Unit 2 economics study guide [complete] (good luck!👍)
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
Discouraged worker
a person who wants a job but has given up looking
How to find unemployment rate
unemployment rate= [(# unemployed)/(# in labor force)] x 100
How does economic expansion affect unemployment?
May have a little effect initially and may even increase unemployment. [Discouraged workers begin to look for work making them employed, thus shifting their presence from NLF (not in the labor force) to unemployed (as they are looking for work)]
Real wage
the wage rate divided by the price level
real wage by current earnings times quantity of hours work of base year
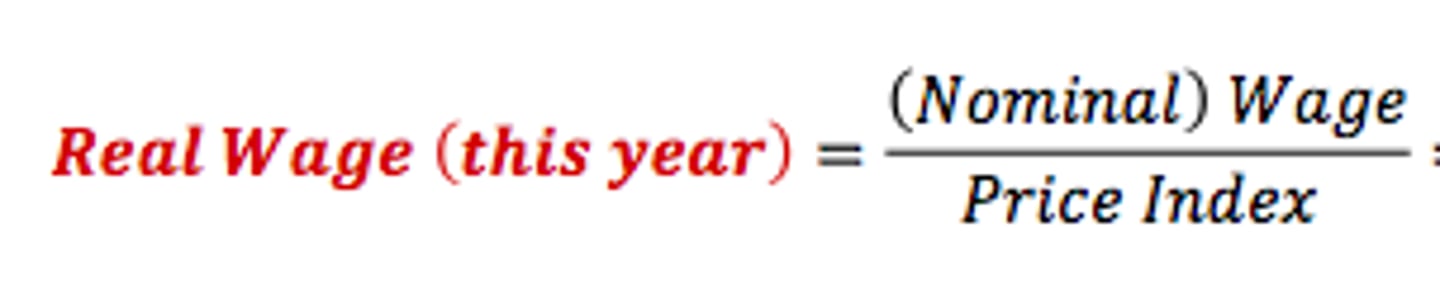
How to find GDP
GDP = private consumption + gross private investment + government investment + government spending + (exports - imports).
How to find real GDP
(Nominal GDP/Price Index) x 100
price of current year and quantity of current year
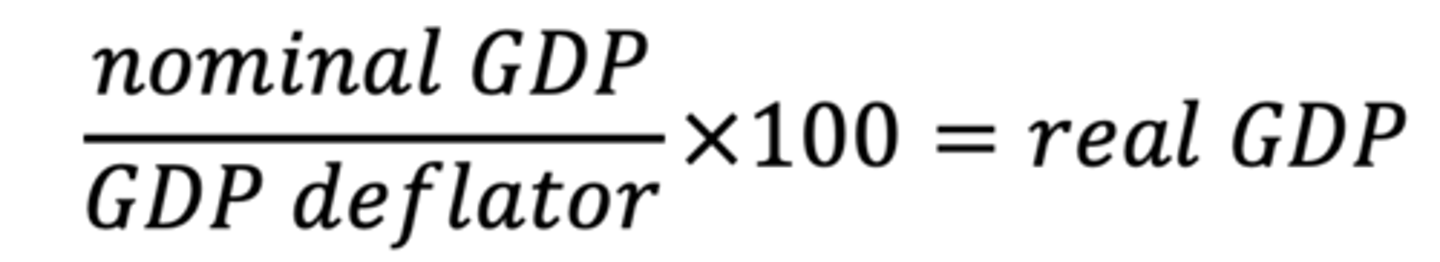
How to find price index
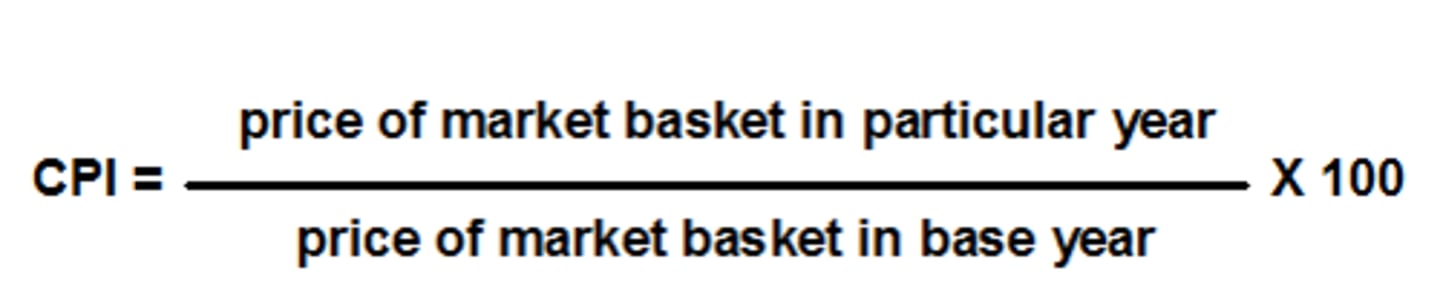
Are housewives counted in employment?
