Human Development and Learning
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what is constructivist theory?
the belief that learners construct knowledge rather than just passively take in information.
connecting new information to current understanding
what is social learning theory?
considers how environmental and cognitive factors interact to influence human learning and behavior.
what is environmentalist theory?
belief that learning is a reaction to the environment, the child’s environment shapes learning and behavior.
what were the four stages of cognitive development in Jean Piaget’s theory?
Sensorimotor Stage - birth to age 2
Pre-Operational Stage - ages 2 to 7
Concrete Operational Stage - ages 7 to 11
Formal Operational Stage - ages 12 and up
what does the sensorimotor stage entail?
Children begin to learn the environment around them through movement and sensation showing behaviors like looking and listening.
object permanence (even if my caregiver walks out of the room, they still exist)
Reflexes (rooting, startling at loud noises)
Self-soothing (thumb sucking)
Mobility
what does the pre-operational stage entail?
Children use pictures and words to represent things with symbols. They are typically not able to understand the logic or perspectives of others.
pretend play
imaginary friends
object representation (drawing family members)
egocentric
curious
what does the concrete operational stage entail?
Children begin to use more logical thinking so this is a good time to teach empathy. They may struggle with hypotheticals and abstract concepts.
Classifying objects (websites vs. books)
idea of conservation
inductive logic (concrete, hands-on problem solving; e.g., using math manipulatives to solve a problem)
less egocentric (more empathetic towards others
what does the formal operational stage entail?
preteens and teens are able to use logic, problem-solving, reasoning, etc. in this stage, it is important to provide opportunities to ask questions, encourage games and free play, as well as teach critical thinking skills.
abstract thinking (thinking more in life’s gray areas)
application of knowledge to complex problems
sense of identity
social and moral questions
what was jerome bruner’s theory and what did it propose?
Bruner’s Theory of Construvisim proposed that knowledge is represented and organized through different modes of thinking (or representation).
what were jerome bruner’s modes of thinking in his theory of constructivism?
Inactive (0-1 year)
this mode is used within the first year of life (corresponding with Piaget’s sensorimotor stage. the child’s thinking is based entirely on physical actions, and infants learn by doing, rather than by internal representation (or thinking).
Iconic (1-6 years)
this second mode describes how information is stored as sensory images (icons). these icons are usually visual ones, like pictures in the mind. this representation is imaged-based. the iconic mode suggests why it is helpful for learners to have diagrams or other sensory supports such as hearing smell and touch.
Symbolic (7+ years)
this mode develops last
this is where information is stored in the form of a code or symbol, such as in language. this corresponds to Piaget’s concrete operational stage.
knowledge is stored primarily as words, mathematical symbols, or in other symbol systems, such as music.
what is Lev Vygotsky’s theory?
Sociocultural Theory views human development as a social mediated process.
proposes that social interaction within the family and with knowledgeable members of the community is the primary means by which children acquire behaviors and cognitive processes relevant to their own society.
what is the culture-specific concept in lev vygotsky’s theory?
culture specific - real tools and symbolic tools play very important roles in cognitive development
include both technical tools such as books, media, computers and social software, and psychological tools such as language, signs, writing, and symbols
what is the private speech concept in lev vygotsky’s theory?
the act of communicating with oneself for the purposes of self-guidance and self-regulation.
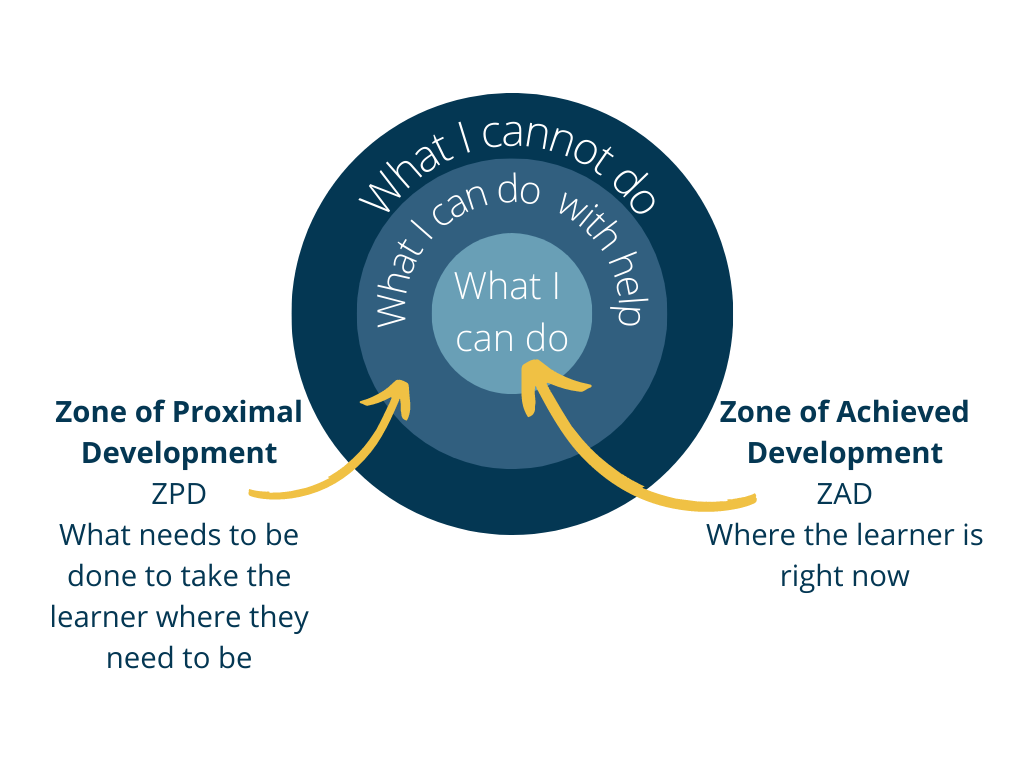
what is the zone of proximal development concept in lev vygotsky’s theory?
