Honors Chemistry Final Exam Review
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
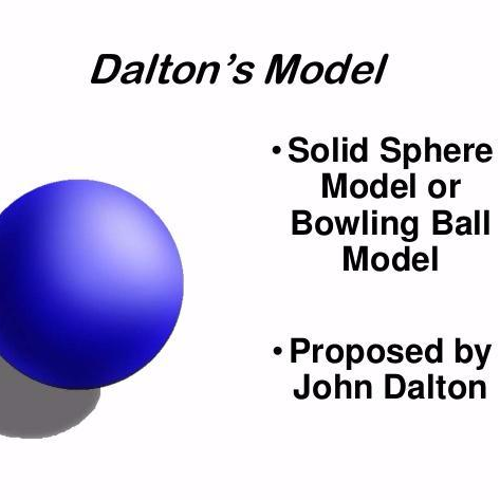
Dalton
Diagram: Billiard Ball Model, Solid, Individual spheres that can bond
Evidence: Priestley Lavoisier + Diamond experiments
Justification: Compounds can be broken apart into simpler substances. Simpler Substances can combine in fixed ratios. In both cases, new properties emerge
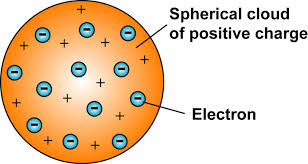
Thomson
Diagram: Chocolate Chip Cookie Model, small negatively charged electrons and positive charged spread spread throughout
Evidence: Cathode Ray Experiments
Justification: The Cathode Ray itself is a beam of electrons. It moves away from the negative end of the magnet. Light dosen’t do that, Matter does.
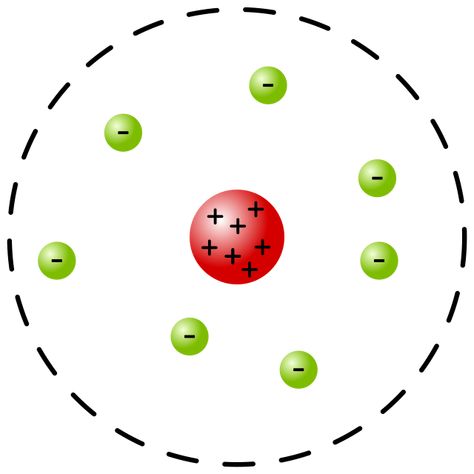
Rutherford
Diagram: Most of the atom is empty space, Positive charge is condensed in the nucleus
Evidence: Gold Foil Experiment
Justification: Most positively charged alpha particles passed right through the gold. The small % that were deflected off that straight path did so because they approached the dense positive nucleus.
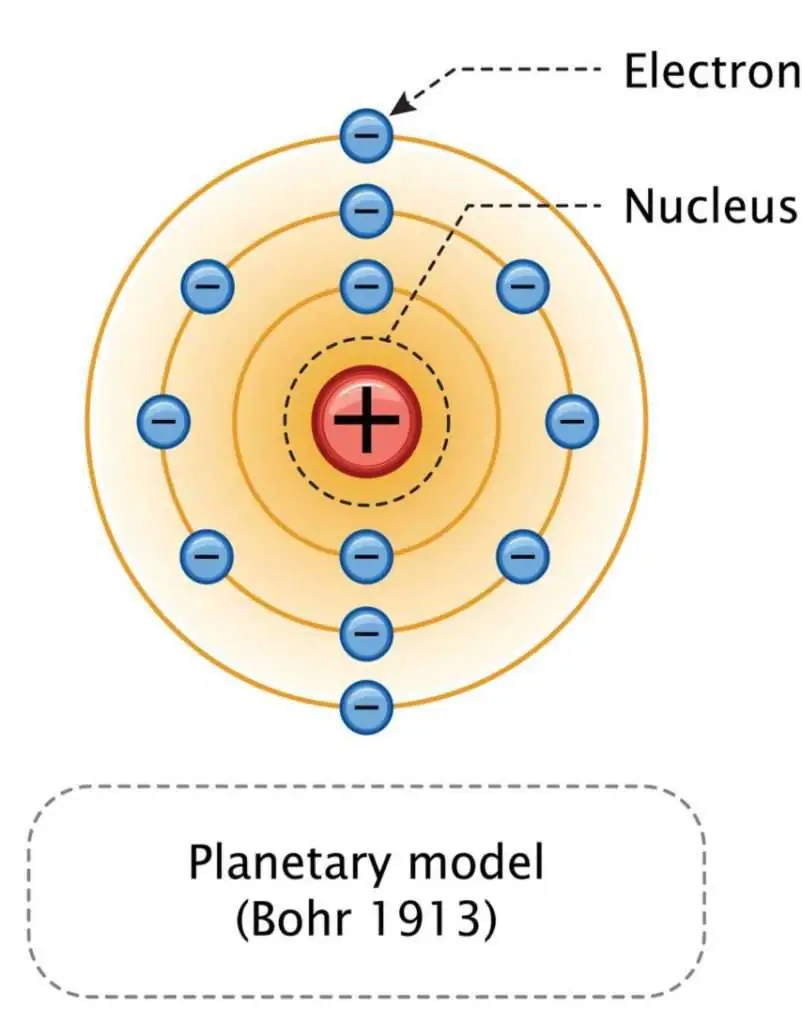
Bohr
Diagram: Electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances (energy levels)
Evidence: Line Emission Spectra
Justification: Electrons jump up to higher energy levels when they absorb energy. When they fall back down, they release energy we can see as light. Each line on the spectrum is a specific fall an electron made. They only have specific colors (not all wave-lengths)
Electronegativity
The tendency to attract electrons
Nonpolar covalent bond
X < 0.3
e- spends equal time around each atom (equal sharing)
Polar Covalent Bond
0.3 < X < 1.67
e- are shared
Ionic bond
X > 1.67
e- are transferred from metal to non-metal
molecular Compound
Low melting and boiling point
Individual molecules
Poor conductor
Ionic compound
High melting and boiling point
Complex crystal lattic
Good Conductor when liquid or dissolved
Anion
an atom that has more electrons than protons
an atom with a negative charge
Cation
a positively charged ion that is formed when a metallic element loses one or more electrons.
positive charge
Mono = 1
