chemistry- reversible reactions, industrial processes and important chemicals
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is a reversible reaction
a reaction which occurred in 2 directions
the products can react to form the original reactants
For A+B {} C+D which are the products for the forward reaction and which are the products for the backwards reaction
forward C+D
backwards A+B
how can the direction of a reversible reaction be changed
by changing the conditions
pressure
temperature
concentration of reactants or products
if the forward reaction is exothermic, will the backwards reaction be endothermic or exothermic
endothermic, the same amount of energy is transferred
what is the reaction in the Haber process
Nitrogen + Hydrogen{} Ammonia
N2 +3H2 {} 2NH3
what can ammonia be used for
to produce nitrogen- based fuels
where can nitrogen and hydrogen gas be obtained from
Nitrogen: from the air
Hydrogen gas: natural gas or other sources
what are the conditions required for the haber process
high temperature (450 degrees)
high pressure (200 atm)
iron catalyst
what happens during the Haber process
purified gases passed over iron catalyst
some nitrogen and hydrogen reacts to form ammonia
some ammonia breaks down into nitrogen and hydrogen( because reaction is reversible
Mixture is cooled, ammonia liquifies and is removed
remaining nitrogen and hydrogen recycled
what does it mean for the Haber process to be in dynamic equilibrium
forward and backward reaction happens at a consent rate once equilibrium is reached
in which way does the equilibrium shift in the Haber process when pressure is increased? why?
equilibrium shifts to the right. the total number of moles of gases is fewer on the right
the forward reaction of the Haber process is exothermic. How can the conditions be changed to produce more ammonia
by lowering the temperature, the forward reaction is favoured
what are the disadvantages of using low temperature and very high pressure
low temperature: slower rate of reaction
high pressure: requires high energy
what are the two things aimed to be maximised when choosing the conditions of the Haber process
rate of reaction and yield of ammonia
how can the presence of ammonia be tested
most red litmus paper will turn blue as ammonia is alkaline
how can the process of ammonium ions be tested? what is the ionic equation for this reaction?
add solution containing hydroxide ions
test for ammonia gas
NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) } NH3 (g) + H2O (i)
what kind of reaction are used to make nitrogenous fertilisers from ammonia
neutralisation reactions
what are some examples of nitrogenous fertilisers? what are their molecular formulas?
ammonium sulfate- (NH4)2 SO4
