APHG Unit 4 (tprosk) Diagram | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Political Geography
the study of the political organization of the world
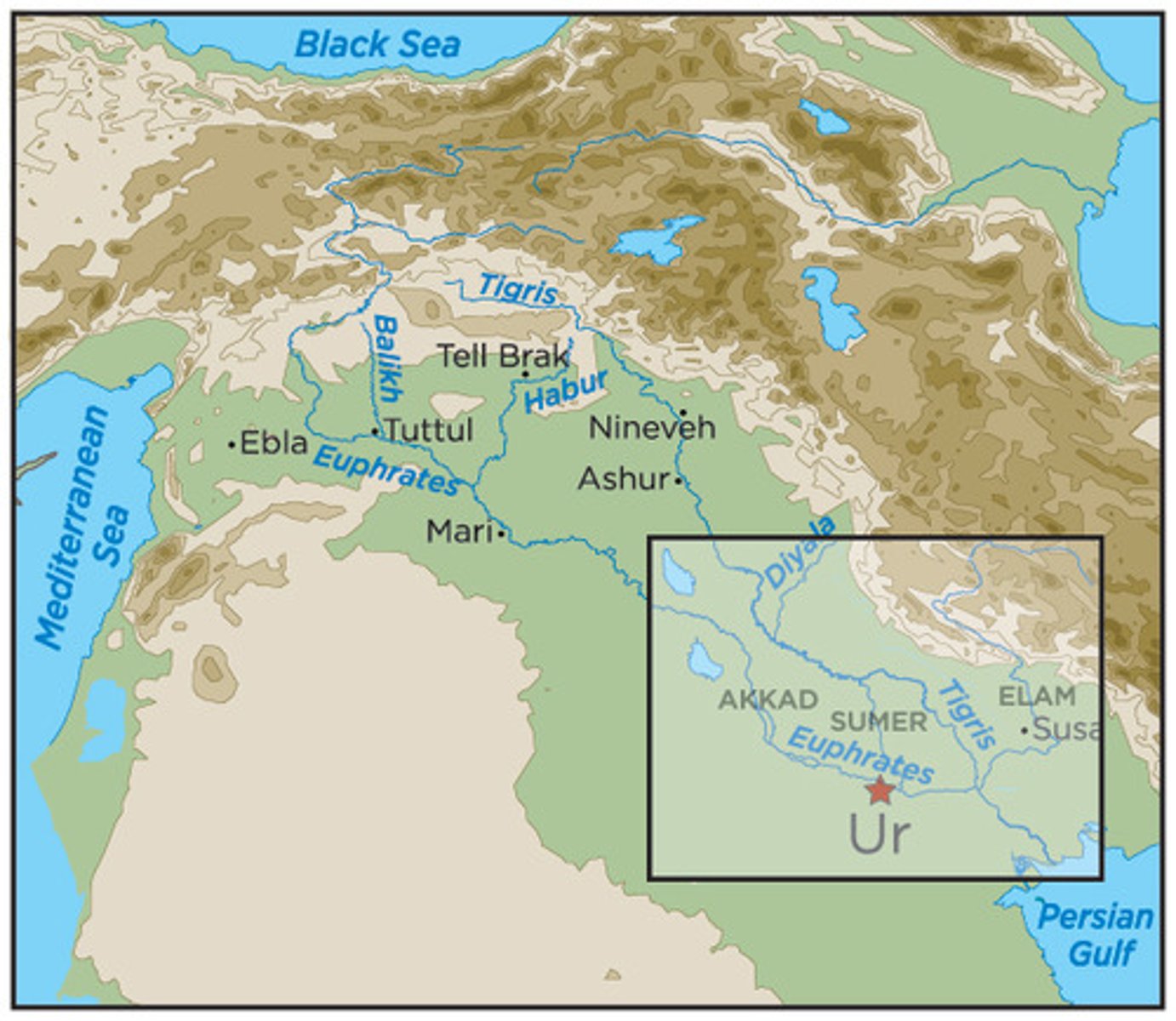
city-state
A city with political and economic control over the surrounding countryside
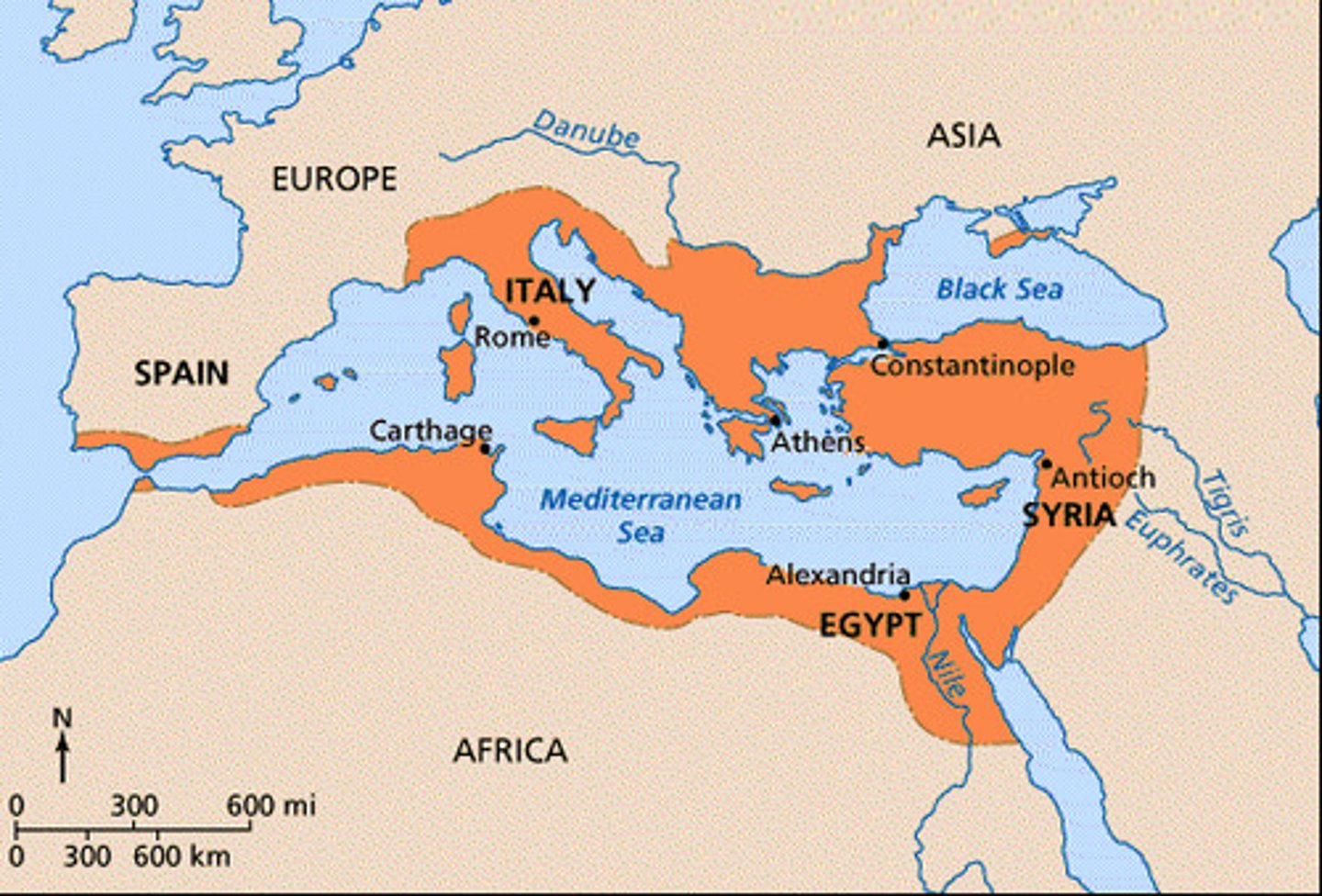
empire
land with different territories and peoples under a single rule
TERM
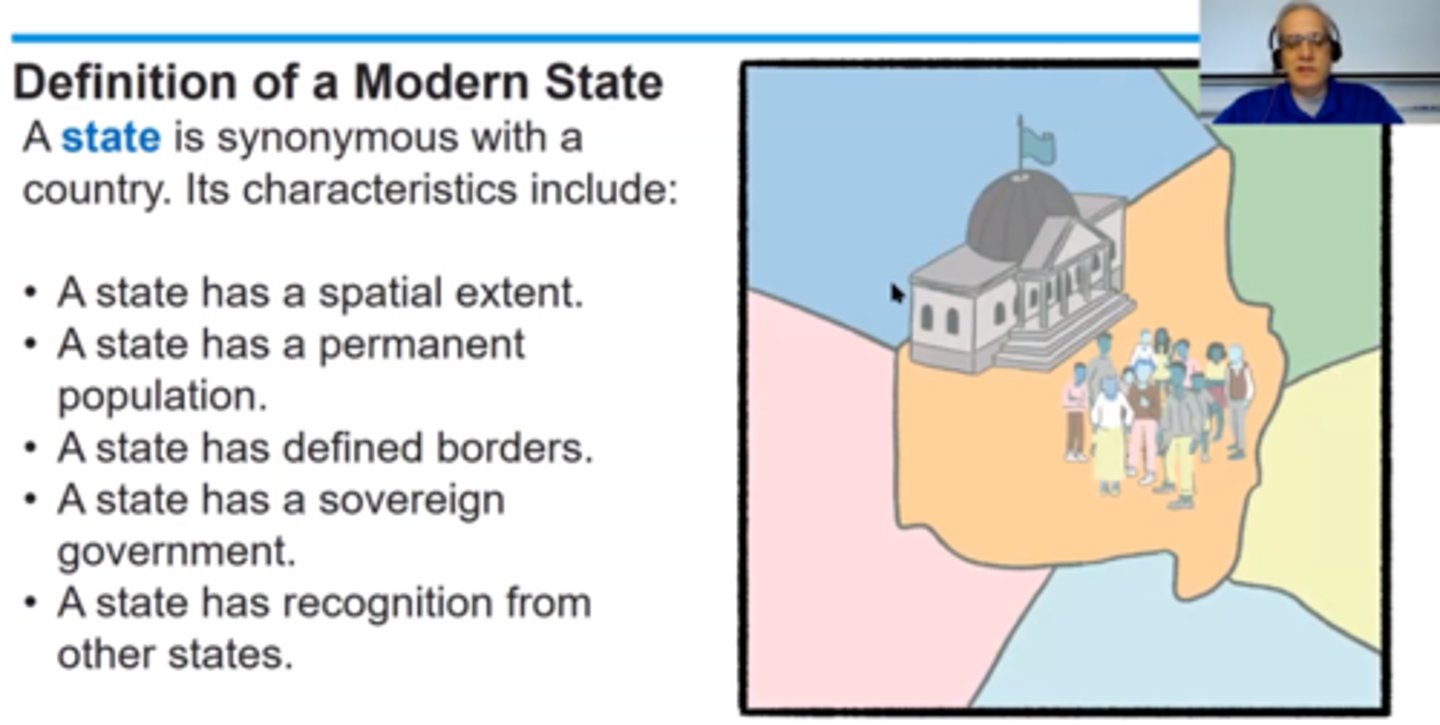
state
DEFINITION
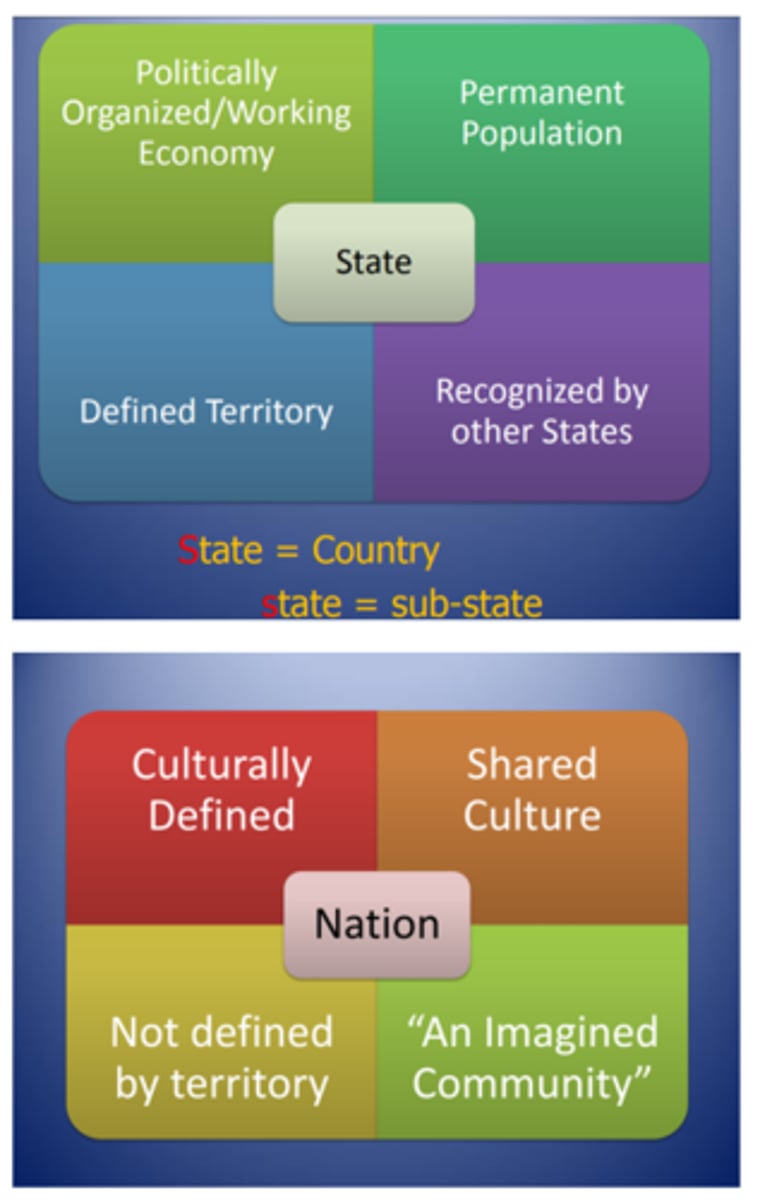
A geographic area organized into one political unit (you might think of this as a "country")
4 characteristics of a state (country)
1. Population (a state has people)
2. Territory (a state has spatial extant and defined boundaries)
3. Sovereignty (a state is independent and self-governing)
4. Government (a state has an established system of government)
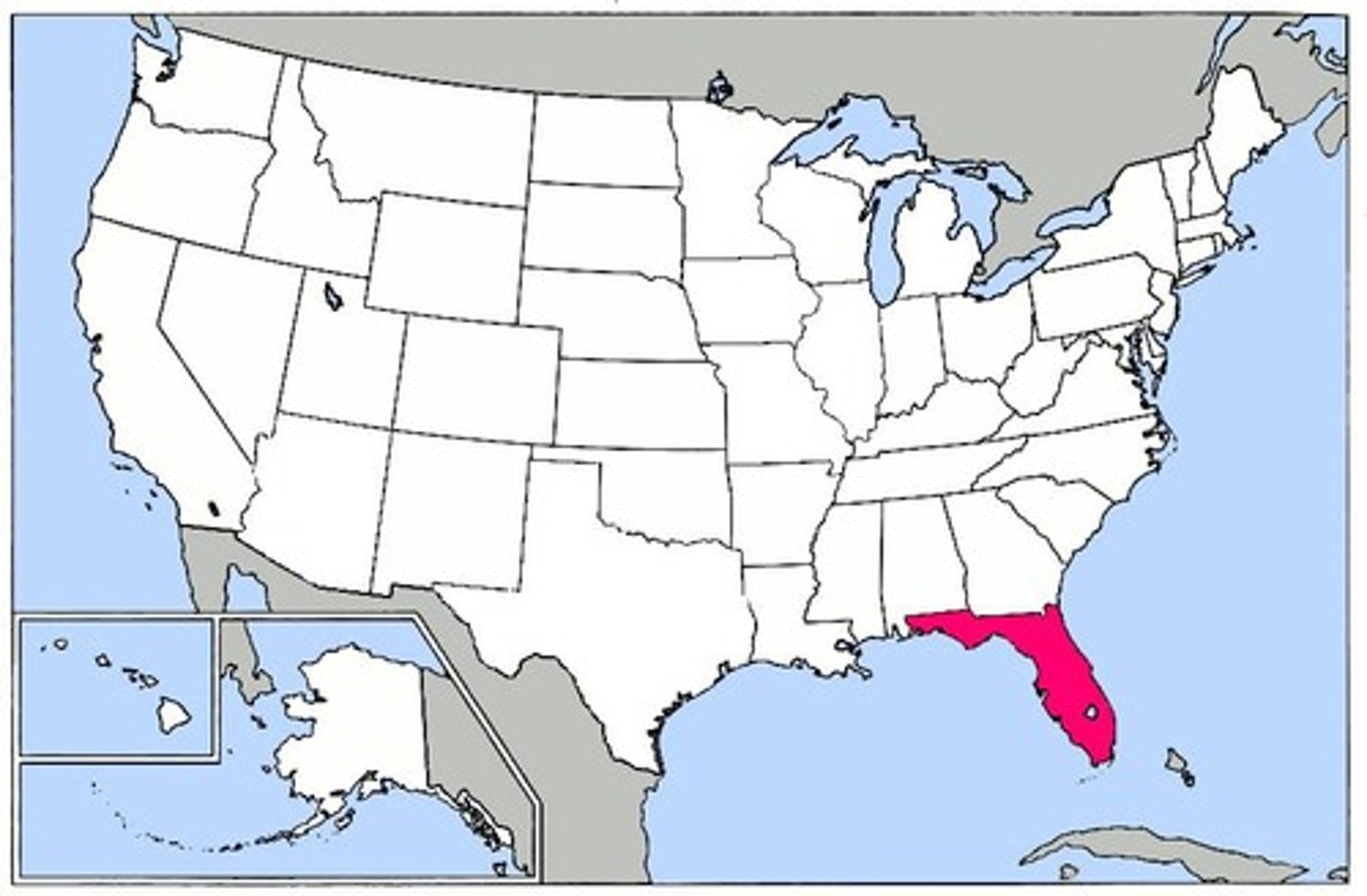
U.S. state
one of the fifty sub-national political divisions in the USA. A state is not a STATE
TERM
nation
DEFINITION
a large group of people united by common descent, history, culture, or language, inhabiting a particular territory.
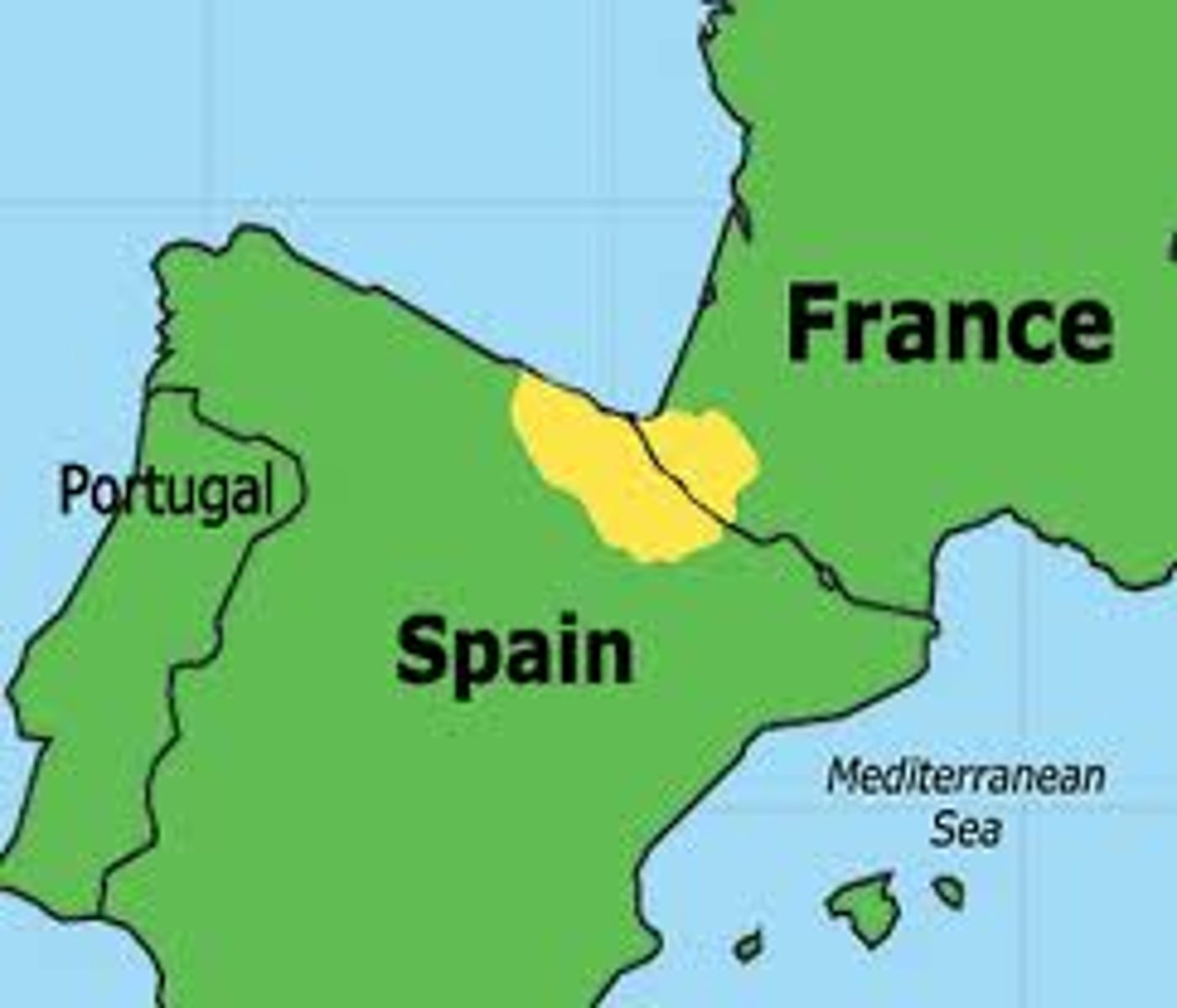
self-determination
The idea that nations have the right to govern themselves

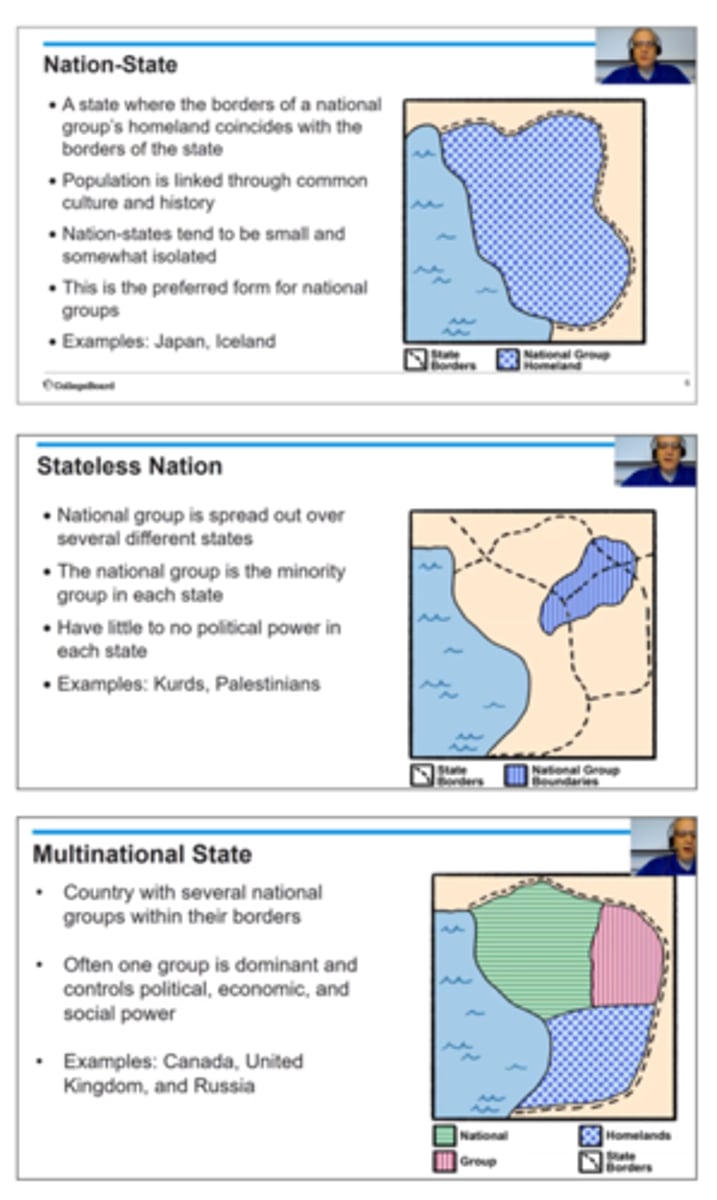
nation-state
a sovereign state whose citizens or subjects are relatively homogeneous in factors such as language or common descent.
around the time of World War 1
when did the idea of the "nation-state" first become common