No
How to find nominal GDP
Price x Quantity
price of current year and quantity of current year
(so sorry just made this correction) FOR REAL GDP IT IS price of current year and quantity of current year

Price of labor
wage rate
Nominal wage
the wage measured in current dollars; the dollar amount on a paycheck
Price of labor
Nominal wage/ price level
Increase in real wage affects what in labor?
Slight increase in the quantity of labor supplies
The lower the real wage
the greater the quantity of labor that firms will demand
What is the natural rate of unemployment
5%
What do business cycles do?
They might generate additional unemployment
Frictional unemployment
A type of unemployment caused by workers voluntarily changing jobs and by temporary layoffs; unemployed workers between jobs.
Structural unemployment
unemployment that results because the number of jobs available in some labor markets is insufficient to provide a job for everyone who wants one
-a skill could be obsolete
cyclical unemployment
unemployment that rises during economic downturns and falls when the economy improves
When the labor market is at the equilibrium
The quantity demanded of labor equals the quantity supplied, there is full employment, Potential GDP is produced.
at the natural level of unemployment (so not FULL full)
Who does unexpected inflation hurt?
lenders
Who does unexpected inflation help?
borrowers
Who does unexpected deflation hurt?
borrowers
Who does unexpected deflation help?
lenders
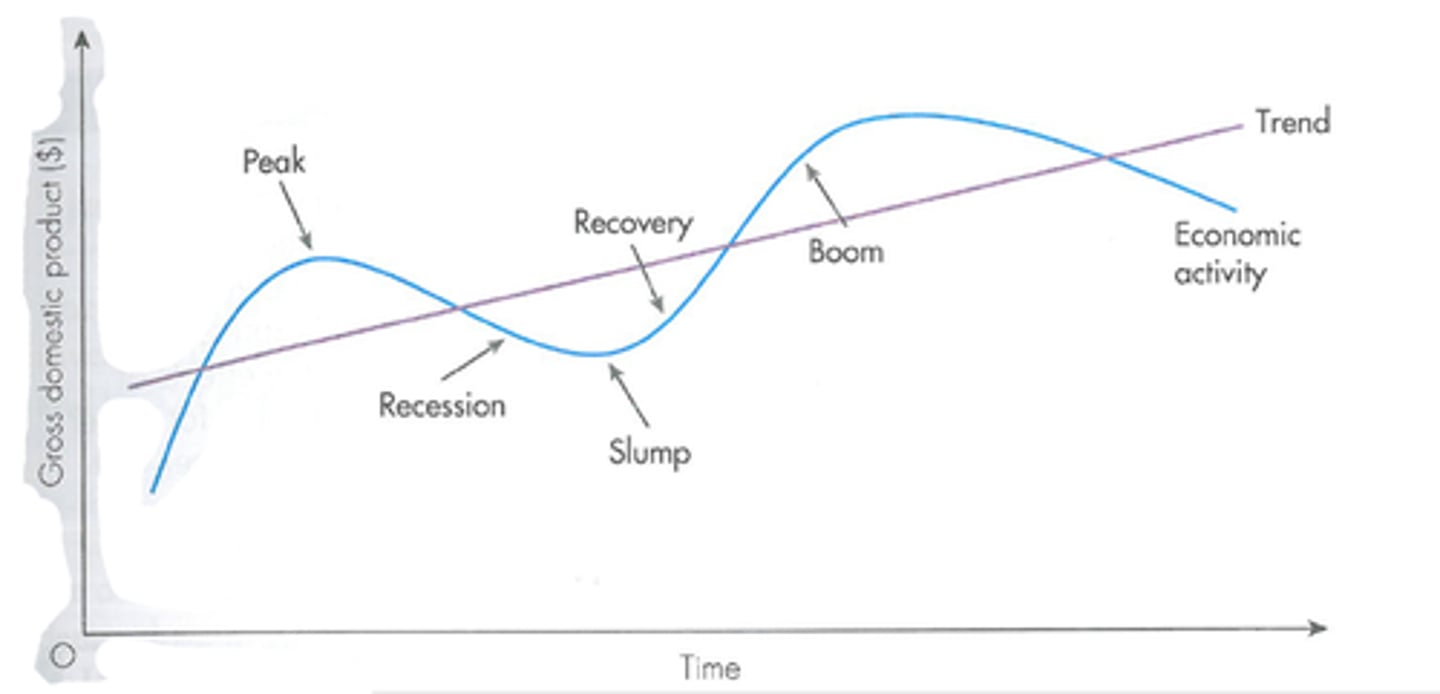
Draw the business cycle