ammonium nitrate- NH4 NO3
how can ammonium slate be formed form sulfuric acid?( 2 different ways)
ammonia + sulfuric acid } ammonium sulfate
ammonium hydroxide + sulfuric acid } ammonium surface + water
what are the 2 ways used to form ammonium nitrate from nitric acid
ammonia + nitric acid } ammonium nitrade
Ammonium hydroxide + nitric acid } ammonium nitrate + water
what are the advantages of using fertilsers
increases crop yield and growth
increases profit for farmers
what are the disadvantages of using fertilisers
eutrophication when fertilisers are washed off into rivers and lakes
increase of nitrate and phosphate in water encourages algae growth
algae bloom blocks sunlight from water plants underneath
water plants die and are broken down by bacteria
oxygen is used up by bacteria, killing other living organisms in the water
many stages in manufacture
changes of pH in the soil
can cause baby blue syndrome
what does it mean for cultures acid to be a strong acid
it completely dissociates in water and releases H+ ions
what is the molecular formula and the structure of sulfuric acid
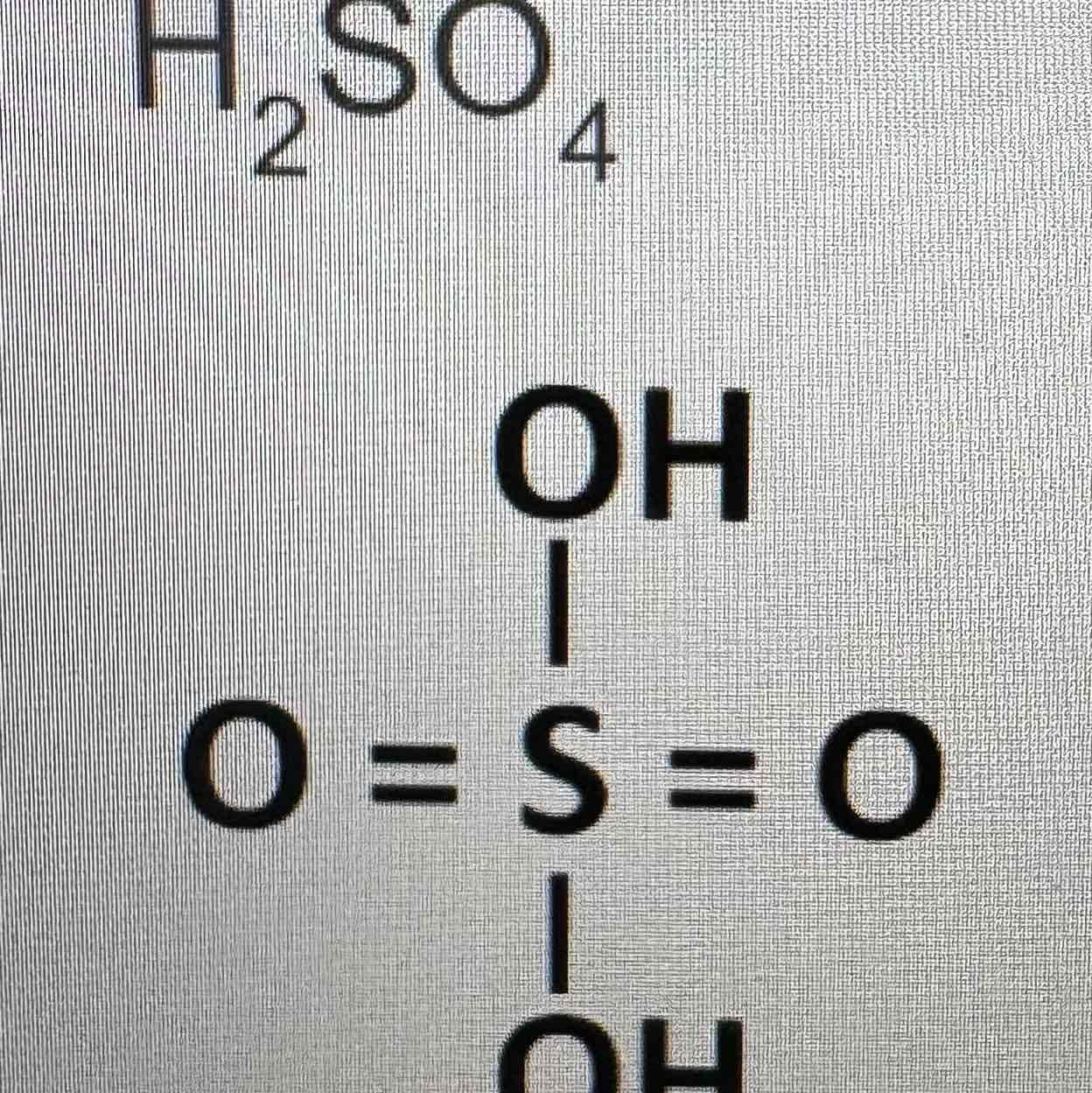
what is the contact process
the manufacture of sulfuric acid
what is the first step of the contact process
Silver is burned in the air and reacts with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide
what is the second step of contact process
sulfur dioxide reacts further with oxygen to form sulfur trioxide
reversible
catalyst: vanadium (V) oxide(V2O5)
temperature: 450 degrees
pressure: 2 atm
what is the third and final step of the contact process
sulfur trioxide reacts with water to form sulfuric acid
what is the reversible step in the contact process and what are the conditions for this reaction
the second step
catalyst: vanadium (V) oxide( V2O5)
Temperature 450 degrees
Pressure:2atm
what are the uses of sulfuric acid
mostly used to make fertilisers
manufacture of chemicals ( HCI, HNO3, sulfate salts, synthetic detergents, fibers, plastics, dyes, and pigments, explosives and drugs )
petroleum refining: waging impurities out of gasoline and other refinery products
processing metals
manufacture of rayon which is used as electrode in the lead- acid storage battery
what does a dehydrating agent do
removed water form other compounds
how does concentrated sulfuric acid act as a dehydrating agent with sugar
concentrated sulfuric acid removes 6 water molecules per glucose molecule
highly exothermic reaction
water molecules released as steam and a black mass of carbon forms
what change can be observed when concentrated sulphuric acid act as a dehydrating agent on hydrated copper(III) sulfate
blue crystals ( hydrated copper sulfate) } white powder ( anhydrous copper surfate)