difference between "nation" and "state"
a nation is GROUP OF PEOPLE with similar culture and history, while a state is a GEOGRAPHIC AREA controlled by a specific government
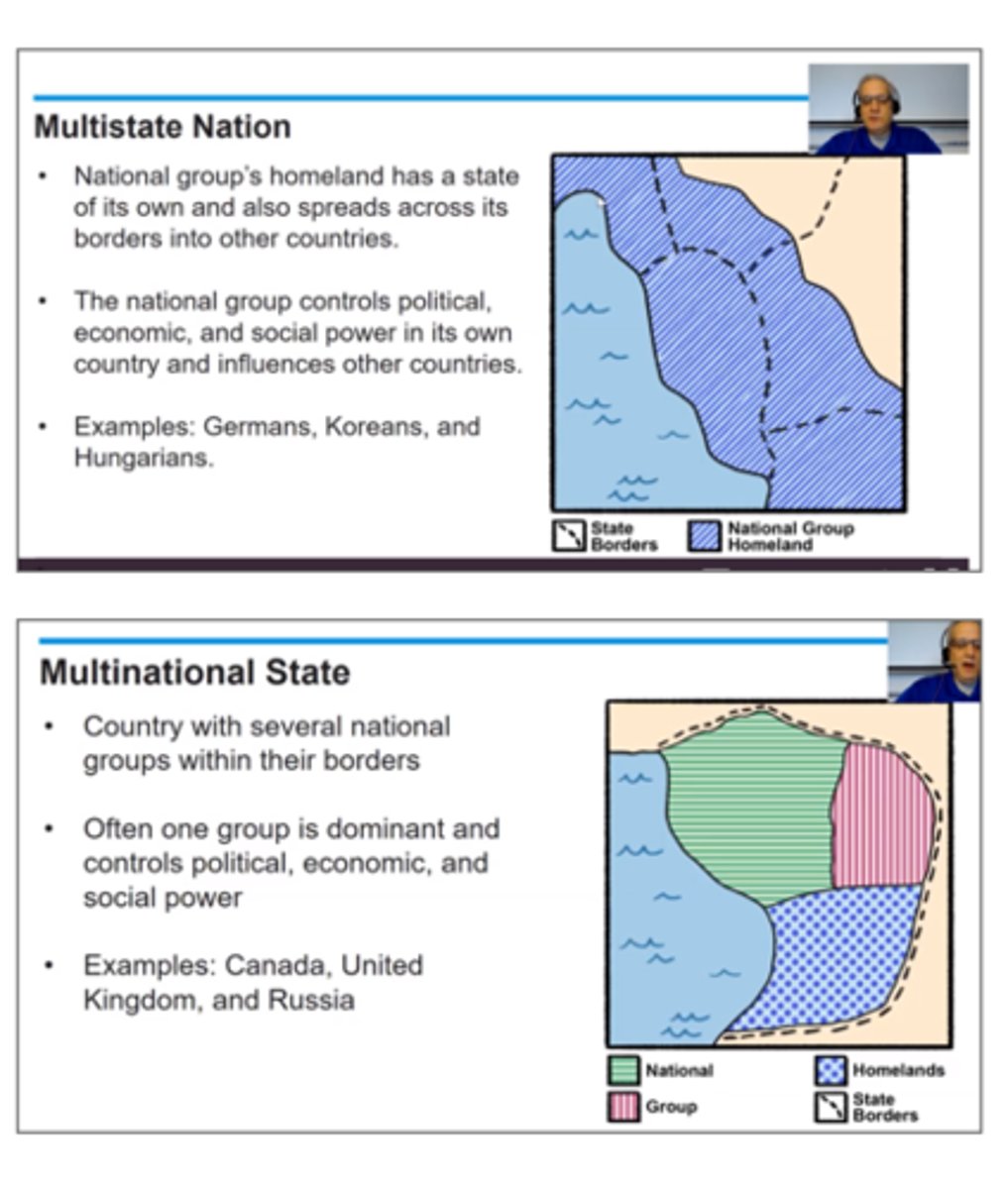
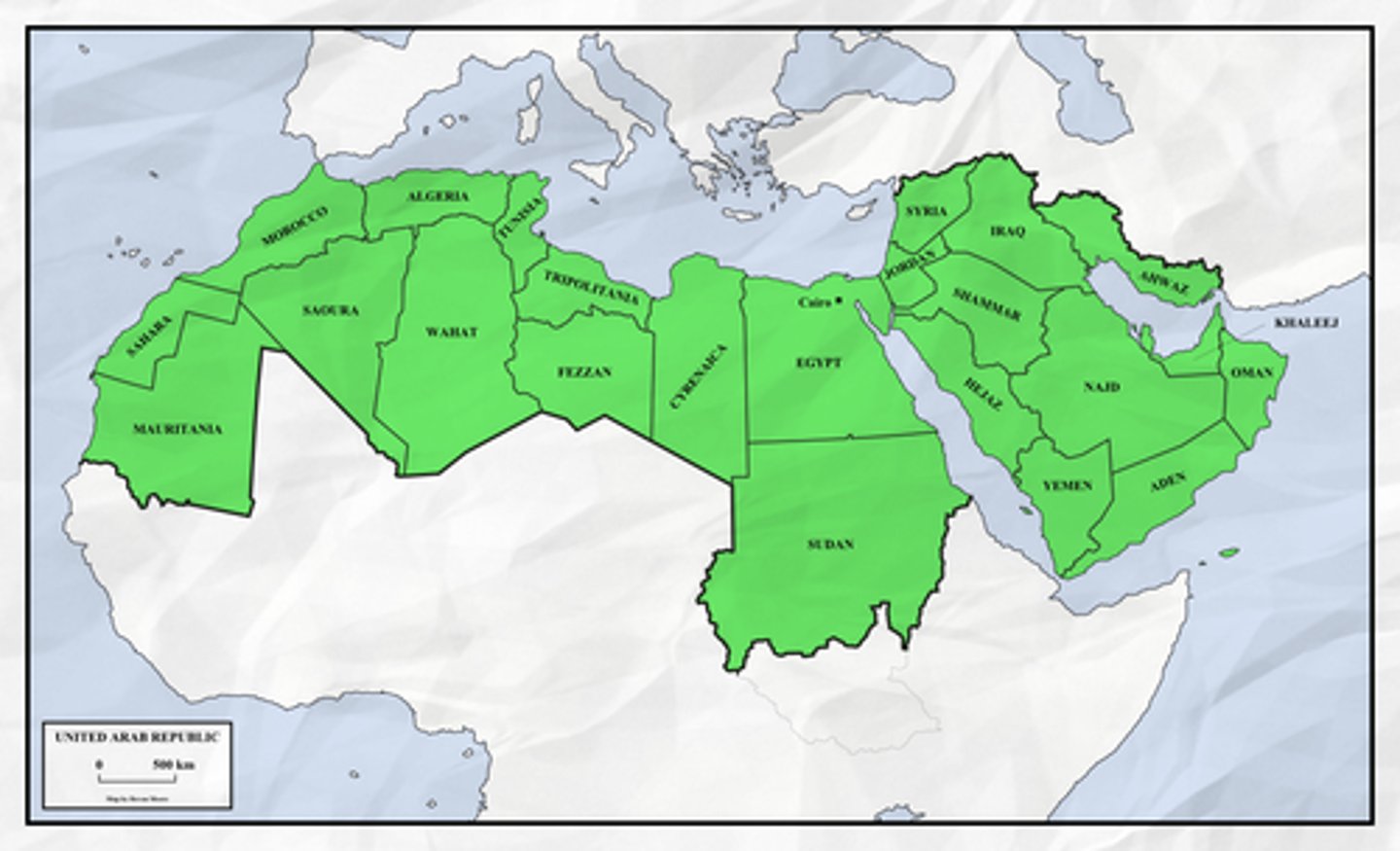
multinational state
State that contains two or more ethnic groups with traditions of self-determination that agree to live peacefully together as one state
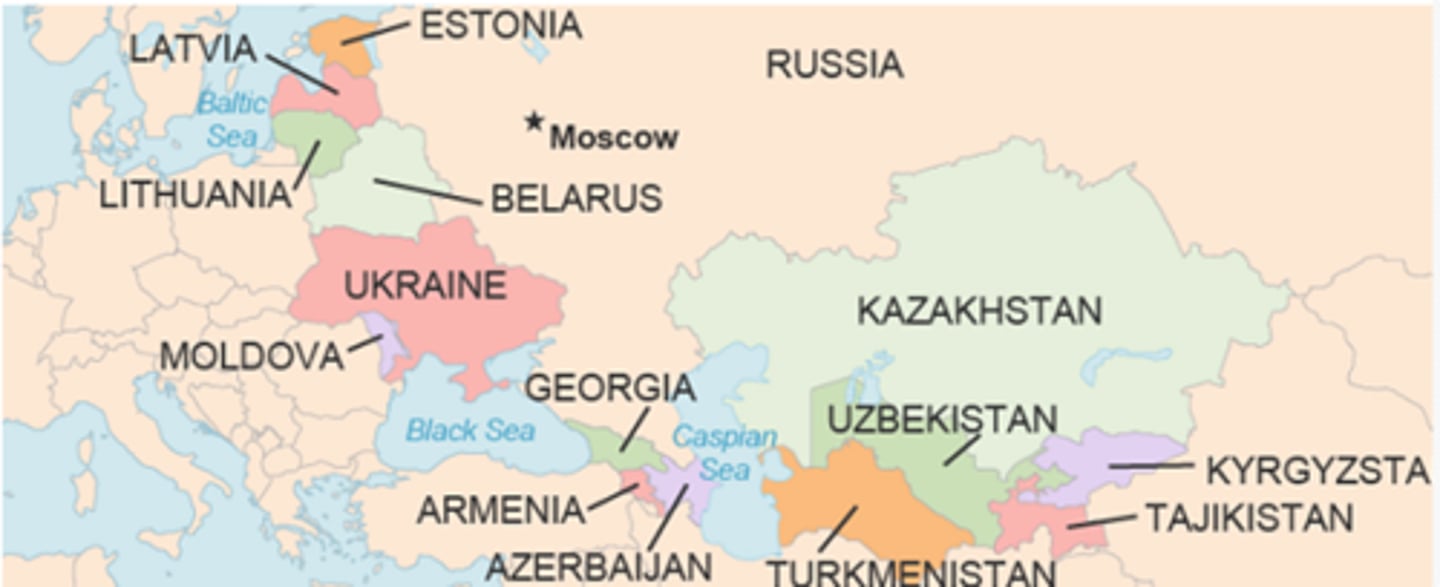
nations of the former Soviet Union
Ukraine, Belarus, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, etc...
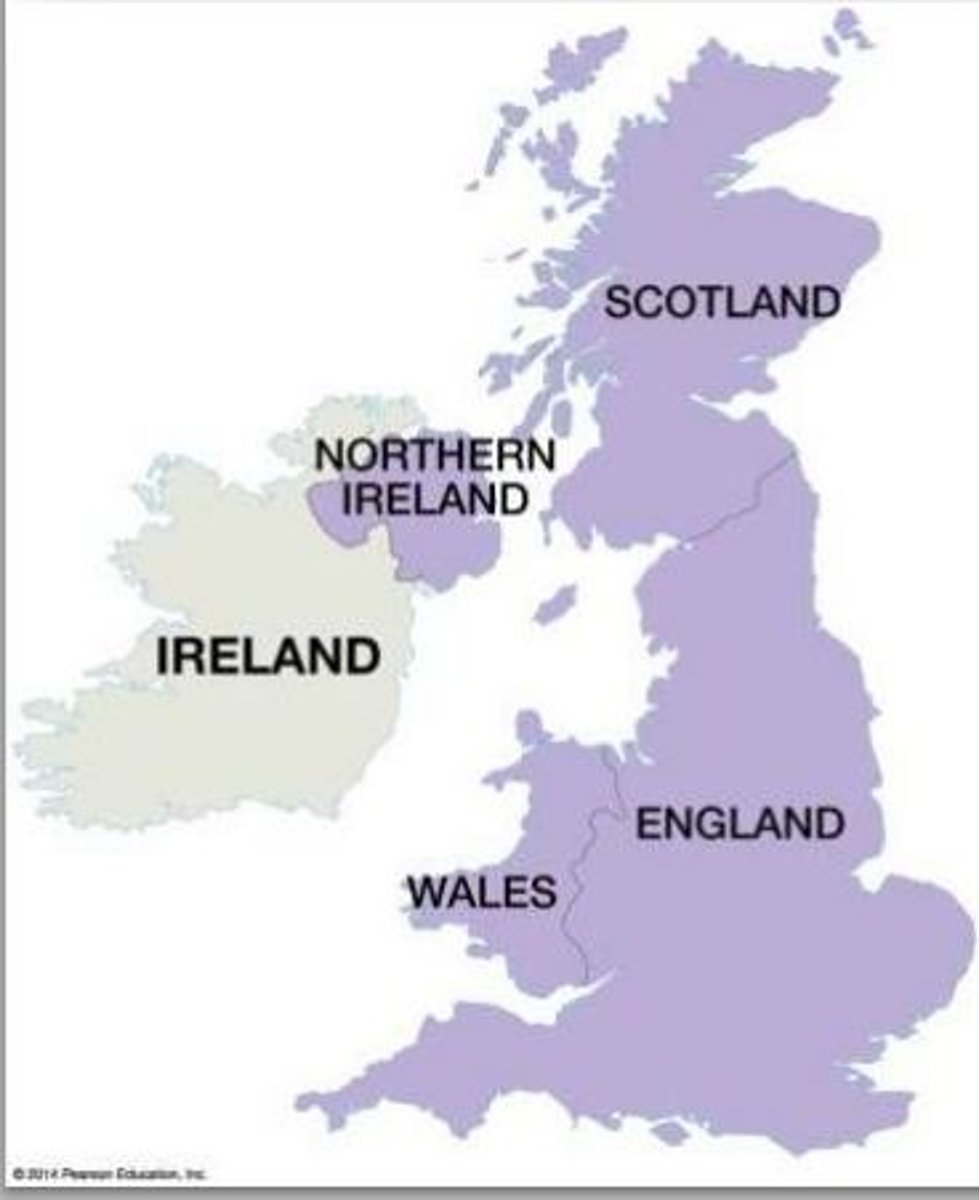
examples of multinational states
Soviet Union, United Kingdom, Canada, Belgium, Afghanistan, China
multistate nation
nation that transcends the borders of two or more states (there are members of that ethnic group in multiple countries)
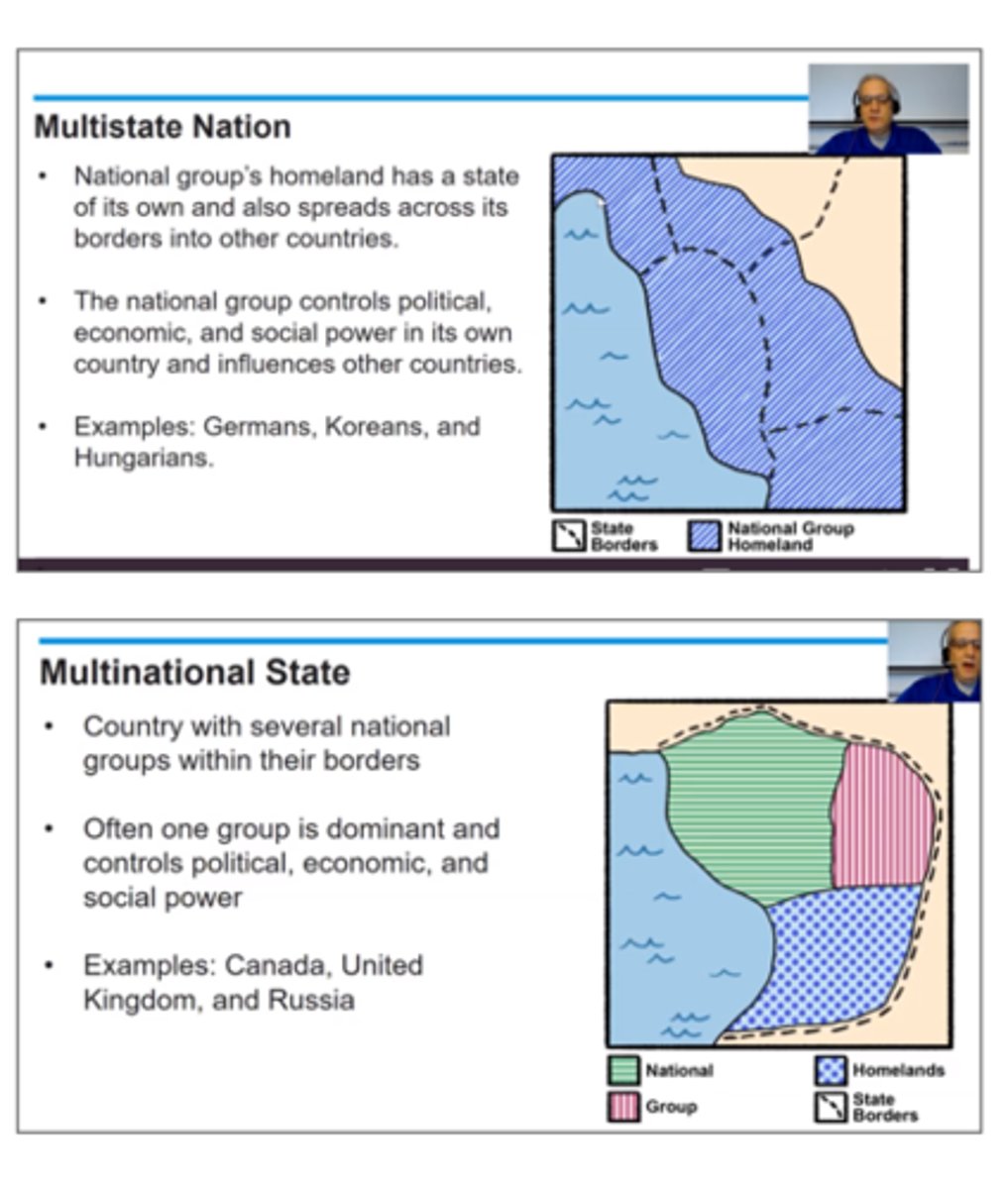
examples of multistate nations
Koreans (there are Koreans in North and South Korea), Arabs (throughout North Africa and Middle East), Germans (in Germany, parts of Switzerland, northern Italy, Belgium, Poland), Kurds (they are also a stateless nation)
stateless nation
when an ethnicity has a history of self-determination but does not have a recognized state
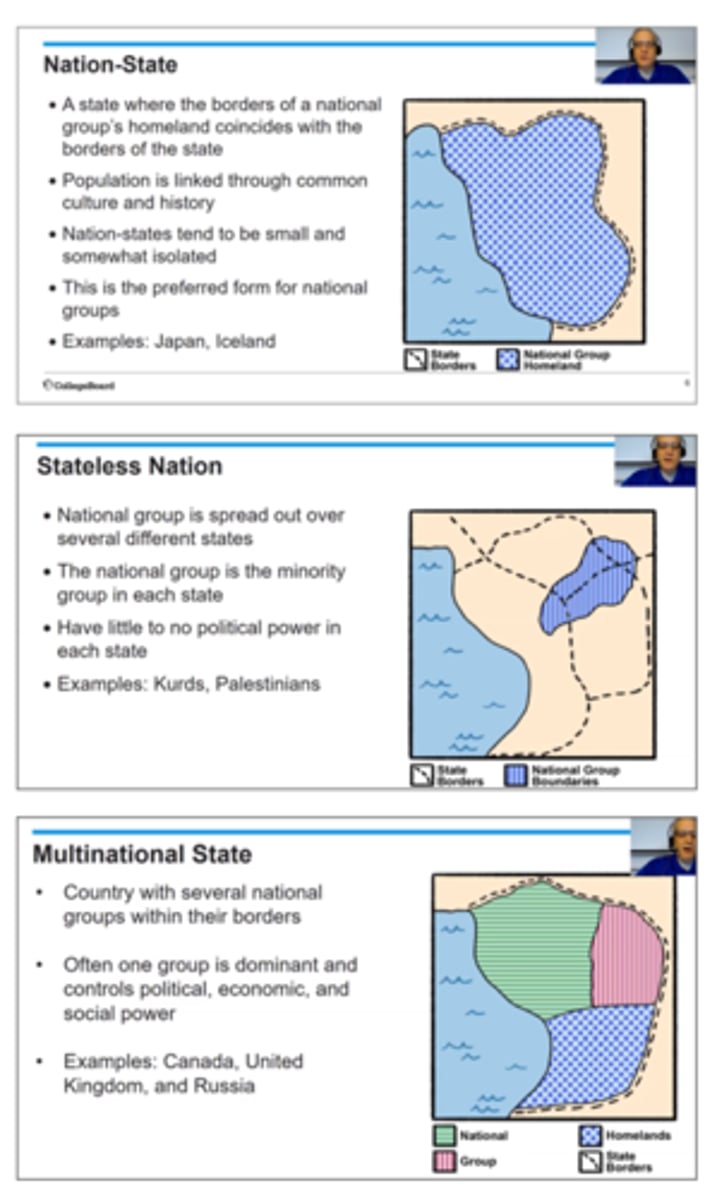
examples of stateless nations
Kurds, Romani, Palestinians, Uyghurs, Tibetans, Tamils, Plemish, Hmong, Basques

autononomous
self-governing
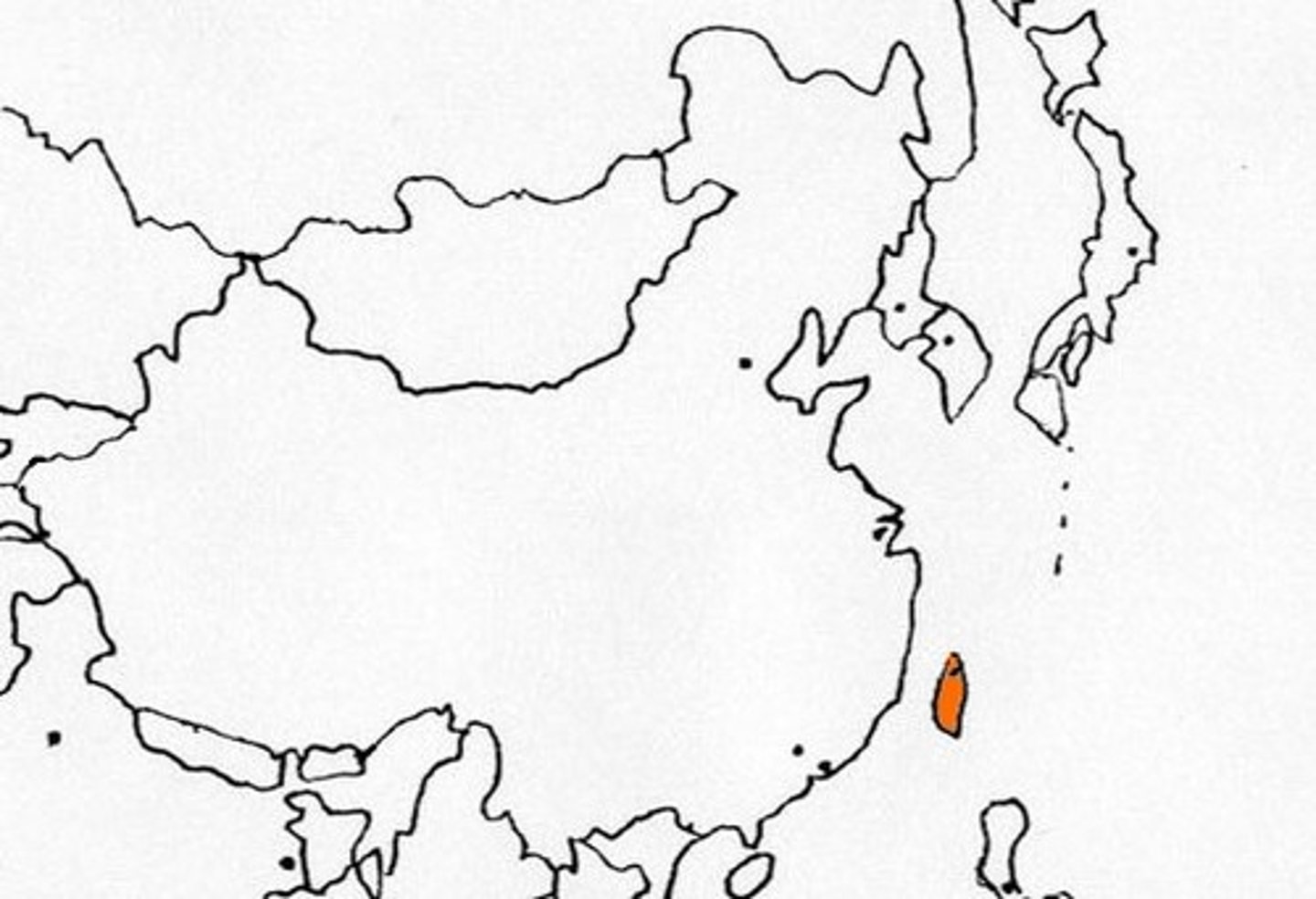
autonomous regions
regions with a certain degree of autonomy from an external authority, and power over their own affairs (usually are geographically distant from the external power)-- Example- Taiwan
semi-autonomous region
regions with some control over their own affairs, but another state also controls the region
examples of semi-autonomous regions
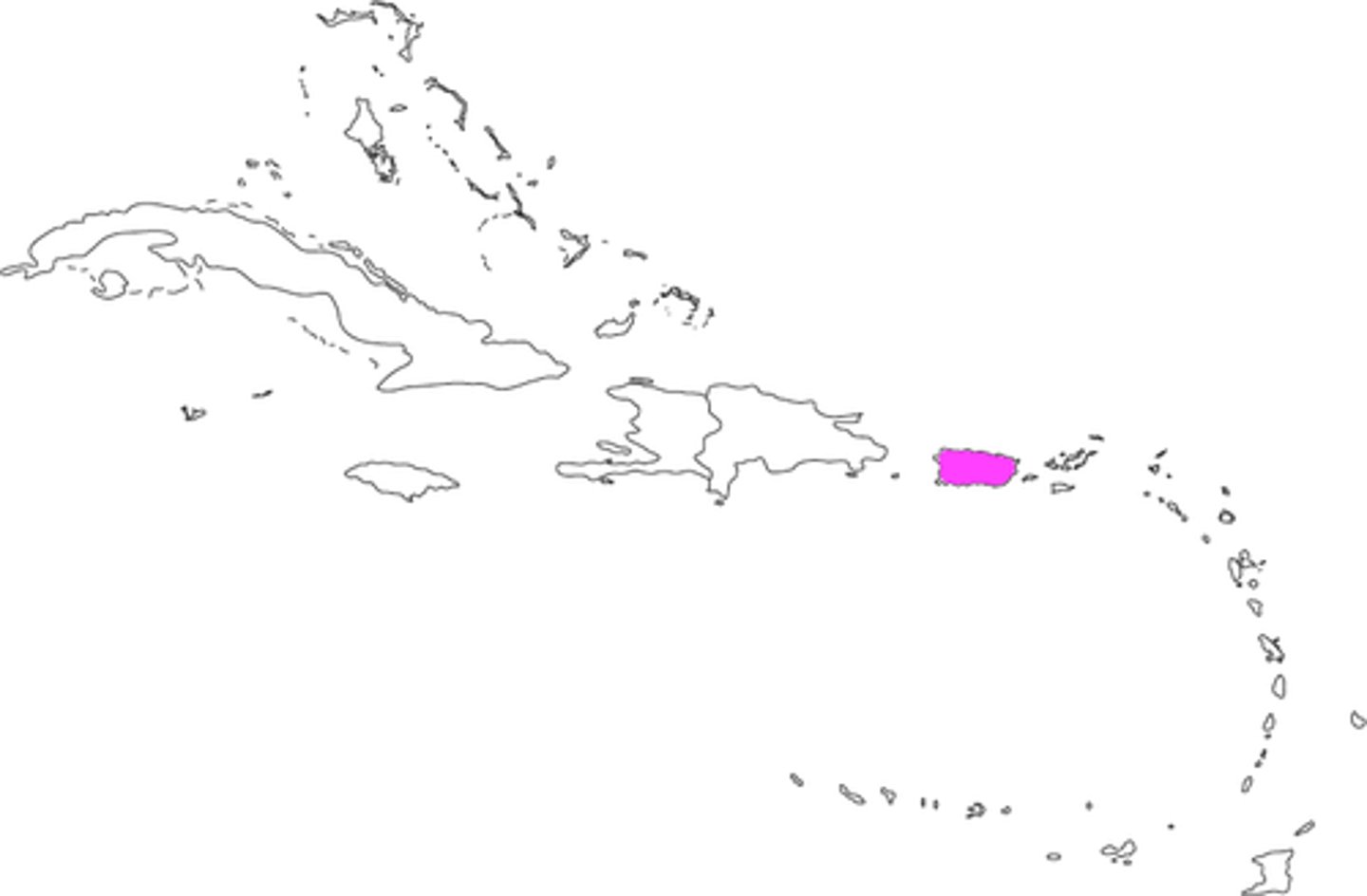
Native American reservations, Hong Kong, Puerto Rico
195
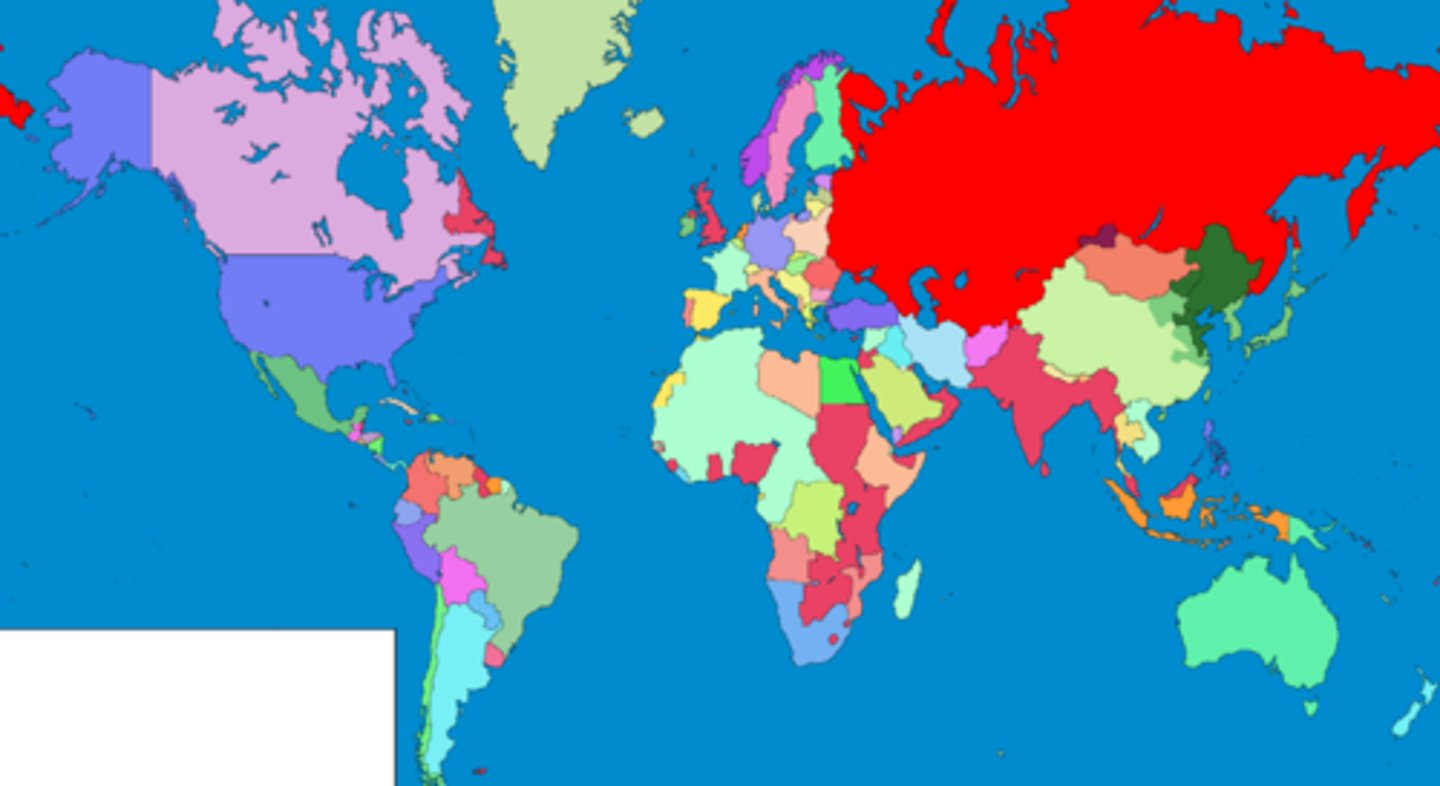
# of states (countries) recognized today (2020)
35
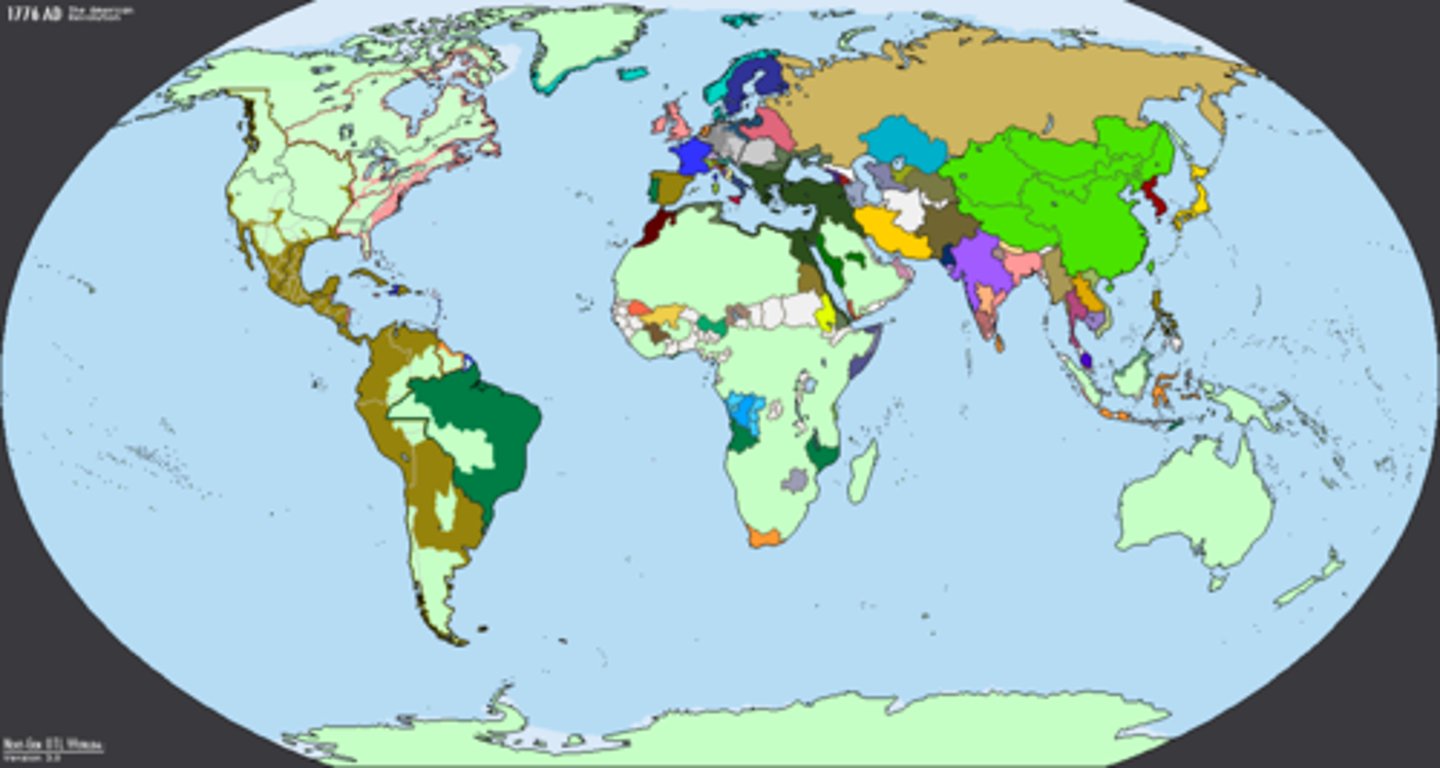
# of states (countries) recognized in 1776 when the US became a country
70
# of states (countries) recognized in 1939 when WW2 began
historical political processes
processes that happened in the past, such as colonialism and imperialism
contemporary political processes
process that are going on right now, such as devolution, independence movements, and immigration
sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states.

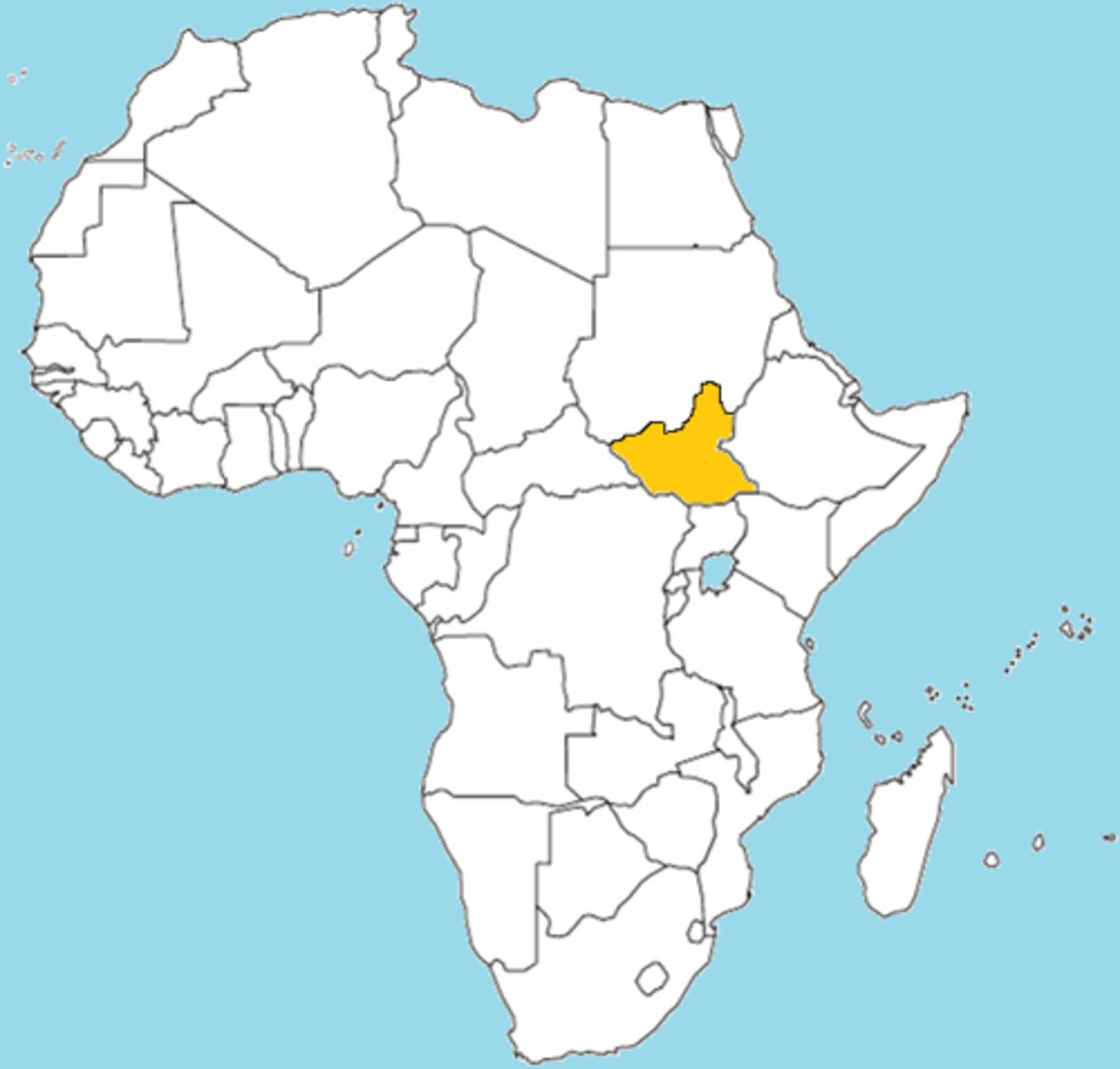
South Sudan
the most recent state to have achieved sovereignty (2011)
nation-state
a sovereign state whose citizens or subjects are relatively similar (homogeneous) in factors such as language or common descent.
"perfect" nation-state
There are actually no perfect nation-states in the world. Most states have people from various ethnicities, languages, and religions. There are varying degrees of diversity (or heterogeneity) in every state.

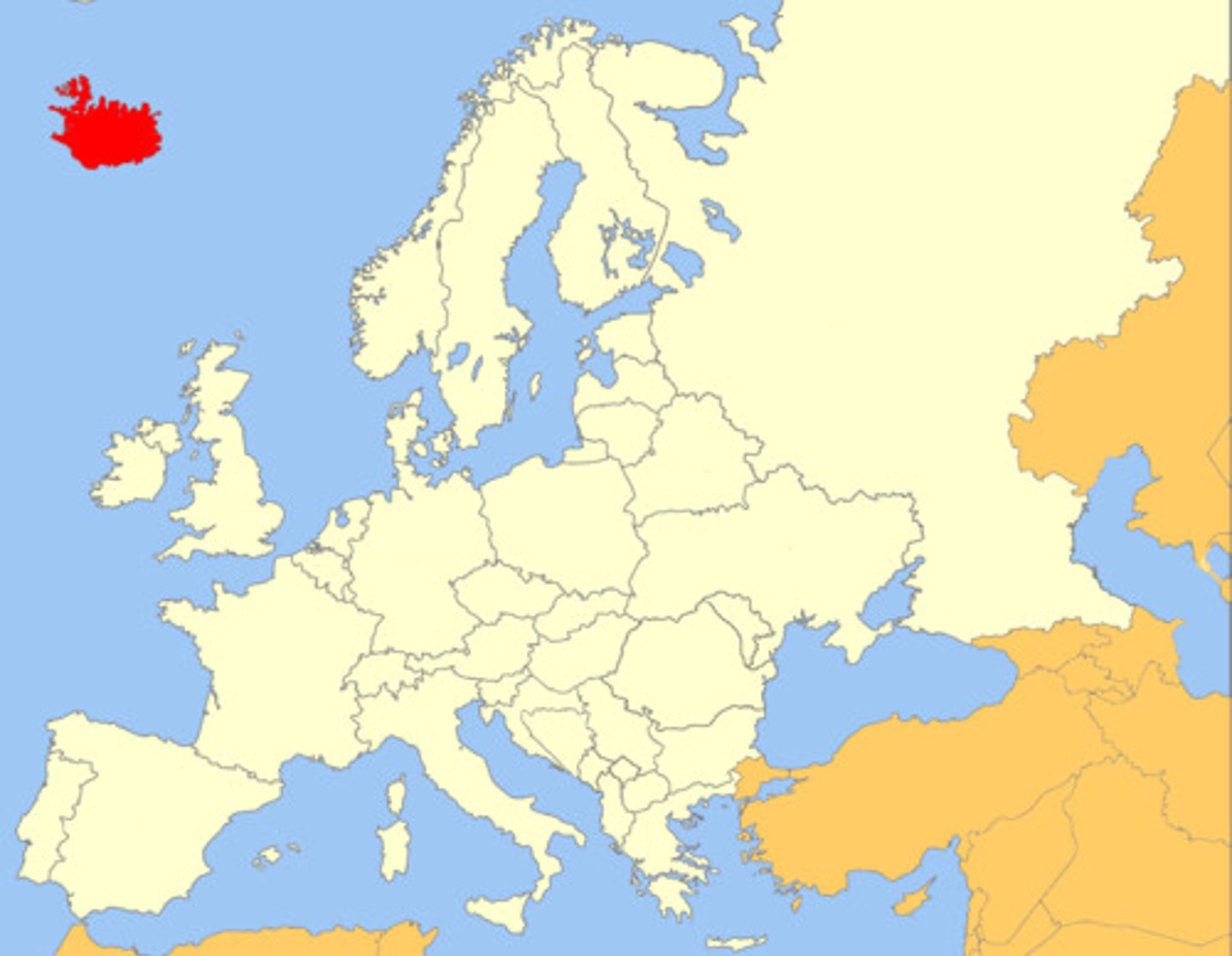
examples of nation-states
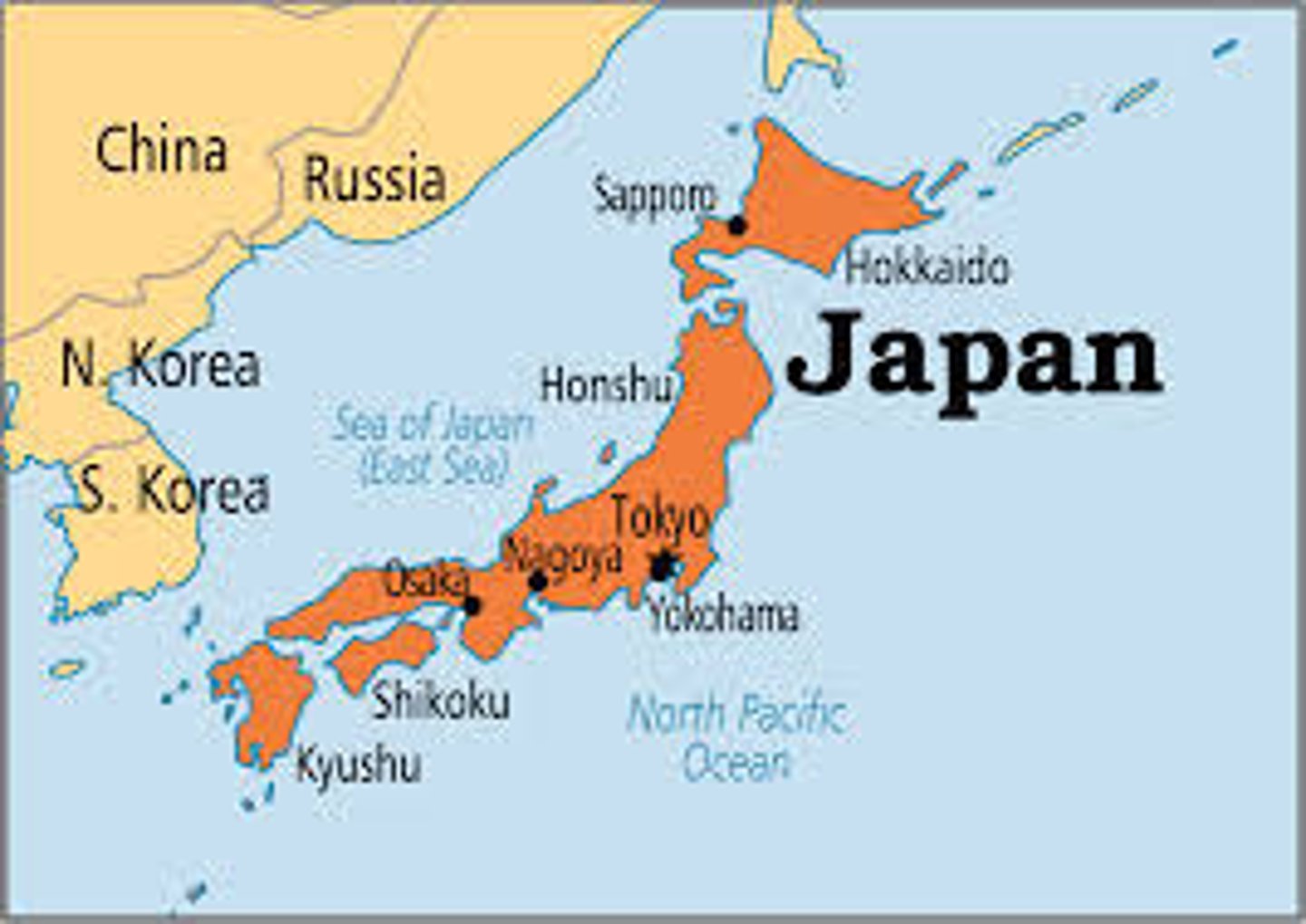
Japan and Iceland are over 95% made up of people with similar nationality
Self-determination
the idea that a nation or ethnic group has the right to govern themselves

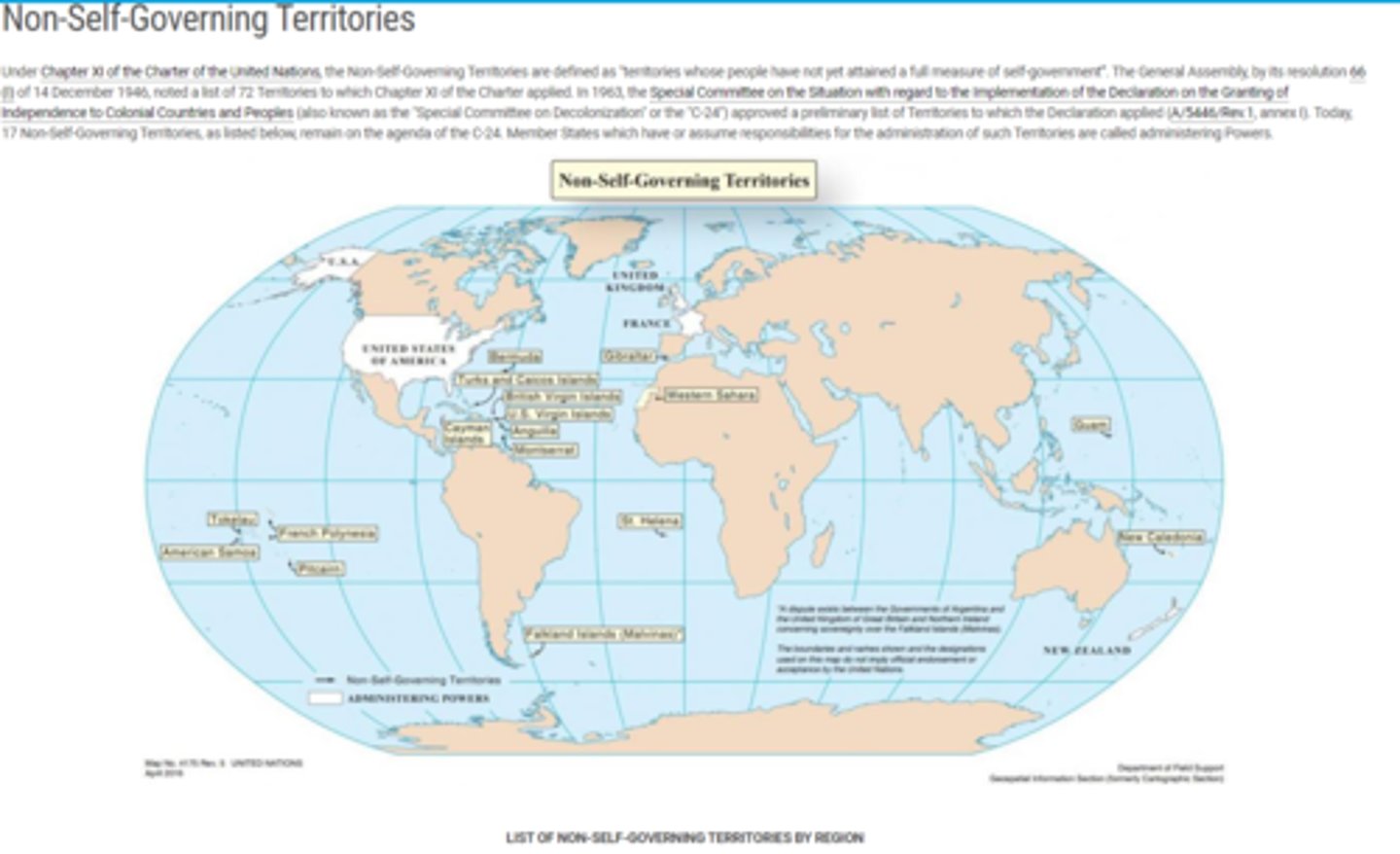
Non-Self-Governing Territories
Under Chapter XI of the Charter of the United Nations, defines these as "territories whose people have not yet attained a full measure of self-government". The UN recognizes only 17 left in the world. (Puerto Rico is not listed as one of them but the Virgin Islands are)
colony
A territory that is legally tied to a sovereign state rather than completely independent.
colonialism
Attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory.
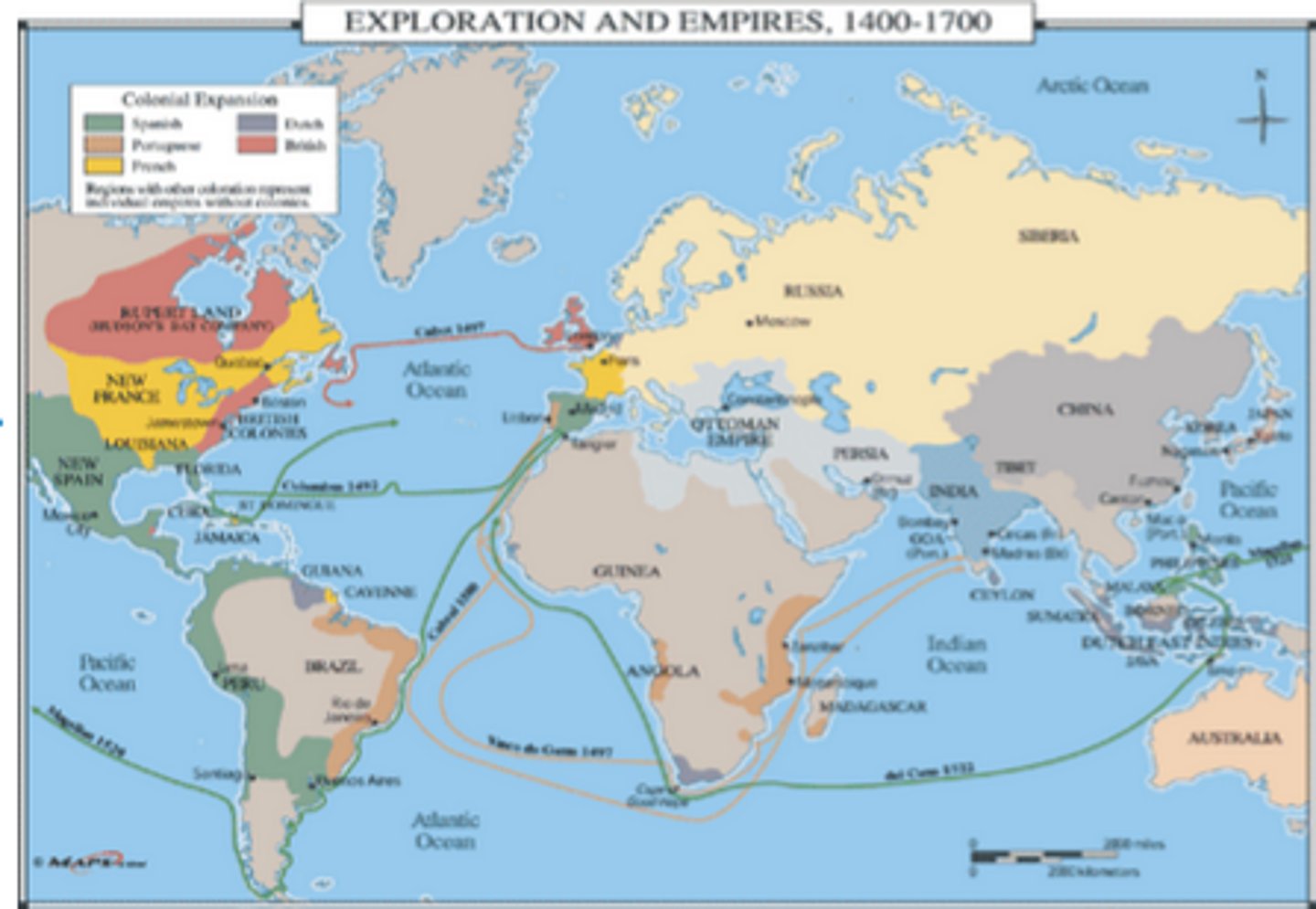
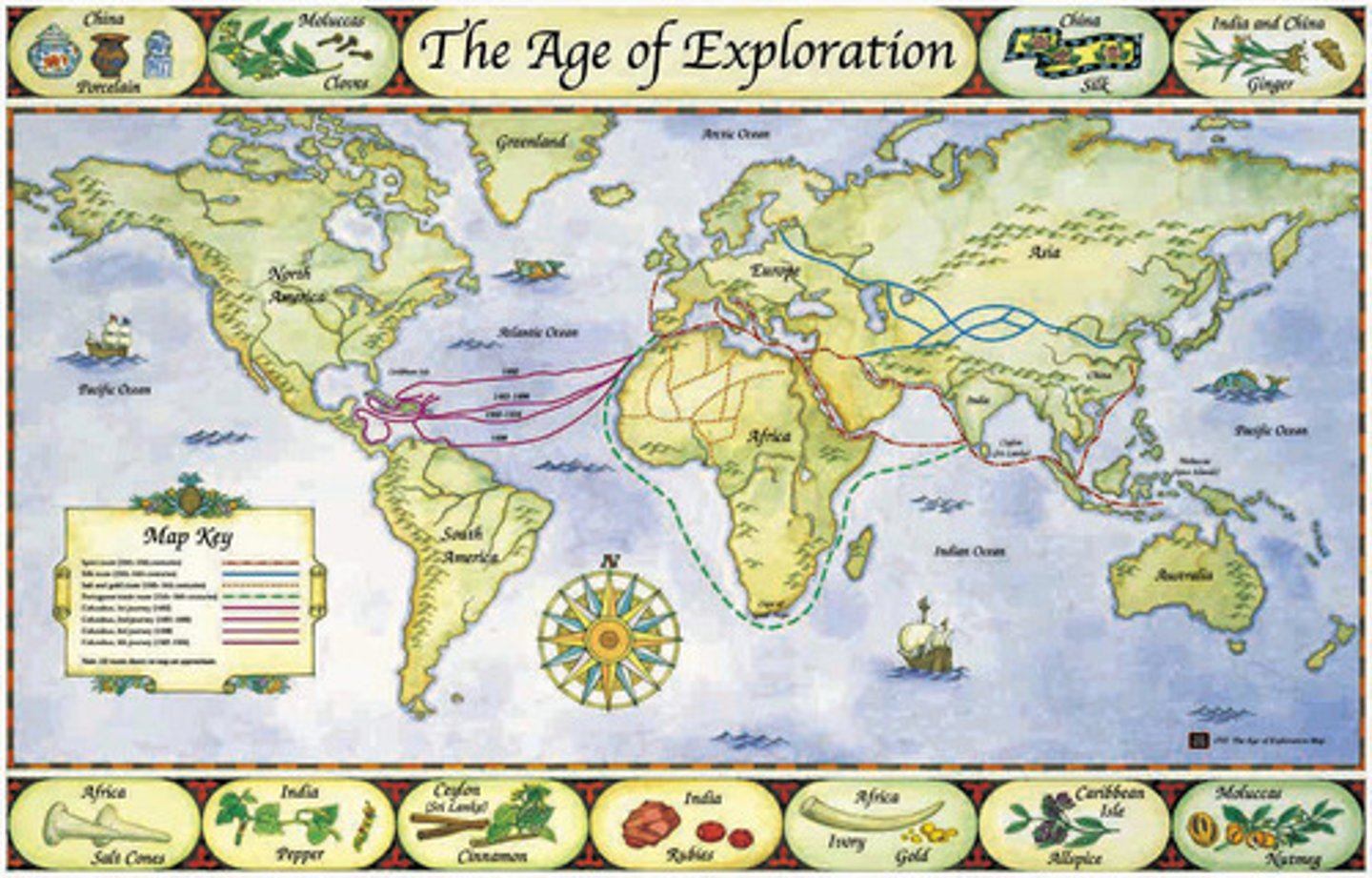
Age of Exploration
Time period during the 15th and 16th centuries when Europeans searched for new sources of wealth began colonizing in the Americas
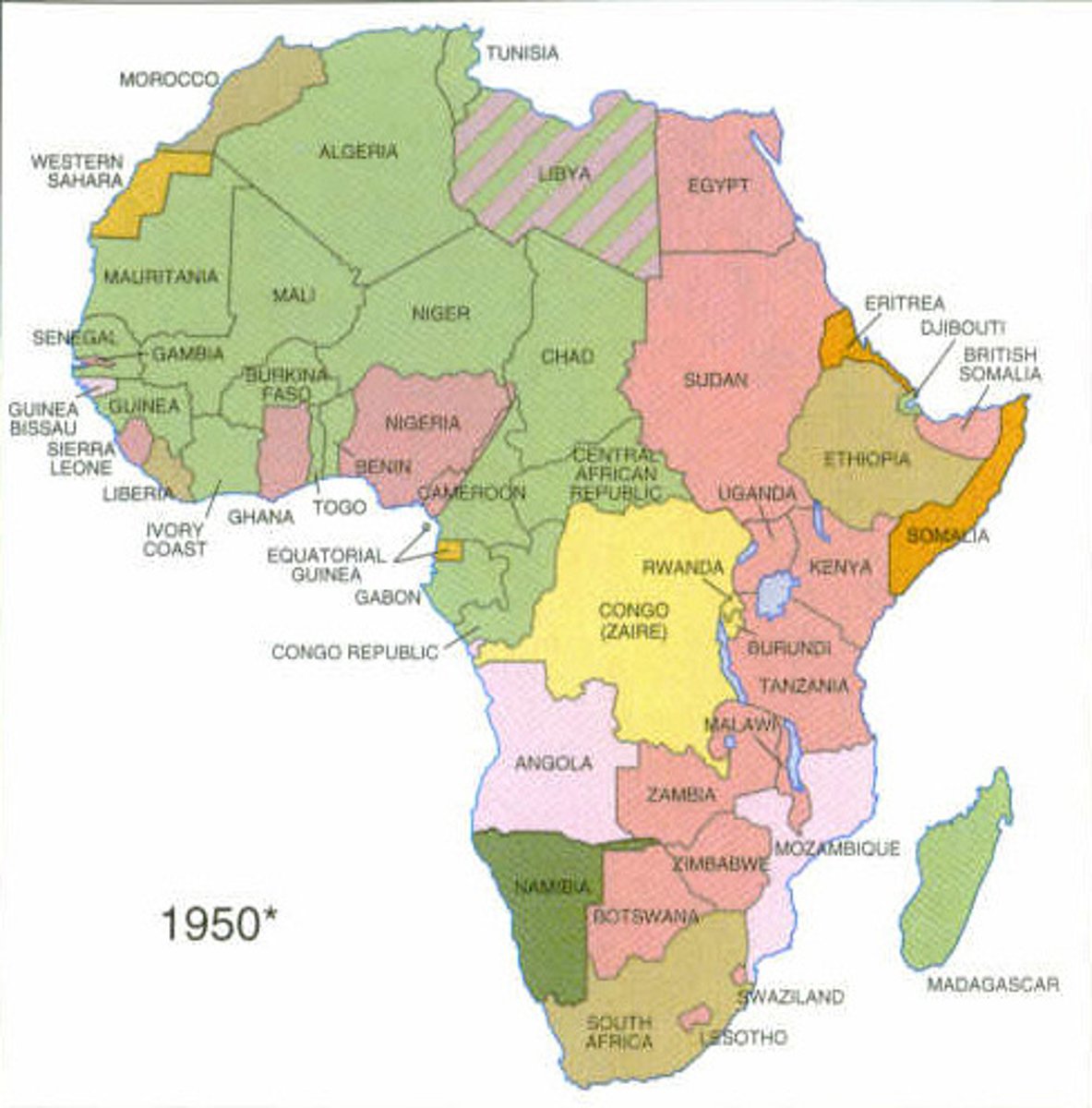
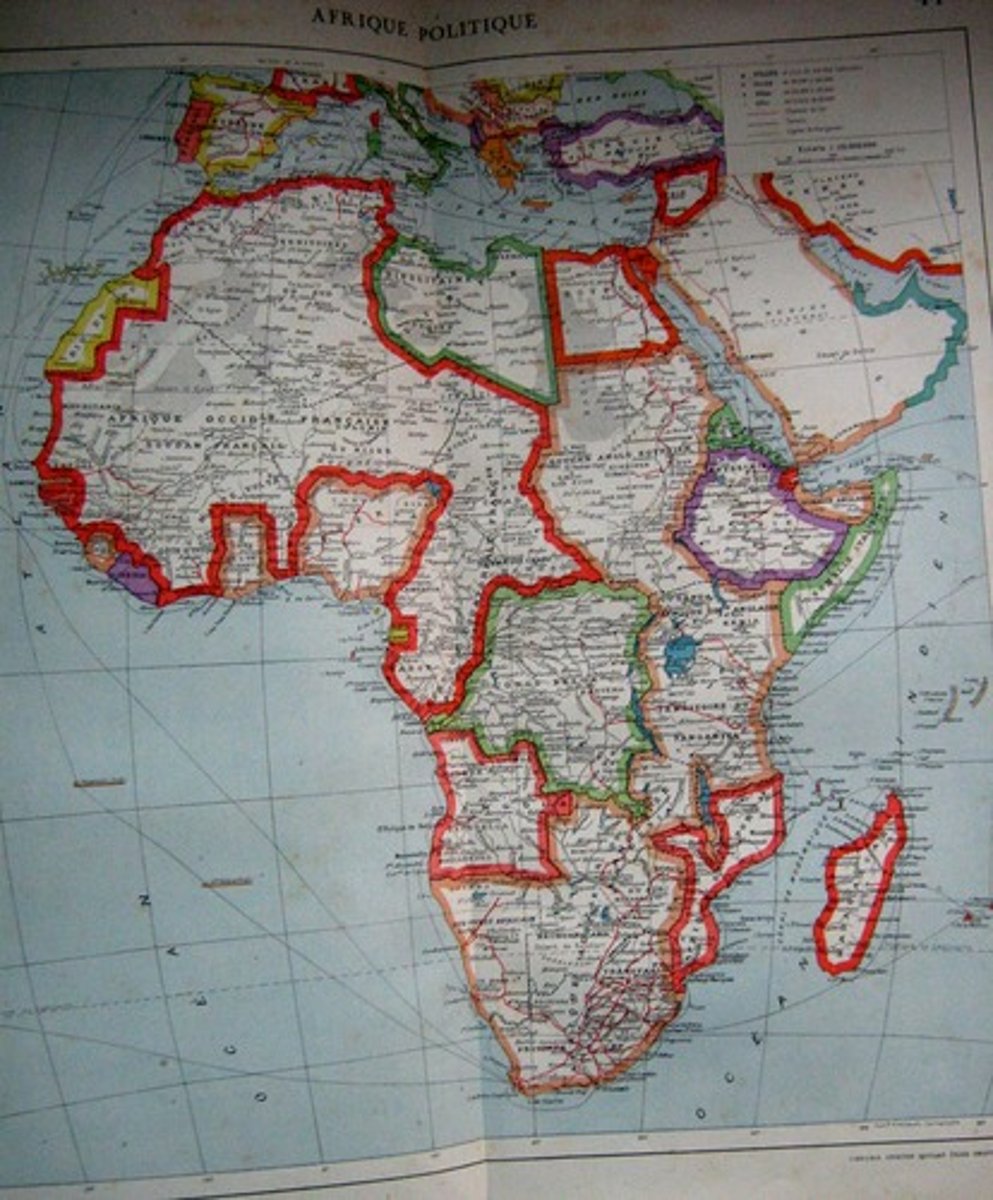
Scramble for Africa
Sudden wave of conquests in Africa by European powers in the 1880s and 1890s. Britain obtained most of eastern Africa, France most of northwestern Africa. Other countries (Germany, Belgium, Portugal, Italy, and Spain) acquired lesser amounts.
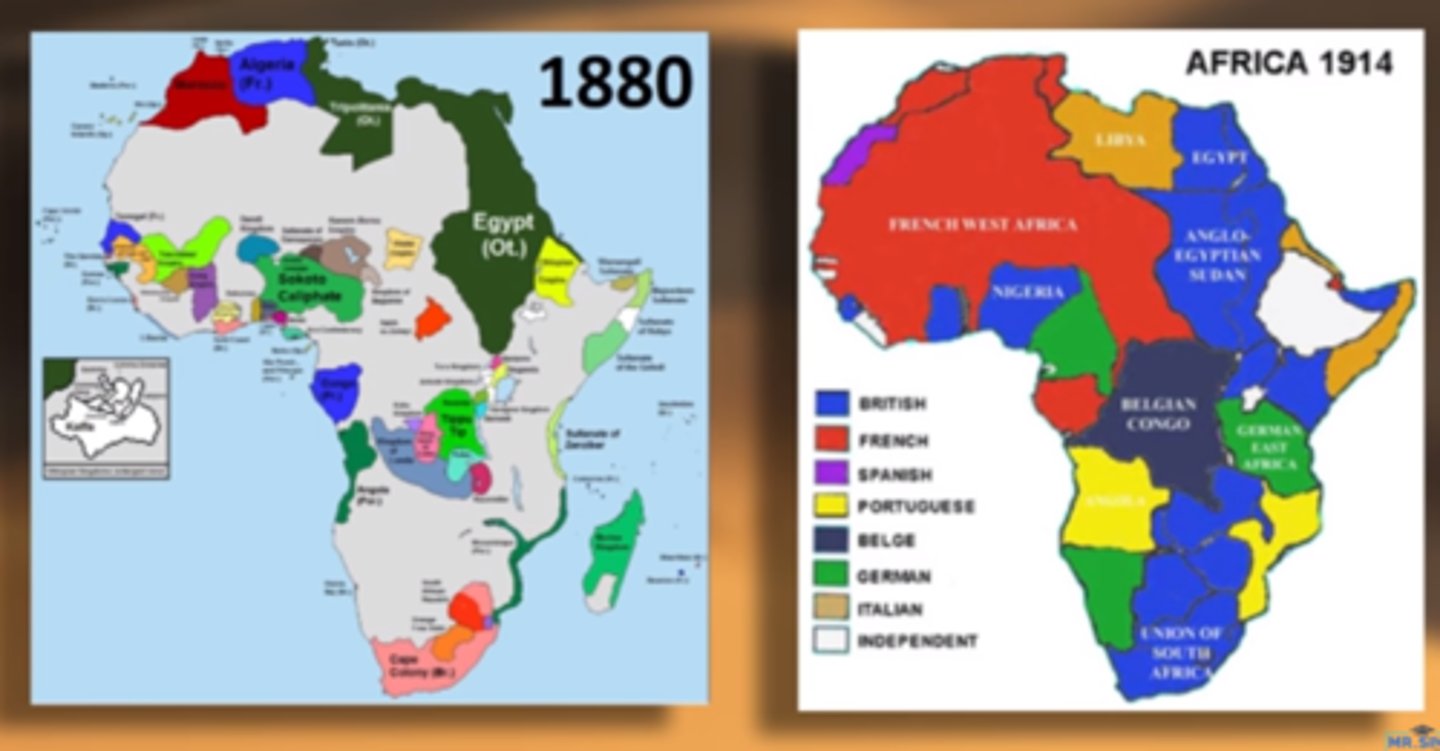
Berlin Conference
Meeting at which Europeans agreed on rules for colonizing Africa (1885)
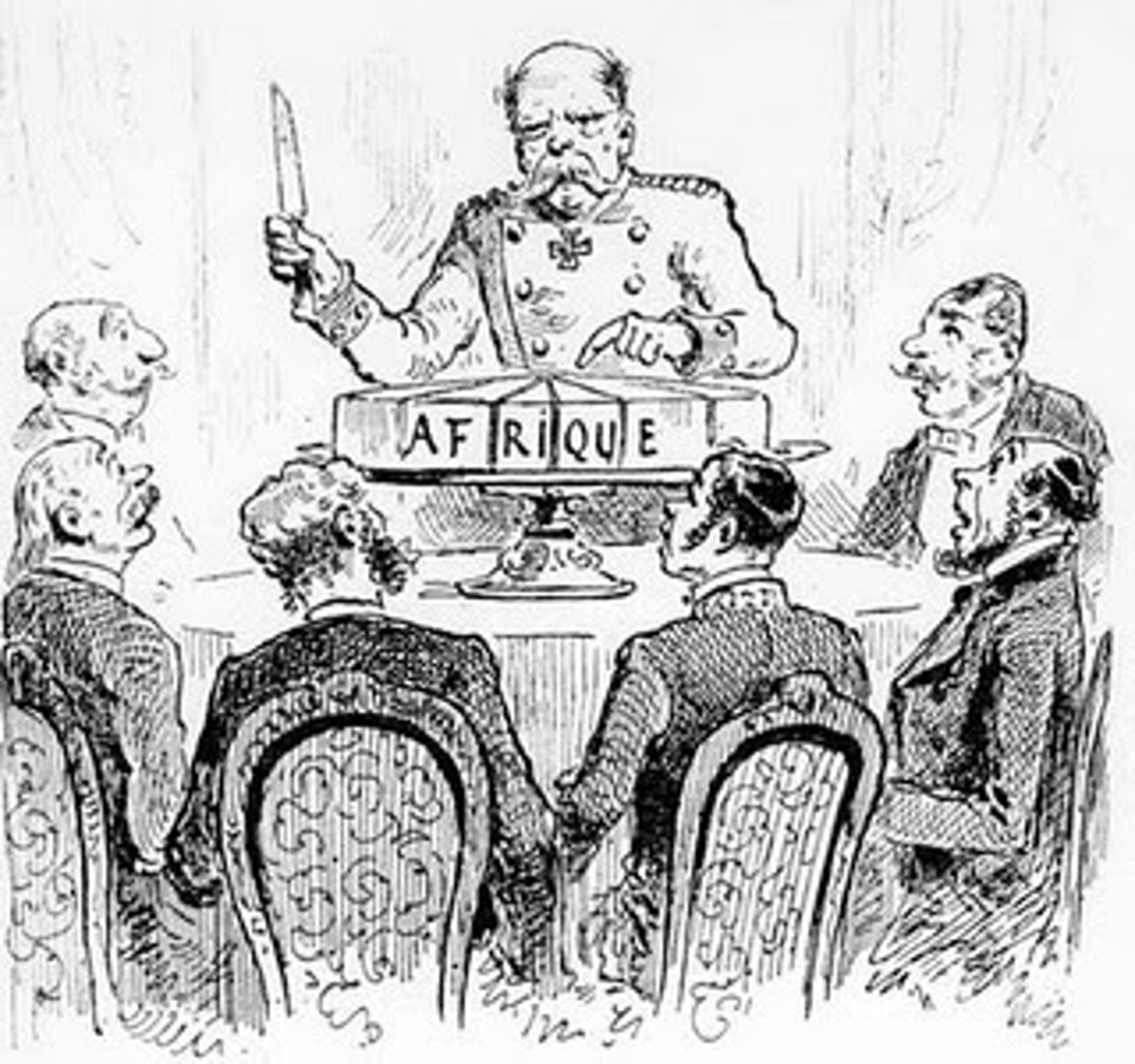

