1.3 - muscle and nerve excitability
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
chemical
thermal
physical
what are the 3 physiological response to electrical current
NaCl (ECM is like salt water, split into Na+ and Cl- ions)
what is the ionic compound that is split due to electro stimulation from electrochemical effects
cathode (Na is + so it attracts negative)
Na will be attracted to (anode or cathode)
anode (Cl is - so it attracts +)
Cl will be attracted to (anode or cathode)
cathode (because it is - and has a lot of + around it)
it is easier to generate action potential under a (anode or cathode)
HCl (remember it attracts Cl-)
anode will form (HCl or NaOH)
NaOH (remember it attracts Na+)
cathode will form (HCl or NaOH)
acidic; down (AAA - anode, attracts, acid)
anode will have a _________ reaction so pH will go ____________
alkaline; up
cathode will have a _________ reaction so pH will go _________
sclerotic
an anode reaction has a (sclerotic or sclerolytic) process
sclerolytic
a cathode reaction has a (sclerotic or sclerolytic) process
hardens
the skin (softens or hardens) with an anode reaction
softens
the skin (softens or hardens) with an cathode reaction
heat
“Energy is neither created nor destroyed, but rather exchanged.”
during this exchange, some energy is lost in the form of ________.
amount of current flowing
resistance to current
duration
the amount of energy that is lost in the form of heat is dependent on what 3 things
F (this means that it does accumulate heat, this is not normal)
T/F: the skin resists the transcutaneous delivery of current so it doesn’t accumulate heat
tissue impedance
____________ is the resistance of the tissue to the passage of electrical current flow
high
bone, fat, fascia are examples of high or low impedance
low
nerves and muscle are examples of high or low impedance
increases
impedance (increases or decreases) with edema, ischemia, scarring and denervation
decreases
impedance (increase or decreases) with open wounds and abrasions
F (it increases… duh)
T/F: dry skin will decrease skin impedance
T
T/F: oily skin will increase skin impedance
-70 mV
what is the action potential threshold


pos; neg
the resting membrane potential has more (pos or neg) outside and more (pos or neg) inside
amplitude and duration
with sufficient _________ and _________, electrical stimulation will cause the nerve to depolarize and generate an action potential
FALSE!!!!!!!! ITS THE NERVE!!!!!!!!!!
T/F: the electrical stimulation is polarizing the muscle to initiate a physiological stimulation
T (the nerve dont care where the buzz comes from, it’s gonna do it’s thang)
T/F: The body responds the same way to the action potential as it would if initiated by physiological stimulation (i.e., the brain)
blue, orange, purple
which dot(s) depolarize
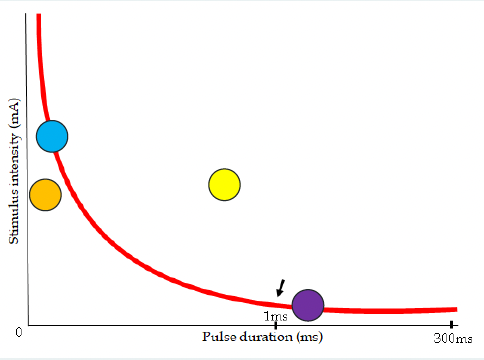
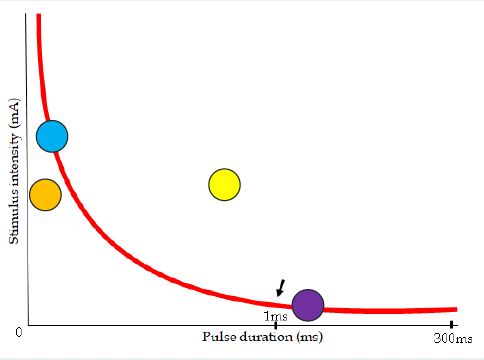
suprathershold (yellow dot, gonna be uncomfy)
____________ stimulus triggers a response in an excitable cell and it is stronger than the minimum threshold
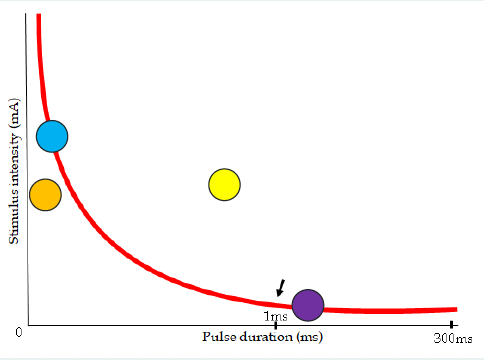
subthreshold (orange dot)
a ____________ stimulus doesn’t trigger a response because it didn’t meet the threshold
rheobase
____________ is the minimum intensity capable of eliciting minimally detectable motor response
nope
can you stimulate a nerve if the intensity is below the rheobase
chronaxie
__________ is the time needed by a current, whose intensity is double the rheobase, to excite the nerve
less (this is how the nerve is depolarized first and not the muscle)
chronaxie in nerves is (less or more) than muscle fibers
greatest; lowest (like myelin on the nerves)
nerve fibers with the (least or greatest) diameter and (lowest or highest) resistance depolarize first
A-alpha (proprioception, motor)
A-beta (touch, pressure)
A-delta (pain, temperature)
C
what is the nerve fiber order of depolarization (first to last)
A-alpha
the __________ nerve fiber detects proprioception, motor
A-beta
the __________ nerve fiber detects touch and pressure
A-delta
the __________ nerve fiber detects pain and temperature
C
the __________ nerve fiber detects pain
sensory → motor → pain
A-beta
(fibers are proprioception, motor → touch, pressure → pain, temp)
(we feel the other way around bc we are human and have skin)
disregard the order or nerve fibers that are stimulated first, what do we ACTUALLY feel first with electrode stimulation? what is that nerve fiber?
closest (this is why we feel/A beta before motor response)
the fibers that are (closest or furthest) away to the electrode will be excited first
A alpha
in order to stimulate the _________ nerve fiber, you need to increase the intensity/amplitude or pulse duration for a motor response