the space between what a learner can do without assistance and what a learner can do with adult guidance or as the child interacts with peers who are stronger in a specific skill.
what does Maria Montessori’s theory entail?
fosters children to seek to develop natural interests and activities
fosters a sense of independence with each child
classrooms place an emphasis on hands-on learning and developing real-world skills
what does Reggio Emilia’s theory entail?
it is an educational philosophy that is student-centered and includes the following key characteristics:
children can construct their learning; children are driven primarily by their interests
children learn their place in the world through interactions; it focuses heavily on social collaboration, encouraging children to work in groups and develop knowledge through communicating with others
a child’s environment is also their teacher; a child learns just as much from the environment they are in as they do from their parents and teachers
document your child’s thoughts; focus on documenting these thought progressions as your child learns
children have many languages, and the focus is on encouraging children to explore all these various aspects and learn how to communicate not only through speech but also through art and play
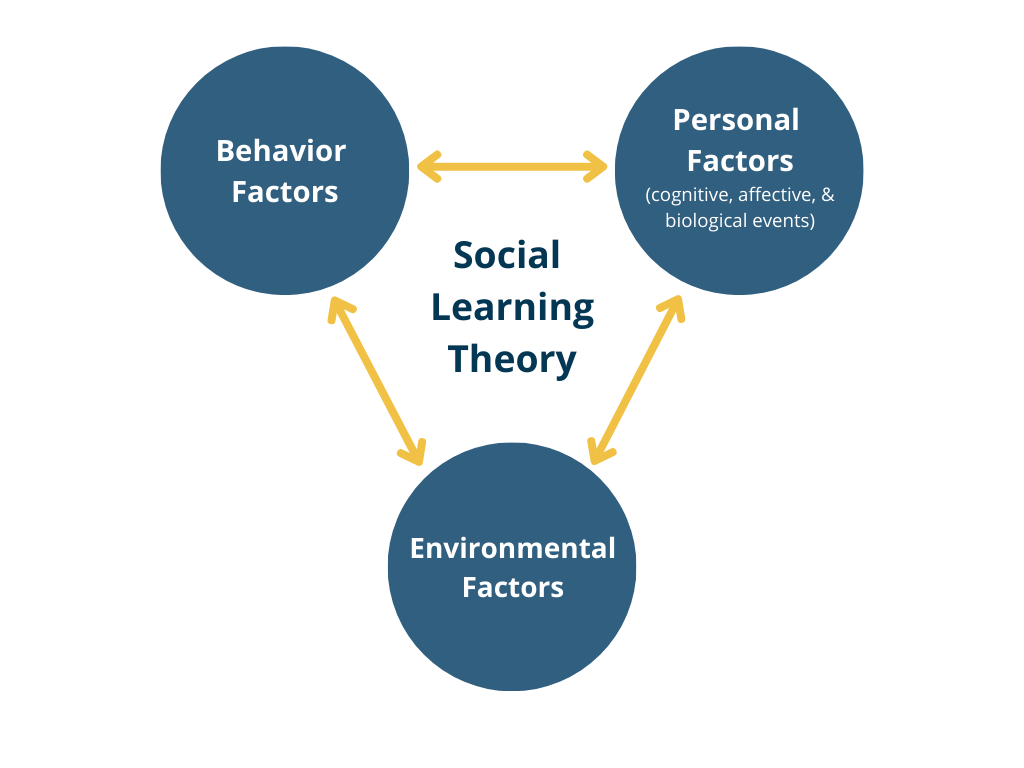
what does Albert Bandura’s Social Cognitive Theory entail?
provides a framework for understanding how people actively shape and are shaped by their environment, including how children’s schemas for knowledge are impacted heavily by their interaction with other children and adults.