Could not upload a picture. search it
this pic is kinda weird w labels
What is inflation
a general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money.
What is the rate of inflation or deflation
the percentage rate of change in a price index
Biases in CPI (consumer price index)
substitution bias, increase in quality bias, new product bias, outlet bias
S.I.N.O.
A guy wants to earn more money
Frictional unemployment
If people become discouraged workers and leave, does that improve the economy? UR rate decreases
No, labor force shrinkage, reduced economic growth, and unemployment rate decline (artificial manipulation)
implicit price deflator
A price index for all final goods and services produced; it is the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP.
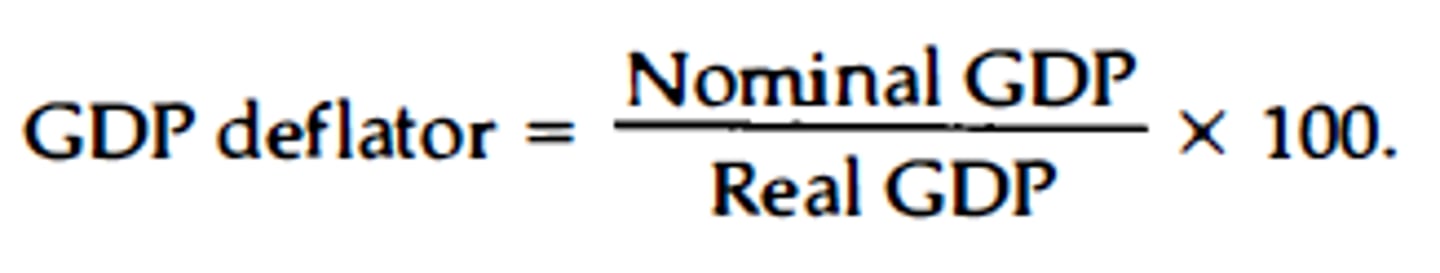
Okun's law (CRUCIAL)
1 percent more unemployment results in 2 percent less output
The generalization that any 1-percentage-point rise in the unemployment rate above the full-employment unemployment rate will increase the GDP gap by 2 percent of the potential output (GDP) of the economy.
classical theory
a concept in which an item derives its worth from consumers from the resources that it took to make that item.
keynesian theory of unemployment
A set of ideas that assumes unemployment begins when businesses cut wages and can be controlled by increasing demand and encouraging spending
3 U.S. economic goals
1. full employment
2. economic growth
3. price stability
Is the full unemployment level of GDP determined as macro or micro economic?
