Biodiversity of California Midterm
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
extirpated
extinct in the area where it once existed, but extant (existing) elsewhere
abiotic
not alive (ex. rocks, water)
biotic
alive or once alive (ex. dead living things, plants, animals, bacteria)
winter solstice
shortest day of the year
spring (vernal) equinox
equal day to night length
summer solstice
longest day of the year
autumnal equinox
equal day to night length
latitudinal zones
arctic zones: northernmost and southernmost tips
temperate zones: between the polar and tropical zones
tropical zones: directly above and below the Equator
bioregions
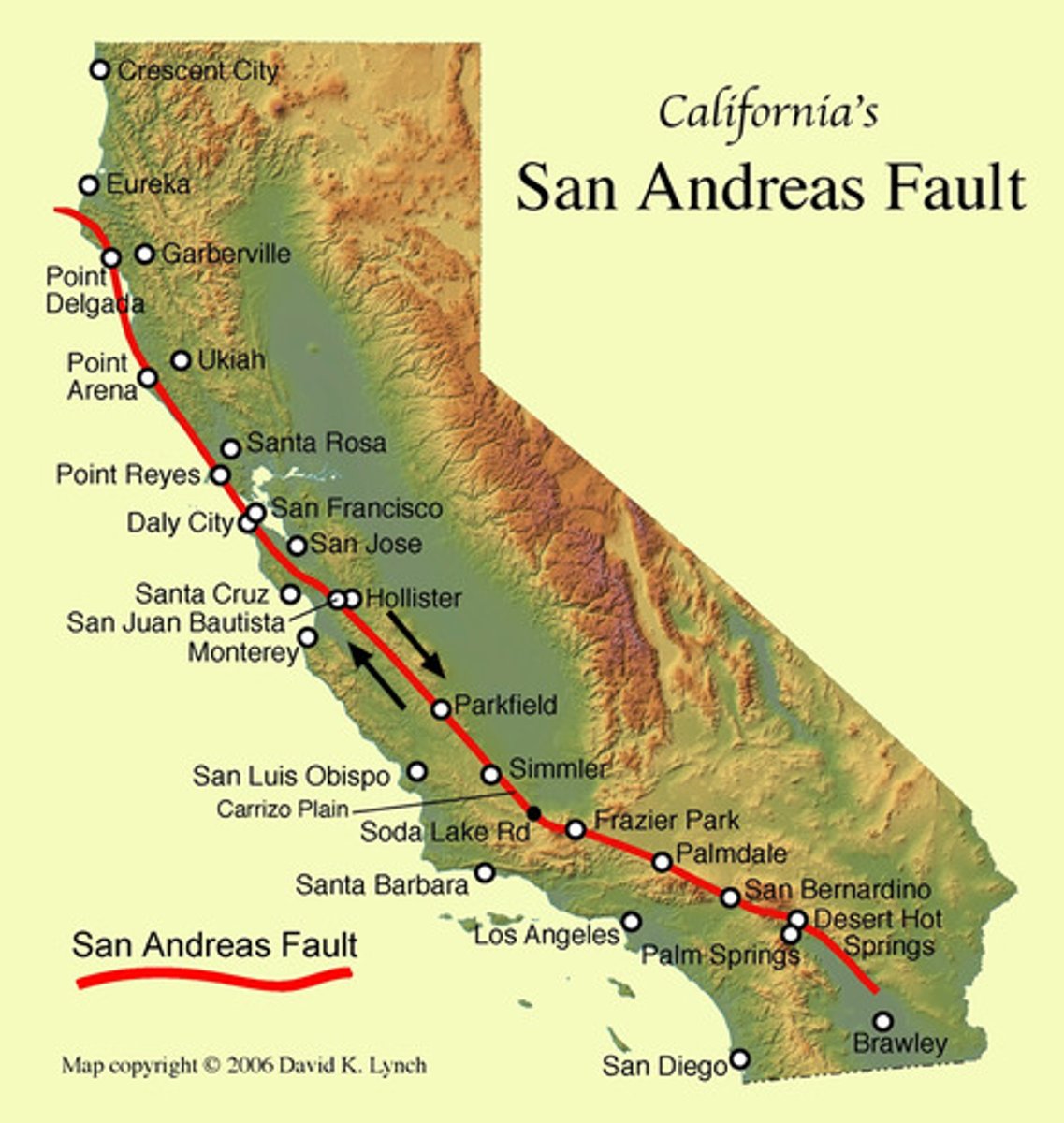
San Andreas Fault in California
a transform fault boundary
Death Valley
the lowest point in North America and hottest place in CA
Mt Whitney
the tallest mountain in continental US at 14,505 feet
Clear Lake
the oldest natural lake in North America
San Francisco Bay/Delta
