Plant Science Test 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
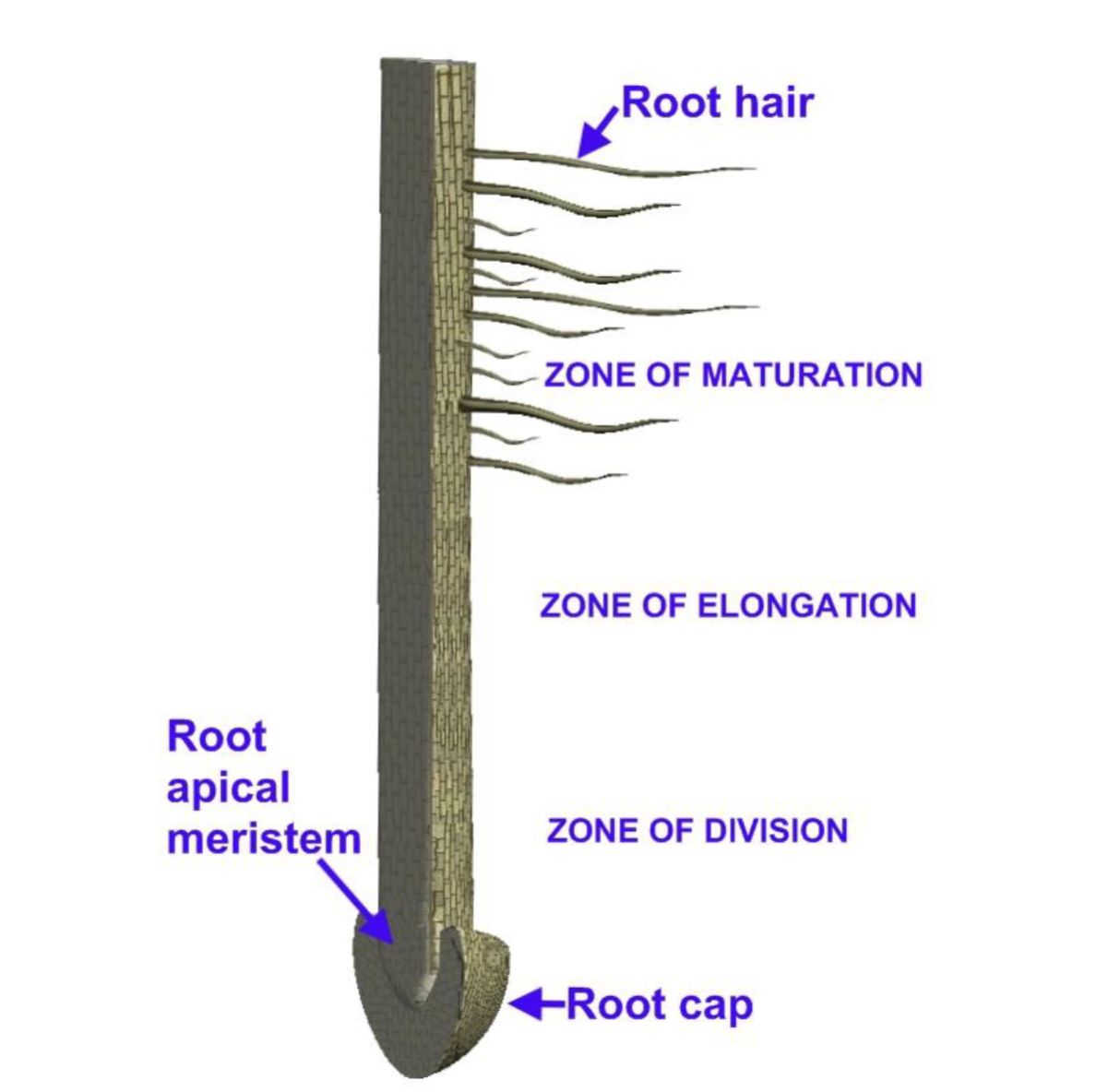
Where does growth mainly occur?
At shoot and root tips and in special growth zones like buds
How does growth occur?
