CSD 4010 - Exam 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Speech breathing
regulation of breathing for voice and speech production
Vegetative breathing
life-sustaining breathing
Inhalation/inspiration
incoming air
Exhalation/expiration
outgoing air
Tidal volume
the volume of air that is exchanged during any particular cycle or inhalation/exhalation
Diaphragm
large, flat muscle attached at lower border of rib cage; dome-shaped at rest (exhalation) and flattens when it contracts (inhalation)
Inspiratory checking
counteracts the relaxation pressures and promotes the steady lung pressure necessary for phonation; used only when the pressure generated by the lung volume is greater than would be necessary to sustain phonation
Dysfunctional breathing
the disruption of normal breathing patterns occurs in the absence of or in excess to the magnitude of physiological disease
Phonation
generation of speech sounds by vibration of VF
Vocal quality
listener's perception of the voice
Pitch
perceptual correlate of fundamental frequency
Glottis
space between the true VF
Stress
perpendicular force on the VF
Strain
parallel force on the VF
Phonation onset
the initiation of phonation divided into three categories: simultaneous, breathy, and glottal attack
Jitter
a measure of cycle-by-cycle variability in frequency
Shimmer
the variation in amplitude of a sound wave or intensity of vocal emission
Resonance
the process by which an object is made to vibrate by absorbing energy at its natural frequencies; the cavities of resonance include the larynx, pharynx, oral cavity, nasal cavities, and sinuses
Boyle's Law
as the volume of a container increases, air pressure within the container (lungs) decrease (& vice versa); the negative pressure in the thoracic cavity causes the air from the atmosphere to flood into the lungs
Lung pressure
the force of subglottal air on VF
- key in regulation of intensity and frequency control
- increased lung pressure = larger amplitude
- larger volume of air = larger acoustic power
- greater effect at lower frequencies than higher
- a manometer is used to measure lung pressure
Lung volume
tidal volume (TV)
inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) - the amount of air that could be inhaled
expiratory reserve volume (ERV) - the amount of air that could be exhaled
residual volume (RV) - the volume of air that remains in the lungs after max exhalation
Pleural Iinkage