2nd largest estuary in the US
Methuselah
oldest living tree in Western Hemisphere at 5,000 yrs old
General Sherman Tree
largest tree in the world by volume
mediterranean climate
only 5 region in the world (CA is one of them)
CA Floristic Province
biodiversity hotspot
endemic species
species that occur in one place and nowhere else
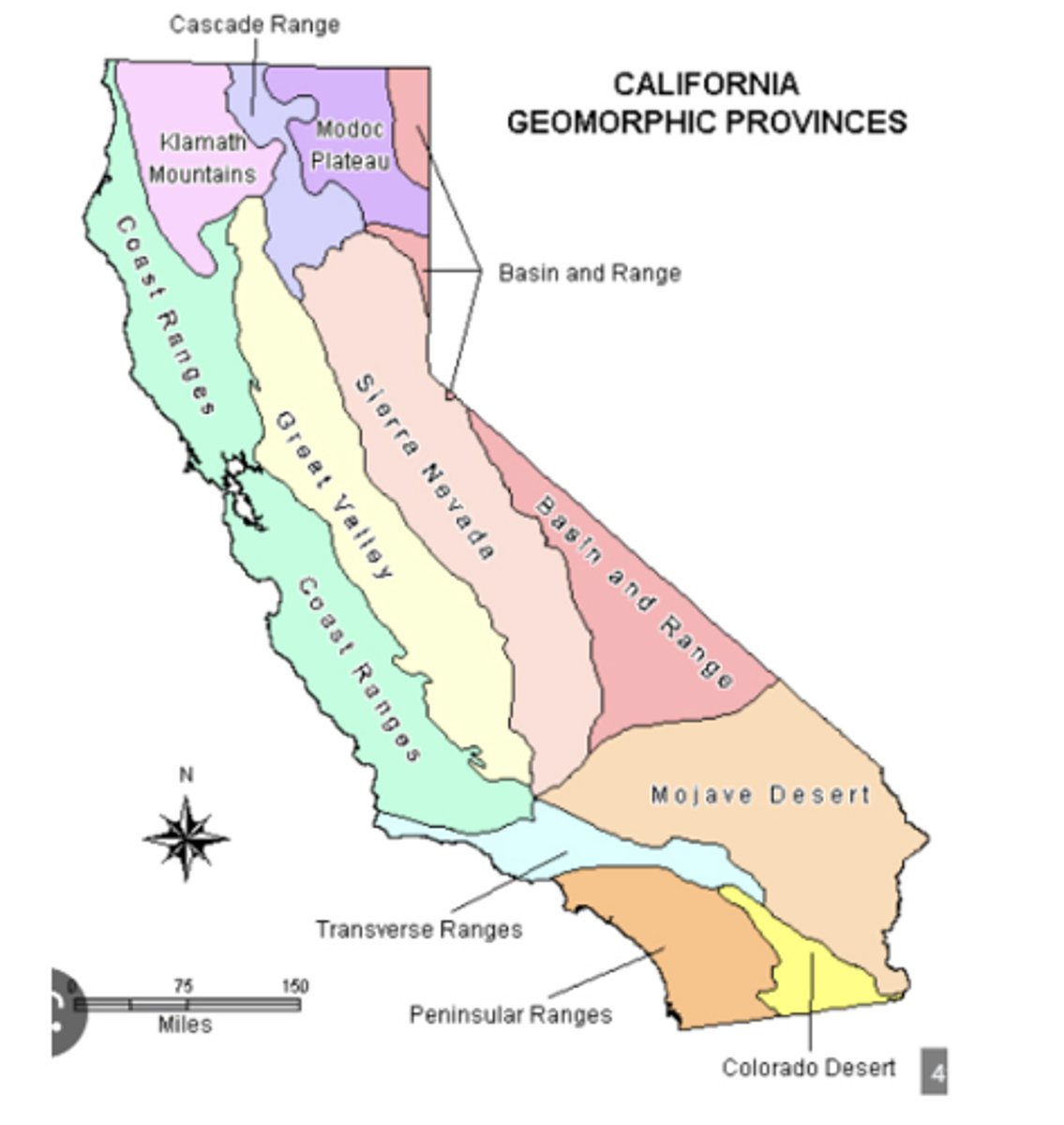
Geomorphic Landform
shape of the land
Geomorphic Provinces
rock types
igneous/volanic (cooled lava),
sedimentary (dust in creek bed),
metamorphic (rock affected by heat/compression;
ex. Serpentinine)
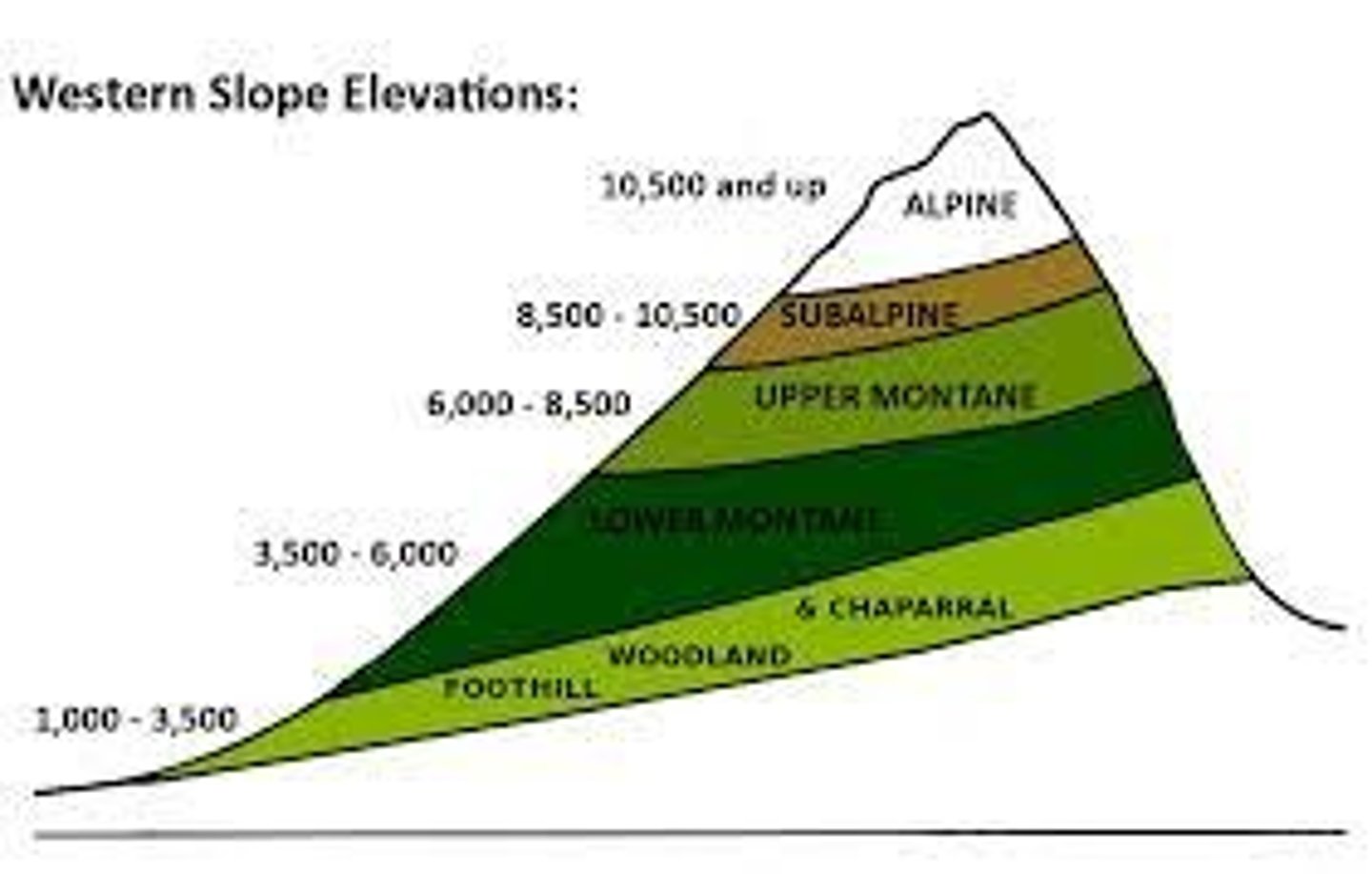
elevation and zonation
Symbiosis
a mutualistic relationship between two organisms and neither can live without the other (ex. Lichen or Micorrhizae)
Mutualism
When two species both benefit from their relationship
Lichen
Symbiotic relationship between Alga and Fungus:
Alga: Photosynthetic and supply energy
Fungus: Decomposer and supplies matter and nutrients