Di = 2
Tri = 3
Tetra = r
Penta = 5
Hexa = 6
Hepta = 7
Octa = 8
Nona = 9
Deca = 10
Mono =
Di =
Tri =
Tetra =
Penta =
Hexa =
Hepta =
Octa =
Nona =
Deca =
Relative Mass
Mass relative to (compared to) the least massive item in the comparison group
Molar Mass
Mass of one mole of a substance; found on periodic table
Br H O F I N Cl
Diatomic Elements
Empirical formula
Is the simplest ratio of elements in a compound based on experimental evidence
Molecular formula
Is the actual mole ratio of elements in a compound based on the amount and empirical formula
Coefficient
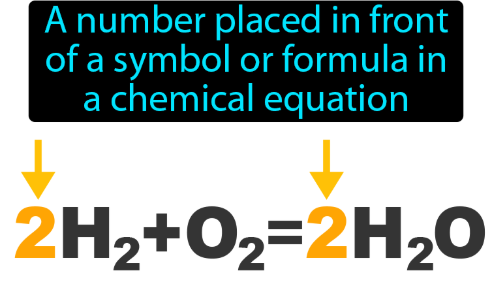
Subscript

Double Replacement
A reaction in which the positive and negative ions of 2 ionic compounds exchange places to form 2 new compounds
FeS + 2HCI —> H2S + FeCl2
Combustion
A carbon compound is burned in oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water
( Carbon compound + O2 —> CO2 + H2O )
CH4 + 2O2 —> CO2 + 2H2O
Synthesis
Reaction in which multiple reactants combine to form a single product
( Exothermic)
N2 + 3H2 —> 2NH3
Decomposition
Reaction in which one reactant breaks down into 2 or more products
( Endothermic)
8Li2S —> 16Li + S8
Single Replacement
Reaction in which a single, more reactive element replaces an element in a compound, producing a new compound and a pure element
ZnBr2 + F2 —> ZnF2 + Br2
Color change
New Odor or Texture
Bubbling/Smoke/Gas (Effervescence)
Release of light
Solid form from liquid mixture (precipitate)
What are some examples of evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place?
energy in reactions
All chemical reactions absorb and release energy
Breaking bonds require an input of energy (Endothermic)
Making new bonds release energy (Exothermic)
Eth-Motion of particles
Eph-Spacing of particles
Ech-Bonding within particles
Atoms rearrange
Total # of atoms involved stays the same
Reactant bonds are broken, product bonds are formed
No matter (atom) is created or destroyed. All atoms are accounted for before (reactants side) and after (products side)
Describe key characteristics of all chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry
Using mole rations in a balanced equation to answer: How much do I need? How much can I make?