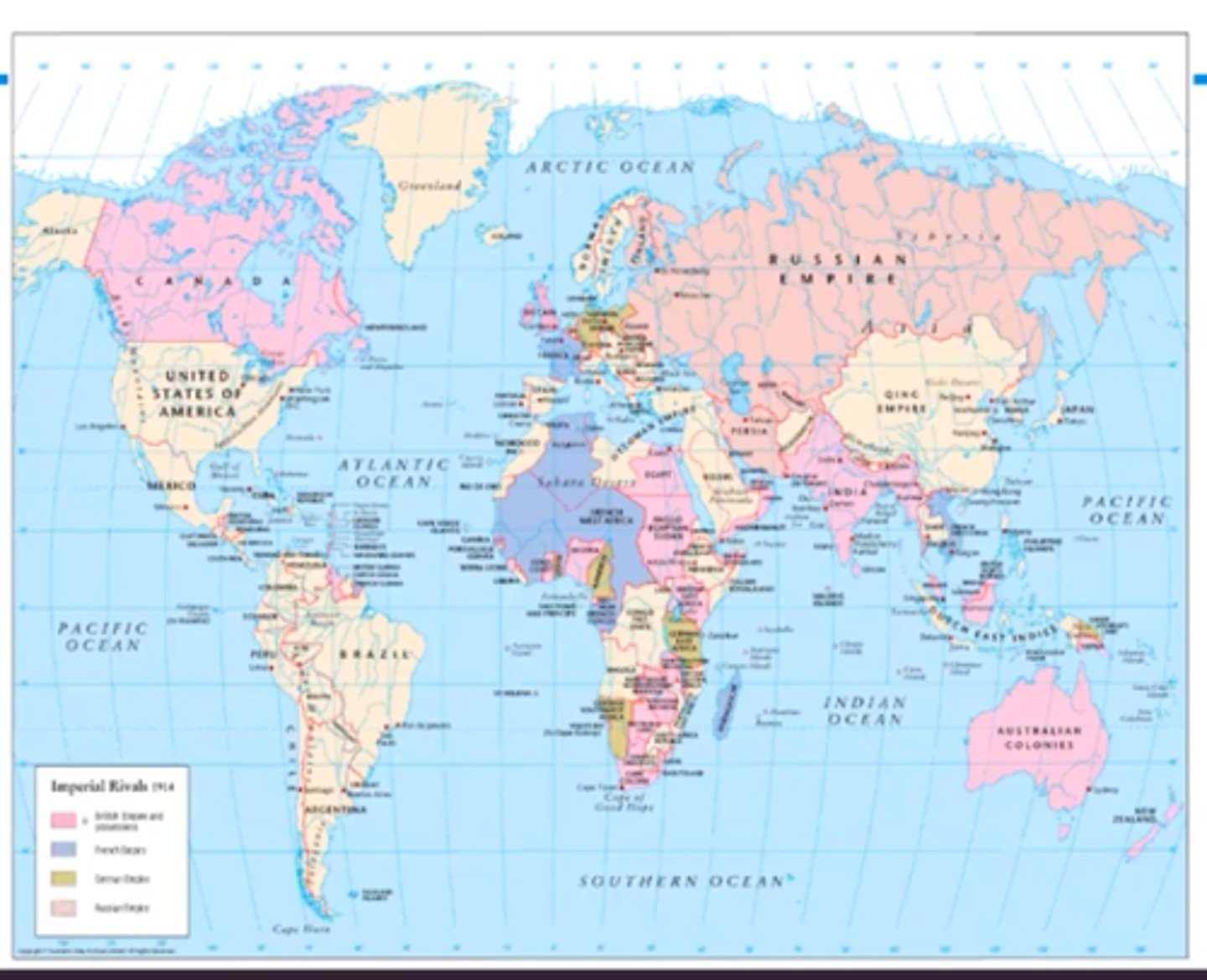
imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence over other territories through military force or political power

commodity dependence
An economy that relies on the export of primary commodities for a large share of its export earnings and hence economic growth. Imperialist countries extracted wealth from the natural resources of their colonies, leading to commodity dependence even after they became independent

Age of Imperialism
A time period lasting from 1850-1914, where colonial powers (Great Britain, France, United States) were able to seize control over many territories, mainly in Africa and Asia.
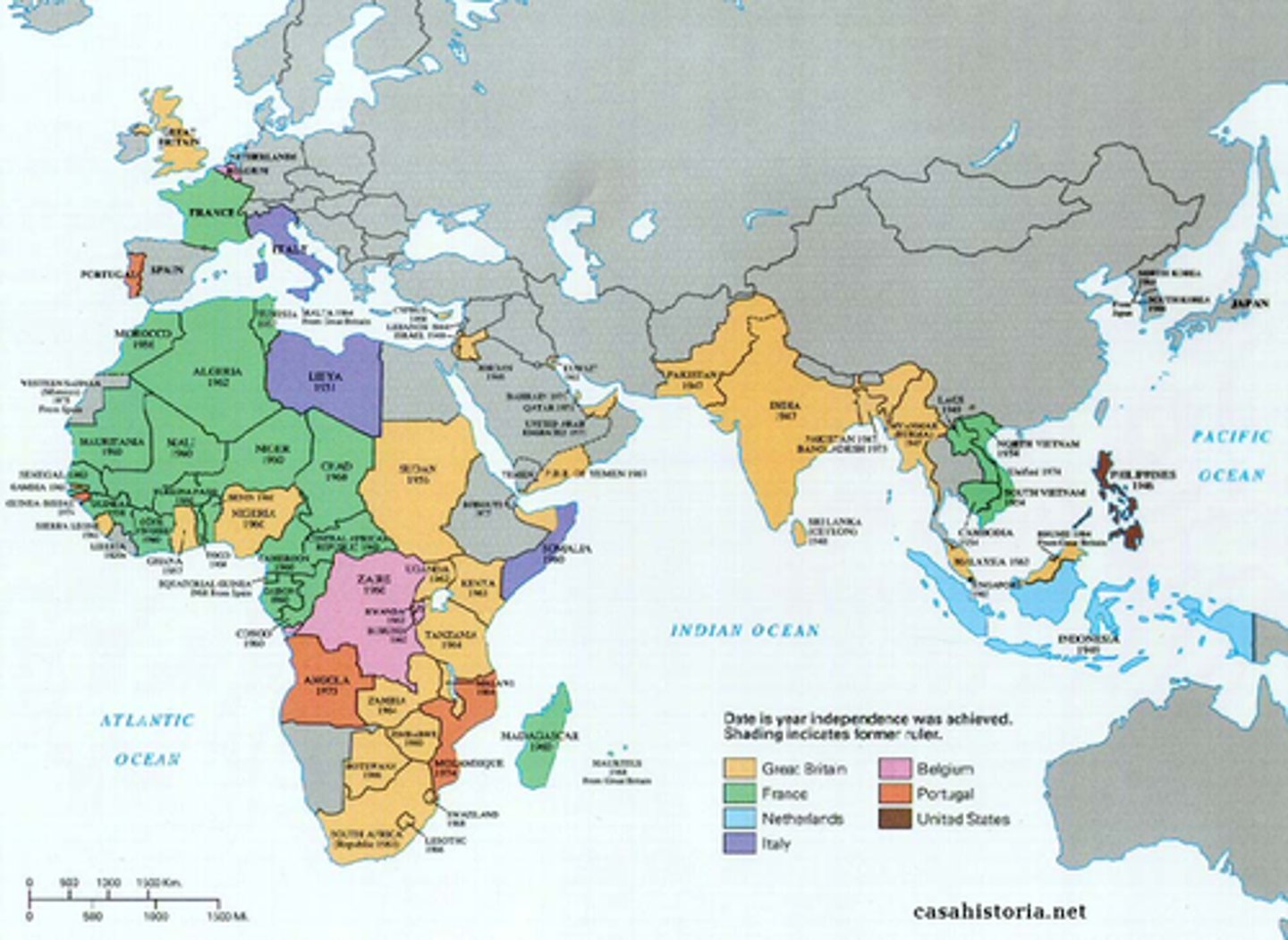
decolonization
the action of changing from colonial to independent status. Decolonization happened on a world-wide scale after World War 2 (1945-1970)
independence movement
a movement that is trying to gain political independence for some area that it thinks should be its own country

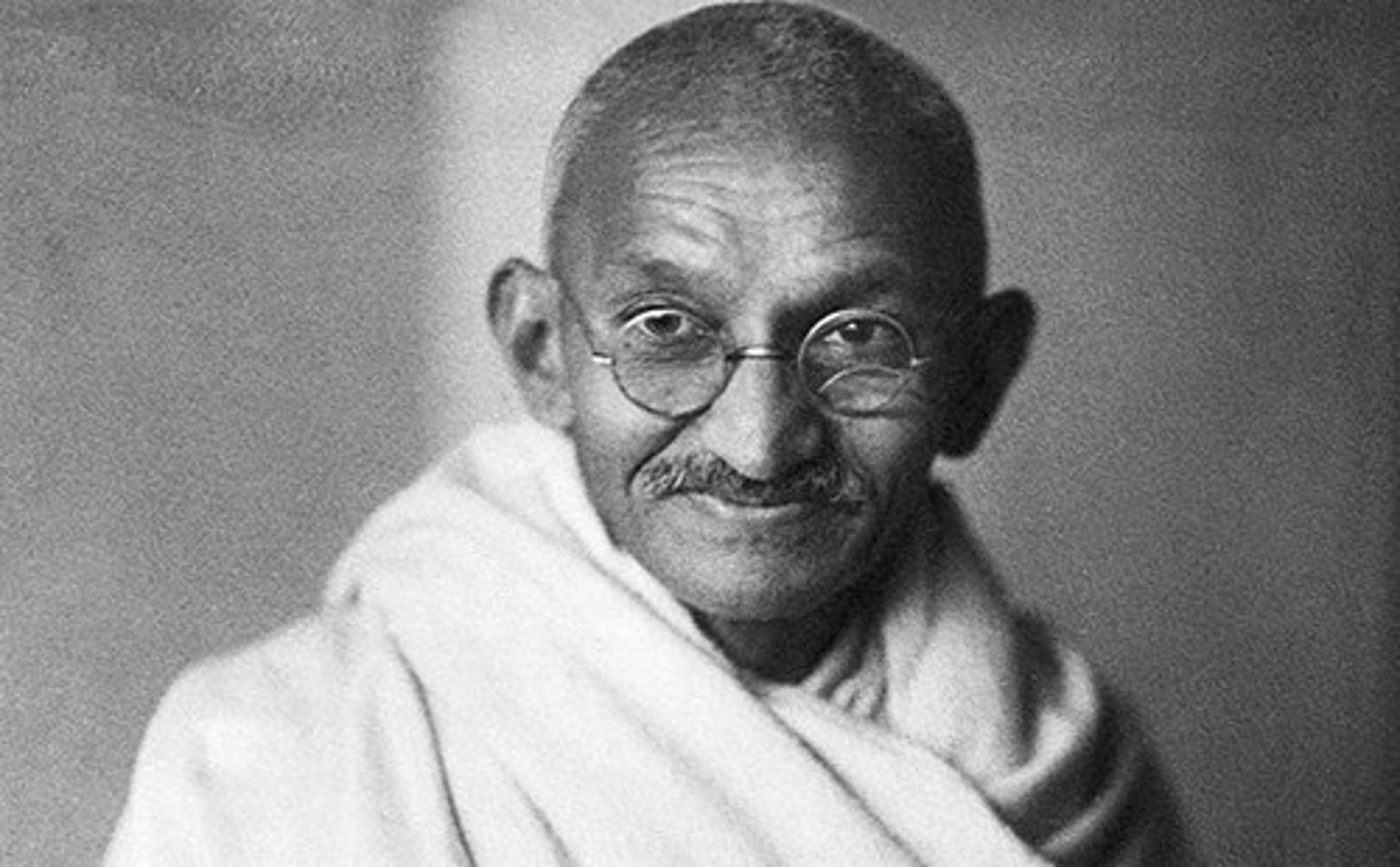
Gandhi
This was a leader of the Indian independence movement in mid-20th century known for his nonviolent protests.