Mycorrhiza
symbiotic association between a fungus and plant
Earth age
4.5 billion years old
3 Domains
Archaea, Bacteria, Eurkaya
4 Kingdoms of Eukarya
Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia
Dear King Phillip, Come Over For Good Supper
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Human Taxonomy: Domain
Eukarya
Human Taxonomy: Kingdom
Animalia
Human Taxonomy: Phylum
Chordata (has a spine)
Human Taxonomy: Class
Mammalia (mammal)
Human Taxonomy: Order
Primates
Human Taxonomy: Family
Hominidae
Human Taxonomy: Genus
Homo
Human Taxonomy: Species
Sapiens
Bloom's Taxonomy
hierarchy of learning
environment
the complete range of external conditions, physical + biological, in which an organism lives
ecosystem
the combination of all living organisms + nonliving features of a given geographic area, with emphasis given to interdependence
habitat
a smaller ecosystem
Abiotic Factors affecting biodiversity
Latitude: amount of solar radiation reaches the area
Precipitation: essential for plant growth
Geology: influences soil type and what plants grow
Topography: influences altitude... temp., and climate
Air Currents: influences temp. and precipitation
abiotic components and ecosystem
rock: geosphere or lithosphere
water: hydrosphere
air: atmosphere
Ecosystem Services definition
a balanced ecosystem that provides valuable benefits for all living things within that ecosystem
Ecosystem Services: Provisioning
what nature provides directly i.e. food, water, building materials, natural resources...
Ecosystem Services: Regulating
air quality, clean water, temp., flood control, growth of crops
Ecosystem Services: Cultural
benefits to humanity i.e. shelter, spiritual comfort, companionship, recreation
Traditional Ecological Knowledge
mutual exchange between nature and people
Franciscan Melange
land mass (plate) went under another plate
Which two tectonic plates is CA at the juncture of?
