Equilibrium Law
1/18
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
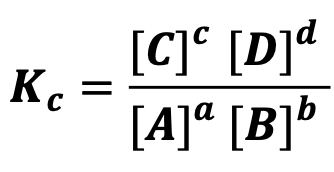
State the observation for equilibrium law
At equilibrium, the ratio of the concentrations of reactants and products each raised to their stoichiometric coefficients is constant if temperature is constant
State what the exponents in the equilibrium constant equation refer to.
Coefficient of reactants and products in a balanced equation at an equilibrium state.
State the only time when Kc changes
When temperature changes.
State three special considerations for equilibrium constants.
Species with constant concentrations are not written in the equilibrium constant equation (SOLIDS & LIQUIDS)
In solutions (aqueous), solvent concentrations are not included in the Kc expression.
In non-aqueous solutions (liquid + liquid), the solvents must be included in the equilibrium constant equation.
Define the equilibrium constant (Kc).
Value that shows the extent of reactions at equilibrium.
Define extent of reactions at equilibrium.
Percentage of reactants that were converted into products.
State the relationship between reactants (R) & products (P) and reactants (R) & equilibrium constant (Kc).
Inverse
State the relationship between products (P) and the equilibrium constant (Kc).
Direct
State what Kc>103 implies.
reaction is almost completed when an equilibrium is reached.
more products than reactants
the equilibrium mixture is almost only composed of products
State what Kc<10-3 implies.
The reaction is far from completion when at equilibrium.
More reactants than products.
The equilibrium mixture is almost only composed of reactants.
State what 10-3< Kc<103 implies.
the reaction neither favors reactants nor products.
The equilibrium mixture has almost the same concentration of reactants and products.
[R]=[P]
State the equation for a multiple of a in a reaction using Kc.
Kca
State the equation for a reverse reaction using Kc.
Kc-1
Express Koverall if the equation for a reaction consists of several steps using K1 and K2.
K1K2
Define reaction quotient (Q).
Value that shows the extent of a reaction at any given time.
State what Q>Kc implies.
Favor reverse reaction
State what Kc>Q implies.
Favor forward reaction
State what Kc=Q implies.
At the given time, the reaction is at an equilibrium.
Explain why concentration changes do not affect the value of Kc.
Kc is only measured for a reaction at an equilibrium.
THEREFORE, the concentration of reactants and products do not change or are at a constant.