General Medicine I Exam II
1/261
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
262 Terms
Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Includes disorders of arterial and venous blood vessels
- Classified by underlying pathology
Peripheral Vascular Disease - Types
- Arterial occlusive
- Inflammatory
- Vasomotor
- Venous
Peripheral Vascular Disease - Arterial Occlusive Disorders
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
- Arterial Thrombosis/Embolism
- Causes Ischemic signs and symptoms
Arterial Thrombosis/Embolism
- Commonly due to atherosclerosis
- Also caused by vasomotor and clotting disorders
Ischemic Signs and Symptoms
- Pain
- Numbness
- Coldness
- Pallor
- Sensation changes
- Weakness
- Muscle spasm
Peripheral Vascular Disease - Inflammatory Disorders
- Vasculitis = inflammation
- Result in narrowing or occlusion of the blood vessel lumen or weakening of the vessel wall and formation of aneurysm
Vasculitis - Types
- Polyarteritis Nodosa
- Arteritis
- Allergic or hypersensitivity angiitis
- Kawasaki disease
- Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger's Disease)
- Wegener's Granulomatosis
Peripheral Vascular Disease - Vasomotor Disorders
- Raynaud's Disease
- Complex regional pain syndrome
- Can lead to focal areas of ischemia affecting tissue and nerves -> TEMPORARY!
- Increasing activity -> increases vasoconstriction
Peripheral Vascular Disease - Venous Disorders
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency
- Venous Thromboembolism -> Thrombophlebitis
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
- incompetence of valves allows venous blood to pool and flow backward
- Causes hypertension, obstruction of venous flow, and veins become enlarged and weak
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) - Causes
- Incompetent venous valves
- Inadequate muscle action
- Venous obstruction
*Physiological consequences of venous thromboembolism
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) - Risk Factors
- Age
- Genetics
- Obesity
- Prolonged standing
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking
- Female hormones
- Pregnancy
Venous Insufficiency - Spider Veins
- Dermal veins
Venous Insufficiency - Varicose Veins
- Subcutaneous veins
- large!!
Venous Insufficiency - Swelling
- Can cause build-up of wastes which can lead to infection
Venous Insufficiency - Skin Changes
- Ex: Cellulitis
Venous Insufficiency - Hemosiderin Staining
- RBCs stuck in skin
- Redness/brownish skin
Venous Insufficiency - Chronic Leg Ulceration
- 80% of all ulcerations
- Due to waste build-up
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) Treatment
- Promote venous return
- Wound care
- medical and surgical management
**Poor prognosis for resolution of CVI
How to promote venous return in CVI?
- Rest and elevation throughout the day
- Avoid dependent position (decrease amount of standing)
- Raise foot of bed 6 inches
- compression stockings, pumps
- ROM exercise, progressive ambulation
**Caution must be taken with compression dressings and elevation due to common co-morbidities of arterial insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, and congestive heart failure
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Symptoms
- Aching or cramping that is predictable with activity and elevation
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Edema
- May or may not be present
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Muscle Mass
- Reduced
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Elevation
- Worsens symptoms
- Dependency improves symptoms
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Walking Exercise
- Aching begins at specific time/distance, goes away with rest, returns with exercise
- Intermittent claudication
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Pulses
- Decreased or absent
- Bruits may be present
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Skin
- Reduced hair
- tight, shiny skin
- thick/brittle nails
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Skin Color
- Cyanotic or pale
- Dependent rubor
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Skin Temperature
- Cool
Arterial Vascular Disorder - Ulcers
- Pale base
- Found at high-pressure sites such as heel or tip of toes
Venous Vascular Disorder - Symptoms
- Aching, burning, cramping
- Fatigue while standing
- Heaviness
- Night cramping
- Swelling
- Throbbing
Venous Vascular Disorder - Edema
- Worse at end of day
- Improves with elevation
Venous Vascular Disorder - Muscle Mass
- Unaffected
Venous Vascular Disorder - Elevation
- Lessens symptoms
Venous Vascular Disorder - Walking Exercise
- Lessens symptoms
Venous Vascular Disorder - Pulses
- Pulses still strong! but may be difficult to palpate due to edema
Venous Vascular Disorder - Skin
- Chronic cellulitis, dermatitis, ulceration
Venous Vascular Disorder - Skin Color
- Hyperpigmented
- Brown discoloration
- Often superior to medial malleolus
Venous Vascular Disorder - Skin Temperature
- May be warm with infection, phlebitis
Venous Vascular Disorder - Ulcers
- Often near medial malleolus and gaiter area of lower leg
- Irregular border
- Pink/red base
Venous Thromboembolism
- Partial or complete occlusion of a vein by a thrombus (clot) with secondary inflammation of the vein
- Ex: Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
- Typically occur in lower extremities or pelvis
- Small percentage occur in UEs
- Can progress into pulmonary emboli -> thrombus will got to right side of heart and then into pulmonary system
*~ 50% are asymptomatic
**80% of symptomatic cases involve proximal DVT (iliac, femoral, or popliteal vein) --> usually more SEVERE b/c bigger veins (bigger clots) --> at diagnosis, more than half already have a PE
Venous Thromboembolism - Signs and Symptoms
- Pain or tenderness in the calf
- Leg or calf swelling
- Dilation of superficial veins
- Warmth
- Pitting edema
Venous Thromboembolism - Risk Factors
- Previous DVT
- Increasing age
- Active cancer/cancer treatment
- Severe infection
- Estrogen-containing oral contraceptives
- Hormonal replacement therapy
- Pregnancy or given birth < 6 wks ago
- Immobility (bed rest, flight travel, fractures)
- Surgery/anesthesia/critical care admission
- Central venous catheters
- Inherited thrombophilia
- Obesity
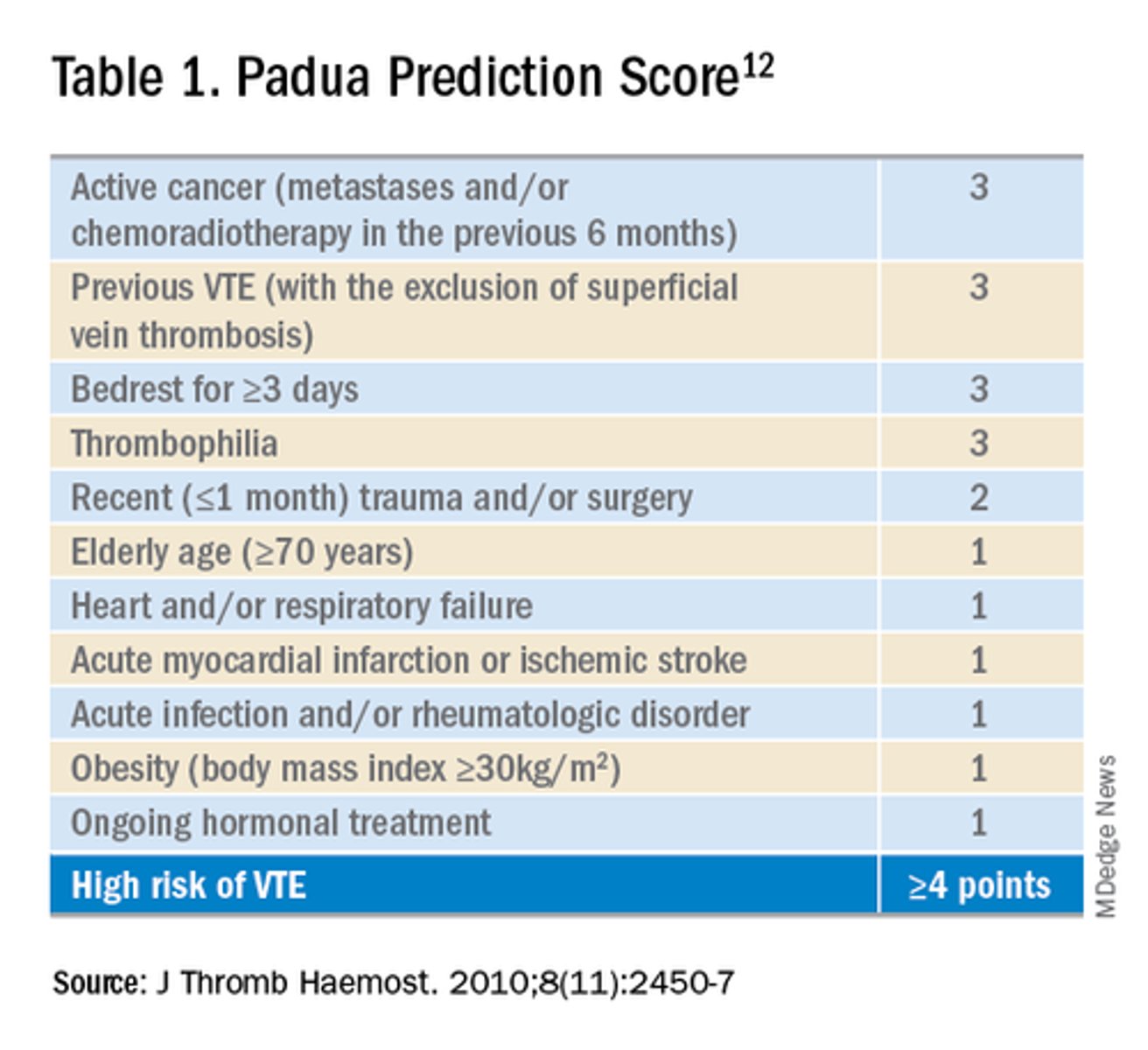
Padua Prediction Score
- Used to evaluate patient's risk of DVT
- Score >/= 4 indicates a high risk of DVT
Venous Thromboembolism - Prevention
- Education
- Hydration
- Activity
- Mechanical ventilation -> not first option if patient mobile
- Medical management -> decrease hypercoagulability of blood, LMWH, warfarin, greenfield filter (not common)
Wells' Clinical Prediction Rule
- Reliable and valid tool for clinical assessment for predicting the risk of DVT in the LE
- Score of 2 or more = DVT likely
- Score less than 2 = DVT unlikely

Venous Thromboembolism - Treatment Goals
- Prevent pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Limit extension of thrombus
- Limit damage to vein
- Prevent another clot
Venous Thromboembolism - Medical Management
- Anticoagulation (LMWH, DOACs)
**Will not get ride of clot, but will stop body from making more clots
Venous Thromboembolism - Surgical Interventions
- Thrombolysis
- Thrombectomy
- Embolectomy
- IVC filter
**These are only performed in unable to anticoagulate
LMWH - Time to Mobilize
- Mobilize at > 5 hrs since administration
- Ex: Lovenox, Fragmin
Fondaparinux - Time to Mobilize
- Mobilize at > 3 hours since administration
- Ex: Arixtra
UFH - Time to Mobilize
- Mobilize at > 24 hours since administration
- Ex: Heparin
DOAC - Time to Mobilize
- Mobilize at > 3 hours since administration
- Ex: Eliquis, Xarelto, Pradaxa
Pulmonary Embolism - Signs and Symptoms
- Pleuritic chest pain, diffuse chest discomfort
- Tachypnea, tachycardia
- Hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Anxiety, restlessness, apprehension
- Dyspnea, persistent cough
- Sudden death
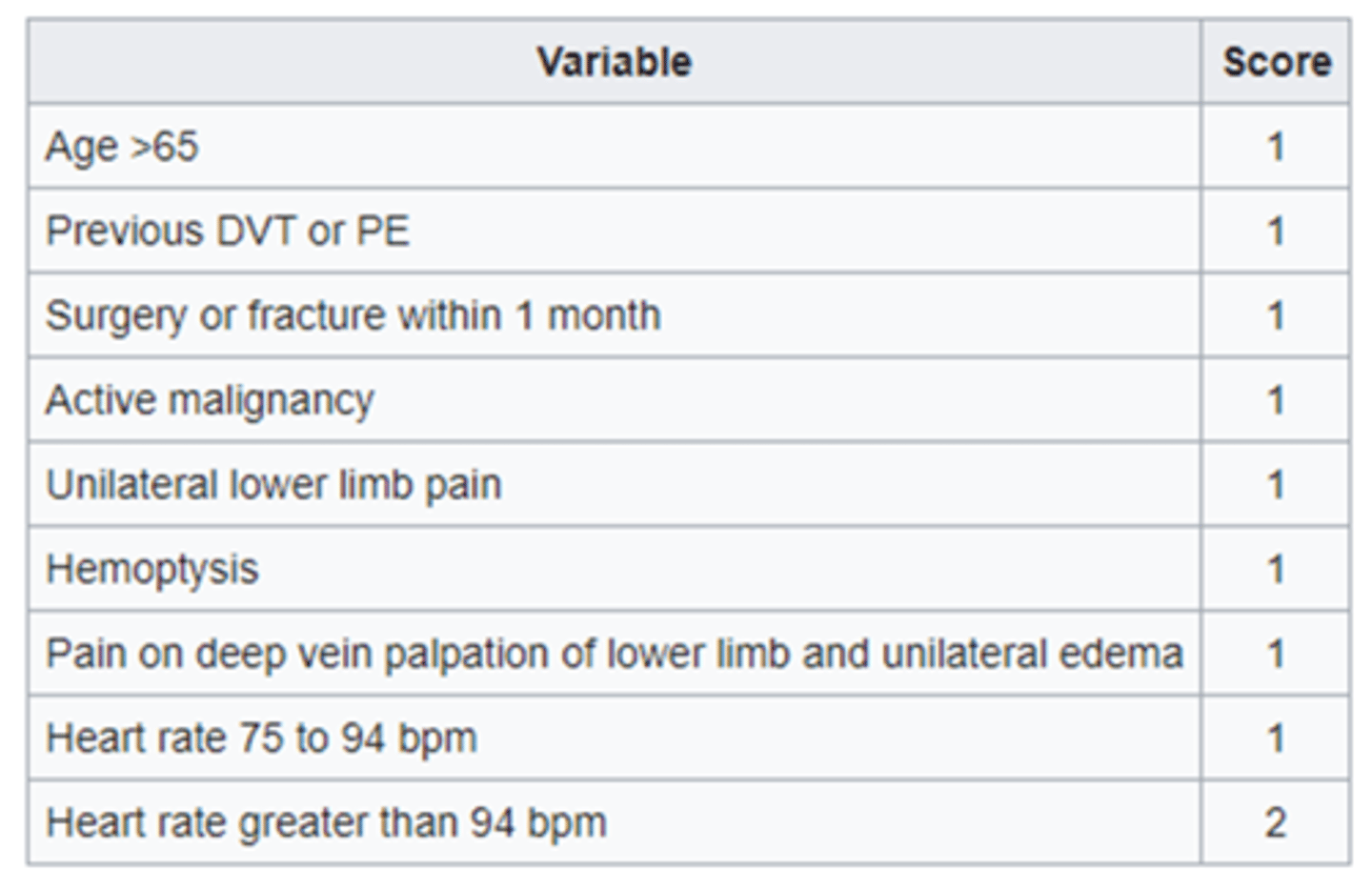
Simplified Geneva Score
- Assesses clinical probability of PE
- Low probability = score 0-1
- Intermediate = score 2-4
- High = score >/= 5
Mobilization with PE
- Communicate with medical team before mobilizing
- Need to determine risk of mortality
- Low risk vs high risk dependent on clinical parameters of PE severity, hemodynamic stability, signs of R ventricular dysfunction, and elevated troponins