Theorectical Yield
If nothing does wrong the amount of product you can produce
Acids
H+ Donor
Low pH
Sour
Reaction to Mg
Reaction with baking soda
No reaction with lemon
Good conductors (have ions)
Base
H+ Acceptor
High pH
Bitter
No reaction with Mg
No reaction with baking soda
Turned a different color with PTP
Good conductors (have ions)
Solute
The substance that is dissolved
Solvant
The thing in which the substance is dissolved in
Strength
Degree to which it ionizes
Concentration
Measured in Molarity (M)
Strong Acids
HCl - Hydrochloric Acid
HNO3 - Nitric
H2SO4- Sulfuric
HClO4 - Perchloric
HClO3 - Chloric
HBr - Hydrbromic
HI - Hydroidoic
Atomic Number
Is determined by the amount of protons
Mass number
Is determined by Neutrons + Protons
Element Symbol
Is determined by the amount of protons
Isotopes
Same amount of protons but different amount of neutrons
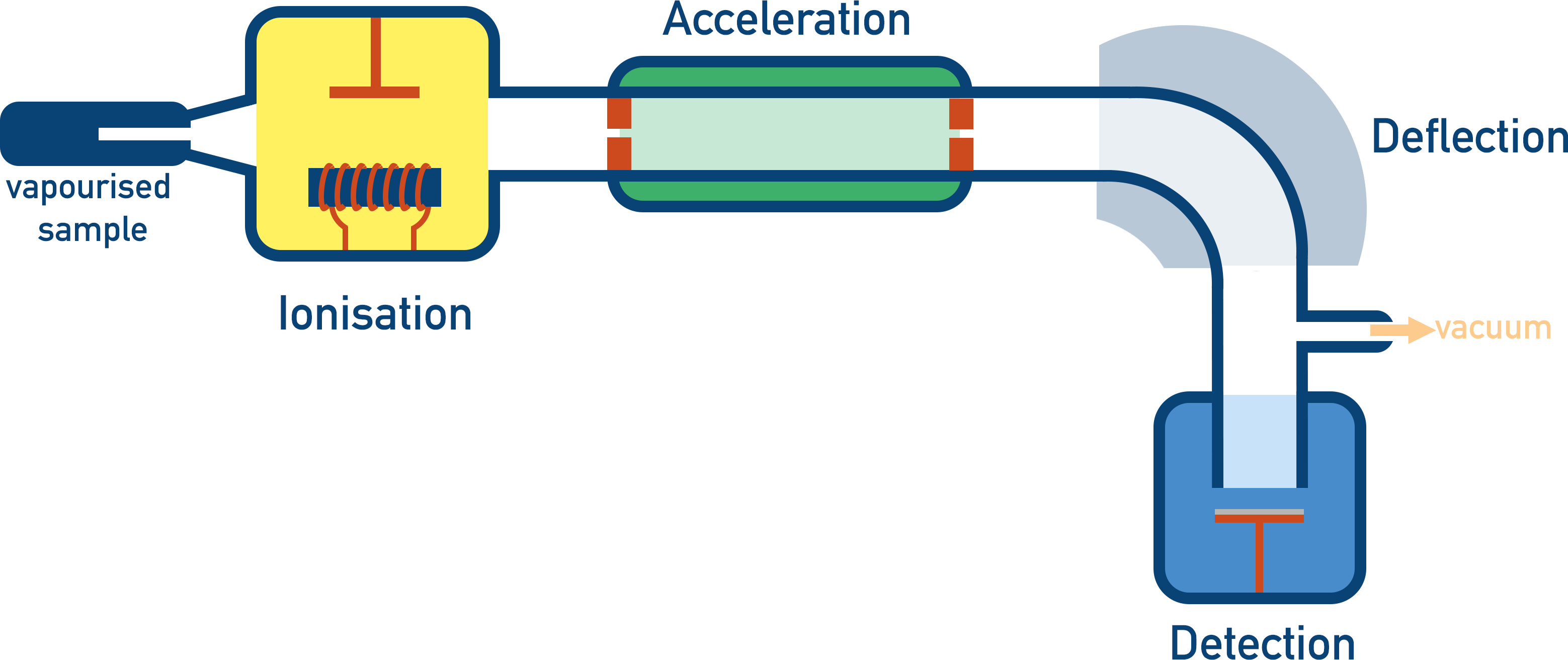
Mass Spectrometer
to analyze the composition of a sample by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of ions produced from it
Bigger particles are harder to deflect of their path