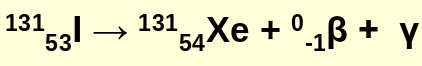Chemistry Final - Unit 8 (Chemical Equations and Reactions)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
what is a chemical equation?
a short hand expression for describing a chemical change
____ and ____ information is contained in chemical equations
qualitative, quantitative

what is this chemical equation symbol?
“yields”, indicates result of reaction

what is this chemical equation symbol?
Used in place of a single arrow for a reversible reaction
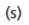
what is this chemical equation symbol?
A reactant or product in the solid state

what is this chemical equation symbol?
Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate formed in a solution
what is this chemical equation symbol?
A reactant or product in the liquid state
what 4 things are NOT given in a chemical equation?
whether the reaction will actually occur
the speed of the reaction
the actual pathway atoms and ions take in moving from reactants to products
the ratio of the masses of the products and reactants
what 2 things are given in a chemical equation?
states when the reaction goes to completion
states when the reaction reaches equilibrium or is reversible
all combustion reactions have the products ___ and ___
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
in a single replacement reaction, a cation replaces a ____
cation
in a single replacement reaction, an anion replaces a ____
anion
in a single replacement reaction, a metal will only replace another metal if it is ___ reactive
more (higher on the activity series)
in double replacement reactions, ions exchange places in ___ solutions
aqueous
in a double replacement reaction in an aqueous solution, only 1 ion reacts, while the _____ do not.
spectator ions
a _____ are used to show the actual reaction taking place in an aqueous solution
net ionic equation
all compounds containing Br-, Cl-, or I-, are soluble, except when combined with ions of ___, ___, or ___.
Ag+, Hg22+, or Pb2+
compounds containing HCO3-, are only soluble with ____ and ___.
alkaline earth metal ions and alkali metal ions (group 1 and 2)
compounds containing OH- are only soluble with ____, ____, or ___.
Ba, group 1, or NH4
all compounds containing CO3, PO4, or S, are only soluble with ____ or ___.
Group 1 or NH4
what is a redox reaction?
a chemical reaction in which elements undergo changes in oxidation number.
the only type of reaction not included in redox reactions is ____
double replacement reactions
what is a reducing agent?
the element being oxidized in a redox reaction; donates electrons
what is an oxidizing agent?
the element being reduced in a redox reaction; accepts electrons
an oxidation half-reaction is a way to write the equation for ____
ionization energy
a reduction half-reaction is a way to write the equation for ______
electron affinity
half-reactions are only combined if _______
the electrons all cancel (same amount for both oxidation and reduction)
in nuclear fusion, the nucleus gets ____ by combining ____ nuclei
heavier, small and light
in nuclear fusion, a more ____ nucleus is formed
stable
another term for nuclear fusion is ___
thermonuclear reactions
in nuclear fission, a ____ nucleus divides to form ___ nuclei
heavy, smaller
what is radioactivity/radioactive decay?
the spontaneous decomposition of a nucleus to form a lighter, more stable nucleus (while emitting particles and/or electromagnetic radiation)
notation for a proton in nuclear reactions:
11p or 11H
notation for a neutron in nuclear reactions:
01n
notation for an alpha particle in nuclear reactions:
24a or 24He
what is an alpha particle?
a helium nucleus with a charge of +2
alpha particles are common in ____ nuclei
heavy
notation for a beta particle in nuclear reactions:
-10β, -10e, -β, β-
what is a beta particle?
an electron emitted from the nucleus
how is a beta particle formed?
from the breakdown of one neutron into a proton and an electron
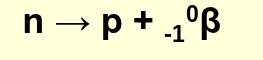
notation for a positron in nuclear reactions:
+10β, +β, +10e, β+
what is a positron?
a particle with the same mass of an electron but has a positive charge
how is a positron formed?
from the breakdown of a proton in the nucleus
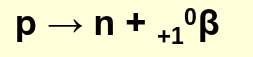
what’s another name for a positron?
anti-electron
gamma radiation is emitted from the ___ as it changes from an excited state to a ____ state
nucleus, ground
gamma radiation is a product of _______
all nuclear reactions
what is alpha decay?
radioactive decay that emits an alpha particle
alpha decay example:

what is beta decay?
radioactive decay that emites beta particles
beta decay example:
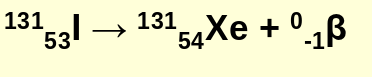
beta particles are _____ ___ electrons
high speed
what is positron decay"?
radioactive decay that emits a positron
positron decay example equation:
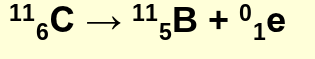
what is electron capture?
the capture, by a proton, of an electron from the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus
electron capture example equation:
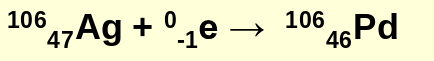
what is gamma decay?
radioactive decay that emits gamma rays
gamma rays are ___ ___ protons with ____ wavelengths
high energy, very short
gamma particles ____ change the mass number and atomic number
do not
gamma decay example equation: