Intro to Plant Science - Exam 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Protoplast
organized living unit of single cell
Middle Lamella
Holds cells together
Plasmodesmata
Channels between plant cell walls that allow communication and transport of substances between adjacent cells.
What are the functions of the cell wall
protects protoplast
provides structure
Primary cell wall
made of cellulose
Plasma Membrane
Lipid bilayer
semipermeable
Cytoplasm
gel-like fluid in plasma membrane
allows smooth movement of compounds among organelles
Rough ER
network of membranes with ribosomes
ribosomes - site of amino acid and protein synthesis
Smooth ER
Synthesizes and stores lipids
Golgi Apparatus
has vesicles and folded membranes
sorts and processes proteins
Main Root Functions
anchor plants in soil
absorb water and nutrients
store carbohydrates
Seminal Roots
secondary root that emerges from seed
Nodal Root
roots that emerge from mesocotyl part of the stem (above seed)
Primary Roots
Tap root for dicots
Provide stability
Larger in diameter
Secondary and Tertiary Roots
Secondary - originate from primary roots
Tertiary - fine root form the secondary roots
Meristems
Region of cell division on roots
Allelopathy
root gives off chemicals to inhibit growth of surrounding plants
Stems main fuctions
structure
support
translocation
Primary Stems
stalks (monocots)
trunks
central stem
Tillers
additional stems on grasses
Types of Stems
Cladophyll - flattened stem
Vine - helps optimize light absorption
Stolens - aboveground
Underground - stores carbohydrates
Trichomes
hairs that emit chemicals, toxins, or nectars
Apical Meristems
primary growth
tips of shoots
produces leaves
Cotyledon
leaf from seed
Leaves main purpose
photosynthesis
Gas exchange through stomata
Controls transpiration
Monocot leaves
parallel veins
leaf forms sheath that clasps around stem
Dicot leaves
netted veins
petiole that attaches leaf to stem
Lamina
Green photosynthetic tissue
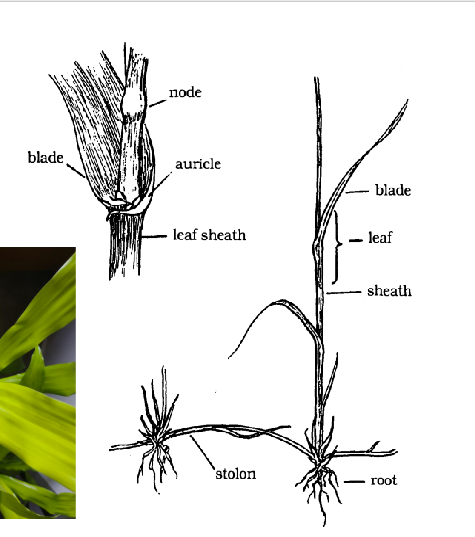
Monocot leaf parts
Monocot leaf parts
Abscission
leaves cut off from water/nutrients then fall to ground
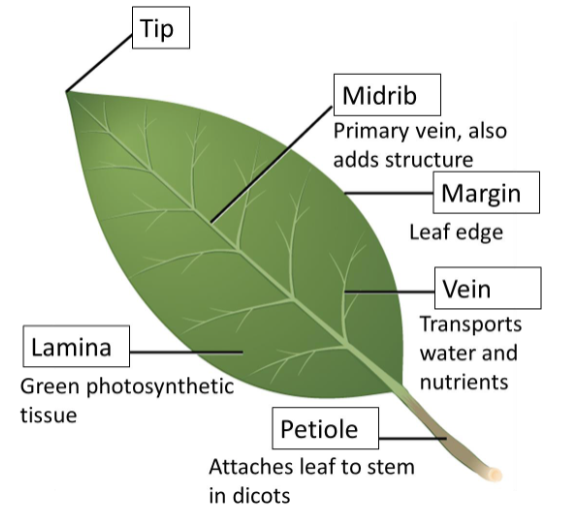
Dicot leaf parts
Dicot leaf parts
Colorful Bract
modified leaf that attracts pollinators
Leaf Structures and Purpose Dicot leaf
Cuticle - protection
Epidermis - protection
Lower Epidermis - protection
Palisade mesophyll - photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll - photosynthesis
Stomata - gas exchange
Vein - water and nutrient transport
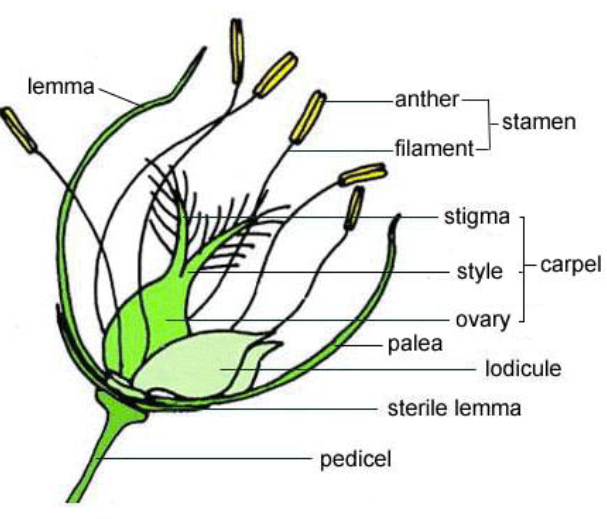
Monocot Flower parts
Monocot flower parts
Fertilization
formation of zygote due to the union of egg and sperm nuclei
Monoecious
stamen and pistil on same plant
Dioecious
stamen and pistil on different plants
Fruit
Ripened ovary of the flower which is controlled by ethylene
Pericarp - ovary wall
exocarp
mesocarp
endocarp
Parthenocarpy
hormones induce fruit set without pollination
3 main seed components
Embryo
Endosperm/cotyledons
seed coat
Gibberellins
plant hormone that is produced when in contact with water
Epigeal Germination
cotyledons are pushed above soil surface
Hypocotyl
Region of stem between cotyledons and radicle
Epicotyl
Region of stem above cotyledons
Hypogeal Germination
cotyledon stays below soil
Coleoptile
protects shoot as it emerges from soil
Dormancy
delay in germination also known as rest
Physiological Dormancy
specific treatment must be given to embryo to initiate growth
Physical Dormancy
when a hard seed coat prevents imbibition (need scarification)
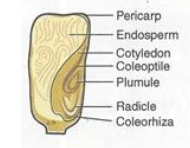
Monocot seed parts
Monocot seed parts
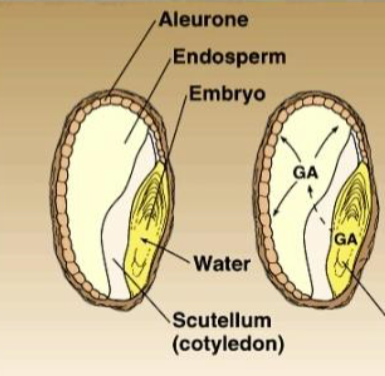
Dicot seed parts
Dicot seed parts