building blocks nucleic acids purines and pyrimidine metabolism
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
what is the difference between nucleotide and nucleoside
nucleotides contain a phosphate
what are the shared components of nucleotides and nucleosides
pentose sugar
5 types of nitrogenous bases
what is the pathway that forms an intermidate metabolite ribose-5 phosphate
pentose phosphate shunt/hexose monophosphate HMP shunt
where is ribose found
RNA
where is deoxyribose found
DNA
which carbon is considered the 1° carbon
the carbon containing the nitrogenous base
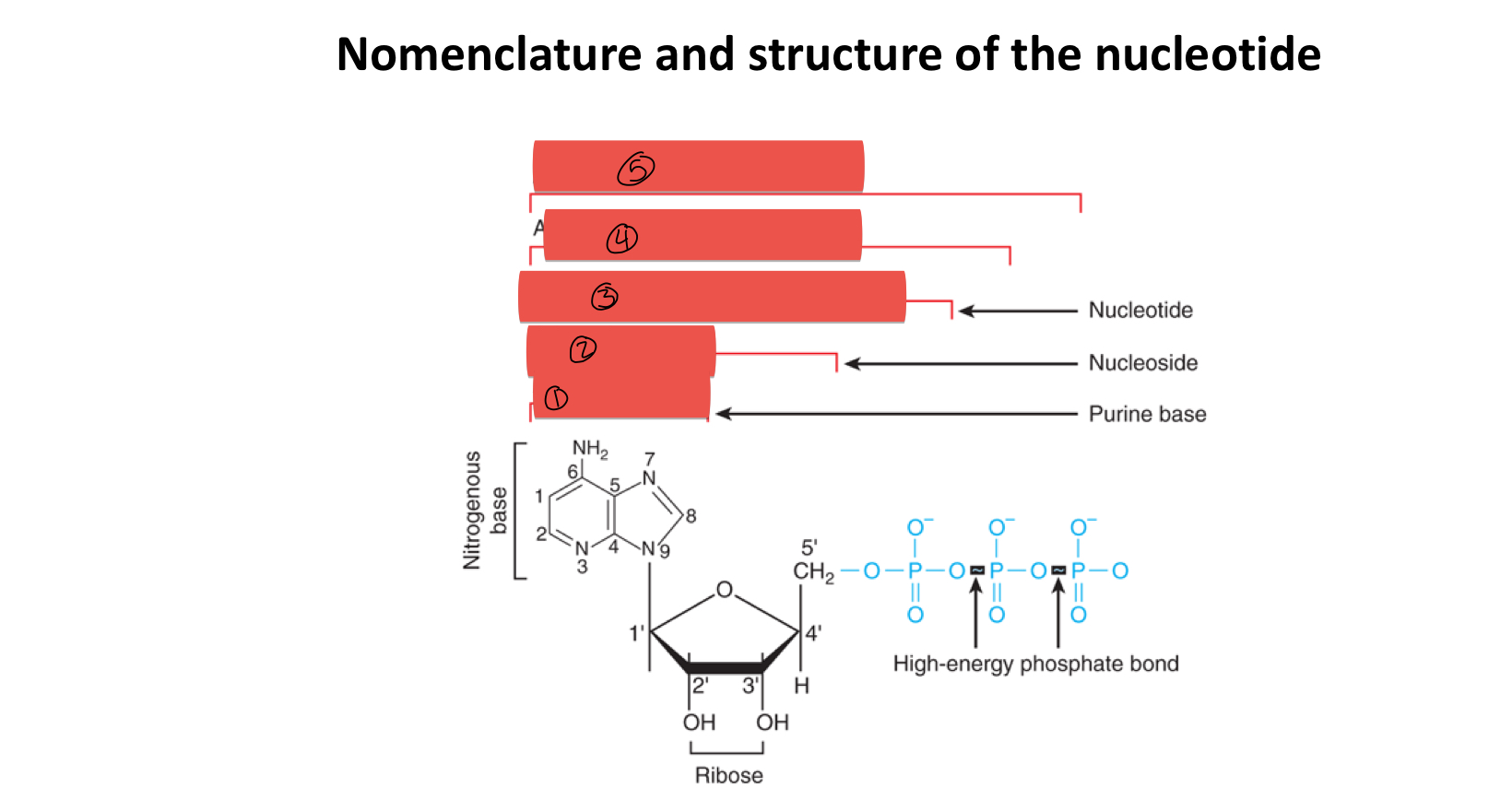
what is 1
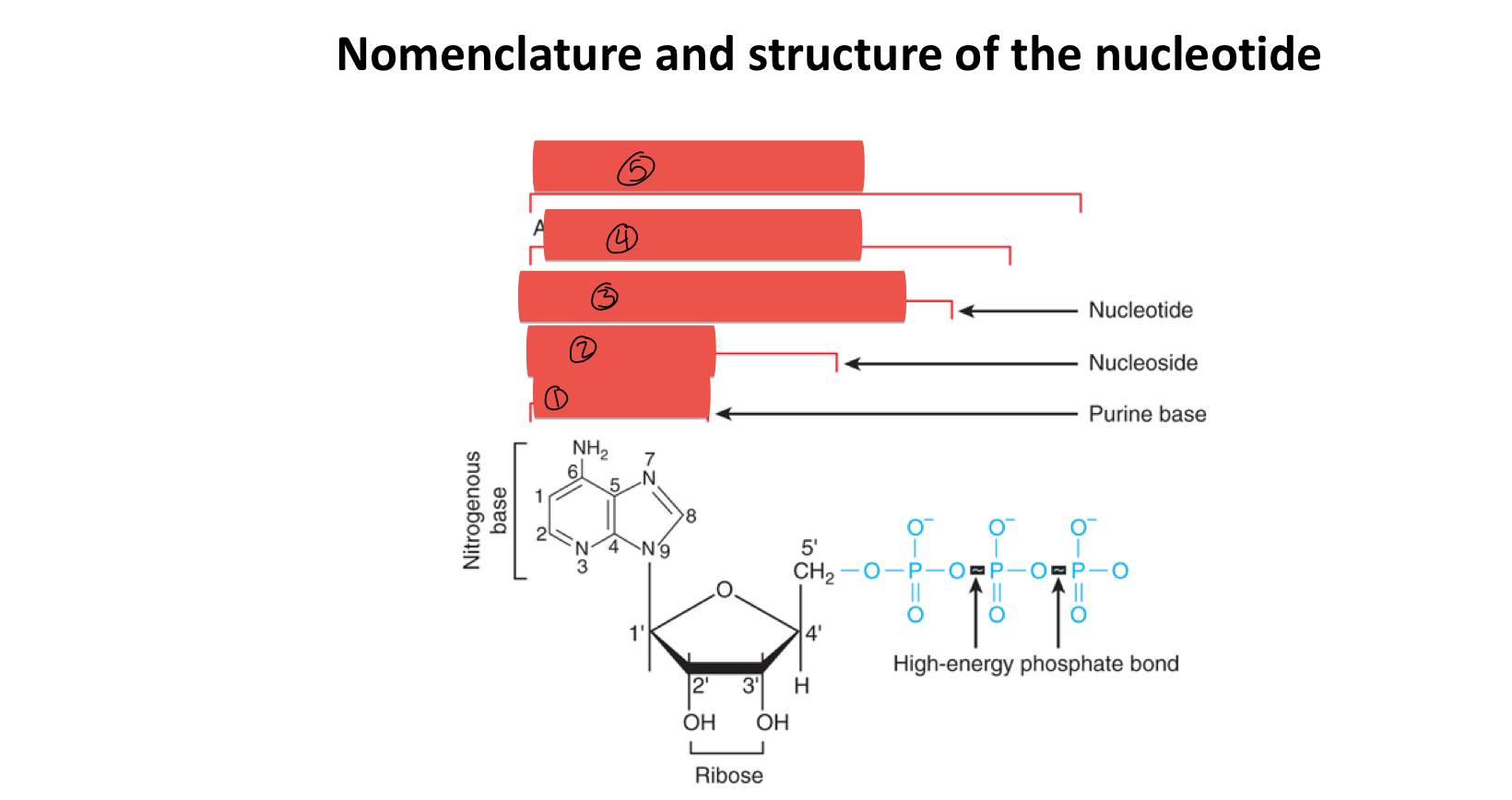
what is 2
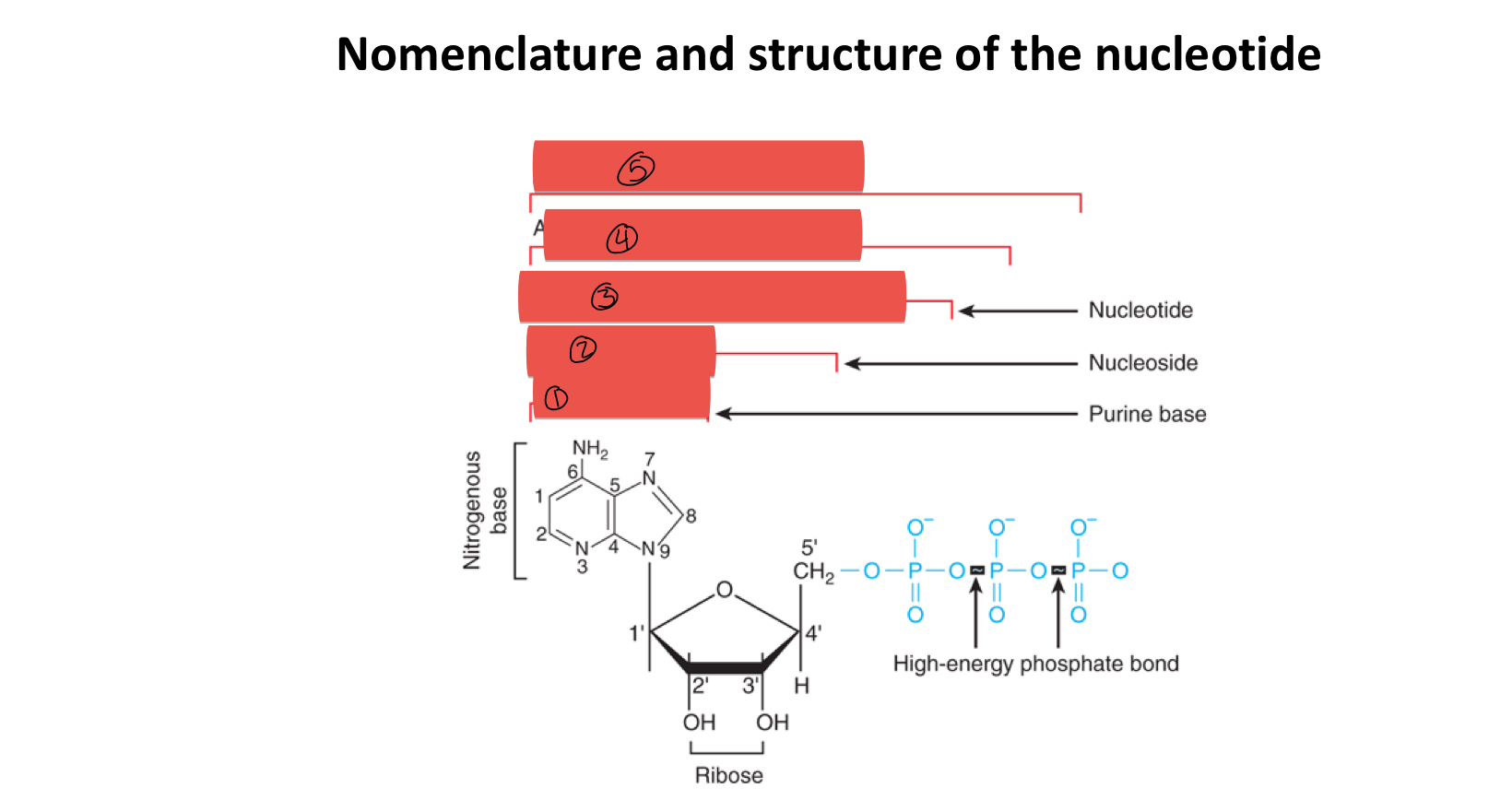
what is 3