Macro
What does a circular flow diagram show?
shows how households and firms interact in the goods and services market, and in the labor market
What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
A measure of all the goods and services produced by a nation in a given year
What are two ways GDP can be calculated?
1. expenditures approach 2. income approach
Expenditures Approach to GDP
GDP = C + I + G + Xn
where consumption (C) represents private-consumption expenditures by households and nonprofit organizations, investment (I) refers to business expenditures by businesses and home purchases by households, government spending (G) denotes expenditures on goods and services by the government, and net exports (NX) represents a nation's exports minus its imports.
Income Approach to GDP
National income= wages + rent + interest + profit
Does the expenditures approach count only the final goods and services?
Yes. Intermediate goods do not count
Intermediate goods
goods used in the production of final goods
Income approach to calculating GDP includes...
all income earned by foreigners in U.S. but not:
income and profits by U.S. citizens abroad
transfer payments like (SS, unemployment compensation, or certain interest payments)
social security
federal program of disability and retirement benefits that covers most working people
transfer payments
Benefits given by the government directly to individuals. Transfer payments may be either cash transfers, such as Social Security payments and retirement payments to former government employees, or in-kind transfers, such as food stamps and low-interest loans for college education.
How are price changes over time calculated?
The price level in the base year has an index number of 100. the price level in other years is expressed in relation to the price level in the base year.
percentage change
(new-old)/old x 100
CPI
(can be used in multiple formulas)
If domestic prices increase relative to prices in other countries then...
, imports will increase while exports decrease because people want to purchase the goods and services where they are relative cheaper.
The labor force participation rate
% of the adult population that is in the labor force (16 and above)
The unemployment rate associated with full employment is above zero because...
frictional and structural employment will always exist. full employment occurs where cyclical unemployment equals zero.
The unemployment rate at full employment is called...
the natural rate of unemployment
Income approach
The process of estimating the value of an income-producing property through capitalization of the annual net income expected to be produced by the property during its remaining useful life.
Expenditures approach
viewing GDP as the sum of all the money spent in buying it
The basic flow of economic activity has leakages from...
leackages and injections happen through the gov, financial insittiutions (e.g. banks), and inernationaltrade
Draw the circular flow of resources, goods, services, and money payments
search it or use the activity 2-1 in binder (can't add pic)
what is on the circular flow?
the movement of output and income from one sector of the economy to another
aggregate spending
the sum of consumer spending, investment spending, government purchases of goods and services, and exports minus imports, is the total spending on domestically produced final goods and services in the economy
bond
A financial security that represents a promise to repay a fixed amount of funds
national income
total income earned by everyone in the economy
factor markets
the markets where productive resources are bought and sold
Financial market
a mechanism that provides the means for purchasing and selling stocks, bonds, commodities, and other financial instruments
product markets
where goods and services are bought and sold
net exports
exports minus imports (Xn in the formula)
exports
Goods and Services sold to other countries
imports
goods produced abroad and sold domestically
Practice Problems!
Indicate whether each of the following is counted as GDP or not
1. Hats produced in France
2. Buying a used car
3. Both cards Ford sold this year
4. Buying a new fry machine at McDonalds
5. The grease used to make the fries at McDonalds
6. Building the new Taco Bell across the street
7. Buying dollar tree stock during a depression
Hats produced in France: Not counted as GDP of a specific country if you're referring to another country's GDP. It would count in France's GDP, as it reflects production within that country.
Buying a used car: Not counted as GDP. The sale of used goods is not included in GDP calculations because GDP measures only new production.
Both cars Ford sold this year: Counted as GDP. New vehicles produced and sold contribute to GDP.
Buying a new fry machine at McDonald's: Counted as GDP. This is a business investment in new equipment, which is included in GDP.