Size increase often caused by increasing the size of cells by absorbing water into the vacuole
Cell Specialization
Most plant cells can differentiate into different cell types
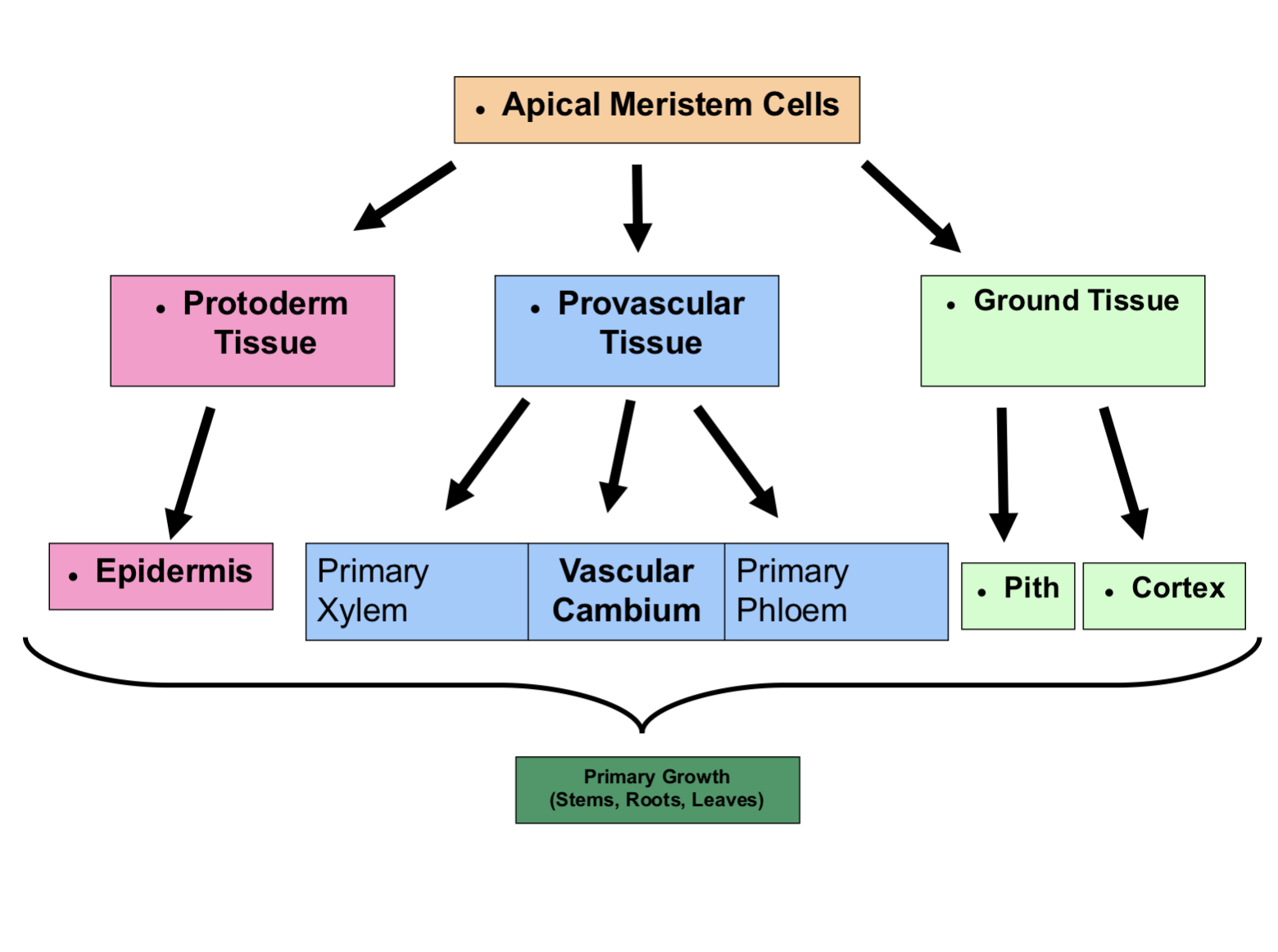
2 Main Meristems in Early Plant Growth
Shoot apical
Stem, leaves
Root apical
Roots
Shoot Apical Meristem
Corpus produces tissues that divide and differentiate into 3 new growth zones
Protoderm
Provascular
Ground Tissue
Protoderm
Produced very early as egg divides
Produces epidermal cells
Provascular
Produces xylem, phloem, & vascular cambium
Xylem = interior
Phloem = exterior
Vascular cambium = middle
Produces wood later
Ground Meristem
Produces all other tissues
Mainly parenchyma
Pith
Cortex
1st Vascular Plant Stem
Protosteles
Roots
2nd Vascular Plant Stem
Siphonosteles
1st seed plants
Protosteles
Xylem cells mature outside to inside (exarch maturation)
Siphonosteles
Xylem cells mature from inside to outside (end arch maturation)
Last Vascular Plant Stem
Eustele
Seed plants
2 Types of Stems
Woody
Herbaceous
Woody Plants
Plants that produce wood as its structural tissue
Have a strong stem
Stem is covered with a bark
Tallest and largest plants on Earth
Mainly perennials
Herbaceous Plants
Plants that have no persistent woody stem above ground
Have a flexible stem
Stem stays green
Comparatively short and small
Annual, biennials, or perennials
Functions of Stems
Producing leaves
Places leaves in optimal photosynthetic position
Long-distance water and food conduction
Storage (food, water, minerals, etc)
Perennating organs
Dispersal agents
Housing symbiotic organisms