the visceral pleura surrounds the lungs, parietal pleura lines the inside of the thorax (NOT 2 separate membranes - continuous); acts as a surfactant between membranes to help achieve negative pressure (and in turn inhalation)
Forced inhalation and expiration
forced inhalation - above 60% of vital capacity; helps to engage more musculature, supports physical exertion, supports effortful speech, uses more air than tidal breathing
forced exhalation - greater air expired than in tidal breathing; internal intercostals and abdominal muscles are involved, active process
Airway resistance
due mainly to the diameter of the airways (airflow has an inverse relationship to resistance)
- narrow = more resistance
- wider = less resistance
influenced by lung volume, the upper airway (nose, pharynx, and larynx), & the nervous system (sympathetic widens the airway, parasympathetic constricts the airway)
smooth, unobstructed airflow is laminar, but our airway is turbulent
Airway humidification
the major purpose of the upper airway is to condition the air (add humidification & remove pollutants)
turbinates (folds of tissue in the nose) are covered in vascular mucosal tissues which condition the air we breathe in
asymmetric breathing - works to warm and humidify
mouth breathing can dehydrate the mucosal lining of the airway and VF compared to nose breathing
Structural framework of larynx
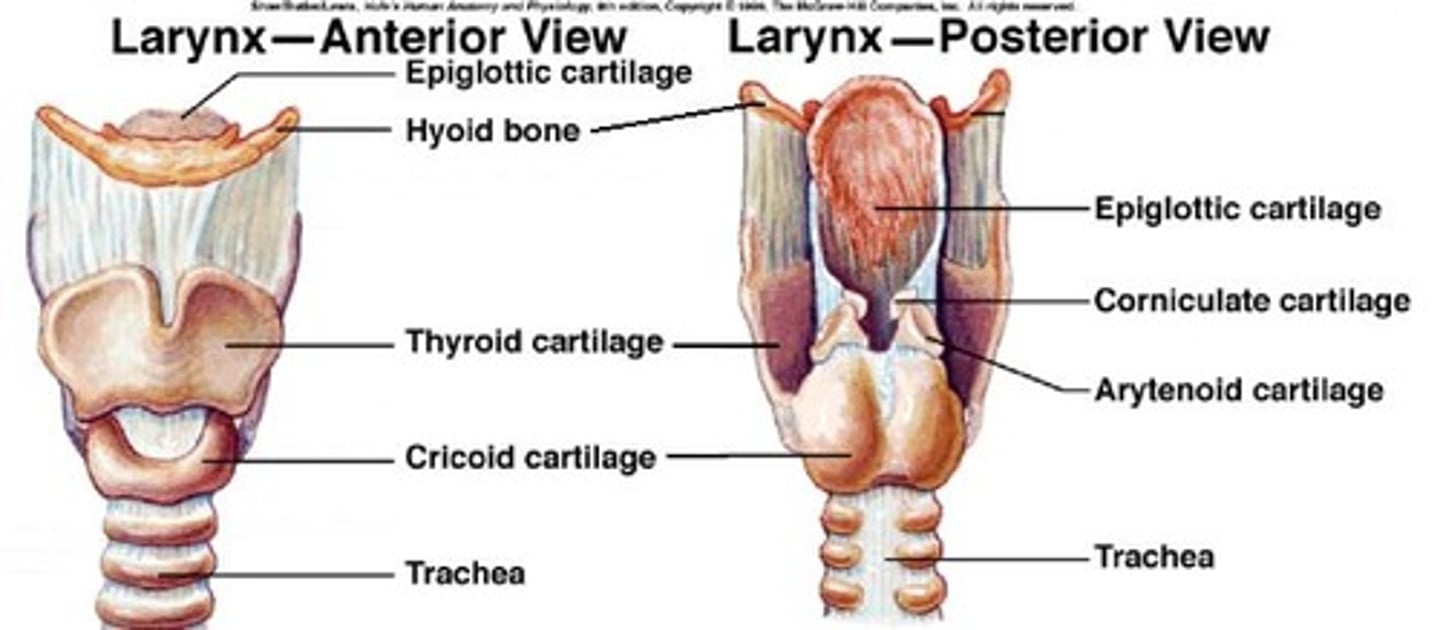
Innervation of the larynx
CN X - Vagus; recurrent laryngeal nerve
Extrinsic muscles of larynx - purpose
suprahyoid muscles
digastric - elevates hyoid
geniohyoid - moves tongue and hyoid anteriorly
mylohyoid - elevates hyoid, depresses mandible
stylohyoid - elevates and retracts hyoid
infrahyoid muscles
thyrohyoid - depresses hyoid, elevates thyroid
sternohyoid & sternothyroid - depresses hyoid
omohyoid - depresses and retracts hyoid
Intrinsic muscles of larynx - function
abductor
- posterior cricoarytenoid (sole abductor of VF)
adductors
- oblique arytenoid
- transverse arytenoid
- lateral cricoarytenoid
tensors/relaxers
- thyroarytenoid - relaxes the vocal ligament
- cricothyroid - stretches & tenses the vocal ligament
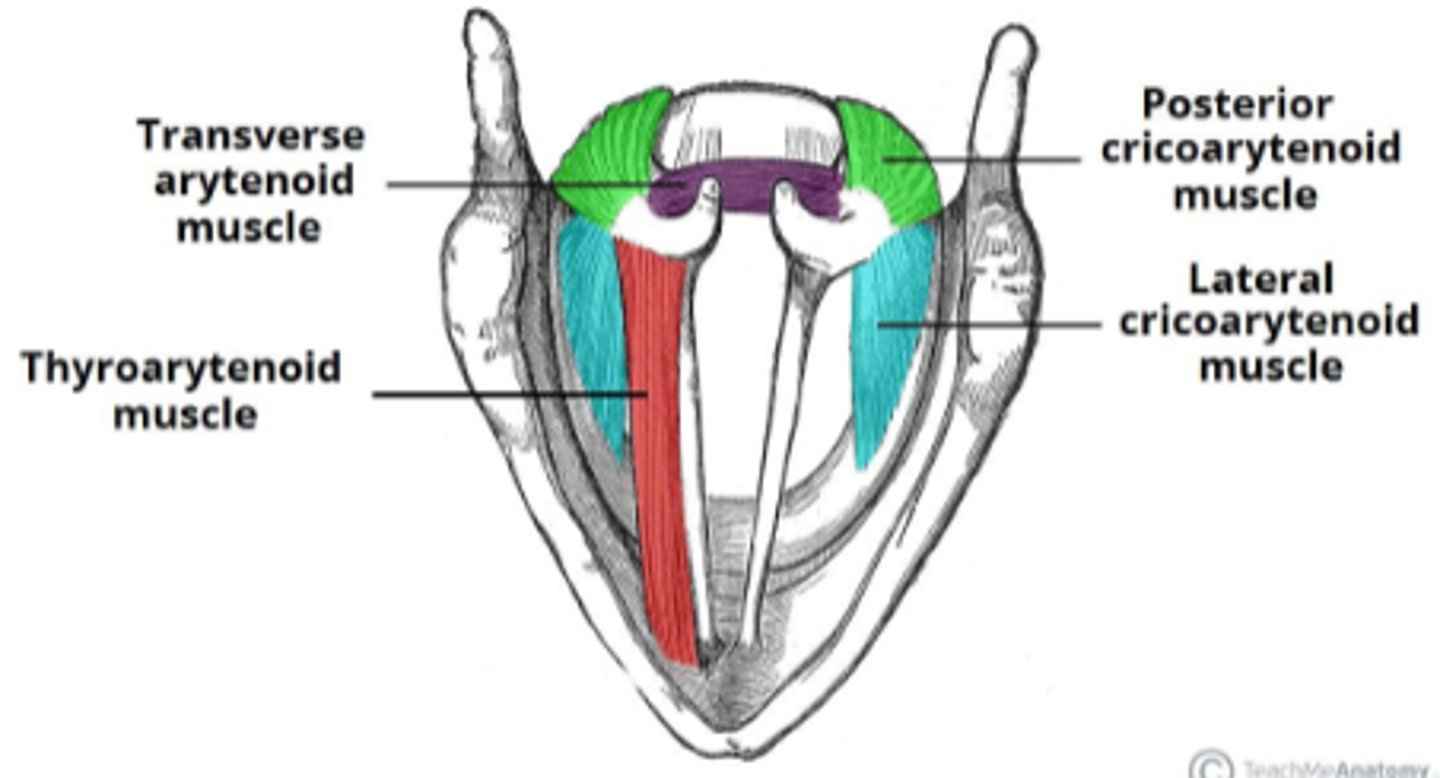
3 functions of the larynx
1. protecting the lungs from intruders (coughing, throat clearing)
2. participates in breathing (widens/decreases airway lumen to decrease/increase resistance)
3. stabilizes torso (lifting, pushing/pulling, VF seal airway thereby fixing thorax)
Lamina propria - layers
multi layered membranes, each layer having different biomechanical properties
