Unit 5: Factor market Ap exam review
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
When do markets happen
When consumers and producers meet to exchange goods, services or factors of production
What is derived factor demand
The fact that demand for goods and services in the product market creates demand for factors of production to produce these goods or services
What is Marginal revenue product
The change in total revenue generated when one additional input is employed
As additional workers are hired, what happens to MRP
It decreases due to diminishing marginal returns
What is the formula for MRP
Marginal revenue X Marginal product or in perfectly competitive situations Marginal Product X price
Why do imperfect competition firms have less MRP then perfectly competitive firms
because marginal revenue is decreasing at a faster rate
What is MRP a factor of
A factor of demand
What causes a rightward shift in MRP
increase in worker training programs
technological advancments
increase in popularity of a good
What is marginal Factor cost
The extra cost a firm incurs when employing one additional unit of input
In a perfectly competitive factor market, what is MFC equal to
The wage rate or rental rate
What is a perfectly competitive market like in a factor market
Large number of firms are acting to hire similar workers, each firms decisions cannot affect the market wage rate because each firm is hiring only a small percentage of industry quantity-wage takers
What does a labour market look like
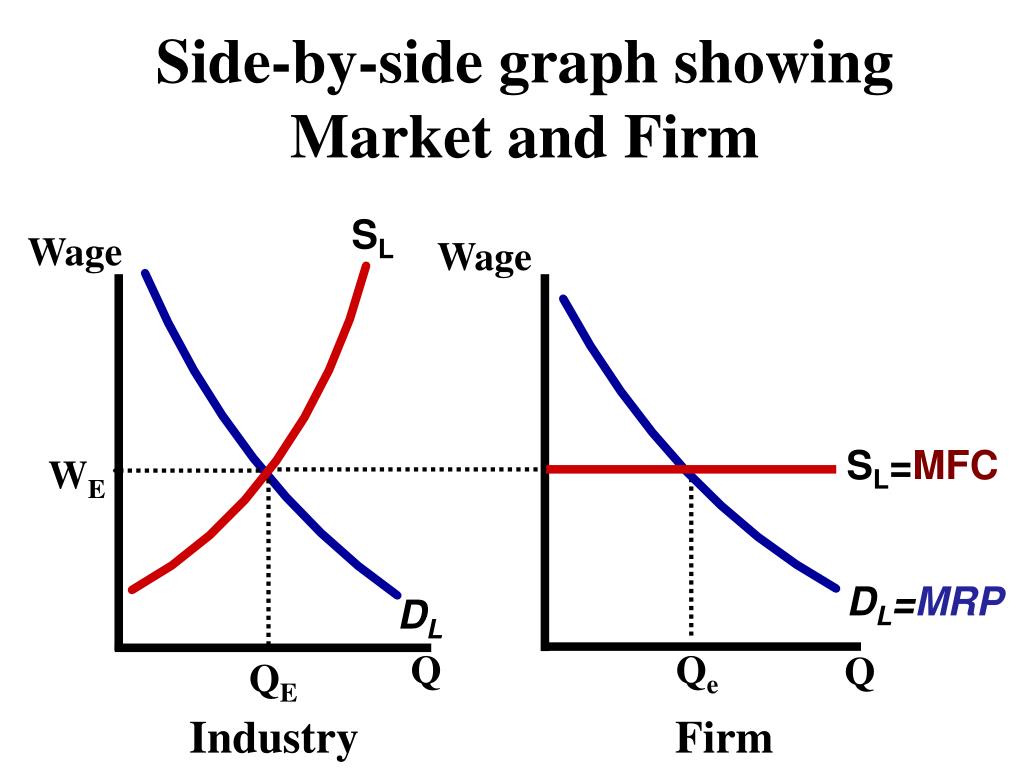
Why is the wage rate horizontal in a perfectly competitive labour market
They can employ as much labour as the market wage as they are willing to hire
What is the wage rate equal to
MFC=S
Proft maximizing output:
Marginal product of labour/ Price of Labour = Marginal product of capital/Price of capital
What is a monopsnoy
It occurs when there is only one consumer in a market - there is only one employer in the market
In a monopsony, what happens to the marginal factor cost
It increases at a faster rate than the labour supply curve
What does a monopsony graph look like
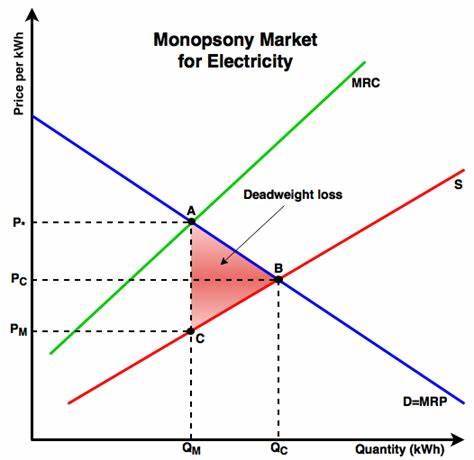
Why does the MFC increase at a faster rate than the labour supply curve
because the price of the last unit employed must be paid to all previous units as well, as you hire more labour there has to be higher wages offered
What is the result of a monoposny in a factor market
Lower price for factors of production and a lower quantity of factors employed
what is VC equal to
vc = q x mfc