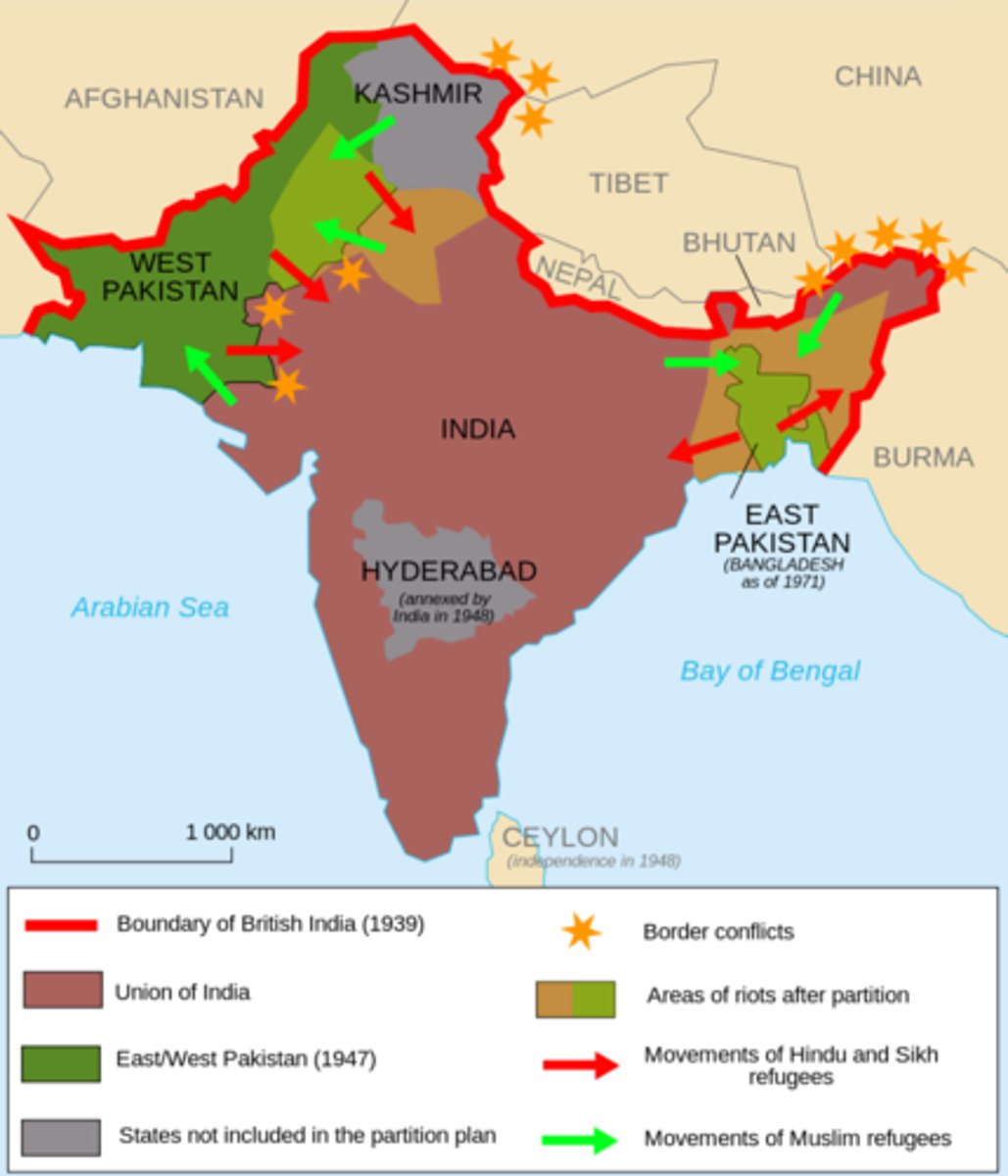
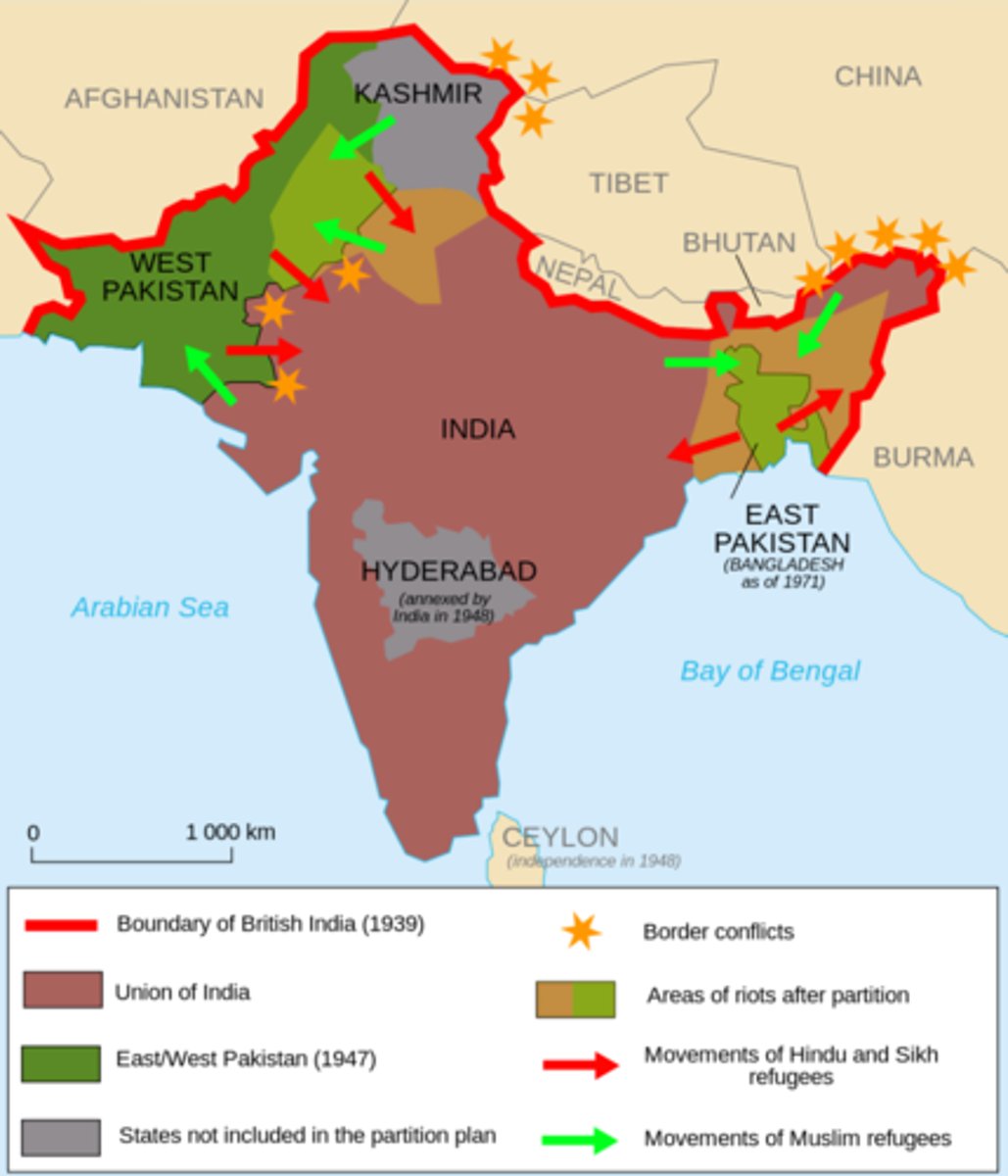
"the Partition"
India was separated into 2 countries Pakistan for Muslims and India for Hindus (1947)
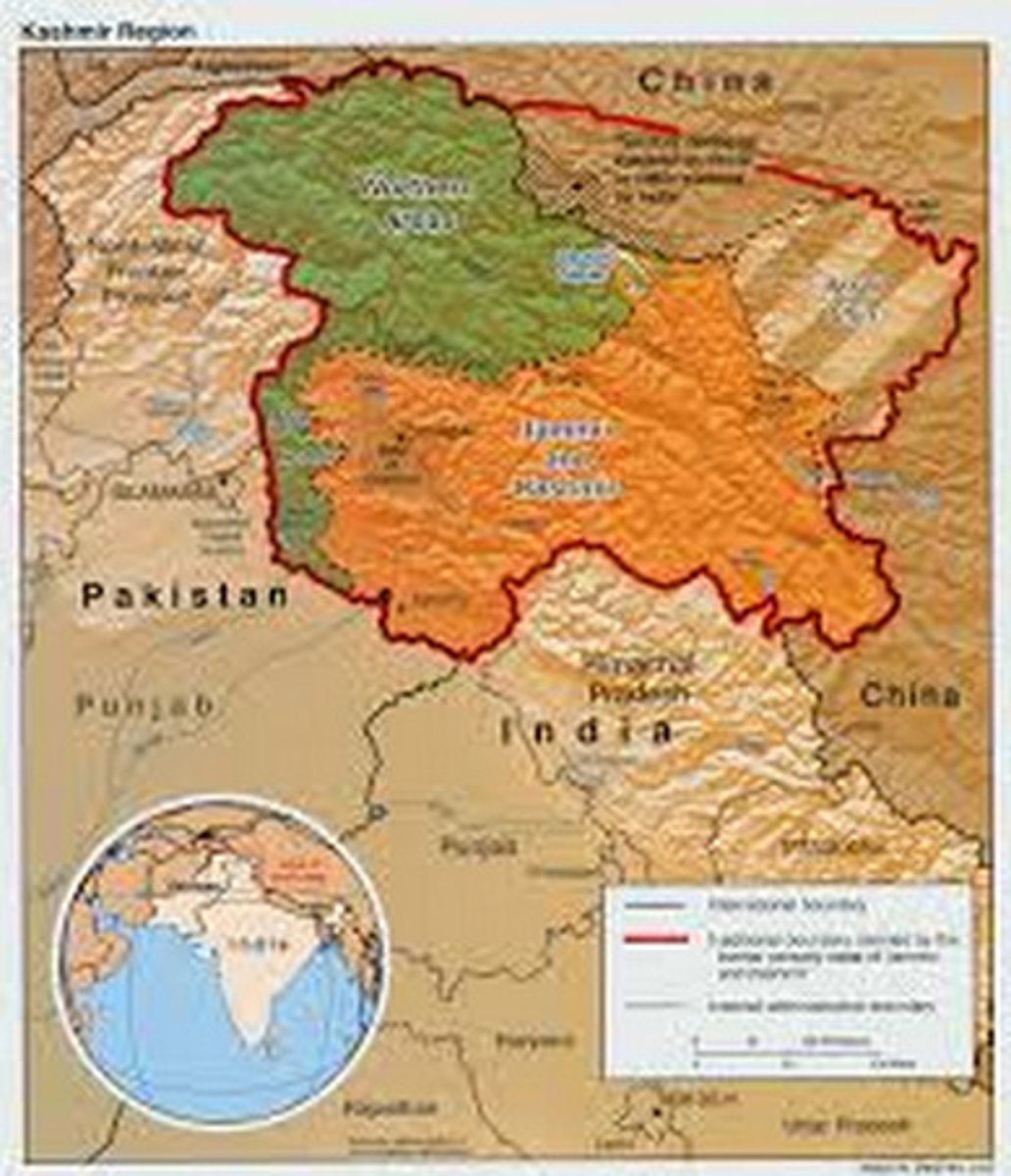
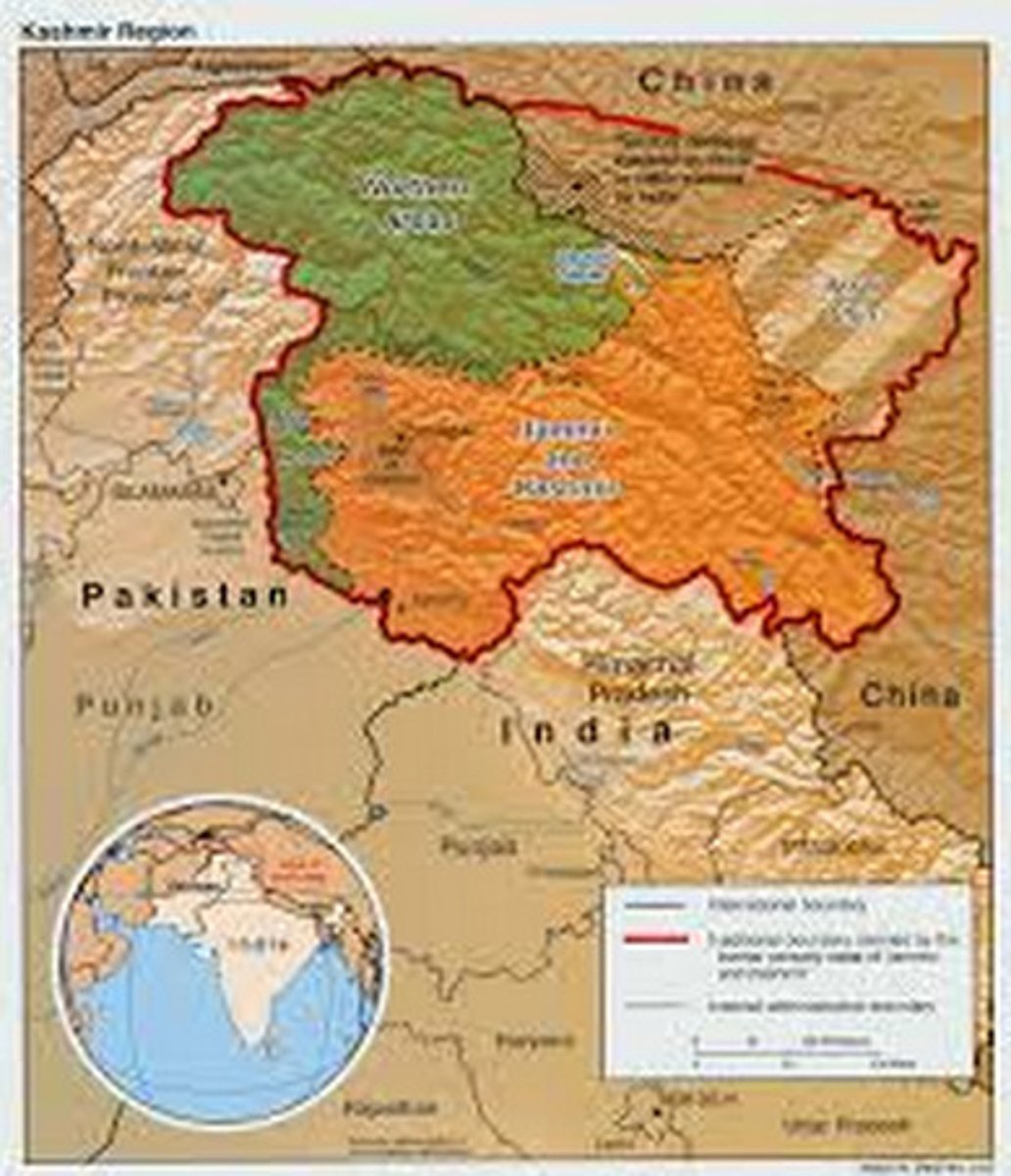
Kashmir
an area in southwestern Asia whose sovereignty is disputed between Pakistan and India
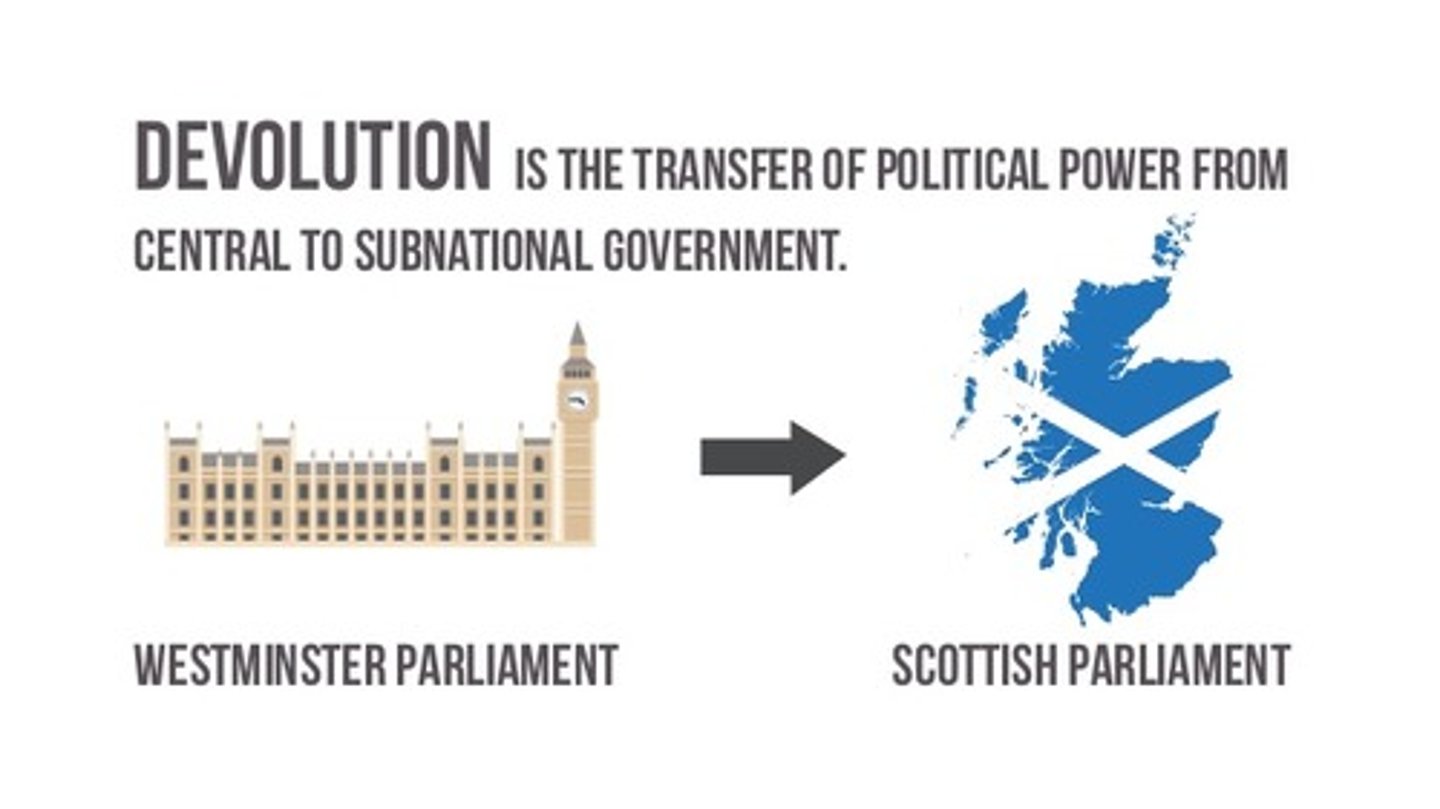
devolution
1) the shifting of power from the central government to regional/local governments within the state OR (sometimes defined as) 2) the breaking up of a country into smaller countries
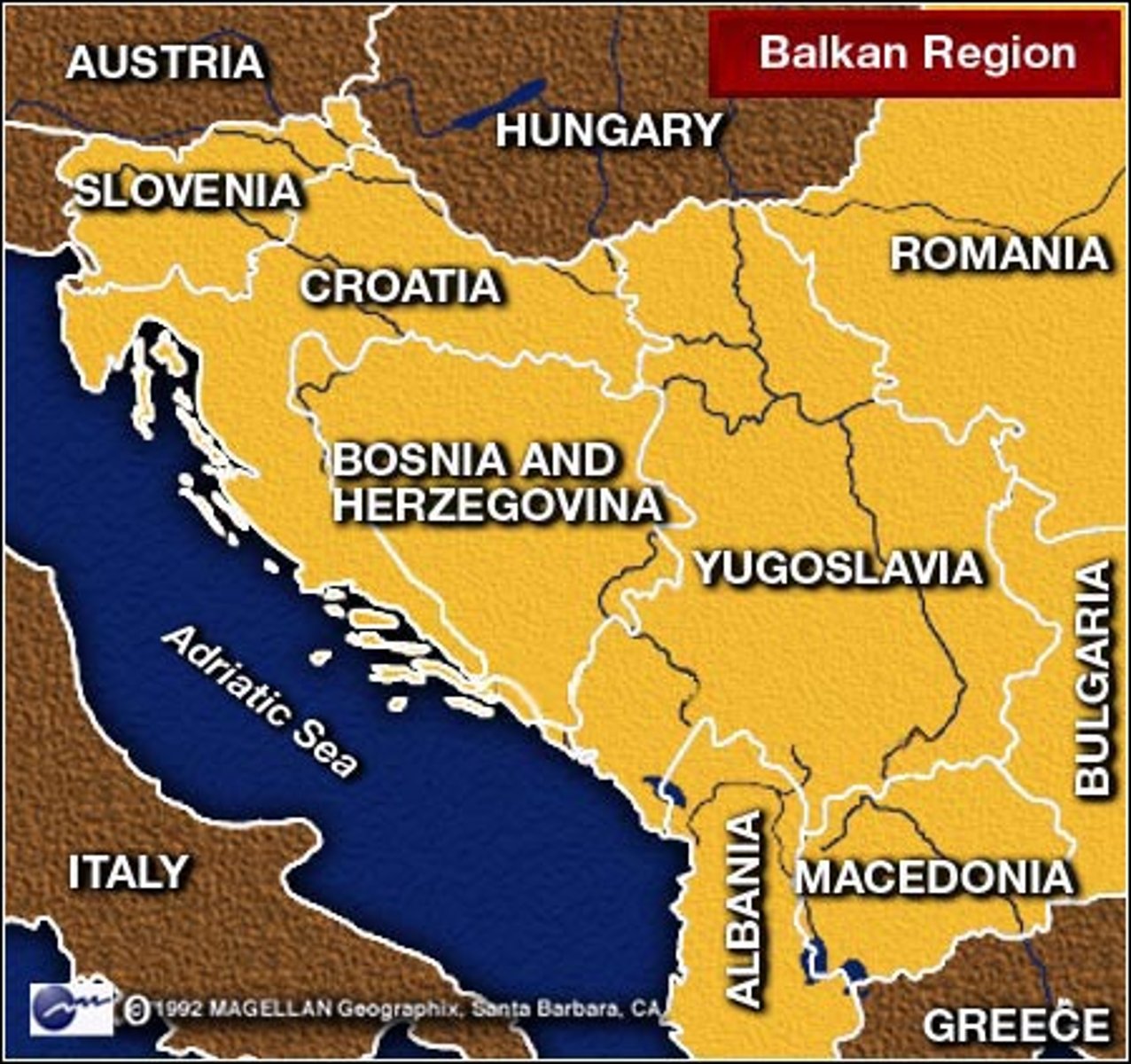
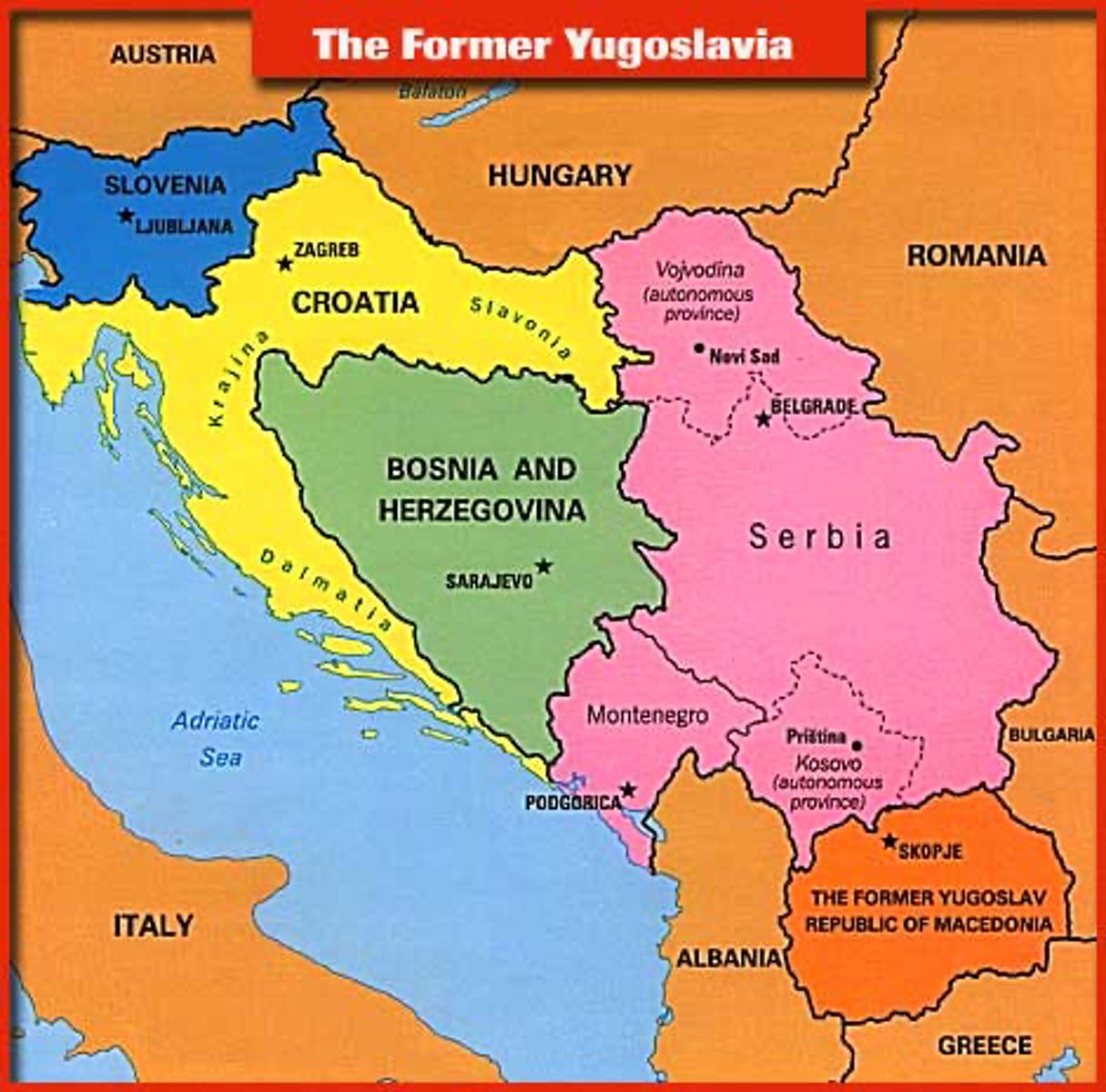
Balkan Peninsula
A large peninsula in southern Europe bounded by the Black, Aegean, and Adriatic seas. It is a politically tense part of the world. For example, an assassination of an Austrian prince in Bosnia by a Serbian started World War 1.
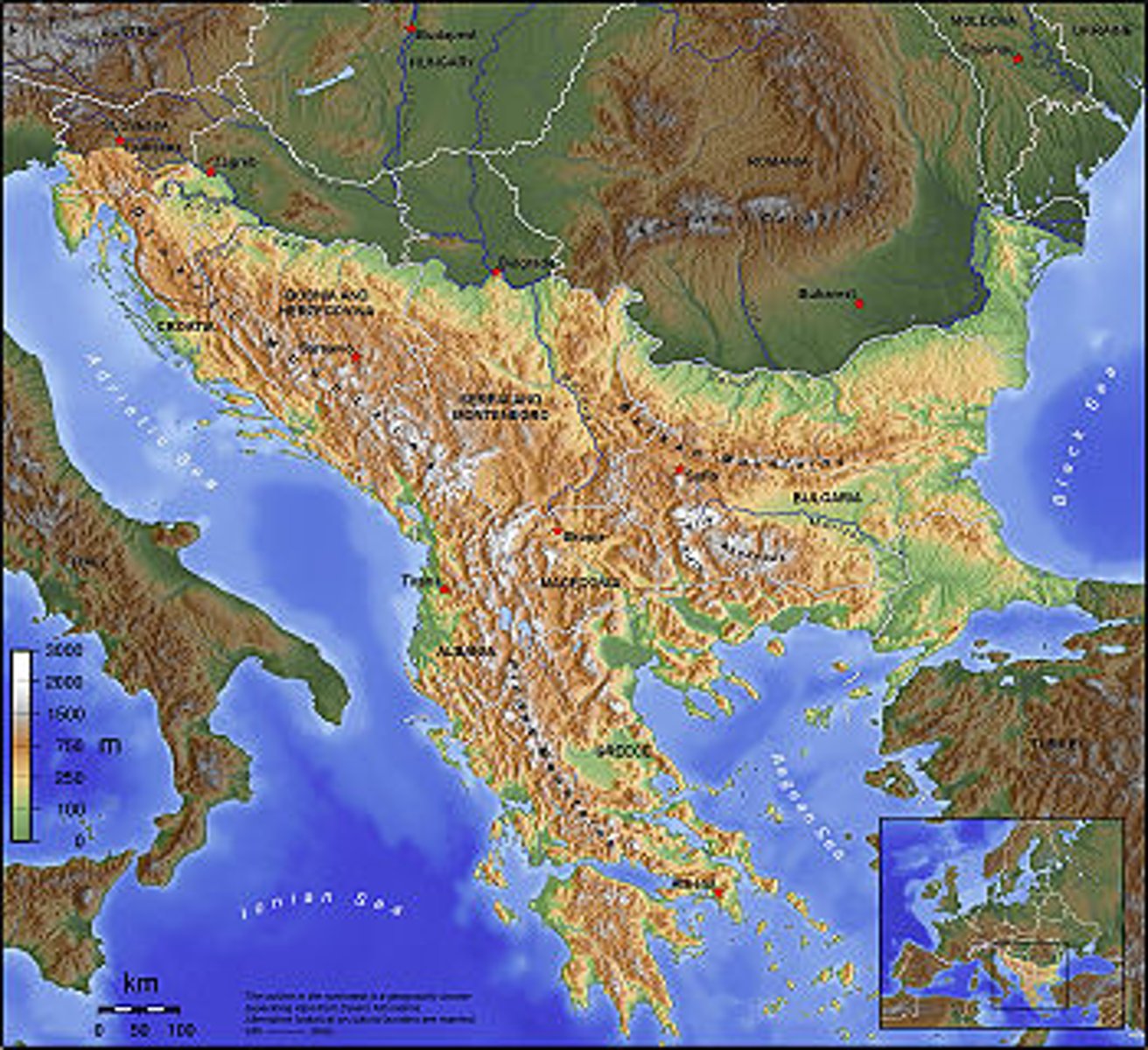
origin of the term Balkanization
The Balkan nations were united as "Yugoslavia" during the Cold War. When communism collapsed after 1990 the country broke up into multiple new states, with lots of conflict.
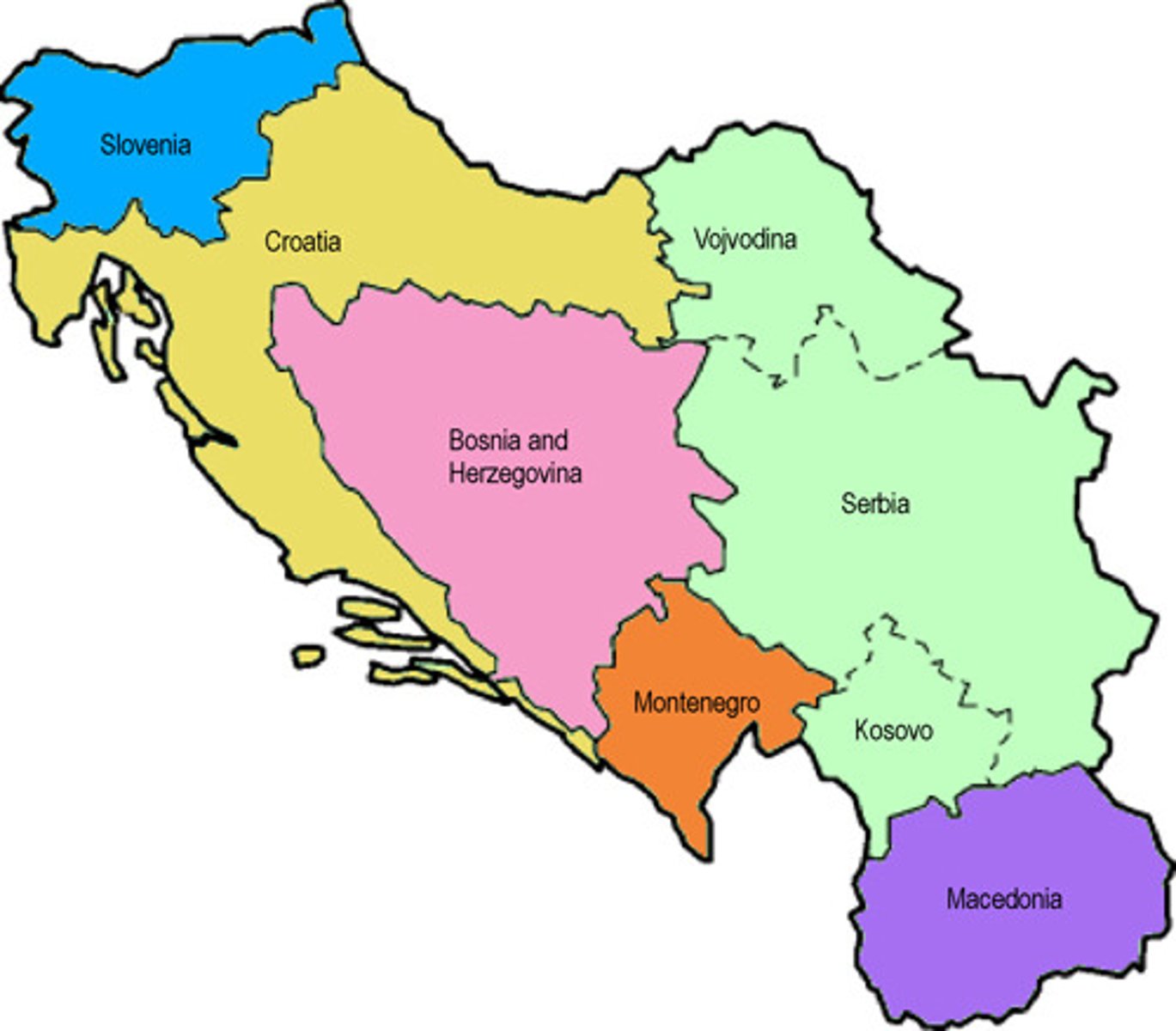
Balkanization
The contentious political process by which a state may break up into smaller countries.
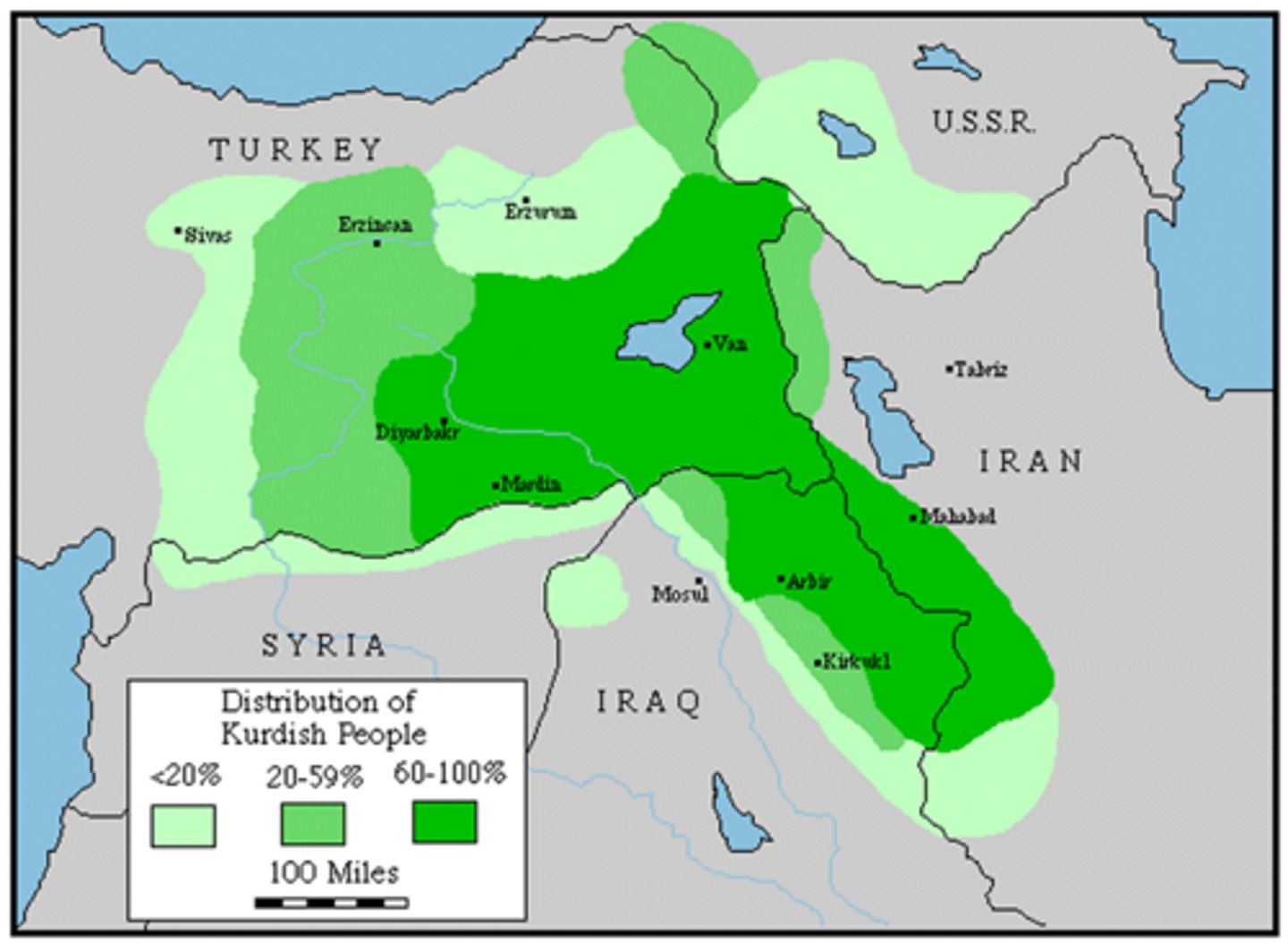
Kurds
Ethnic group that lives in parts of Iraq and Turkey. They often suffer persecution in both countries, and are currently under the protection of the United Nations in Iraq.
territoriality
how people use space to communicate ownership or occupancy of areas of land