What is Social Cognitive Theory?
Albert Bandura
views children as active learners who both influence and are influenced by their environment
a major component is observational learning: the process of learning desirable and undesirable behaviors for observing others
reproducing learned behaviors in order to maximize rewards
individuals’ beliefs in their own self-efficacy include whether or no they will reproduce an observed behavior.
what is Lawrence Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development?
attempts to explain how children develop in terms of morality, ethics, and decision-making.
occurs in a series of 6 stages
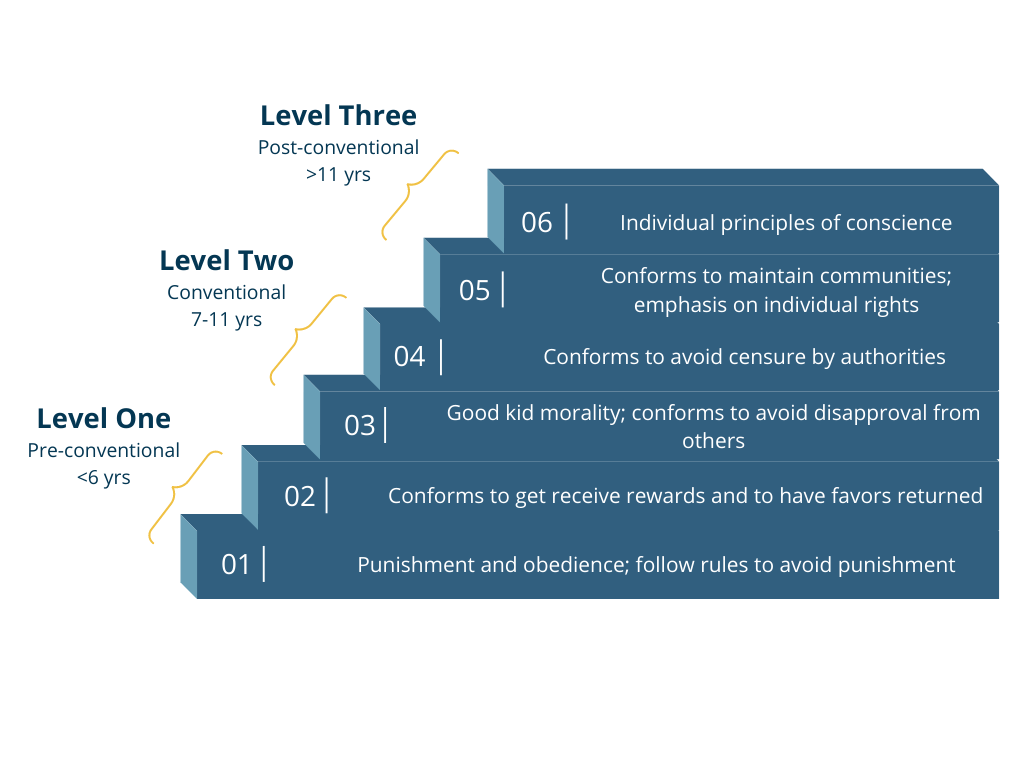
what are the 6 stages of Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development?
Level 1: Pre-conventional Morality
Stage 1 - Obedience and Punishment
Stage 2 - Individualism and Exchange
Level 2: Conventional Morality
Stage 3 - Developing Good Interpersonal Relationships
Stage 4 - Maintaining Social Order
Level 3: Post-Conventional Morality
Stage 5 - Social Contract and Individual Rights
Stage 6 - Universal Principles
what is the pre-conventional morality stage?
the earliest period of moral development. a child’s decision is primarily shaped by the expectations of adults and the consequences of breaking rules.
stage 1 - obedience and punishment - a child sees rules as fixed and absolute - obeying rules is important because it is a way to avoid punishment
stage 2 - individualism and exchange - a child accounts for individual points of view and judges actions based on how they serve the child’s interest
what is the conventional morality stage?
adolescents and adults internalize the moral standards they have learned from their role models and from society. focuses on the acceptance of authority and conforming to the norms of the group.
stage 3 - developing good interpersonal relationships - the person is focused on living up to social expectations and roles.
stage 4 - maintaining social order - focused on ensuring that social order is kept. people begin to consider society when making judgments.
what is the post-conventional morality stage?
people develop an understanding of abstract principles of morality
stage 5 - social contract and individual rights - cause people in the next stage to begin to account for the differing values, opinions, and beliefs of other people
stage 6 - universal principles - people follow these internalized principles of justice, even if they conflict with laws and rules
what is benjamin bloom best known for?