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1: Inpatient
- Immediately after CV accident
- Hospital stay could be 24 hour for PCI (angioplasty)
- Often less than 5 days for uncomplicated MI, CABG
- Exercise physiologist, PT
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1 - Goals
- Offset effects of bed rest
- Patient monitoring and assessment of hemodynamic responses to allow safe return to activity
- Identify impairments that influence prognosis
- Prepare patient and support system for home progression
- Recommendations for continued cardiac rehab
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1 - Frequency
- 2-4x/day, at least 1x/day
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1 - Intensity
- Patient hemodynamic and symptomatic responses, ECG findings
- RPE
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1 - Duration
- 10-15 minutes
- Begin with short bouts (3-5 minutes), use frequent rest periods (goal 2:1 exercise/rest)
- Include warm-up and cool-down exercises
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1 - Type
- Functional activities
- Large muscle group activities -> challenges CV system, alters vital signs more reasonably
**targeting small muscles can drastically increase vital signs
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1 - Progression
- INDIVIDUALIZED based on daily assessment
- Progression can include less rest breaks and/or shorter rest breaks
**Discontinue exercise if the pt shows signs of an adverse response and DOCUMENT
Cardiac Rehab Phase 1 - Documentation
- Patient position, level of assist and time
- Type of sitting and/or standing exercises
- Time period and distance ambulated, number of stairs
- Number and duration of rests
- Vital sign response to each activity
- Education provided
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2: Outpatient
- Several weeks after CV accident
- Includes SNF
- Most patients go home w/ cardiac rehab and/or PT
- Formal cardiac rehabilitation programs are multi-disciplinary and involve education, exercise, and behavior change to assist individuals with CVD to achieve optimal physical, psychological, and functional status within the limits of their disease
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2 - Goals
- Supervision and monitoring of the patient, and assisting with implementation of a safe and effective physical activity program
- Helping the patient to return to vocational and recreational activities
- Risk factor reduction
- Improve psychosocial well-being, which influences recovery from heart disease
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2 - Frequency
- At least 3x/week, ideally 5-7x/week
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2 - Intensity
- RPE 12-16
- Patient may have exercise test ~ 4-6 weeks post hospital discharge -> 40-80% HRR or 70-85% HRmax if exercise test available