The grease used to make the fries at McDonald's: Counted as GDP. If it's purchased as part of a new production process, it contributes to GDP through intermediate goods.
Building the new Taco Bell across the street: Counted as GDP. Construction contributes to GDP as it represents investment in fixed assets.
Buying Dollar Tree stock during a depression: Not counted as GDP. Transactions involving the buying and selling of stocks do not contribute to GDP, as they are not related to new production.
Draw the circular flow model of income and output
answer should be in economics worksheet "Module 10: Circular Flow and GDP"
What are the two functions of households in the economy
- spend in the product market
-provide resources to the factor market
What are two functions of the businesses in the economy
Supply/sell goods and services at the product market and provide payments to the factor markets
difference between factor and resource market
Factor market is specific to L,L,C,E while resource is broader
what are two ways that money leaves the economy
-savings and outside investments (Banks?)
-Imports
Draw interactions of the private market to the financial market then the foreign market
check notes
What is not included in GDP
PAPAYAS!! :D
P = Payments from the government: Pensions, SS payments (non-production transactions)
A = anything illegal (non-market transaction)
P = products that aren't final goods (intermediate goods)
A = anything used (non-production transaction)
Y= Your leisure time (non-market transaction)
A = anything for which you don't get paid (non-market transaction)
S= stocks and bonds (non-production transaction)
(IMPORTANT)
name types of money transfer
1. Land
2. Labor
3. Capital
4. Entrepreneurship
1. rent
2. wages
3. interest
4. profit
In the free market irf instead of household there's gov then it would be
(based on what u drew on 75)
(instead of household, there would be government in the case of communist)
Draw transfer between resource market, gov, households, businesses, rproduct market
Check notes
The Employment Act of 1946
-Full employment: when most individuals who are willing to work are employed.
-Price stability: average level of economic prices are neither increasing or decreasing
-Economic growth: economy produces increasing amounts of goods and services over the long term
DRAW THE BUSINESS CYCLE (refresher) include all parts
LABEL AXIS AND PARTS
the up gap is called infaltionary gap the below gap is called expansionary gap.