bloom’s taxonomy - implored the objectives related to cognition could be divided into subdivisions and ranked in order of cognitive difficulty
in childhood development, what is the physical domain?
gross motor skills and fine motor skills
as motor skills cognitive exploration, and physical health impacts cognitive functioning
connected to social and emotional domains physical abilities can influence social interactions and self-esteem
what is cognitive domain?
mentally process information to think, explore, reason, and understand what’s happening around them
intellectual skills- recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills
interconnects with language development support language acquisition and comprehension
influences social interactions understanding social cues and problem-solving in social context
what is social & emotional domain?
ensures children understands their feelings and emotions of others
attachment, sharing, accepting difference, identifying with different groups, using social skills, etc.
children and teens should interact socially with peers and develop healthy relationships with adults outside the family
impacts emotional development as social interactions influence emotional regulations and empathy
what is language & literacy domain?
skills of listening, speaking, and writing
provides the young child with the foundation for a wide range of abilities that they will be use throughout their academic and social life
language skills support cognitive processing and learning
influence social interactions as language enables communications and expression in social context
what is sensory domain?
involves the same senses and proprioception- or bodily awareness of one’s orientation in space
focuses on sensory perception and processing, including sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell
interrelates with cognitive development as sensory input contributes to cognitive understanding and learning
affects physical development as sesory experiences impact motor skills and physical responses
what is aesthetic domain?
involves appreciation of beauty, creativity, and artistic expression
thinking and problem-solving abilities
impacts emotional and social domains as artistic expression can evoke emotions and facilitate social connections
what are factors that can impact development?
Nutrition
sleep
prenatal exposure to drugs
trauma
safe and loving home environment
what are some factors that can influence development?
ENL’S
Socio-economic factors
abuse and neglect
substance abuse
How do English Learners influence development?
learn a new language at the same time they are expected to learn academic content in that new language
they must learn to communicate socially
may need scaffolds for success and English as a second language services
likely have parents/guardians who will need an interpreter at planning meetings and/or conferences
how do socio-economic factors influence development?
challenges like poverty, homeless, and hunger can negatively impact children and families alike
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
self-fulfilment needs
self-actualization
psycholoical needs
esteem
love and belonging
basic needs
security/safety
physiological needs
how does abuse and neglect influence development?
Students who have experience abuse or neglect may
exhibit internalizing or externalizing behaviors
development mental health conditions
struggle to connect with teachers and peers
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
how do substance abuse impact development?
strain
aggression
violence
conflict
loss of trust
neglect
development of codependent behaviors
Children exposed to adults with substance abuse issues run a higher risk of repeating the behavior they see in the home
challenges in academic and social settings and may cause mental disorders and/or emotional behavioral disabilities (EBD)
what are the major foundational theories of language acquisition?
behaviorism (Skinner)
nativism (Chomsky)
interactionism (Vygotsky)
Behaviorism
B.F. Skinner
posit that language is learned through imitation and reinforcement
children acquire language by mimicking sounds and words they hear
positive reinforcement from caregivers strengthens linguistic skills
nativism
Chomsky
suggests that humans are inherently wired with an innate capacity for language
“universal grammar” - implied that children are naturally predisposed to learn language and have an inherent understanding of the rules underlying it
interactionism
Lev Vygotsky
sociocultural theory emphasizes the role of social interaction and cultural context in language development
language acquisition is deeply intertwined with social interactions
children learn through engaging with more knowledgable individuals such as parents, teacher, and their cultural environment
what are the stage of language development?
prelinguistic stage
babbling stage
first words
two-word stage
telegraphic stage
beyond telegraphic stage
what is the role of social interaction?
language acquisition is intricately linked to social interactions with caregivers, peers, and educators
meaningful conversations, dialogues, and interactions with responsive adults enrich children’s vocabulary and comprehension skills
what is cultural context in language development?
children learn language within the cultural context of their community, absorbing cultural nuances, idiomatic expressions, and social conventions
what is a personalized development plan (PDP)?
Objective: To create a structured approach that outlines specific areas for growth, strategies for improvement, and measurable outcomes for students.
Step 1: Initial Assessment:
counselors begin with an initial assessment to understand the students’ strengths, weaknesses, interests and challenges. this can be achieved through interviews, self-assessments, or questionnaires.
Step 2: Goal Setting
counselors work collaboratively with the student to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. these goals should focus on key areas such as self-awareness, decision-making, and personal development
Step 3: Action Plan
counselors and students create a detailed action plan that outlines specific activities, resources, and timelines that should include:
activities, resources, and support
Step 4: Monitoring Progress
counselors schedule regular check-ins to discuss progress, challenges, and adjustments to the plan as necessary