Exercise Intensity if no exercise test available
- Activity should be gradually progressive in logical stepwise fashion of increasing energy costs (METs) with appropriate HR and BP monitoring ) -> typical initial MET ~ 2-4
- Titrate based on RPE, signs/symptoms, physiologic response
- Conservative prescription usually best initially
- Functional capacity evaluation (6 min walk)
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2 - Duration
- 20-60 minutes
- Begin with multiple intervals (<10 min), gradually increase (+1-2 min/day)
- Include 5-10 minute warm-up and cool-down (low intensity aerobic activities)
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2 - Type
- Large-muscle group activities: walking, cycling, functional activity, MAKE IT FUN!!
- Supplement with increase in daily lifestyle activities: gardening, walk break at work, household chores
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2 - Education
- Risk factor reduction (secondary prevention)
- Selecting appropriate exercise intensity
- Patient self-monitoring during activity
- Ability of patient to recognize adverse symptoms
Exercise Prescription and Return to Work
- Assess patient's work environment -> primary movements, muscle groups used, MET demands, environment factors, intermittent heavy work
- Include both resistance and aerobic training
- Include functional exercises -> similar to work demands
- Expose to environment similar to work conditions
Cardiac Rehab Phase 2 - Psychosocial Considerations
- Many patients experience fear, isolation, anxiety, and/or depression post cardiac event
Cardiac Rehab Phase 3: Maintenance
- Patient takes over responsibility of exercise
Cardiac Rehab Phase 3 - FITT
- 30-60 minutes
- 3-5x/wk
- Continues indefinitely
- Compliance is an issue
Considerations for Independent Exercise
- Cardiac symptoms are stable
- Appropriate response to exercise -> HR, BP, ECG
- Demonstrated knowledge of proper exercise principles and awareness of abnormal signs/symptoms
- Motivation to continue exercise without direct supervision
Benefits of Cardiac Rehab
- Risk factor reduction
- improvement in exercise tolerance and symptoms -> decreased myocardial O2 demand due to reductions in HR and BP at any given load
- Increased VO2max and functional capacity
- Improved psychosocial well-being and quality of life
- Decreased mortality
**Can't restore cardiac function, but with training a low EF can be more sustainable
Indications for Cardiac Rehab
- MI
- Stable angina
- CABG
- PTCA or other transcatheter procedure
- Stable heart failure, cardiomyopathy
- Valve disease/surgery
- Heart transplant
- PAD
- At risk for CAD -> DM, dyslipidemia, HTN, obesity
Contraindications for Cardiac Rehab
- Any heart condition that is uncontrolled/unstable = UNFIT FOR PT!!