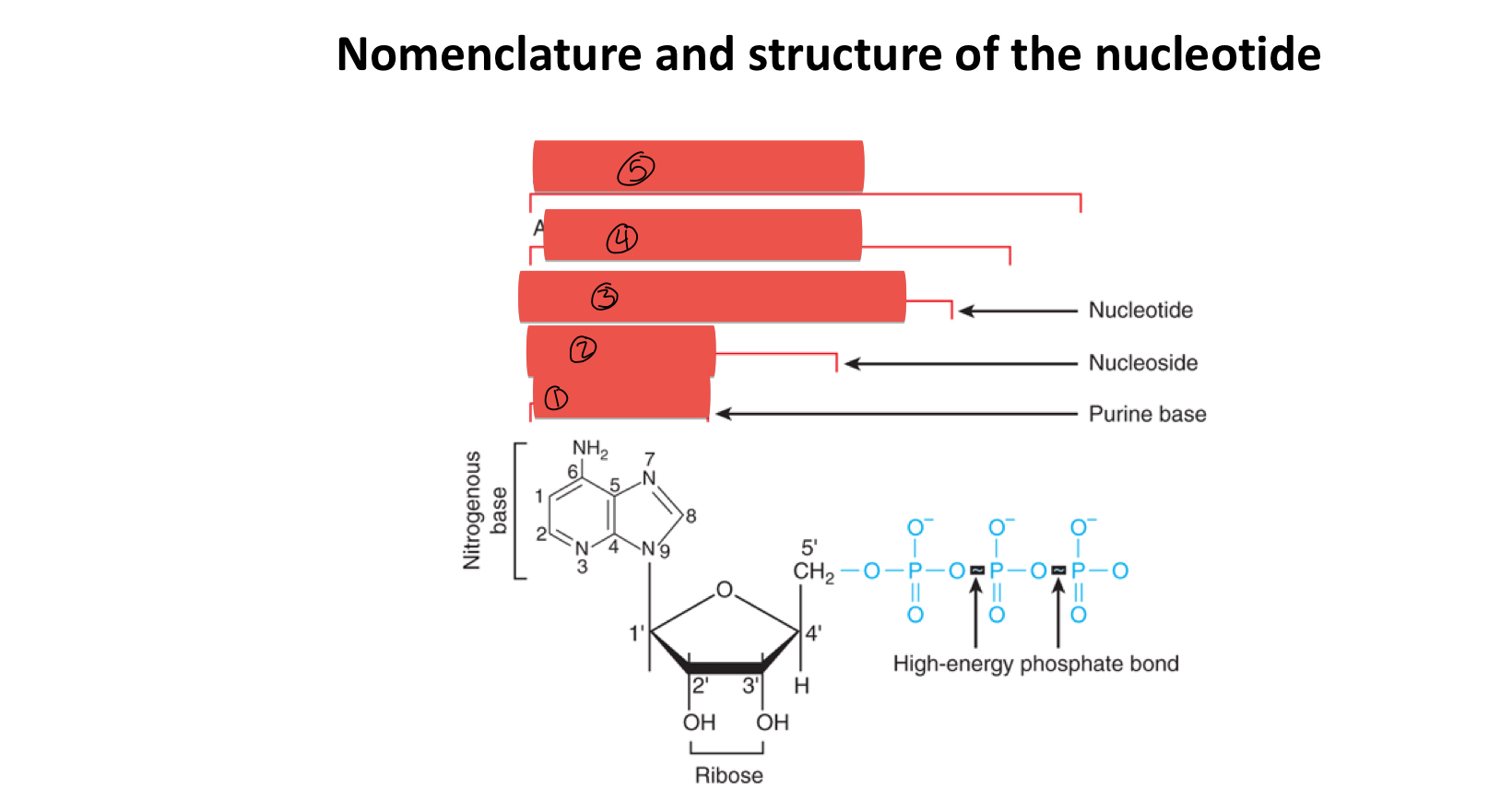
what is 4
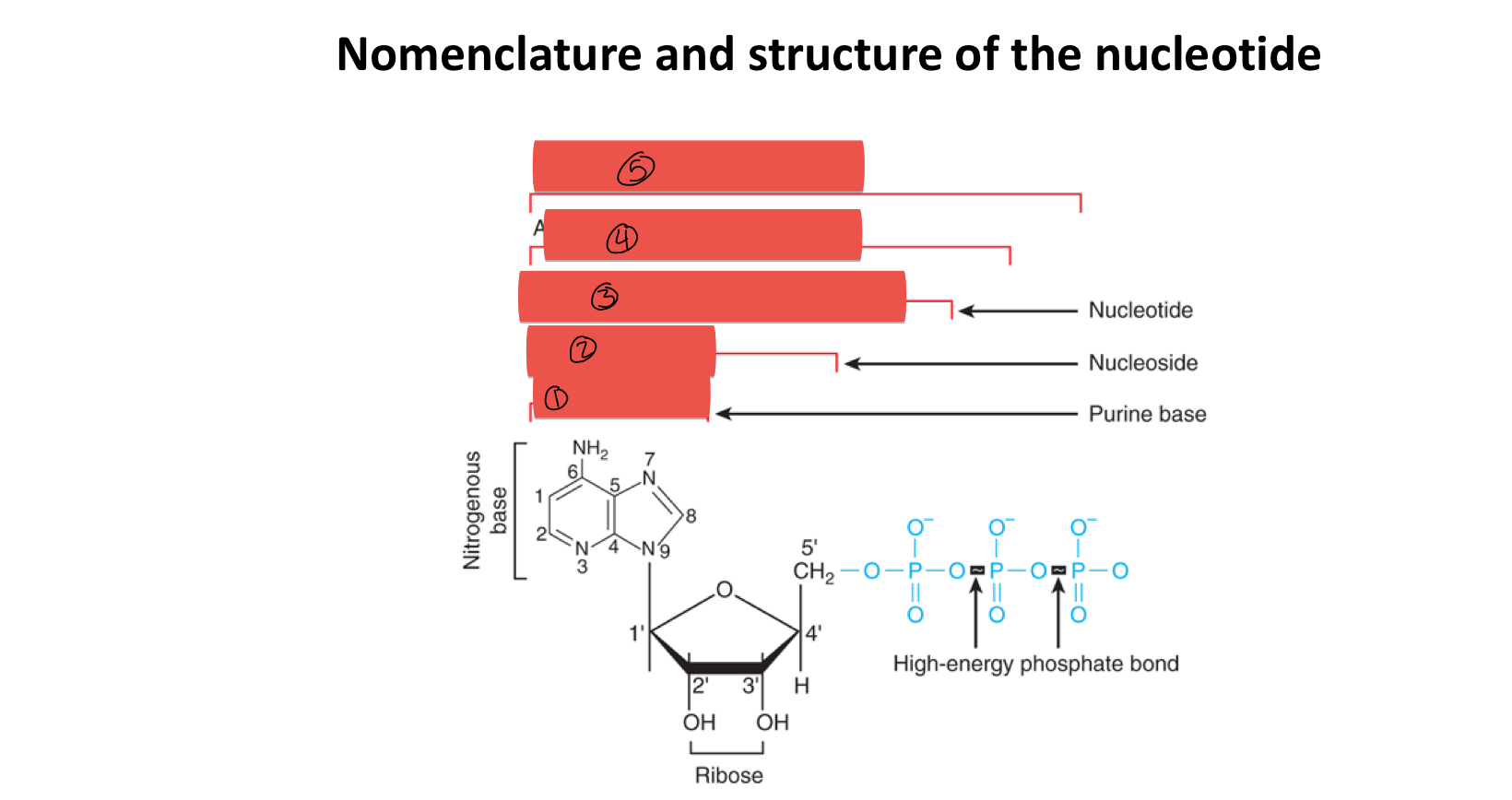
what is 5
how many rings does purine contain
2
how many rings does pyrimidine contain
1
what bases are purine
adenine
guanine
what bases are pyrimidine
cytosine
thymine
uracil
what bases does DNA contain
a
g
c
t
what bases does RNA contain
A
G
C
U
what nucleosides are associated with adenine
adenosine
deoxyadenosine
what nucleotides are associated with adenine
AMP
dAMP
ADP
dADP
ATP
dATP
what nucleosides are associated with guanina
Guanosine
deoxyguanosine
what nucleotides are associated with guanine
GMP
GDP
GTP
what nucleosides are associated with cytosine
cytidine
what nucleotides are associated with cytosine
CMP
CDP
CTP
what nucleosides are associated with uracil