1. most superficial layer - loosely arranged elastin fibers
2. intermediate layer - densely distributed elastin fibers
3. deep layer - tightly packed collagen fibers
3 laryngeal valves
1. aryepiglottic muscle – most superior; runs from sides of epiglottis to top of each arytenoid cartilage, contracts in a circular action to pull epiglottis backwards and close entrance of larynx during swallow
2. ventricular folds (false vocal cords) - superior and parallel to TVC, limited movement, close during swallowing but open during phonation, ventricle separates TVC from FVC
3. true vocal cords (TVC) - epithelium, lamina propria, vocalis/thyroarytenoid muscle
Joints of the larynx
cricoarytenoid joints – allows the arytenoids to glide medially (close), laterally (open), and rock forwards and backwards (tighten)
cricothyroid joints – regulates fundamental frequency (pitch) by elongating and shortening the vocal folds (tension)
Bernoulli Effect
an increase in velocity = decrease in pressure
- conservation of energy
- critical in VF vibration and voice production
- fluid flows faster through narrower sections
Myoelastic-Aerodynamic Theory
myoelastic - physical properties of VF, particularly elasticity, mass per unit length, and tension
tension is the force used to elongate the VF; the result of the pulling force exerted upon the VF and their resistance to that force (stiffness)
aerodynamic - Bernoulli effect
Voice quality
sum of both laryngeal influences and influences of the vocal tract (mode of vibration)
laryngeal influences:
- breathy voice
- pressed voice
Fundamental frequency measures
- habitual use
- maximum performance (physiological limits of the voice)
- degree of regularity (jitter)
Intensity measures
- habitual intensity level
- physiological range
- amplitude (shimmer)
Measure of phonatory aerodynamics
(airflow)
- lung pressure
- vocal efficiency
- laryngeal airway resistance
Fundamental frequency
the rate of vibration of the VF
controlled by length, tension, and stiffness
Maximum phonation time
deep breath, sustain a vowel as long as possible
15-25 seconds in healthy adults
detects impairments of phonatory glottal closure
Control of intensity
major determinants:
- lung pressure (except at high frequencies)
- VF closure
- vocal tract resonance
Biomechanical forces - stress
VF can stretch more than a muscle & builds up stress faster than muscles
Driving pressure
difference between high and low pressure areas that causes air to flow between these areas; created in the ventricles