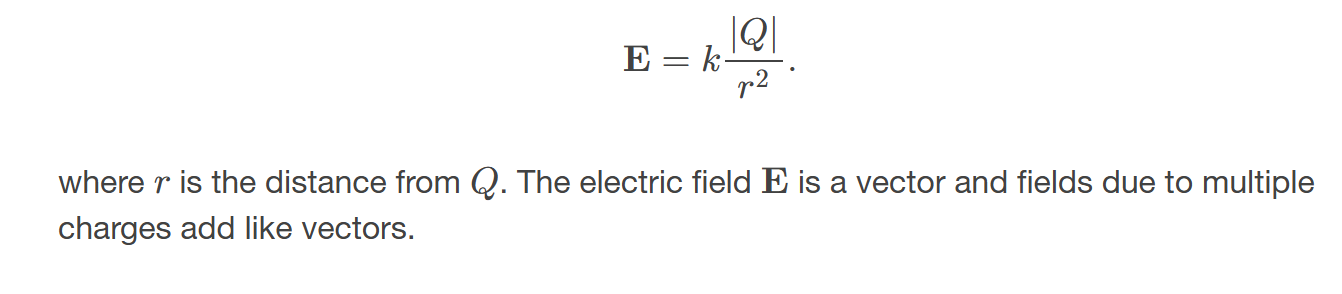Chapter 18: Introduction to Electric Charge and Electric Field
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
conductor
a material that allows electrons to move separately from their atomic orbits; an object with properties that allow charges to move about freely within it
Coulomb Force
another term for the electrostatic force
Coulomb interaction
the interaction between two charged particles generated by the Coulomb forces they exert on one another
Coulomb’s Law
the mathematical equation calculating the electrostatic force vector between two charged particles
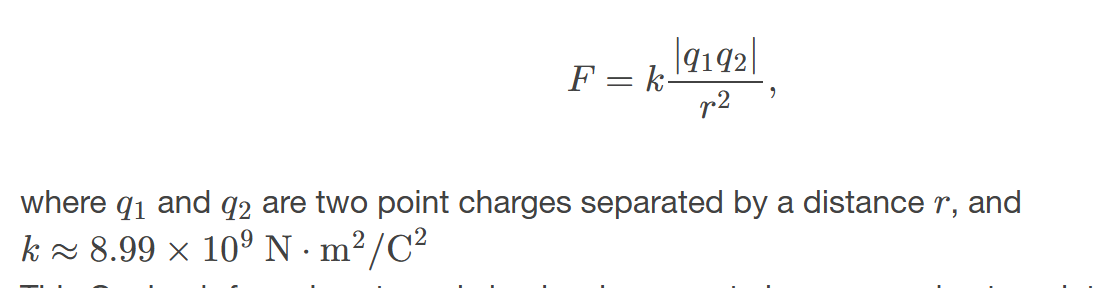
Dipole
a molecule’s lack of symmetrical charge distribution, causing one side to be more positive and another to be more negative
electric charge
a physical property of an object that causes it to be attracted toward or repelled from another charged object; each charged object generates and is influenced by a force called an electromagnetic force
electric field
a three-dimensional map of the electric force extended out into space from a point charge
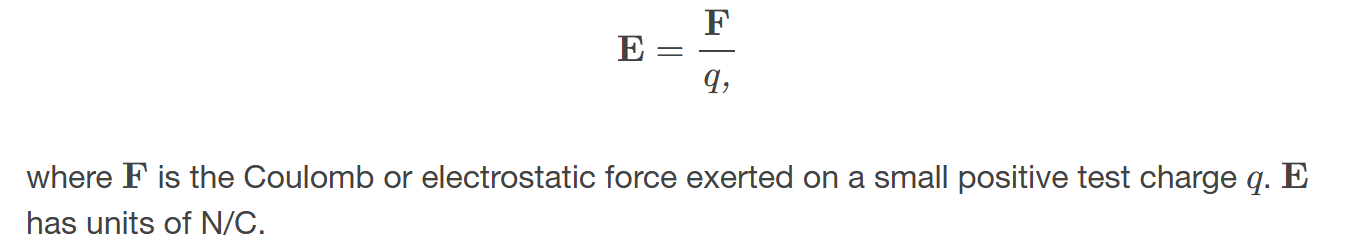
electric field lines
a series of lines drawn from a point charge representing the magnitude and direction of force exerted by that charge
electromagnetic force
one of the four fundamental forces of nature; the electromagnetic force consists of static electricity, moving electricity and magnetism
electron
a particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom and carrying the smallest unit of negative charge
electrostatic equilibrium
an electrostatically balanced state in which all free electrical charges have stopped moving about
electrostatic force
the amount and direction of attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies
electrostatic precipitators
filters that apply charges to particles in the air, then attract those charges to a filter, removing them from the airstream
electrostatic repulsion
the phenomenon of two objects with like charges repelling each other
electrostatics
the study of electric forces that are static or slow-moving
Faraday cage
a metal shield which prevents electric charge from penetrating its surface
field
a map of the amount and direction of a force acting on other objects, extending out into space
free charge
an electrical charge (either positive or negative) which can move about separately from its base molecule
free electron
an electron that is free to move away from its atomic orbit
grounded
connected to the ground with a conductor, so that charge flows freely to and from the Earth to the grounded object; when a conductor is connected to the Earth, allowing charge to freely flow to and from Earth’s unlimited reservoir
induction
the process by which an electrically charged object brought near a neutral object creates a charge in that object
ink-jet printer
small ink droplets sprayed with an electric charge are controlled by electrostatic plates to create images on paper
insulator
a material that holds electrons securely within their atomic orbits
ionosphere
a layer of charged particles located around 100 km above the surface of Earth, which is responsible for a range of phenomena including the electric field surrounding Earth
laser printer
uses a laser to create a photoconductive image on a drum, which attracts dry ink particles that are then rolled onto a sheet of paper to print a high-quality copy of the image
law of conservation of charge
states that whenever a charge is created, an equal amount of charge with the opposite sign is created simultaneously
photoconductor
a substance that is an insulator until it is exposed to light, when it becomes a conductor
point charge
A charged particle, designated 𝑄, generating an electric field
polar molecule
a molecule with an asymmetrical distribution of positive and negative charge
polarization
slight shifting of positive and negative charges to opposite sides of an atom or molecule
polarized
a state in which the positive and negative charges within an object have collected in separate locations
proton
a particle in the nucleus of an atom and carrying a positive charge equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the amount of negative charge carried by an electron
screening
the dilution or blocking of an electrostatic force on a charged object by the presence of other charges nearby
static electricity
a buildup of electric charge on the surface of an object
test charge
A particle (designated 𝑞) with either a positive or negative charge set down within an electric field generated by a point charge
Van de Graaff Generator
a machine that produces a large amount of excess charge, used for experiments with high voltage
vector
a quantity with both magnitude and direction
vector addition
mathematical combination of two or more vectors, including their magnitudes, directions, and positions
xerography
a dry copying process based on electrostatics
Coulomb
The SI unit of charge
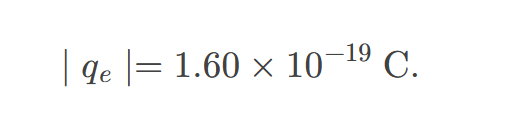
magnitude of the electric field 𝐄 created by a point charge
is directly proportional to the amount of charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the charge.