Pacific plate (moves up)
and North American Plate (moves down)
What are the 3 kinds of fault boundary?
divergent, transform, convergent
weathering
deterioration of rocks, soils, and minerals through contact with water, gases, sun, and organisms
soil structure
air holes, water, and organic (containing carbon) component
soil water availability
the capacity of a soil to hold water for plant use (more organic material = higher capacity)
soil layers (top to bottom)
Humus (organic layer), Topsoil, Subsoil, Weathered rock fragments, Bedrock
CA precipitation
2/3 of rain happens in the North
Water Cycle: Accumulation
the process of water collecting in rivers, lakes, streams, oceans and other bodies of water
Water Cycle: Aquifer
a body of porous rock or sediment saturated with groundwater
Water Cycle: Condensation
the process that changes gaseous water (water vapor) to liquid water
Water Cycle: Evaporation
the process that changes liquid water to a gas (water vapor)
Water Cycle: Groundwater
liquid water stored underground, within cracks in rocks of all kinds and in the pore spaces of sediments and sedimentary rocks
Water Cycle: Infiltration
the process of water being absorbed into the ground
Water Cycle: Precipitation
water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth's surface
Water Cycle: Runoff
precipitation that does not soak into the soil but instead moves on the Earth's surface toward streams
Water Cycle: Streamflow
water moving across the Earth's surface in streams
