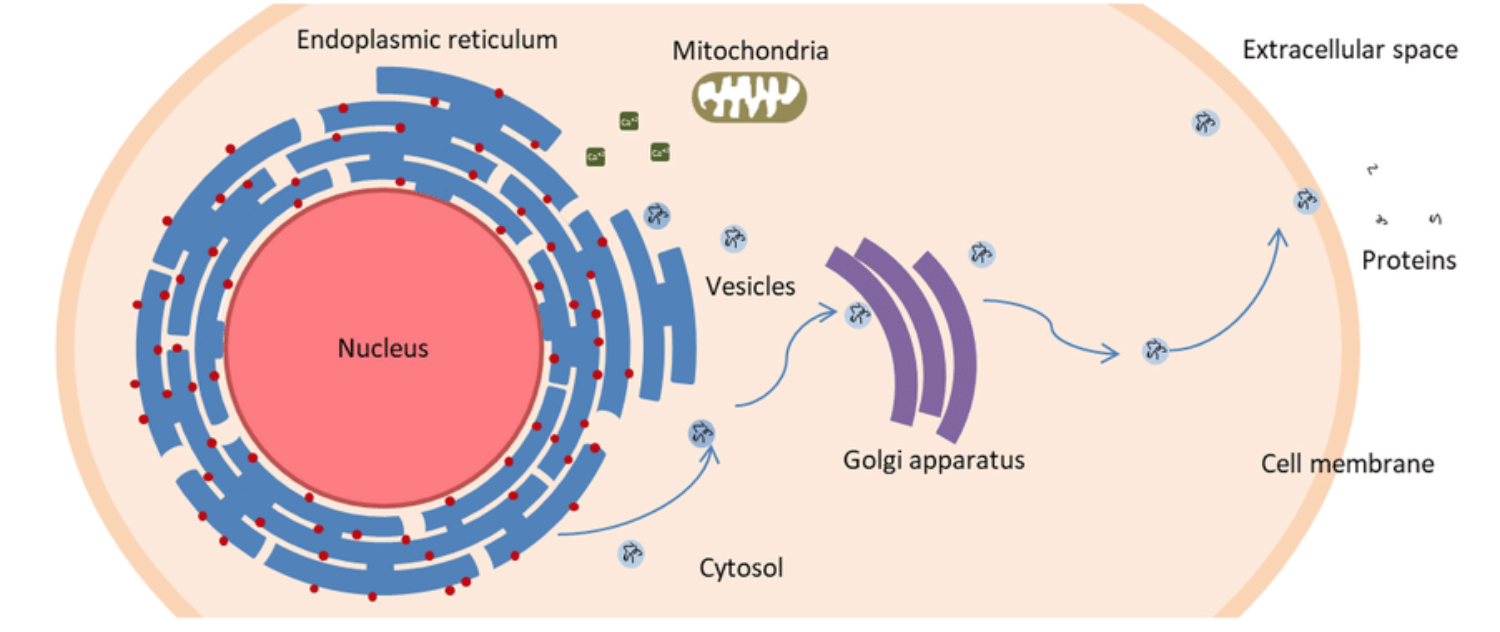
what events take place when a protein is made and sent to the extracellular space?
a gene is transcribed into mRNA in the nucleus
the mRNA leaves through a nuclear pore
the mRNA reaches a ribosome on the RER
the ribosome synthesises a protein into the RER
the protein is packed in a vesicle that leaves the RER
the vesicle reaches the golgi and fuses w/ its cisternae
the protein is released outside
what are lysosomes?
type of Golgi vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes (proteases, lipases, lysozymes)
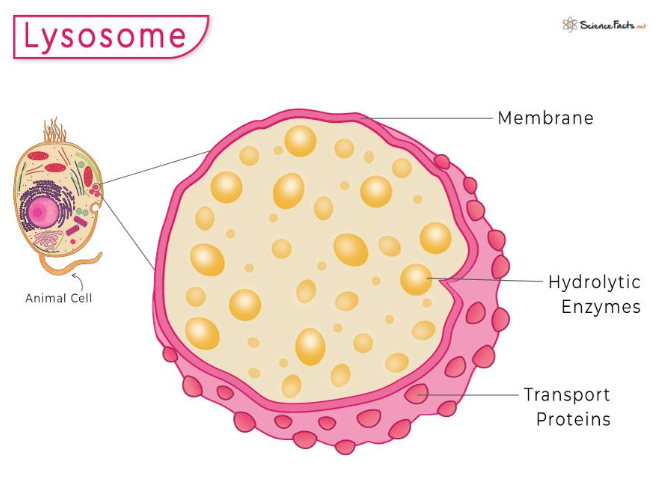
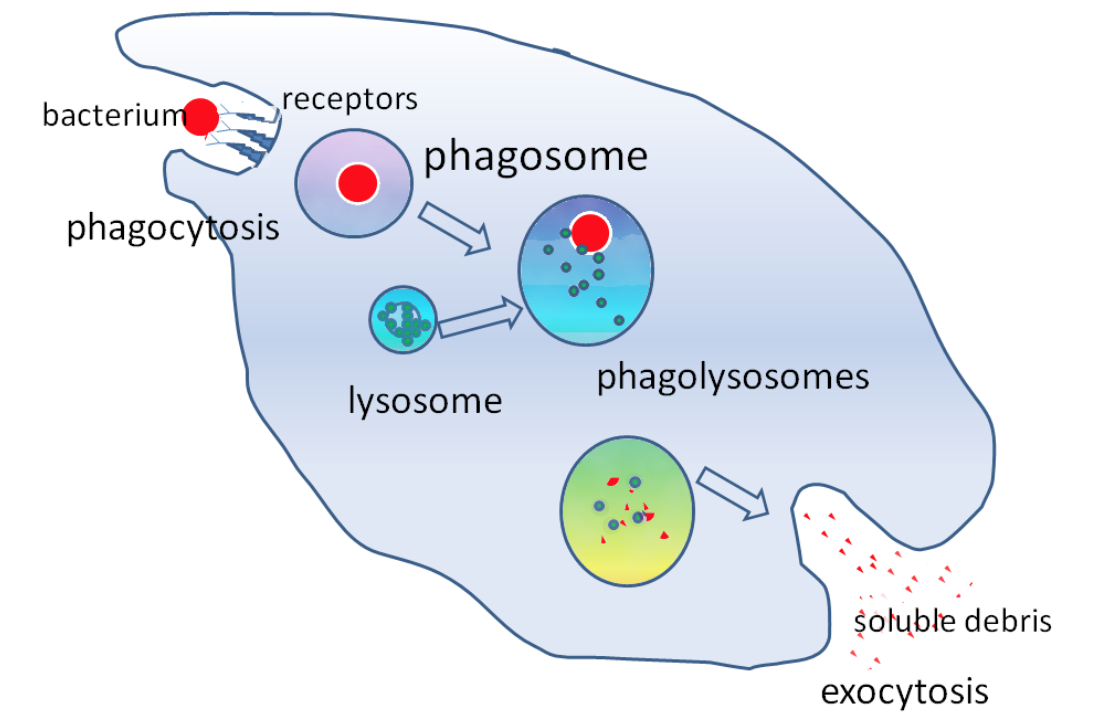
what is the function of lysosomes?
digests unwanted material in the cell:
hydrolyses material ingested by phagocytic cell
exocytosis - releases enzymes to outside of cell to destroy material
digests worn out organelles
autolysis - complete breakdown of cells after they have died
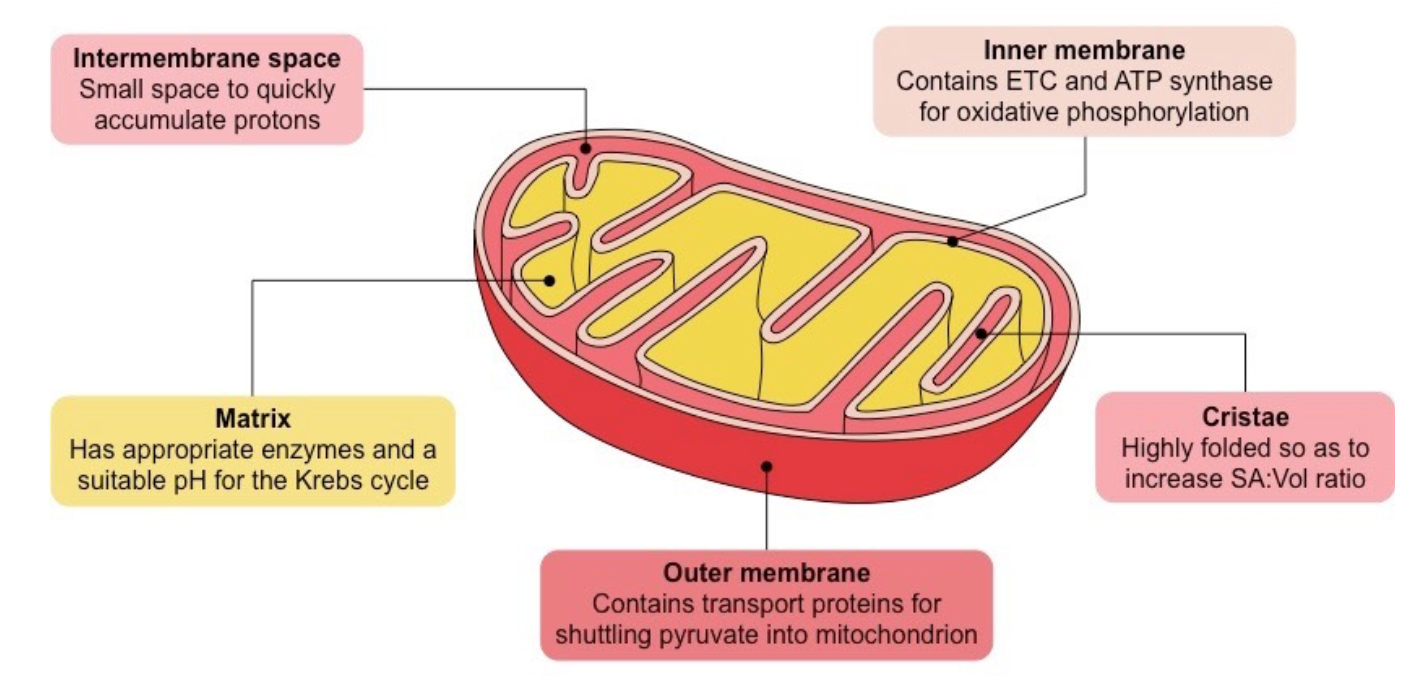
what is the function of the mitochondria?
site of aerobic respiration
releases ATP during respiration - source of energy for cell activities
what is the structure of the mitochondria?
double membraned (membrane bound) - inner membrane folds to form cristae, where respiratory enzymes are embedded
fluid centre = mitochondrial matrix - also contains respiratory enzymes as well as loop of mitochondrial DNA, proteins, lipids and ribosomes