Root underground environment
Stable with little change
Root Functions
Anchoring
Storage
Survival
Support
Form networks to catch organic debris
Haustoria
Hormone / vitamin sources
Taproots
Main anchoring root
Usually weakly woody
Ex. carrot, turnip
Monocot Roots
Coleorrhiza grows a day or two, then dies
Adventitious roots grow from bottom of hypocotyl
Fibrous
Lateral Roots
Initiated by hormone auxin from s.a.m.
Preicycle redifferentiates to produce new r.a.m.
Link new xylem with old xylem
Adventitious Roots
Grow from non-root areas
Add support or increase absorption
Haustoria Roots
Helps penetrate host plate
Usually only exterior organ of parasitic plant
Pulls embryo into host plant
Ex. mistletoe
Mycorrhizae
Type of mycorrhizae
Fungal root
2 Types
Ectomycorrhizae
Endomycorrhizae
Ectomycorrhizae
Fungi that surround and attach to the root exterior
Tap into root epidermis / extreme outer cortex
Endomycorrhizae
Type of mycorrhizae
Actually penetrate cortex inward to endodermis
Don’t pass endodermis
Set up networks to absorb sugars / proteins
Arbuscus
Stem Modifications
Cladodes
Rhizomes
Stolons / Runners
Thorns
Corms
Storage
Vines
Tendrils
How many times did leaves evolve?
Twice
Microphylls
First leaf evolution
Evolved from stem projections that become vascularized
Megaphylls
2nd leaf evolution
Evolved from photosynthetic branches that became smaller than the main axis over time and expand photosynthetic surfaces
More complex than microphylls
Found in more advanced groups
Ferns, flowering plants (angiosperms), gynosperms
What do leaves develop from?
S.A.M.