Neo-colonialism
the practice of using economic or political influence by a richer country (MDC) to control a poorer country (LDC) indirectly (in place of direct military control (imperialism) or indirect political control (hegemony)).
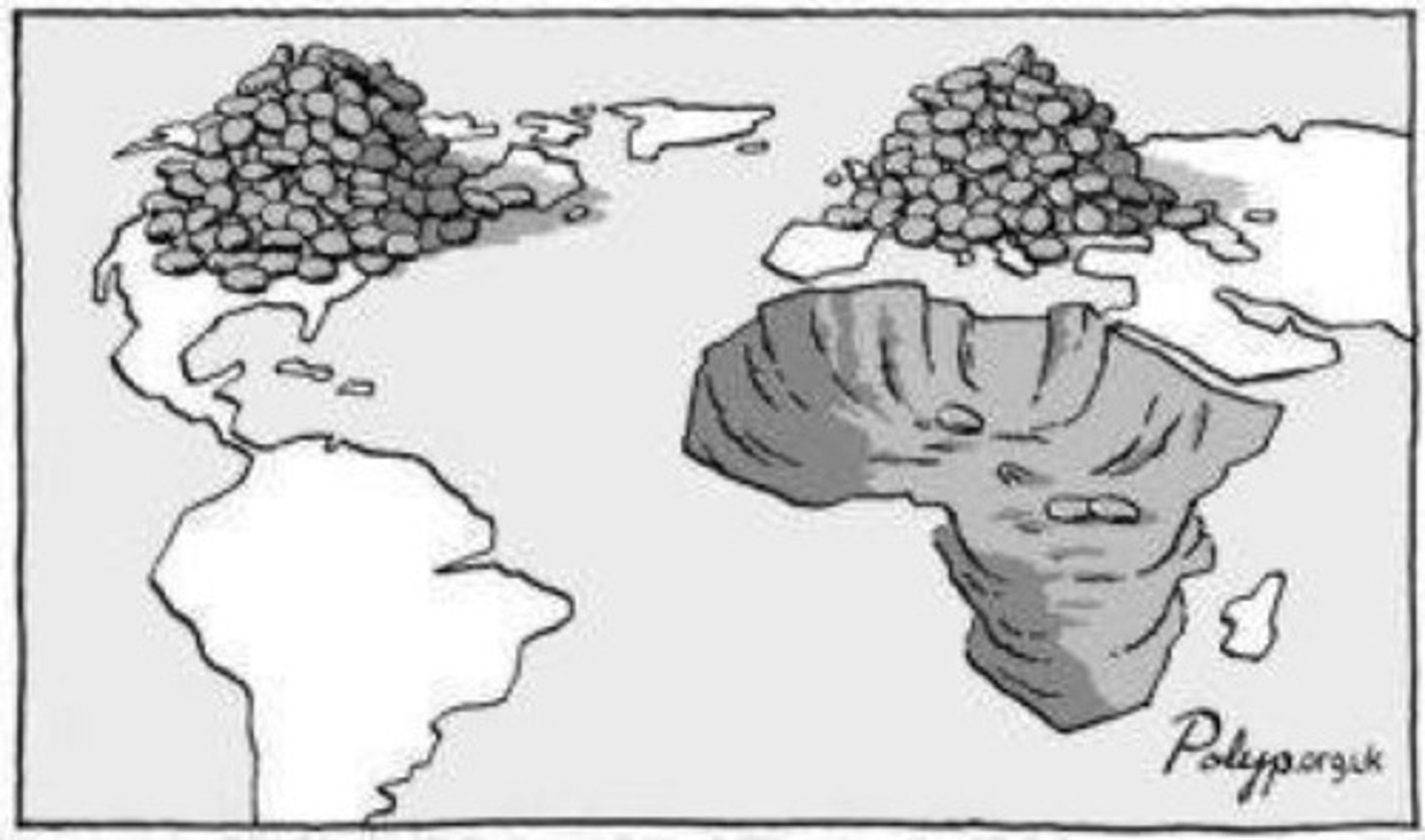
MDCs
More developed countries- countries such as the United States, Germany, and Australia who have the highest levels of economic development

LDCs
Lesser Developed Countries-- Countries that are seeking improved conditions for their residents through economic growth

example of neo-colonialism
Chinese investment in Africa. They give foreign aid in exchange for political power in the continent.

Neo-colonialism
control by a powerful country of its former colonies (or other less developed countries) by economic pressures
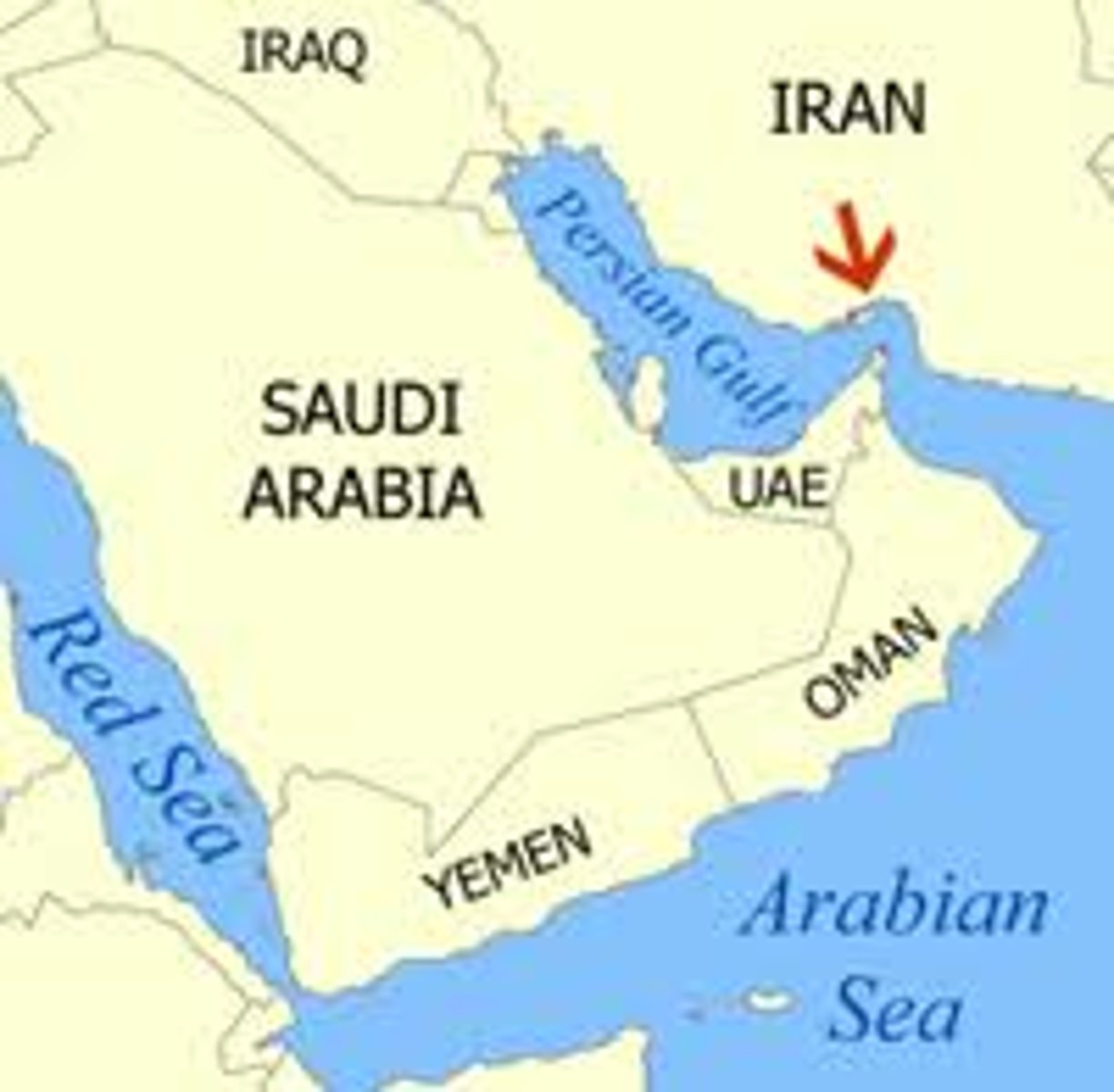
choke point
a strategic, narrow waterway between two larger bodies of water
Shatterbelt Regions
regions caught up in a conflict between two opposing powers or cultures
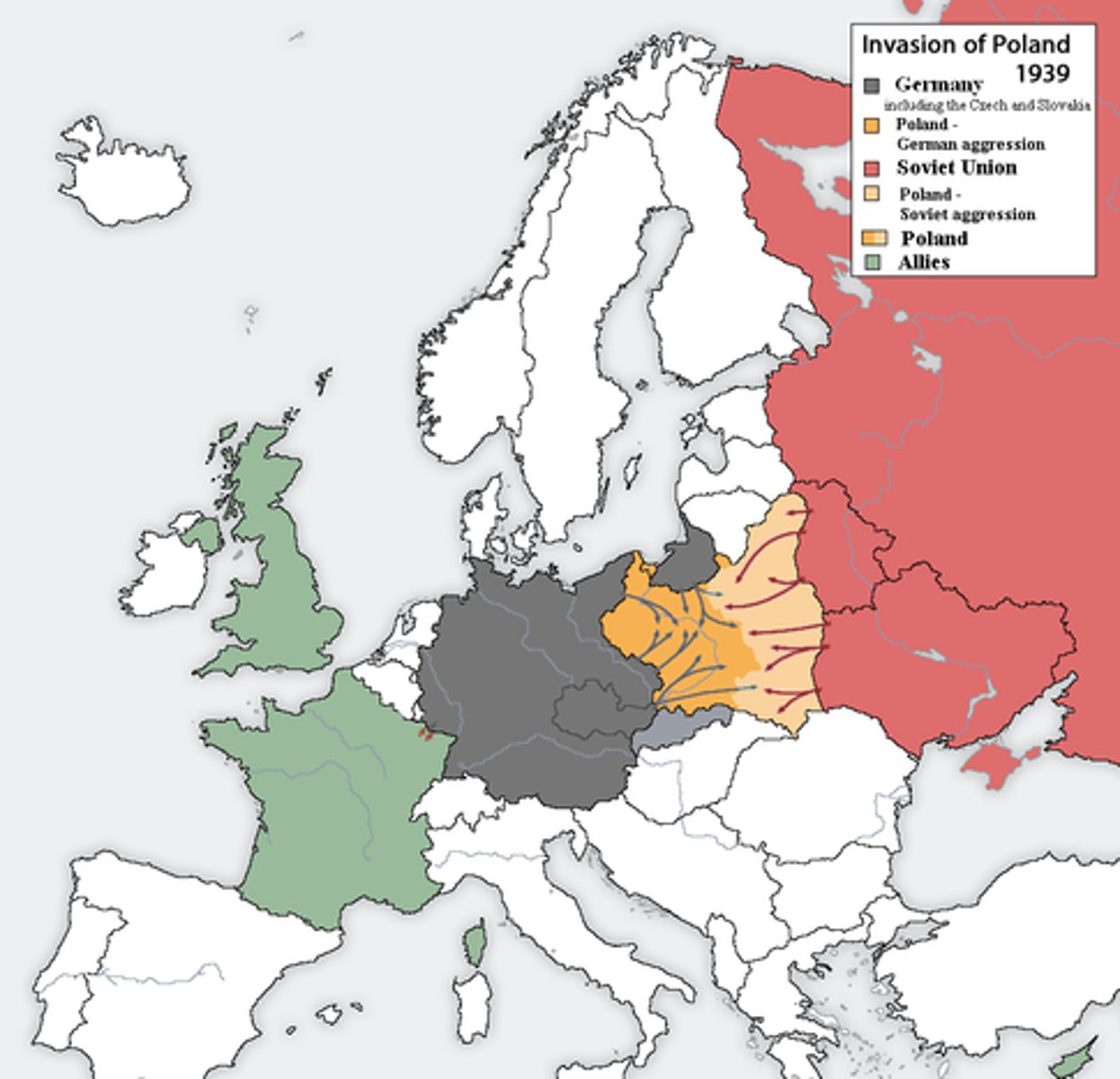
Cultural shatterbelt
A politically unstable region where differing cultural elements come into contact and conflict
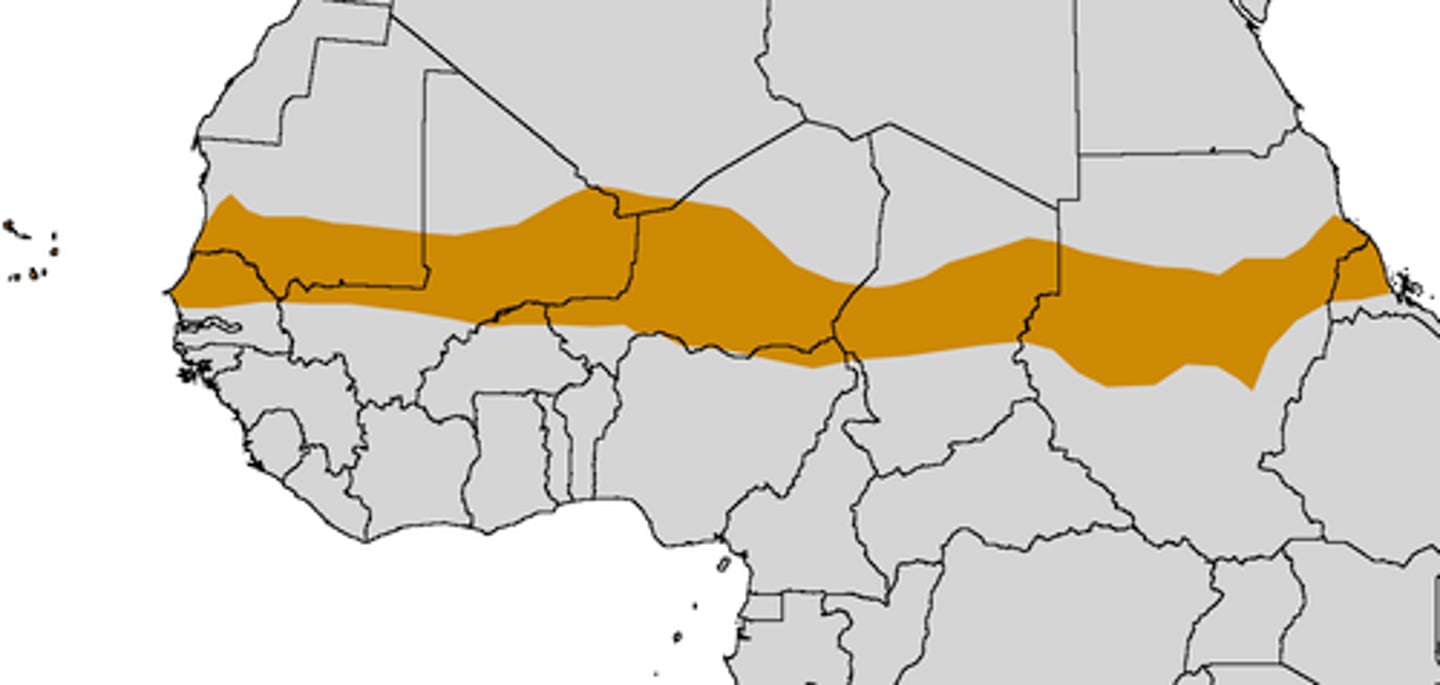
boundary
an invisible barrier or line that separates one state from another
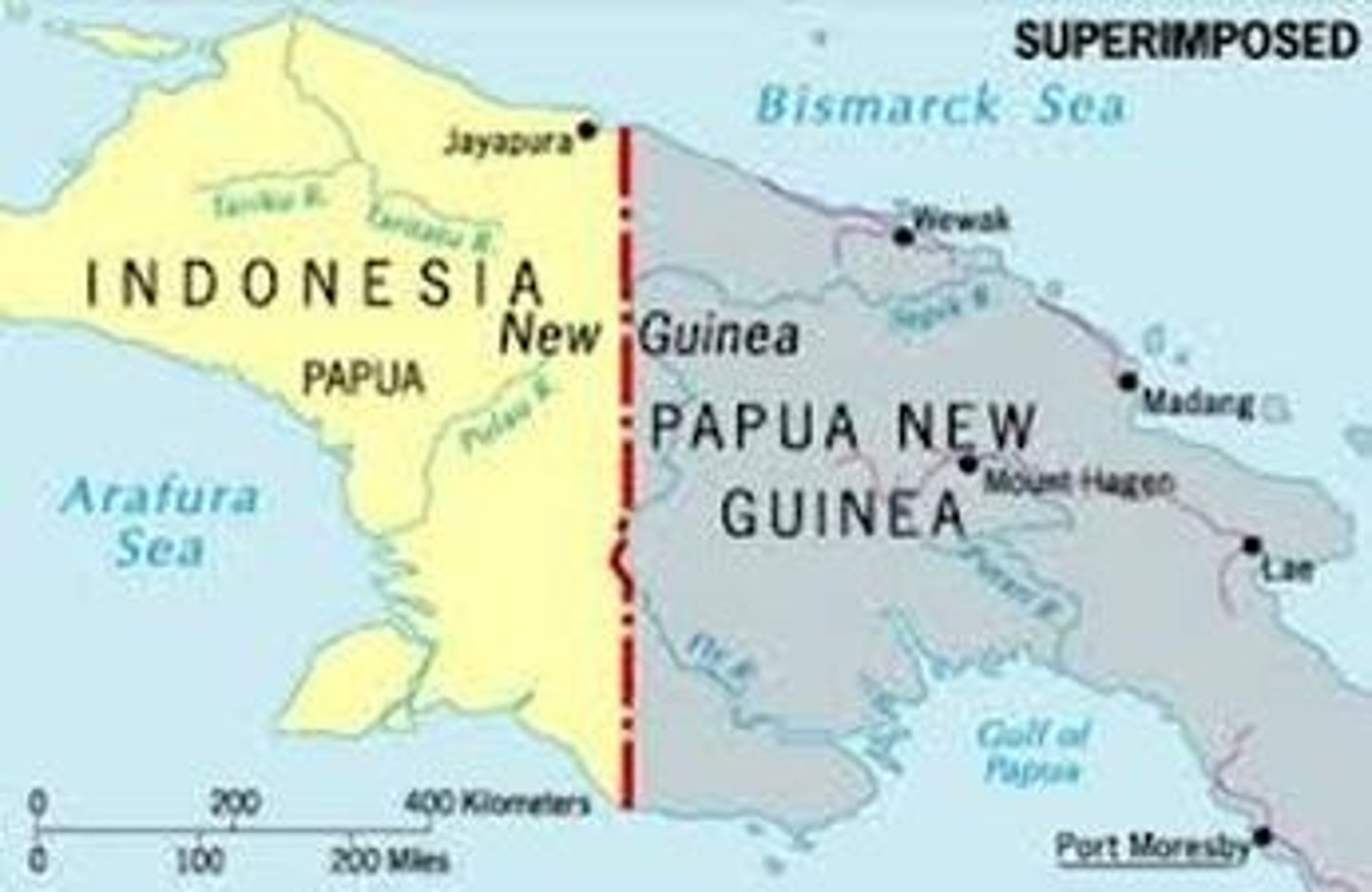
political boundaries
divisions of governance between states and within them that reflect balances of power that have been negotiated or imposed
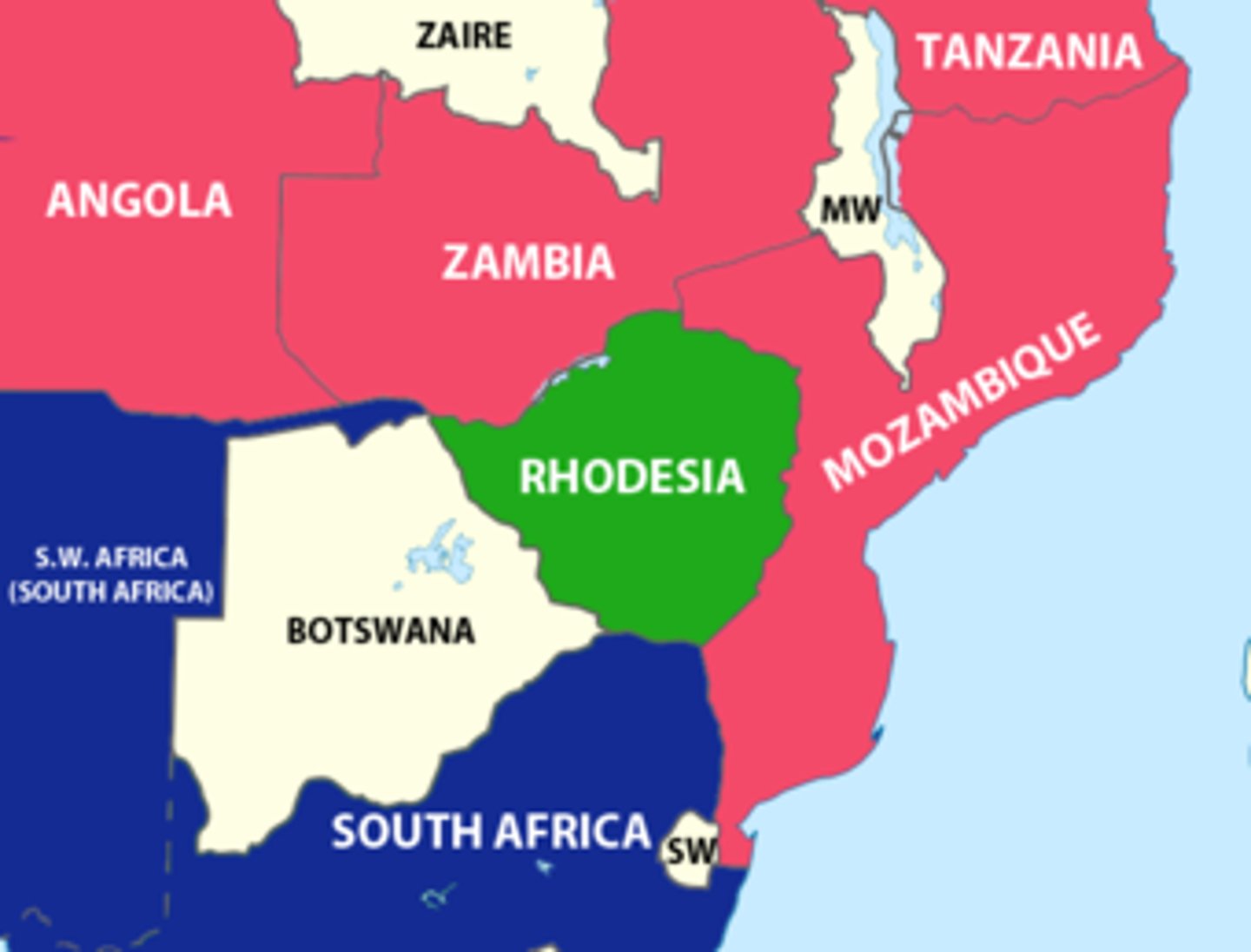
3 types of boundaries
cultural boundary, geometric boundary, physical boundary