uridine
what nucleotides are associated with uracil
UMP
UDP
UTP
what nucleosides are associated with thymine
thymidine
what nucleotides are associated with thymine
dTMP
dTDP
dTTP
what are the functions of nucleotides
building blocks
source of energy
signal molecules
activators for transfer of groups
regulators
carrier molecules
what is the goal of de novo purine synthesis
create AMP and GMP
what are the ingredients for de novo purine synthesis
ribose 5 phosphate
whats the nitrogen source for de novo purine synthesis
amino acids
glycine
aspartate
glutamate
what is the carbon source for de novo purine synthesis
tetrahydrofolate THF
CO2
what is PRPP synthetase stimulated by
intracellular phosphate
what is PRPP synthase inhibited by
AMP
IMP
GMP
what is PRPP glutamyl amidotransferase stimulated by
PRPP
what is PRPP glutamyl amidotransferase inhibited by
AMP
IMP
GMP
what is adenylosuccinate synthase inhibited by
AMP
what is IMP dehydrogenase inhibited by
GMP
what are the inhibitors of purine synthesis
6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) and its prodrug azathioprine
mycophenolate
what does 6-MP inhibit specifically
PRPP to IMP
what does mycophenolate inhibit specifically
IMP dehydrogenase
what is purine salvage pathway
recycled purine bases + PRPP → PPI + purine mono nucletides (AMP, GMP, IMP)
what enzymes are associated with purine salvage pathway
adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT)
hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)
what is the product of purine salvage pathway
AMP
GMP
IMP
what does a dificiency of HGPRT lead to
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
what is purine metabolized into
uric acid
what is purine excreted in
urine as urate anion
what are the steps in AMP degredation
AMP → adenosine → inosine → hypozanthine → xanthine → uric acid
what is the location of deoxyribonucleotide synthesis
all tissues
what are the steps in GMP degradation
GMP → guanosine → guanine → xanthine → uric acid
what substrates are associated with the synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides
ADP
CDP
UDP
NADPH
***must be diphosphates
what are the products of deoxyribonucleotide synthesis
dADP
dCDP
dUDP
dGDP
what does ribonucleotide reductase act to do?