Water Cycle: Transpiration + Evapotranspiration
water evaporation from plants
pH (potential Hydrogen)
hydrogen %/potential
neutral: 7.0
acidic: < 6
alkaline: > 8
watershed
land area than channels rainfall and snowmelt to creeks, streams, and rivers and eventually outflow points (bays and ocean)
CA's Four Bays
Humboldt, SF, Monterey, San Diego
biomass
anything thats alive that takes up space and has weight (branches, leaves, roots, flowers, dead and live animals)
Protista and Plantae (do photosynthesis
)Which two kingdoms are producers?
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight -> C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
aerobic respiration equation (consumers)
C6H12O6 +6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
metabolism
anabolism
+ catabolism
anabolism
building up glucose (photosynthesis)
catabolism
breaking down (aerobic respiration)
Trophic Levels
sun -> primary producers (autotrophs) -> primary consumers (herbivores) -> secondary consumers (primary carnivores) -> tertiary consumers (secondary carnivores)
autotroph
an organism that makes its own food
food chain
follow energy in one transfer from one organism to the next to the next and next...
food web
series of food chains
competition
multiple organisms seek the same limited resources
resource partitioning
to avoid competition, individuals will seek other available resources
scavengers
feed on dead animals
decomposers
feed on the energy & nutrients of other organisms