cultural boundary
a boundary based on divisions of ethnicity, religion, or language
geometric boundary
Political boundaries that are defined and delimited by straight lines. (may also be superimposed and/or antecedent)
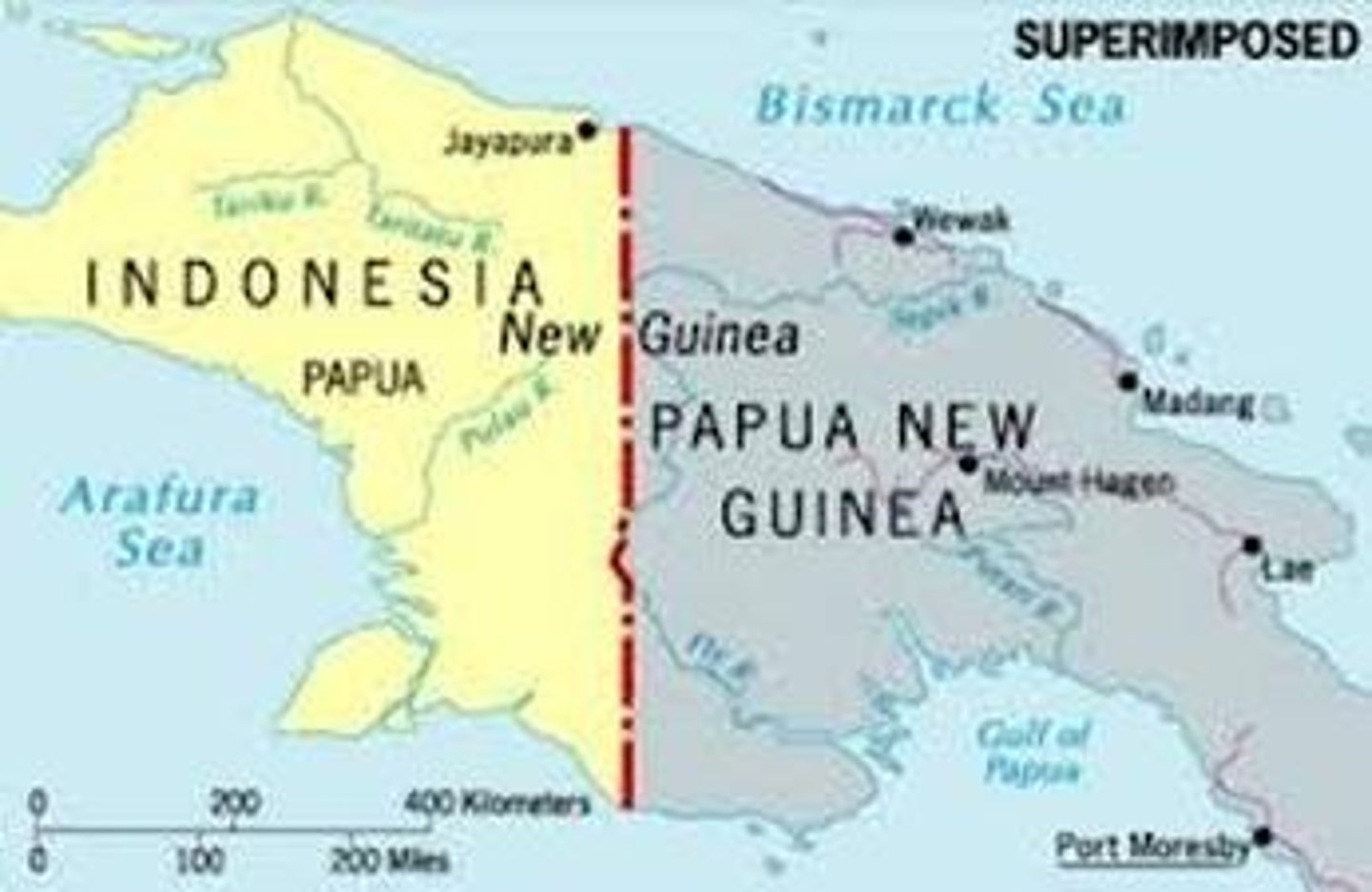
physical boundary
a boundary formed by a geographic feature such as a river, mountain range, or desert
relic boundary
a former boundary line that is still discernible and marked by some cultural landscape features
ways we classify boundaries by origin
superimposed boundaries, consequent boundaries, subsequent boundaries, antecedent boundaries, relic boundaries
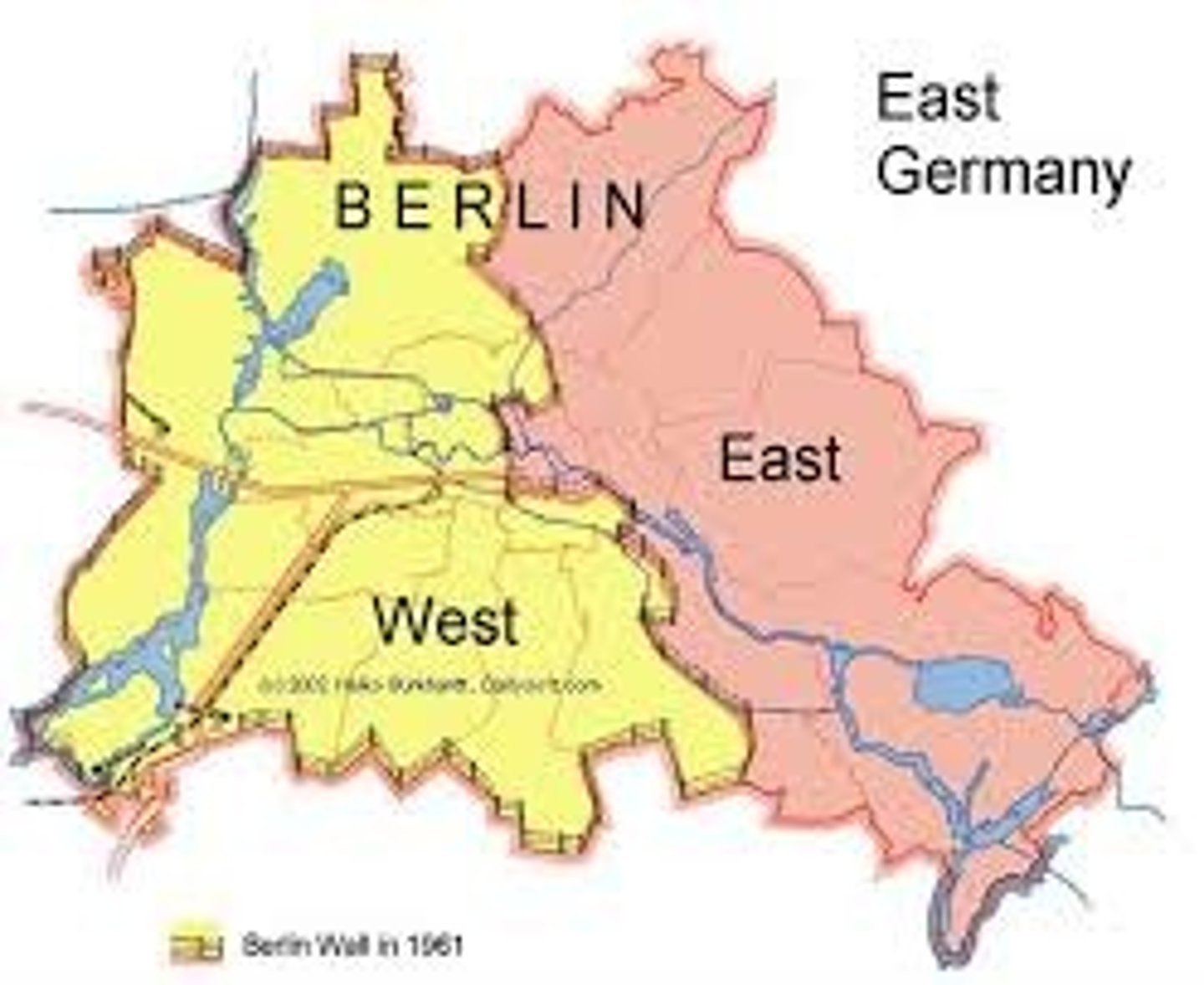
superimposed boundary
a boundary line placed by an outside power, that is placed over and ignoring an existing cultural patterns
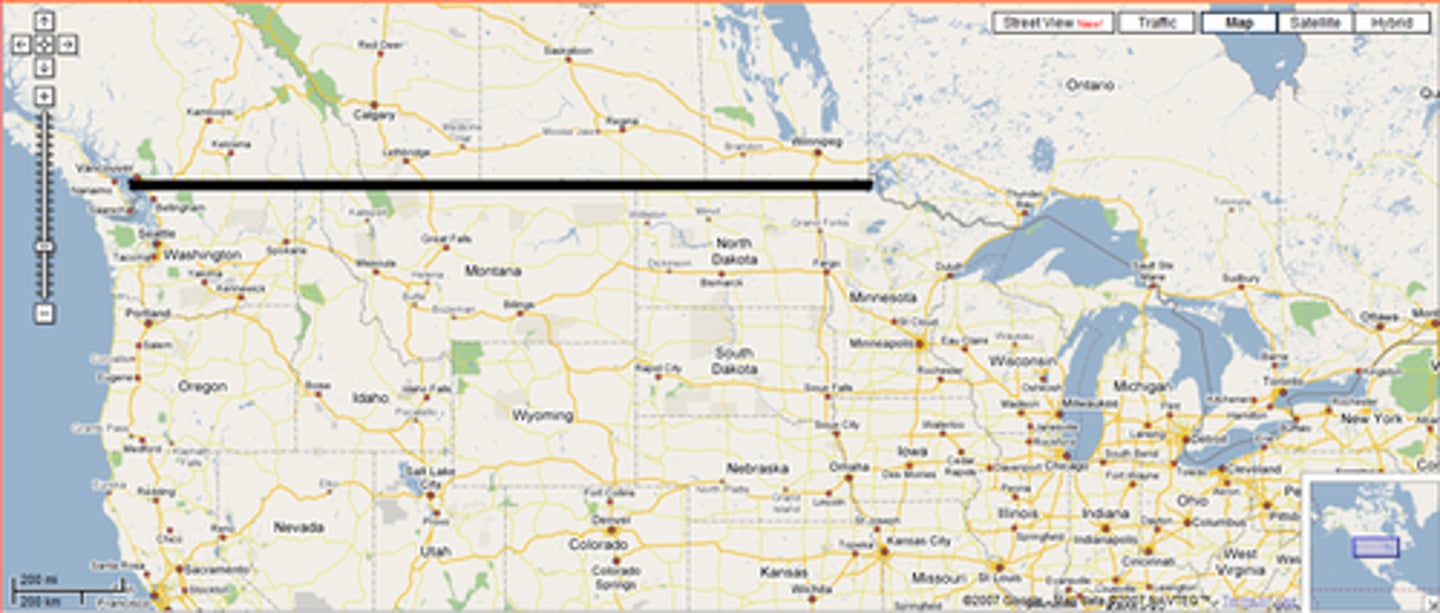
antecedent boundary
a boundary line established before the area in question is well populated
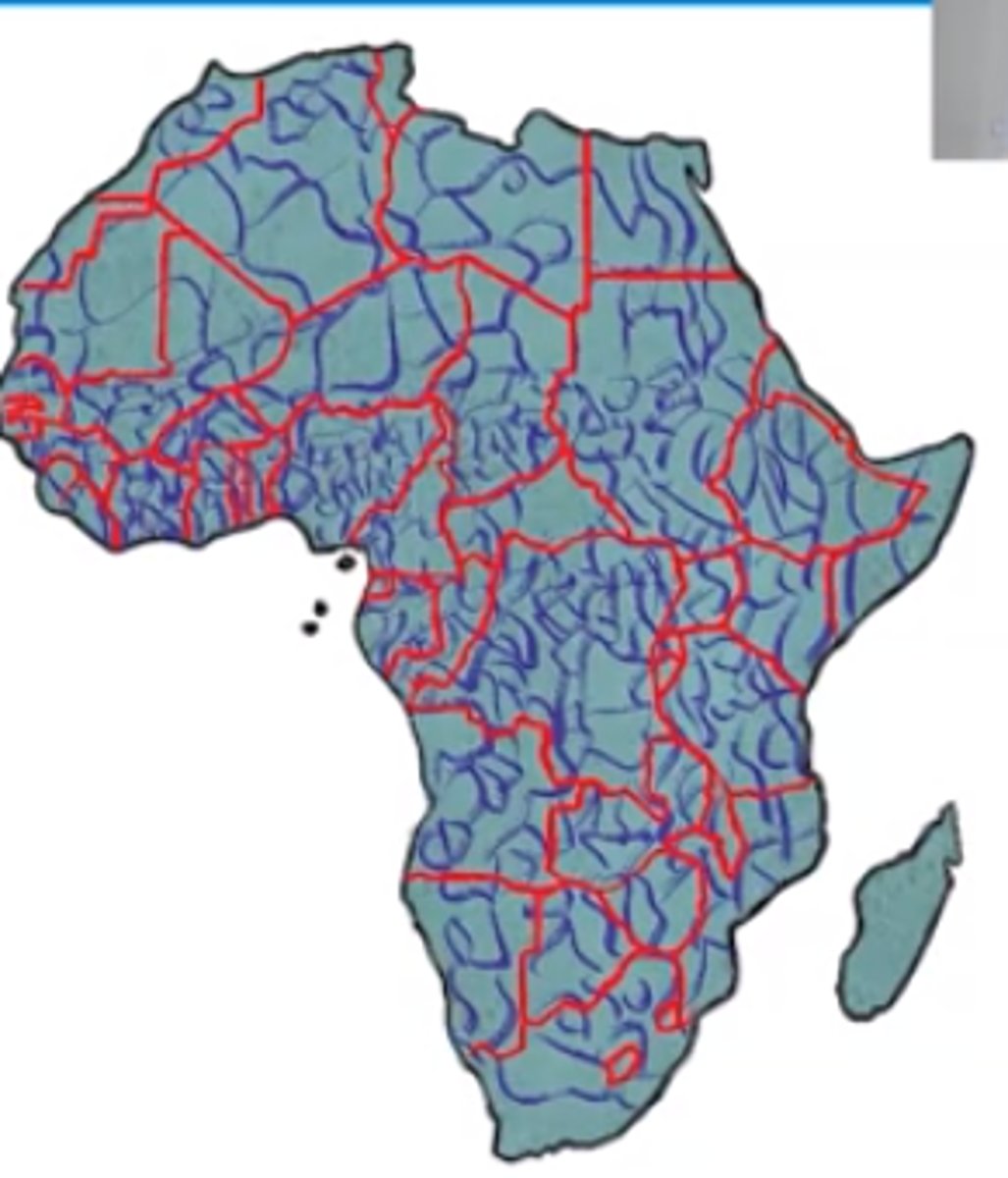
subsequent boundary
a boundary line that is established after the area in question has been settled and that considers the cultural characteristics of the bounded area
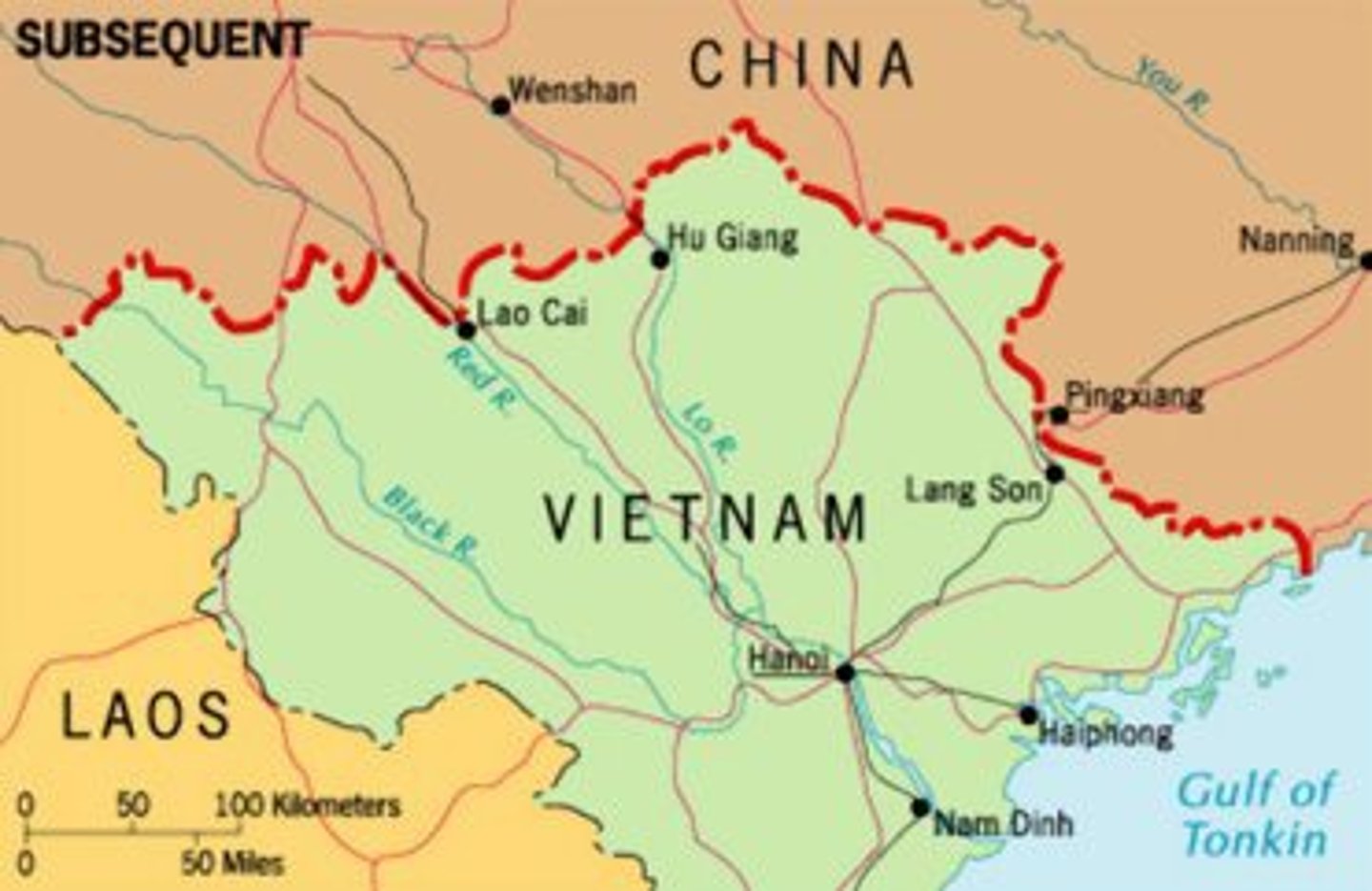
consequent boundary
a type of subsequent boundary that is intentionally drawn to accommodate cultural differences, such as ethnicity, religion or language
difference between subsequent boundaries and consequent boundaries
honestly this difference is super unclear and the two videos you will see describe them differently. My advice is to thing of subsequent as "they people were already there and subsequently the boundary developed" and consequent as "we needed to draw borders and we decided to divide people according to cultural similarities and differences"
frontiers
a geographic area where no state has direct power over the area. (there are few frontiers left today)
Purpose of boundaries
To show the limits of political power
territoriality
what boundaries define and enforce
sense of place
what boundaries help to create

jurisdiction
an area of authority or control
people, businesses and resources
what boundaries allow the government to regulate and control within a jurisdiction
defined boundary
a boundary established by a legal
document, such as a treaty.
delimited boundary
a line drawn on a map to show the limits of a space
demarcated boundary
a boundary identified by physical
objects place on the landscape, such as a sign,
wall, or fence. (Build a Wall!)

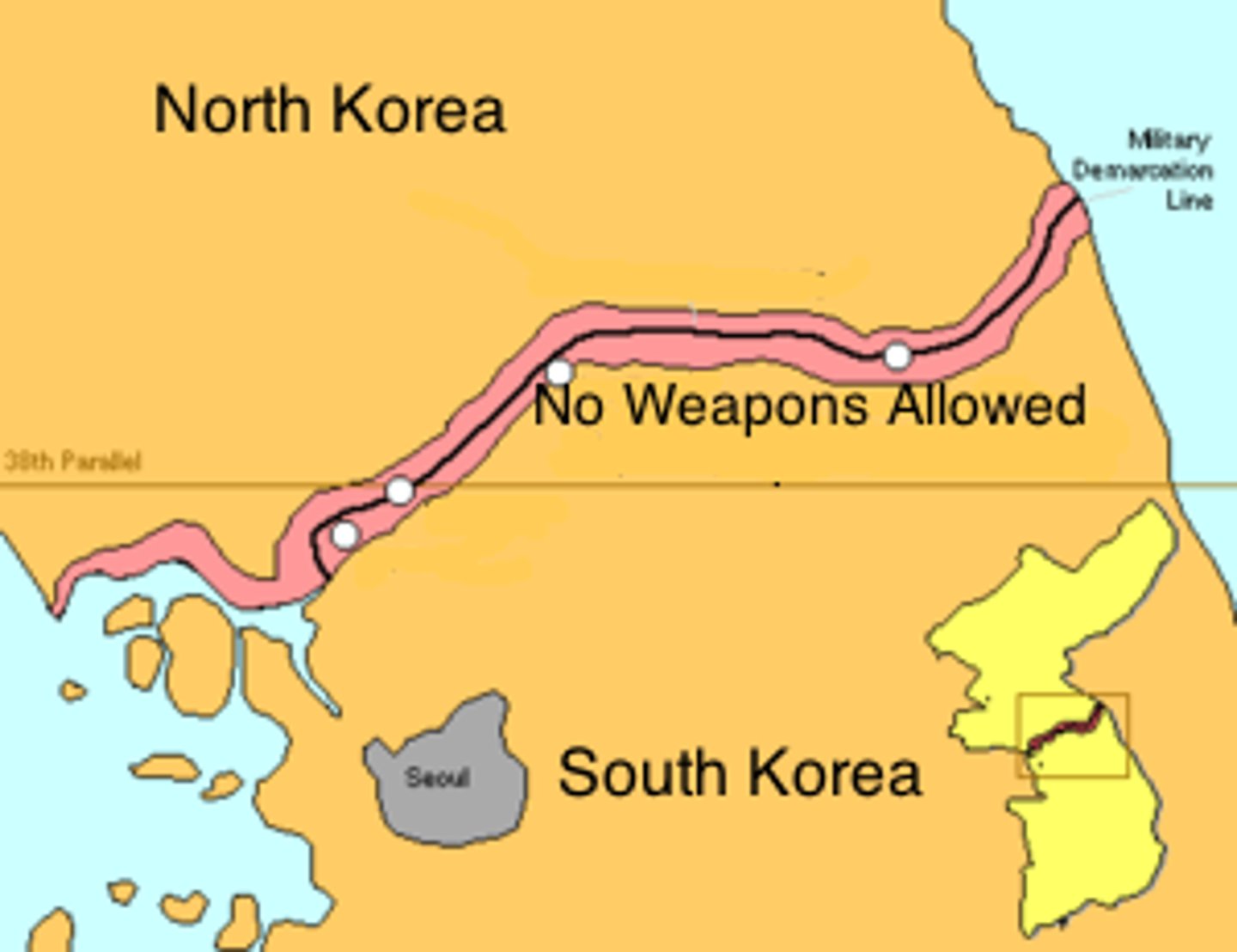
demilitarized zone
A region where no military forces or weapons are permitted.
types of boundary disputes
definitional (positional), locational (territorial), operational (functional), allocational (resource)
Definitional/Positional Boundary Dispute
Conflict over the interpretation of a boundary agreement
International Court of Justice
a court established to settle disputes between members of the United Nations (established in 1946 and located in the Hague, Netherlands)