Healing Process Post MI - Immediately
- ECG Changes
Healing Process Post MI - 12-48 Hours
- Cardiac Enzyme Changes
Healing Process Post MI - 3 days to weeks
- Removal of damaged (necrotic) myofibrils
Healing Process Post MI - 3 weeks to months
- Collagen bundles replace muscle tissue
- Scar formation
Measure for Energy Demands of a Task
- METs
Measure for myocardial Workload of a Task
- Rate Pressure Product = HR x SBP
Ways to Alter Activity Intensity
- Alter grade
- Speed
- Resistance/load
Abnormal Responses to Exercise
- Chronotropic impairment (sinus bradycardia, HR doesn't increase with increasing workload)
- ECG abnormalities -> arrhythmias, ST segment elevation/depression, chest pain
- SBP > 250 mmHg, drop > 10 mmHg from baseline, failure to increase with increasing workload
- Rise or fall of DBP > 10-15 mmHg or DBP > 115 mmHg
- Oxygen saturation below 90%
- Hyperventilation ,dyspnea, wheezing, palpitations, pallor, dizziness, fatigue, confusion
Upper Limits of Exercise Intensity (Peak Exercise HR)
- Angina or other symptoms of CV insufficiency
- Plateau or decrease in SBP
- SBP > 240 mmHg or DBP > 110 mmHg
- ECG evidence of ischemia (ST segment depression)
- Increased frequency of ventricular arrhythmias
- Ventricular arrhythmias > 6/minute
- ECG evidence of L ventricular dysfunction
- Any other ECG disturbance
- Level 3-4 dyspnea
- Any clear signs or symptoms of exertional intolerance
MaxHR Equation
MaxHR = 220 - age
HRR Equation
HRR = MaxHR - RestingHR
%HRR Equation
%HRR = %(MaxHR- RestingHR) + RestingHR
Cardiac Resistance Training Guidelines
- Can start in phase 2 of cardiac rehab, following protocol
- Minimum of 5 wks after MI including 4 wks of continuous program participation
- Minimum of 8 wks post CABG including 3 weeks of continuous program participation
- Minimum of 2 wks following PTCA (angioplasty) including continuous program participation
Cardiac Resistance Training - Frequency
- 2-3x/wk, rest day between workouts
Cardiac Resistance Training - Intensity
- 1 set of 8-10 reps for each major muscle group
- 30-50% 1-RM
- RPE = 11-13
- Large muscle groups before small muscle groups
Cardiac Resistance Training - Cautions
- Slow, controlled movements
- Exhale during exertion, inhale with return to rest position
- Avoid straining, breath holding
Cardiac Resistance Training - Progression
- Typically can progress 2-5 lbs for upper body or 5-10 lbs for lower body when 12-15 reps performed comfortably
Heart Failure and Exercise
- Patients with decompensated (uncontrolled) CHF should not begin aerobic exercise training until CHF is compensated
- Can tell if a person has uncompensated heart failure based on if patient's symptoms keep getting worse
Exercise Prescription w/ Heart Failure - Frequency
- 3-5x/week