reduce the ribonucleotide to deoxyribonucleotide
what provides the reducing power for the ribonucleotide reductase
two sulfhydryl froups
what is oxidized in the process of the synthesis of deoxyribonucleotide
thioredoxin
what does thioredoxin reductase require to convert the oxudized state of thioredoxin back to the reduced state
NADPH
what is the goal of de novo pyrimidine synthesis
create UMP
what is the nitrogen source of de novo synthesis
carbamoyl phosphate
what is the nitrogen source for de novo pyrimidine synthesis
amino acids (aspartate and glutamine)
what is the carbon source for de novo pyrimidine synthesis
tetrahydrofolate THF
CO2
where is CPS 2 present in
cytosol
where is CPS 2 used
pyrimidine synthesis
what is the nitrogen source for CPS 2
glutamine
how is CPS 2 activated
PRPP
how is CPS 2 inhibited
UTP
where is CPS 1 present
mitochondria
where is CPS 1 used
urea cycle
what is the nitrogen source for CPS 1
ammonia
how is CPS 1 activated
N-acetyl glutamate
is adenine and guanine a purine or pyrimidine
pureine
is cytosine, thymine, and uracil a purine or pyrimidine
pyrimidine
what base pair melts/ breaks apart at lower temps and why?
AT bonds because they only share 2 H-bonds.
what two things added together composes a nucleoside
base and sugar
what two things added together gives you a nucleotide
nucleoside and phosphate group
what is the sequence of purine synthesis pathway
ribose 5-P → PRPP → IMP → AMP or GMP
what is the first purine nucleotide formed in the purine synethesis pathway?
IMP
which drug inhibits the enzyme IMP dehydrogenase thereby blocking GMP synthesis?
Mycophenolate
what does hypoxanthine and PRPP combined result in
IMP
what does guanine and PRPP combined result in
GMP
what does adenine and PRPP combined result in
AMP
what is HGPRT inhibitedd by
IMP and GMP
what does a deficency in HGPRT result in
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
what are the clinical features of lesch-nyhan syndrome
high uric acid levels
congenitive issues and delayed development
muscle movement problems (dystonia and chorea)
agressive behavioir, self harm
gouty arthritis
is lesch nyhan syndrome x linked recessive or x linked dominant
x linked recessive
what enzyme does lesch nyhan syndrome lack
HGPRT enzyme
what causes high uric acid in lesch nyhan syndrome
the inability to recycle guanine and hypoxanthine
what causes extra purine production in lesch nyhan syndrome
more PRPP and less IMP and GMP
what are the clinical importance of hyperuricemia
Overproduction or underexcretion of uric acid → hyperuricemia → gout
what are the risk factors of hyperuricemia
High-protein, high-fat diet, fructose, alcohol
what are the clinical features of hyperuricemia
Joint urate crystal deposition → Monoarticular arthritis, tophi, kidney stones
what are the treatment options for hyperuricemia
Allopurinol/febuxostat inhibit xanthine oxidase, increase soluble compounds
what does HCO3 + glutamine + 2ATP result in
carbamoyl phosphate
what does carbamoyl aspartate result in
orotate
what does orotate + PRPP result in
UMP
what does UMP + ATP result in
UDP
what does UDP + ATP result in
UTP
what does UTP + glutamine + ATP result in
CTP
what enzyme is missing in hereditary orotic aciduria
UMP
what are the symptoms of hereditary orotic aciduria
stunted growth
orotic acid crystals in urine
mmegaloblastic anemia