Locational/Territorial Boundary Dispute
Conflict between states or regions over the ownership of a given area
Operational/functional boundary dispute
Disagreement over policies to be applied along a boundary, such as immigration or land use
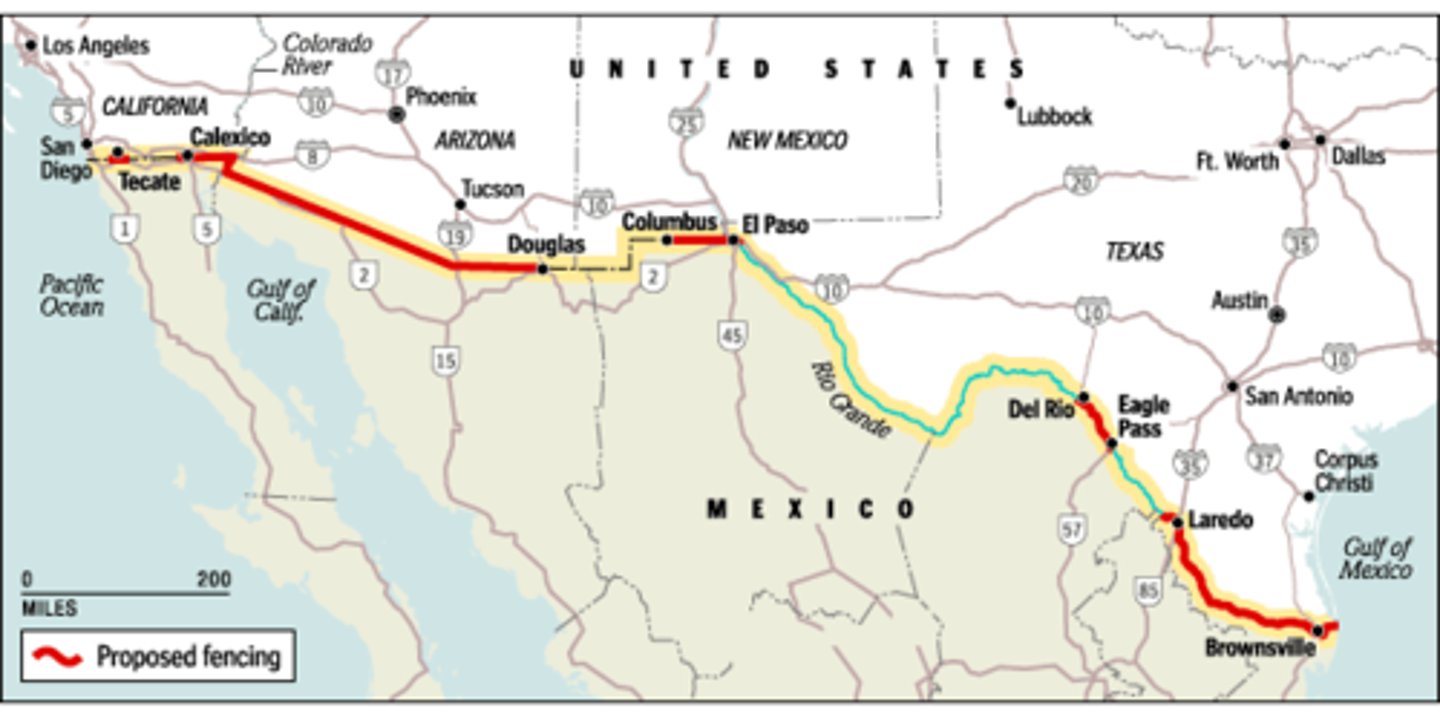
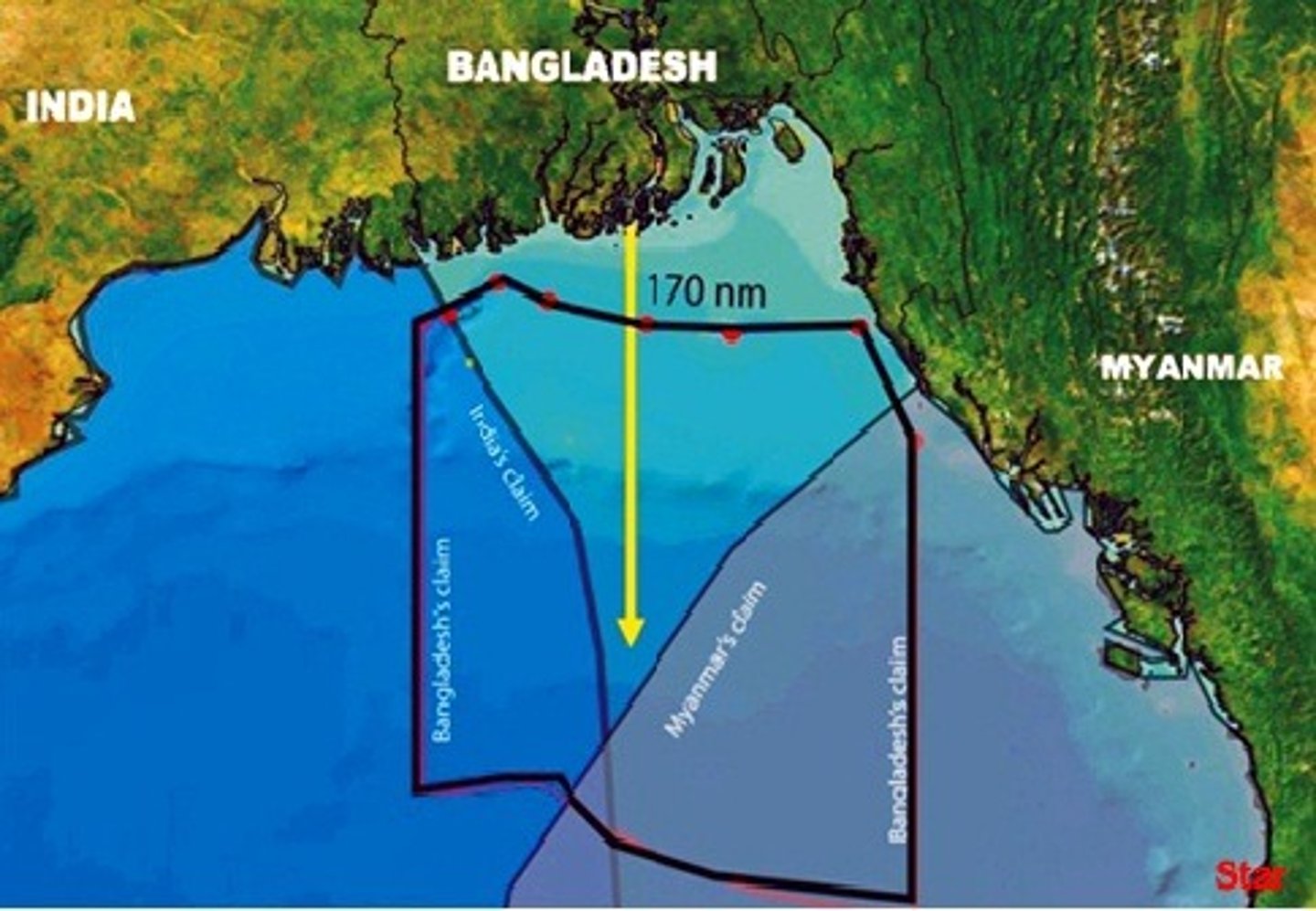
Allocational/resource boundary dispute
dispute over natural resource that occurs on or at the boundary
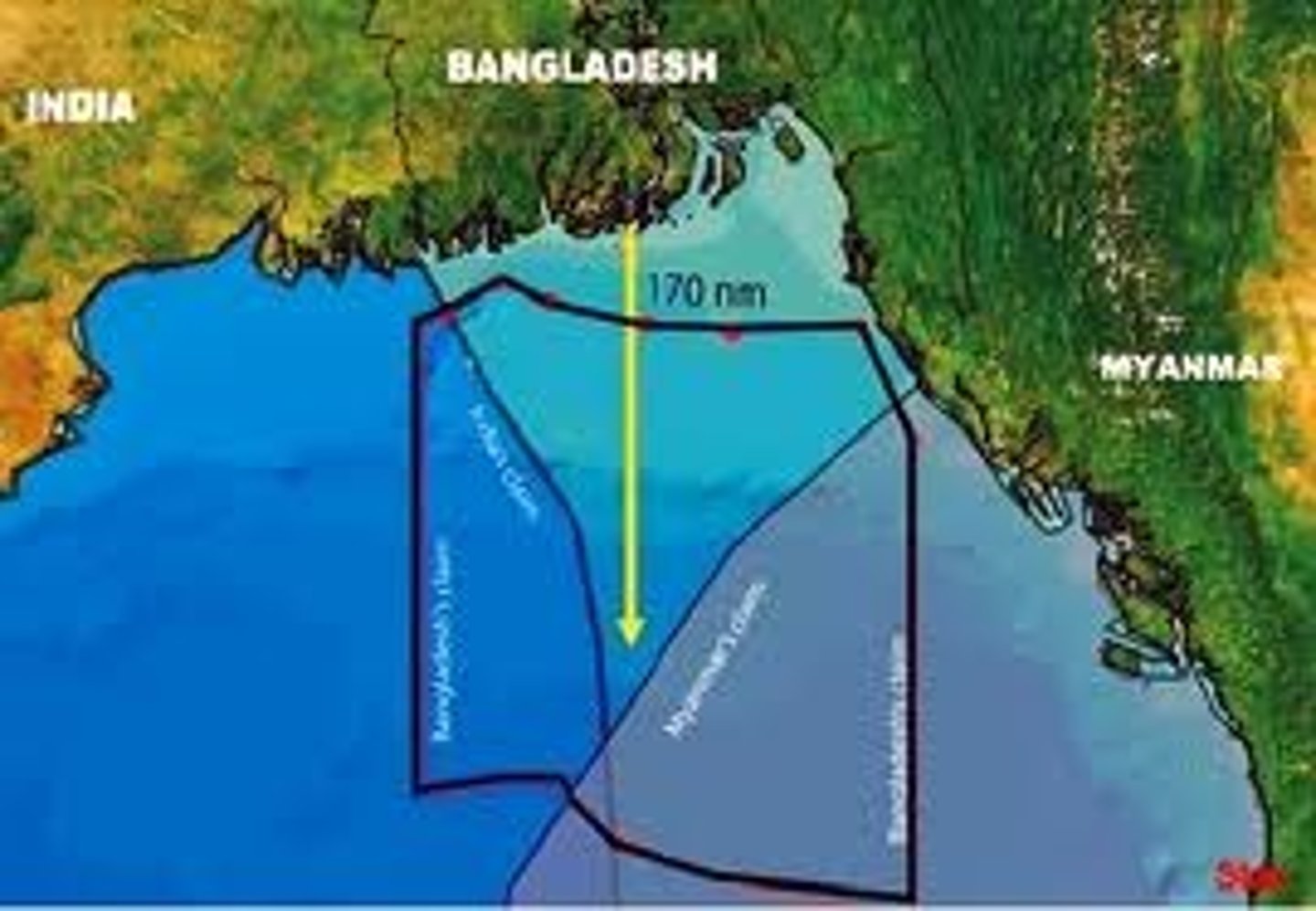
UNCLOS
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea: a code of maritime law approved by the UN in 1982 that authorizes, among other provisions, territorial waters extending 12 nautical miles from shore and 200 nautical mile wide exclusive economic zones. (established 1956)
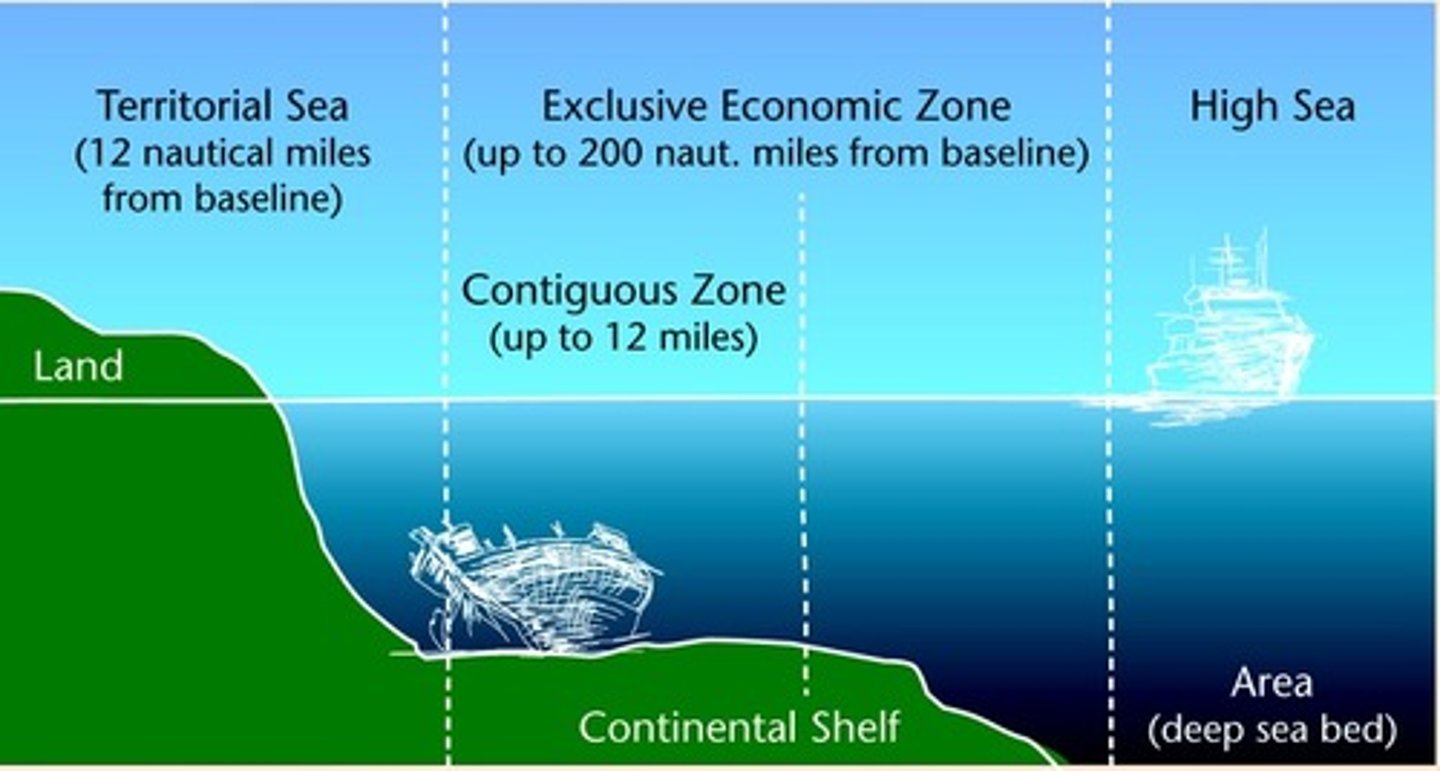
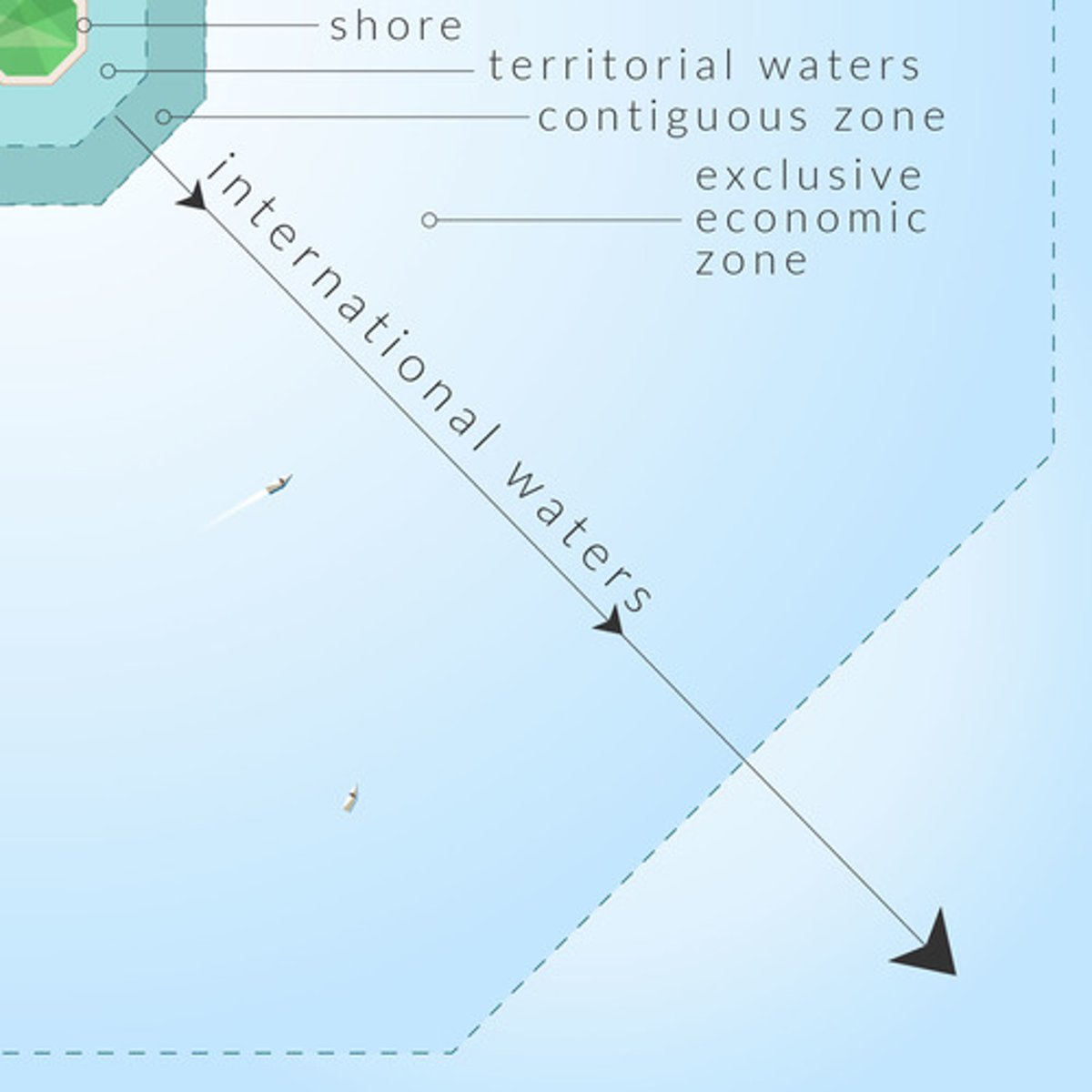
territorial waters
the waters near states' shores generally treated as part of national territory (12 mile limit)
international waters
nautical areas where all states have freedoms of navigation and overflight. In general, that means that ships of any country can transit in that area or airspace (generally begin 12 miles from the coast)
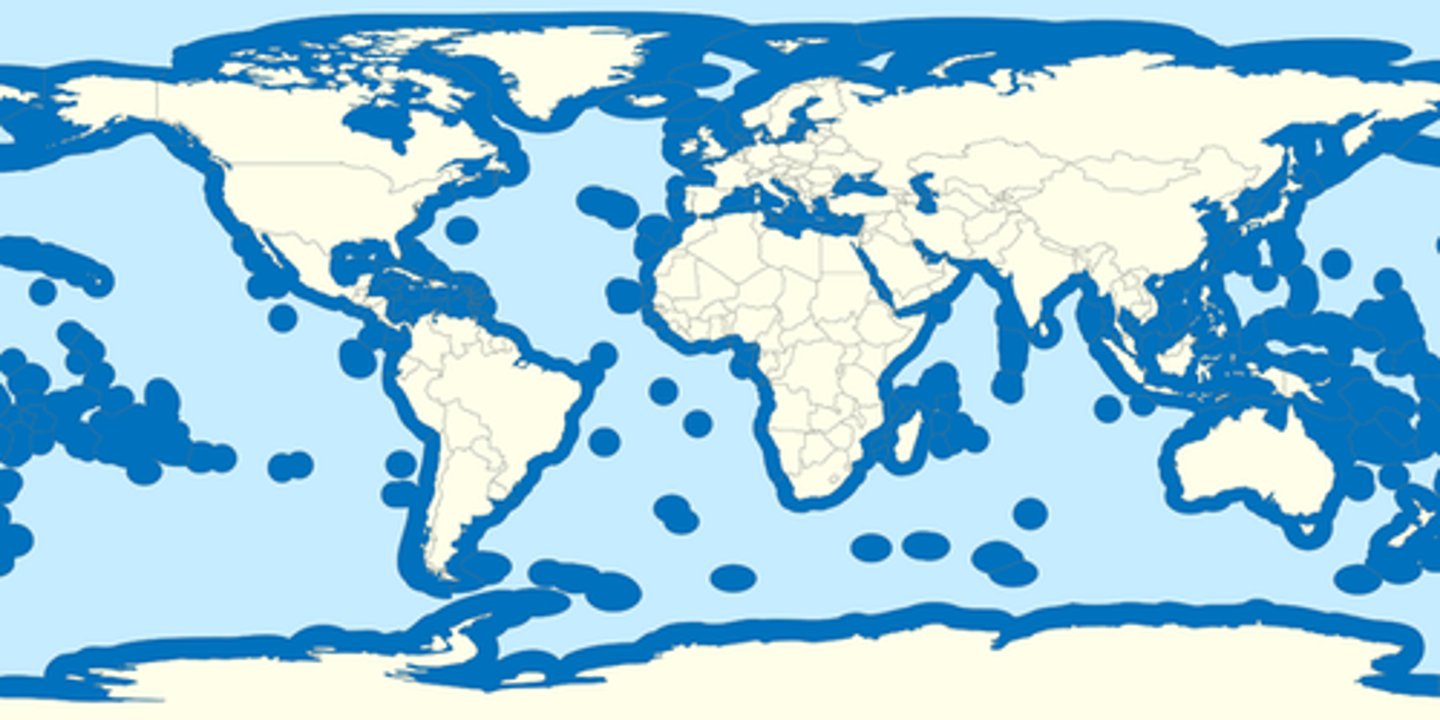
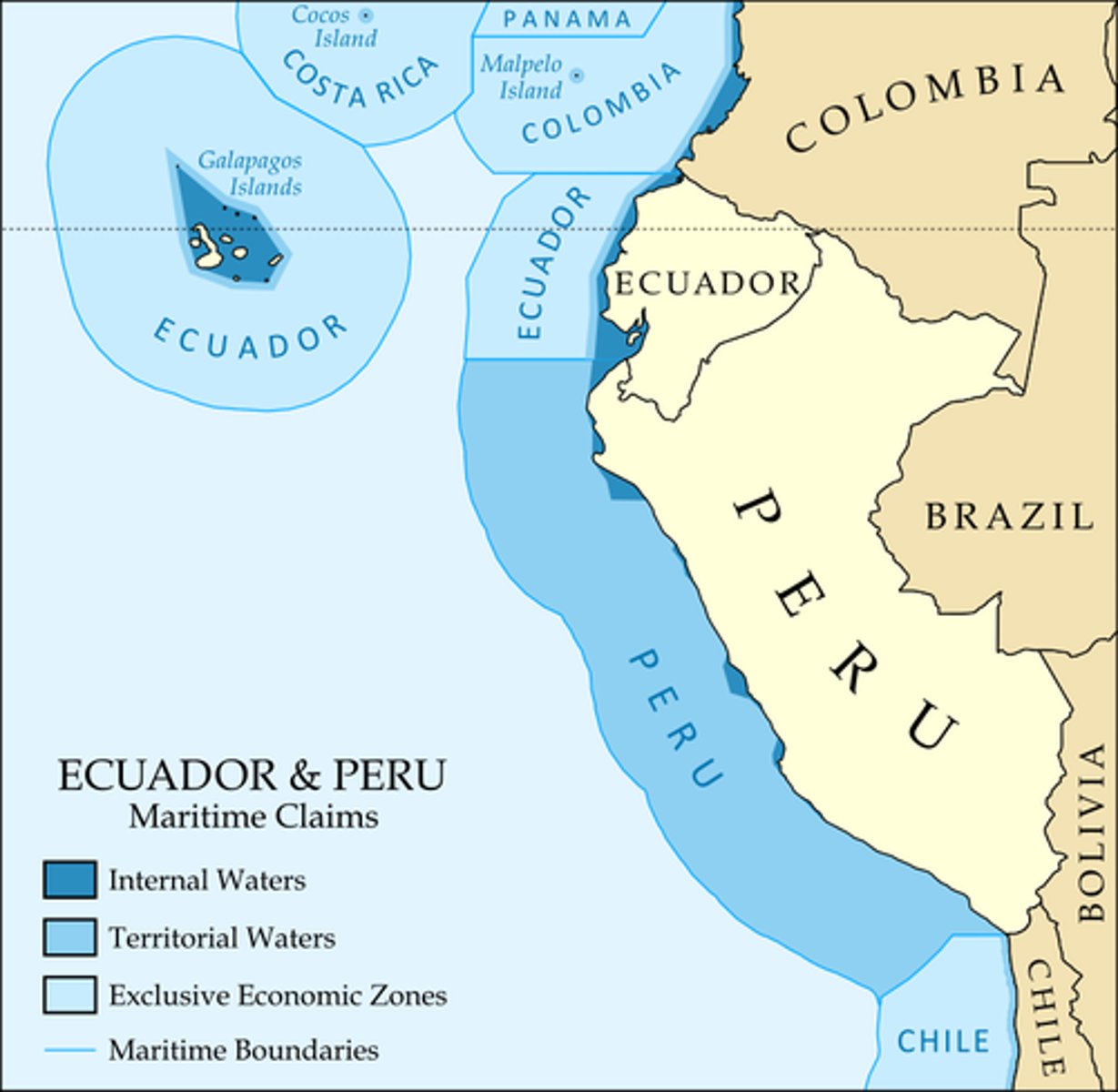
Exclusive Economic Zone
area in which ocean resources belong exclusively to the geographically bordering state (generally within 200 miles of the coast)
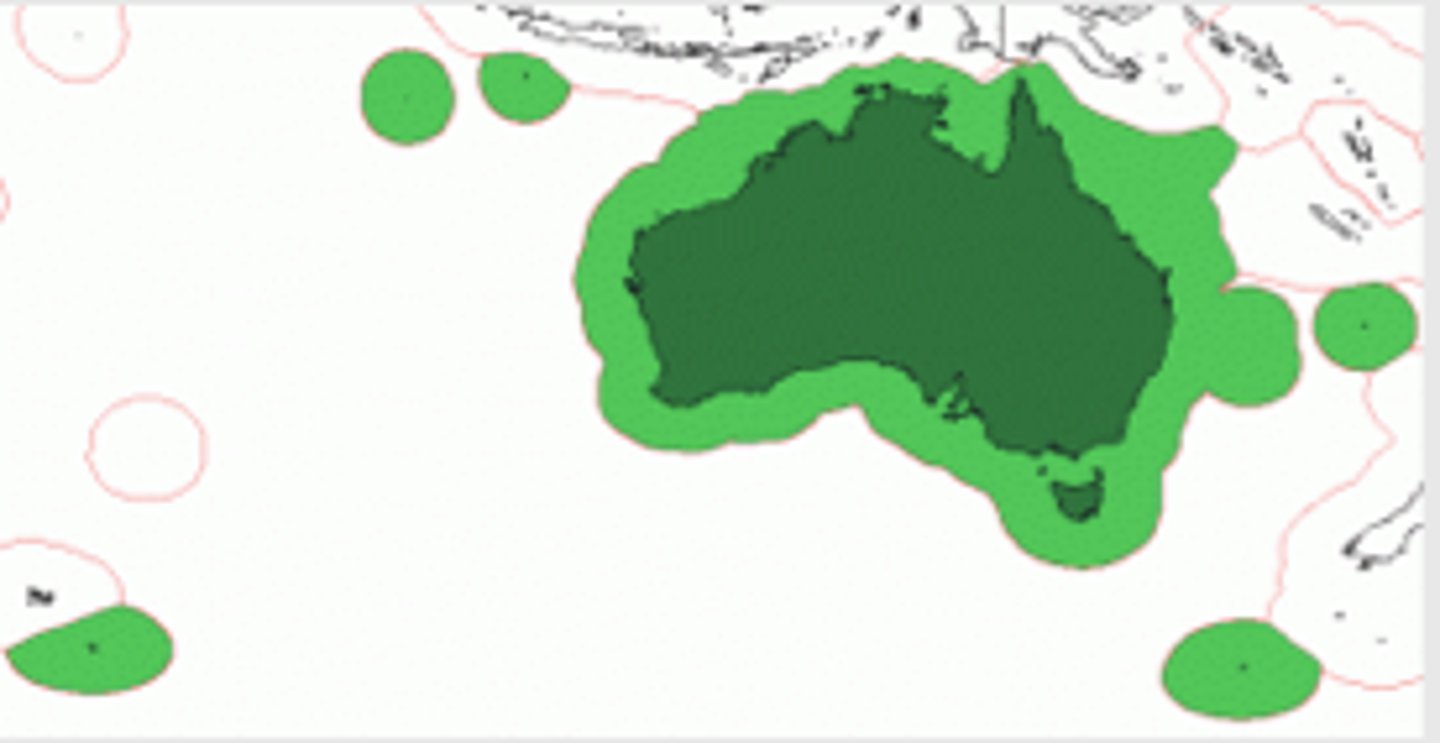
contiguous zone
an intermediary zone between the territorial waters and the high seas. It extends from 12-24 miles out from the coast. States have the right to enforce violations of customs, immigration or sanitary laws in that zone
high seas / open ocean
200 miles and out. All resources are shared and no country has jurisdiction. (resource use can still be regulated by treaty)
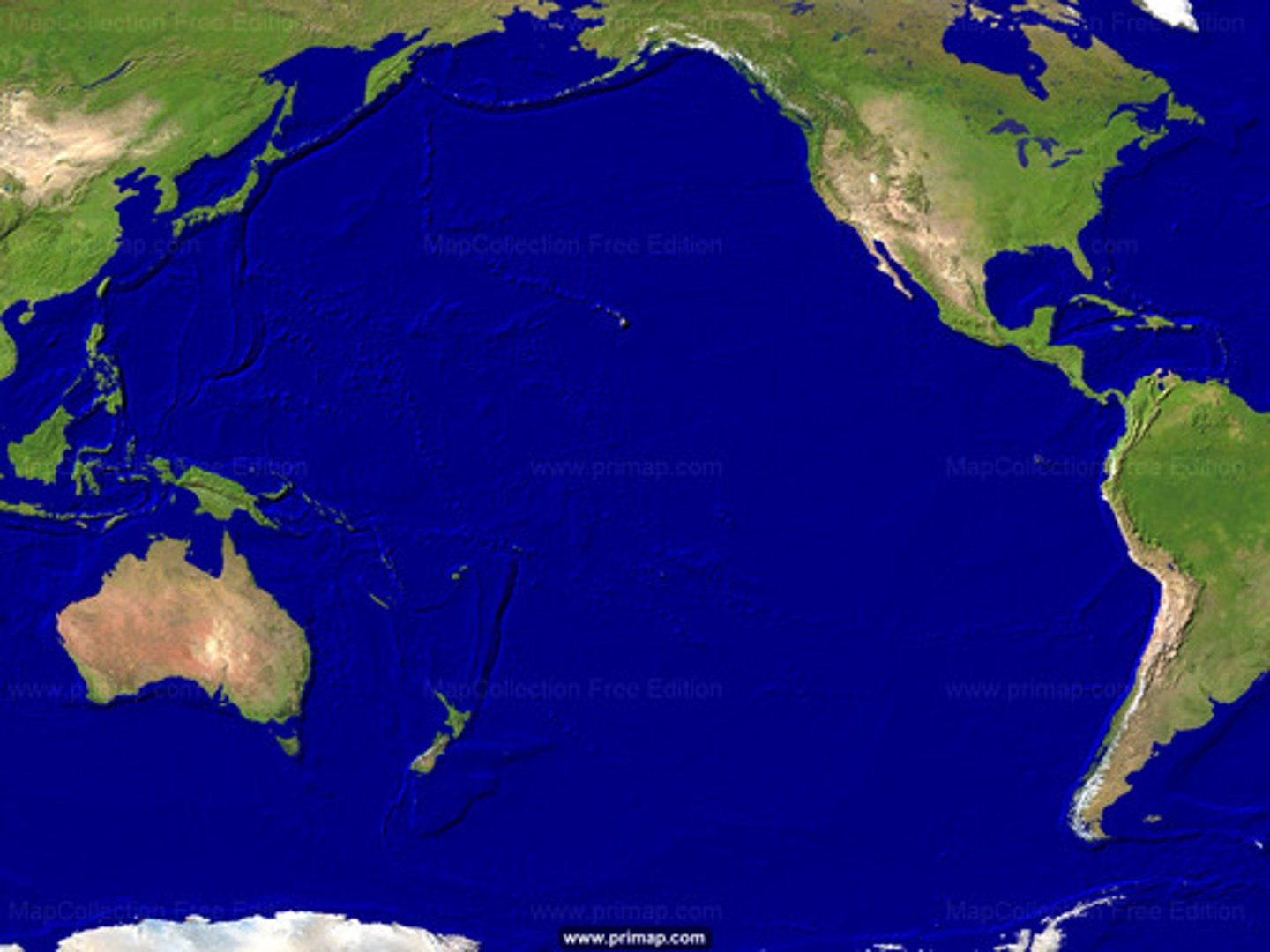
South China Sea
an area of nautical territorial conflict between China, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Malaysia (also Taiwan)
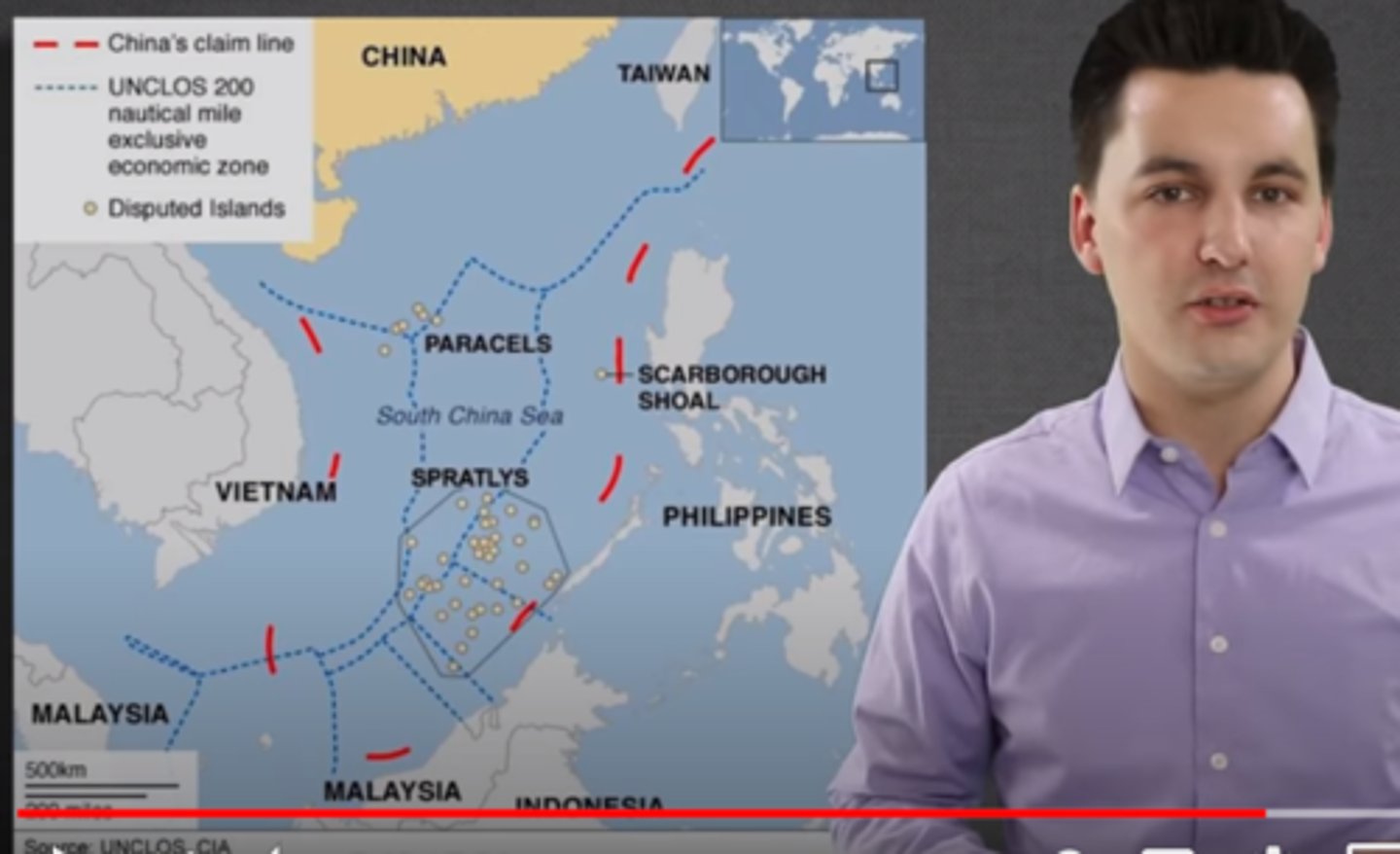
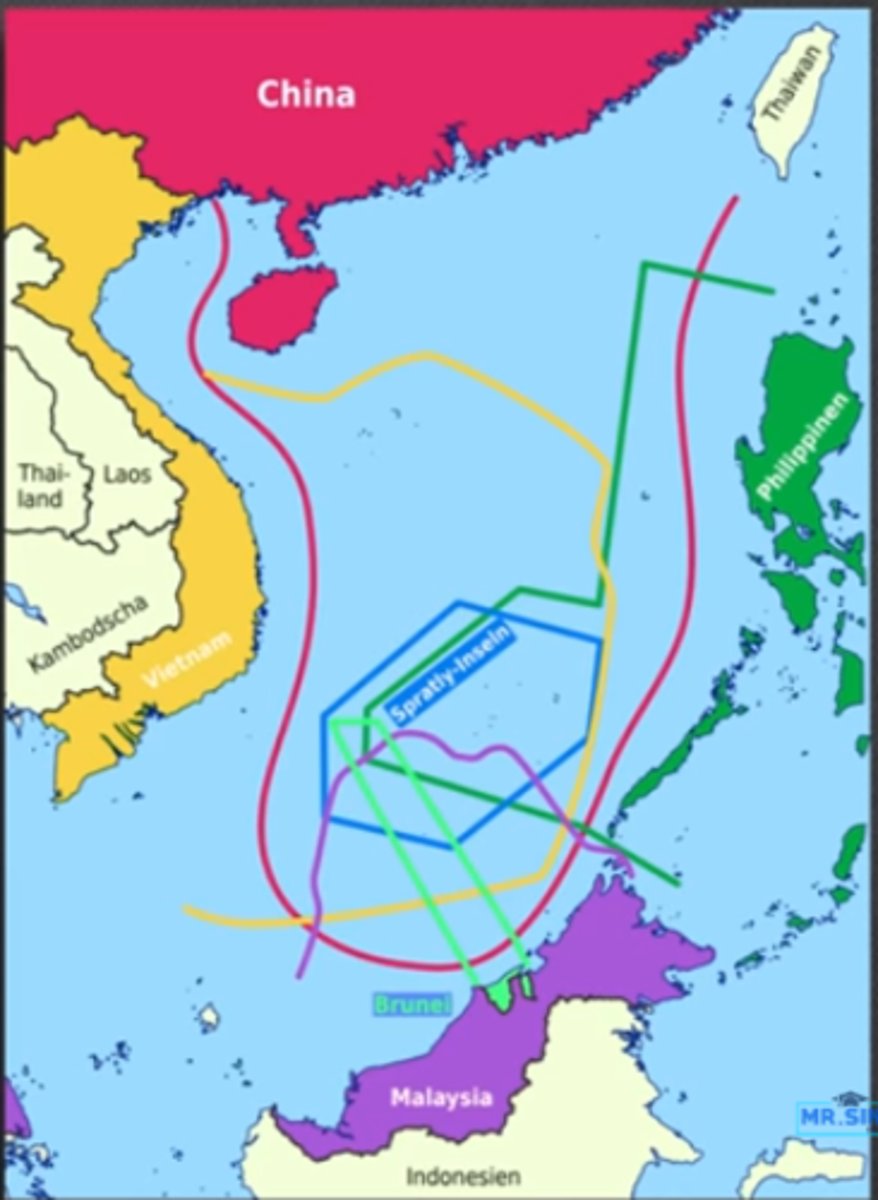
Spratly Islands
a disputed group of more than 750 reefs, islets, atolls, cays and islands in the South China Sea. The archipelago lies off the coasts of the Philippines, Malaysia, and southern Vietnam.
formalize
to give a definite or official form to something

intensify
v. To increase; to strengthen or deepen.