from peak to trough is contractionary and line to peak is expansionary while trough to line is recovery
(check class handout)
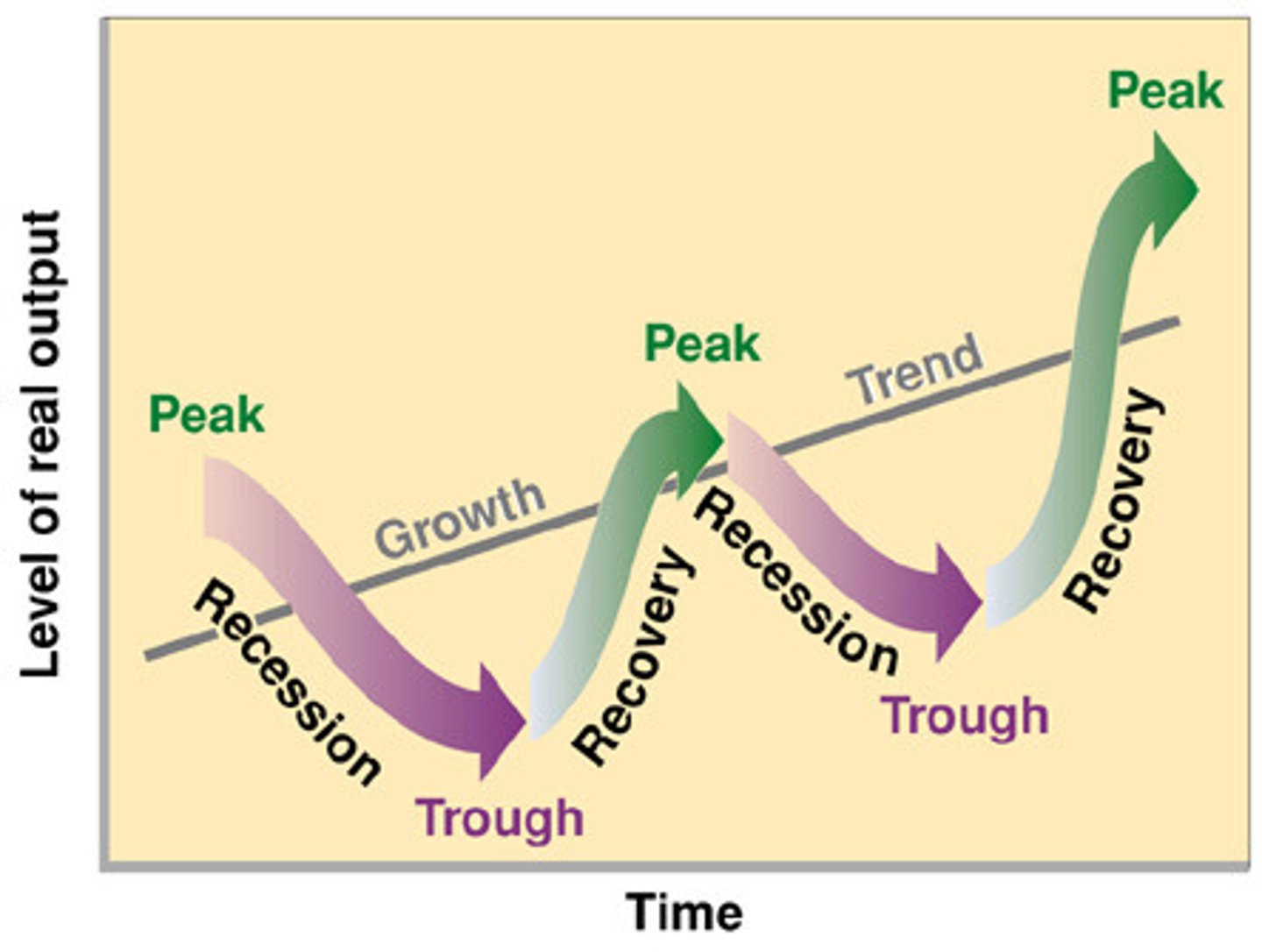
What is the long-run trend of GDP
3% is the long-run trend
Standard of living growth
it also represents 5% unemployment rate
Recession is
2/4 of recessionary growth (2 quarters)
Real GDP can be dependent on
rate of new home construction
stock market activity
manufacturer's _______
What does the business cycle do?
-give a certain order
-does not predict future
-what goes up must come down
Business cycle
positive not normative
Total dollar value
GDP is measured in dollars
Final goods and services
goods and services sold to the final, or end, user
Within a country
GDP measures production within the country's borders
Given time period of GDP
measured every quarter (3 months). most used to compare both yearly and quarterly growth rates
Limitations of GDP
P - population
I - inequality (standard of living/ poverty doesn't matter)
E - environment (pollution)
S - shadow economy (buy smth from a friend/ black market)
how to find GDP per capita
GDP/population
Gross national product
The total value of goods and services, including income received from abroad, produced by the residents of a country within a specific time period, usually one year.
Why is GDP inflated
does not include happiness or wellbeing
LPFR formula (labor force participation rate)
(Labor force)/(population) x 100
Business cycle
peak, trough, inflationary gap, recessionary gap, contraction, recovery, expansionary
peak to peak is a full bsuiness cycle
How to find growth rate of GDP
(GDP in Current Year−GDP in Previous Year)/ GDP in previous year × 100
Four reasons why you cannot assume the citizens in each country enjoy approximately the same level of economic well-being
Income Inequality:
Within countries, there can be significant disparities in income distribution. Wealth may be concentrated in the hands of a small percentage of the population, leading to vast differences in living standards and economic opportunities among citizens. Even in countries with similar GDP per capita, income inequality can result in varying levels of economic well-being.
Access to Basic Services:
The availability and quality of essential services such as healthcare, education, and social security can differ greatly between countries. In some countries, citizens may have access to high-quality healthcare and education, while in others, inadequate services can limit individuals' economic mobility and overall well-being.