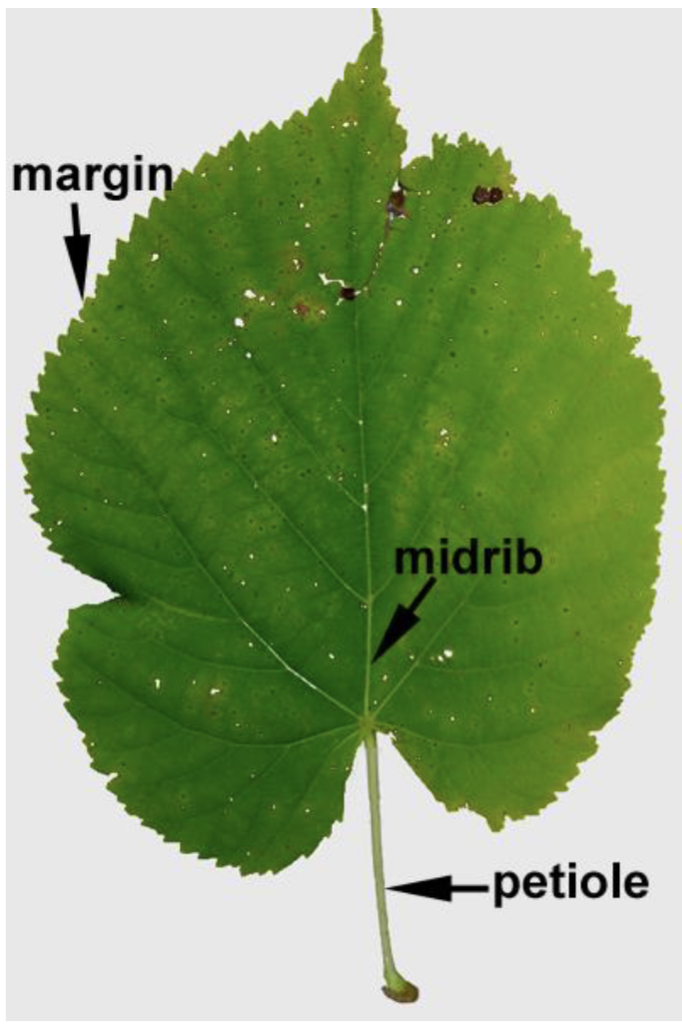
Leaf Veins
Midrib
Areoles
1st, 2nd… order
Opening in leaves that let CO2 in and O2 out
Stomata
Control size of stomata opening
Guard Cells
Modified Leaves
Spines
Bulbs
Tendrils
Glands
Hydathodes
Associated with releasing excess water
Trichomes
Leaf hairs
Insectivorous
Pitcher plants, sundews, bladderworts, Venus fly-traps
Environmental Leaves
Aquatic
Arid / Xeric
Windy
Cold / Dry
How leaves fall off trees in autumn
By using gas ethylene and killing off the cells of the abscission layer
Amount of times vascular cambium has evolved
3 (1 successfully)
Wood formation (secondary xylem)
Highly coordinated
Begins in vascular bundle
Fascicular
Vascular Cambium Function
To produce cells that become almost any other cell type
2 Types of Vascular Cambial Cells
Fusiform Initials
Ray Initials
Fusiform Initials
Most numerous of vascular cambium cells
Produce secondary xylem and phloem
Able to change how they divide in order to produce different sized cells
“S” plane of division
Ray Initials
Produce ray parenchyma
Connect pith to cortex
Allow slow horizontal conduction
Interconvertibility in Fusiform and Ray Initials
Fusiform initials can subdivide to produce stack of ray initials
Ray initials can convert to fusiform initials by lengthening greatly
Growth Rings in Dicots
1 year = 1 growth ring
Consists of spring and summer wood
Springwood: large vascular elements
Summerwood: smaller or no vascular elements
Growth Rings in Conifers
Spring pattern: wider, larger tracheids
Earlywood
Summer pattern: smaller, thicker-walled tracheids
Latewood
Heartwood
Tyloses seal off vessel elements
Climate Data Affecting Growth Rings
Temperature
Moisture
CO2 Levels
O2 Levels
Fire Events
Human Habitation
Secondary Growth in Wood
Bark
Bark
Everything exterior to secondary xylem including vascular cambium
Cork
Hard, airy tissue produced by cork cambium
Why cork is needed
Lenticels
Bark
Large fissures in cork that allow gas exchange
Why lenticels are needed
Economic Uses of Bark
Cork
Mulch
Insulation
Message Boards
Medicines
Pre-Industrial clothes, structures, medicines, etc.
Anomalous 2° Growth
Cambial death
Vascular cambium grows, then dies in sections
Some areas of vascular cambium are more active than others
Anomalous placement
Other vascular cambium arises from cortex, pith, other cells
Sapwood vs Heartwood
Sapwood = outer
Heartwood = inner
Economic Uses of Wood
Lumber
Particle Board
Plywood
Paper
Reasons to conserve woody plants
Provide habitats
Store CO2
Recycle nutrients
Climate stability
Root Anatomy
Apical Meristem Cells Diagram
Haustoria are what kind of roots?
Parasitic
Leaf Diagram
Types of Bug-Eating Plants
Pitcher
Venus Fly Trap