omnivores & carnivores
generalists; switch food sources based on availability
trophic levels diagram
90% of energy lost with each transfer; arrow drawn in order of energy transfer
The Carbon Cycle
Solid: coal, graphite
Liquid: oil
Gas: CO2
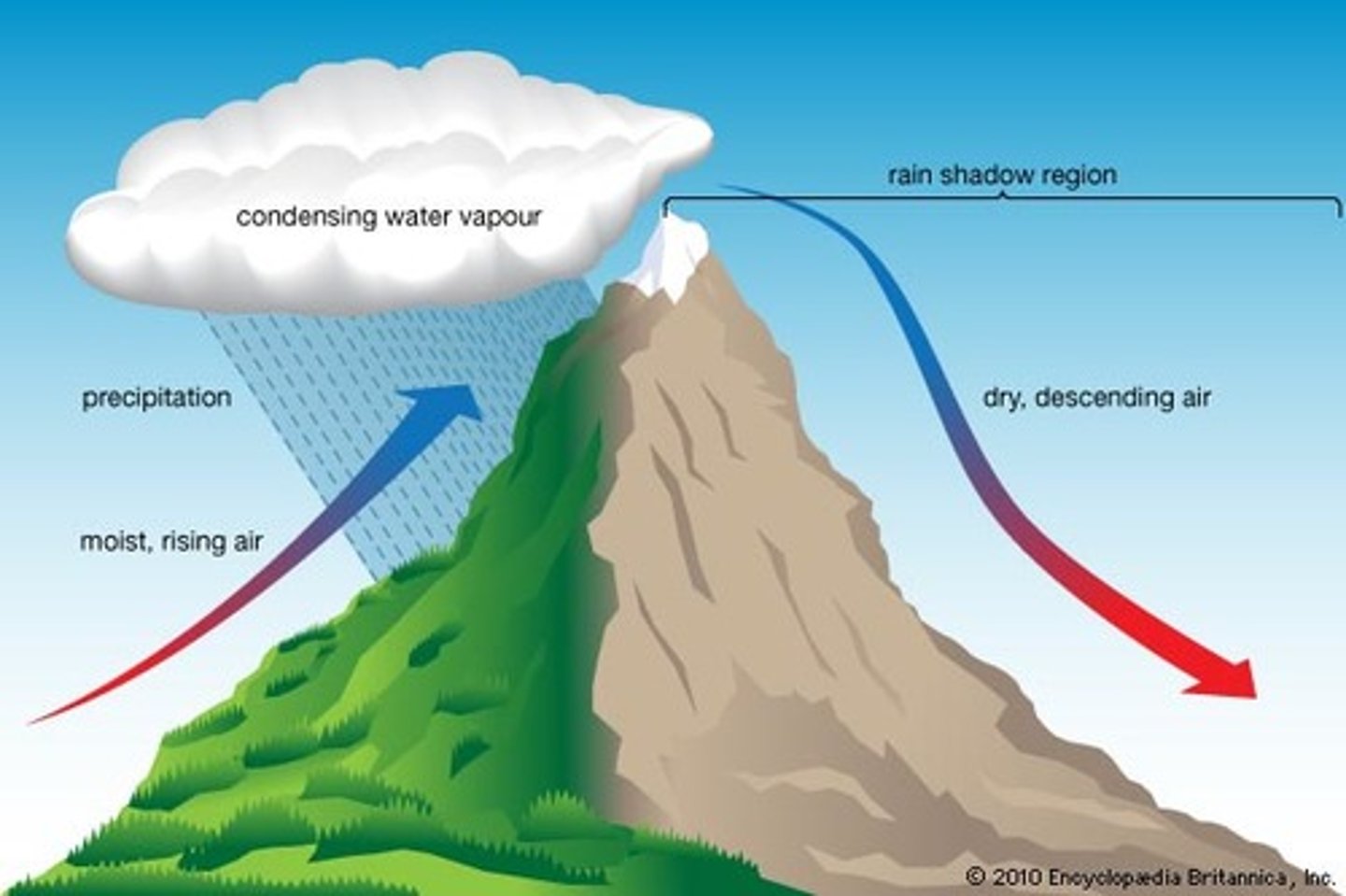
Orographic Effect
The movement of air masses forced to flow over high topography (land). Moist air comes off the ocean as coastal fog (oceanic water vapor turned into clouds) and is lifted over mountains
cooling effect that occurs when air is forced to rise over a mountain, resulting in a wetter windward side and a drier leeward side
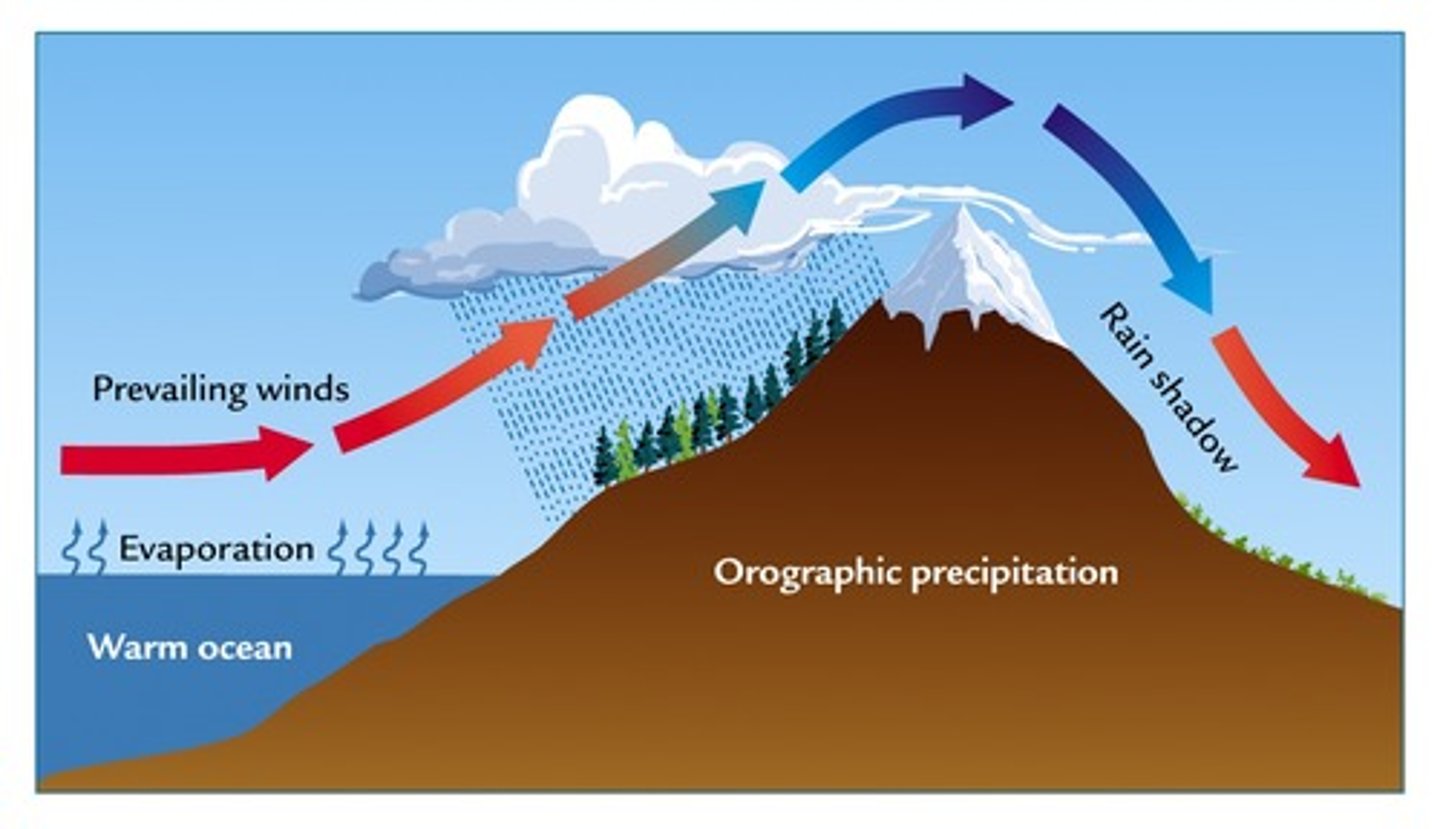
Rainshadow Effect
Caused when moisture is squeezed out of air due to orographic flow
Precipitation falls on the windward side of a mountain range, resulting in lush vegetation & a warm, moist climate on one side, but a desert area on the leeward side.
Homology
the study of how different structures develop similar changes of adaptations
Types of Vertebrates
amphibians, fish, birds, mammal, reptiles
warm-blooded
internal temp. is warmer than outside (birds + mammals)
cold-blooded
internal temp. same as outside ( fish, amphibians, reptiles)
axial skeleton
torso
appendicular skeleton
appendages
How long have scientists documented global climate change?
over 500,000 years
~ 12,000 years ago
\When did the last Ice Age end?
Where is the first CA record of human existence?
Santa Rosa Island, dating back 13,000 years