Economic Structure and Employment Opportunities:
The structure of the economy (e.g., reliance on agriculture, manufacturing, or technology) and the availability of job opportunities can vary significantly from one country to another. Countries with diversified economies and robust labor markets often provide better job opportunities and economic security for their citizens compared to those with limited economic activities.
Social and Political Factors:
Political stability, governance quality, and social safety nets play critical roles in determining citizens' economic well-being. Countries with stable governments, effective legal systems, and strong institutions tend to provide a more favorable environment for economic growth and personal prosperity. Conversely, countries experiencing conflict, corruption, or weak governance can hinder economic progress and diminish citizens' quality of life.
How to find the deflator
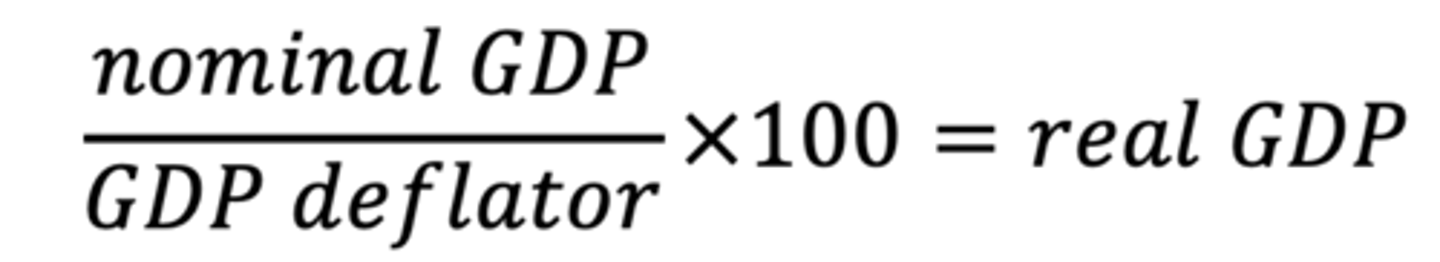
Why do countries have higher GDPs?
Productivity due to
1. Economic system
Capitalist countries have historically higher growth rates
Capital like robots can produce more than people
Countries with more kapital can produce more products than countries without kapital
2. Private ownership of Property
3. Education levels (Human Capital)
Productivity due to
4. Capital Stock
Capital stock is machinery, tools and man-made resources
Examples: India has over a billion people (human resources) but relatively few capital resources and therefore a lower GDP then the US Japan has fewer natural resources but a high GDP
5. Efficient Financial Institutions
6. Free Trade
Other Indices than GDP
Big Mac Index - an index used to measure the purchasing power parity (PPP) between two currencies. How long does it take for a worker to earn the money to purchase a Big Mac. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4yE1wihafgk (6 minutes)
Purchasing Power Parity - a theory that measures the average price level in different countries and is widely used when comparing the GDP of different countries.
OECD better life Index - an index which allows economists to compare well-being across countries, based on 11 topics e.g. quality of housing, average income levels as well as access to education and health services.
Happiness Index - a landmark survey of the state of global happiness that ranks 156 countries by how happy their citizens.
Happy Planet Index - measures what matters: sustainable wellbeing for all. It tells us how well nations are doing at achieving long, happy, sustainable lives.
Value Added
•The increase in the value of a good at each stage of the production process. The value that's being increased is specifically the ability of a good to satisfy wants and needs either directly as a consumption good or indirectly as a capital good.
•A good that provides greater satisfaction has greater value.
In essence, the whole purpose of production is to transform raw materials and natural resources that have relatively little value into goods and services that have greater value.
Net Private Domestic Investment
•Expenditures on capital goods to be used for productive activities in the domestic economy that are undertaken by the business sector during a given time period, after deducting capital depreciation.
•More specifically net private domestic investment is found be subtracting the capital consumption adjustment from gross private domestic investment.
•It's primary function is to measure the net increase in the capital stock resulting from investment.