Tissue Integrity (Class 17)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:53 PM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
1
New cards
Partial Bed Bath
Nurse assists the patient to bathe inaccessible body parts.
2
New cards
Complete Bed Bath
Reserved for patients who are completely dependent and require total assistance.
3
New cards
Edentulous
Without teeth
4
New cards
Cheilitis
Cracked lips
5
New cards
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums
6
New cards
Glossitis
Inflamed tongue
7
New cards
Halitosis
Bad breath
8
New cards
Maceration
Softening and breaking down of skin from prolonged moisture
9
New cards
Perineal Care
Cleaning and care of the perineal area. More frequent care needed for patients at a greater risk for infection.
10
New cards
Stomatitis
Sore or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth. (Ex. cheeks, tongue, gums) Also called “canker sore.”
11
New cards
Xerostomia
Dry mouth. Ex. Cracked tongue.
12
New cards
Chlorohexidine Gluconate (CHG)
* For oral and topical use
* Broad-spectrum microorganism coverage
* Reduces cross contamination and colonization of multidrug-resistant organisms
* Continues antimicrobial activity up to 24 hours after application
* ICU patients and those wit central lines require this every day.
* Broad-spectrum microorganism coverage
* Reduces cross contamination and colonization of multidrug-resistant organisms
* Continues antimicrobial activity up to 24 hours after application
* ICU patients and those wit central lines require this every day.
13
New cards
Denture Care
* Performed on a daily basis
* Handle with care as they can easily break
* Place a towel in the sink during cleaning
* Do NOT clean with toothpaste
* Remove at night
* Store in a cup with a patient label
* Do not:
* Place in a napkin
* Place on a food tray
* Use toothpaste to clean dentures
* Handle with care as they can easily break
* Place a towel in the sink during cleaning
* Do NOT clean with toothpaste
* Remove at night
* Store in a cup with a patient label
* Do not:
* Place in a napkin
* Place on a food tray
* Use toothpaste to clean dentures
14
New cards
True
True or False: Remove a patient’s dentures at night to prevent gum irritation and bacteria build up.
15
New cards
Paralysis/Immobilization Impact on Hygiene
Dependent body parts are exposed to pressure from underlying surfaces. The inability to turn or change position increases the risk for pressure injuries.
16
New cards
Diabetes Impact on Hygiene
Patients are prone to dryness of mouth, gingivitis, periodontal disease, and loss of teeth.
17
New cards
Excessive Secretions/Moisture Impact on Hygiene
Creates a medium for bacterial growth and causes local skin irritation, softening of epidermal cells, and skin maceration. Increases risk for pressure injuries.
18
New cards
Obesity Impact on Hygiene
Patient cannot visualize skin properly and keep it clean and dry. Excessive adipose tissue creates pressure from weight, lack of air circulation, and an increase in moisture with poor tissue perfusion.
19
New cards
Considerations for Caring for an Unconscious Patient
* Reduced gag reflex leads to the pooling of secretions.
* Microorganisms can grow.
* If secretions are aspirated, pneumonia can develop.
* CHG should be used topically and orally.
* Always have suction set up and the patient in semi-fowlers.
* Reduced blinking reflex distribution of tears leads to dry eyes, corneal abrasions, and infection.
* Apply lubricating eye drops.
* Apply an eye patch if the eye does not close completely.
* Microorganisms can grow.
* If secretions are aspirated, pneumonia can develop.
* CHG should be used topically and orally.
* Always have suction set up and the patient in semi-fowlers.
* Reduced blinking reflex distribution of tears leads to dry eyes, corneal abrasions, and infection.
* Apply lubricating eye drops.
* Apply an eye patch if the eye does not close completely.
20
New cards
Considerations When Caring for an Incontinent Patient
* Change when the incontinence occurs.
* Take measures to prevent incontinence associated dermatitis (IAD.)
* Exposure to urine, bile, and stool is common.
* Use urinary diversion methods like condom catheters or purwicks.
* Do NOT use briefs on a patient while they are in bed.
* Take measures to prevent incontinence associated dermatitis (IAD.)
* Exposure to urine, bile, and stool is common.
* Use urinary diversion methods like condom catheters or purwicks.
* Do NOT use briefs on a patient while they are in bed.
21
New cards
False
True or False: If a patient is incontinent, contacting the provider for a Foley catheter is an acceptable solution.
22
New cards
Shear
The sliding movement of skin and subcutaneous while the underlying muscle and bone are stationary.
23
New cards
Friction
The force of two moving across one another such as the mechanical force exerted when skin is dragged across a coarse surface.
24
New cards
Pressure Intensity
Capillary closing pressure as the minimal amount of pressure required to collapse a capillary.
25
New cards
Pressure Duration
Low pressure over a prolonged period and high-intensity pressure over a short period are two concerns related to this.
26
New cards
Tissue Tolerance
The inability of tissue to endure pressure depends on the integrity of the tissue and the supporting structures.
27
New cards
Top Down Damage (Superficial)
Stage I-II
28
New cards
Bottom-Up Damage (Deep)
Stage III-IV
29
New cards
Stage I Pressure Injury
Intact skin with non-blanchable erythema redness of a localized area. Usually over a bony prominence. The area may be painful, firm, soft, warmer, or color compared to adjacent tissue.
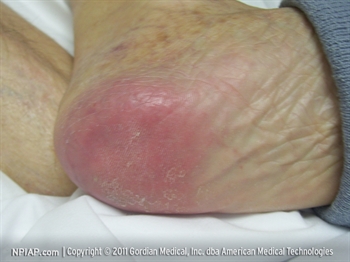
30
New cards
Nonblanchable Erythema
* Indicated compromised circulation
* The erythematous area does not blanch
* The erythematous area does not blanch
31
New cards
True
True or False: Nonblanchable erythema appears blue or violet in patients with darker skin.
32
New cards
Pressure Injury
Localized damage to the skin and underlying soft tissue developing over a bony prominence or related to pressure from a medical device.
33
New cards
Stage II Pressure Injury
Partial thickness loss of dermis presenting as a shallow open ulcer with a pink/red open wound bed without slough. May also present as an intact or open/ruptured serum-filled or serosanguinous filled blister.
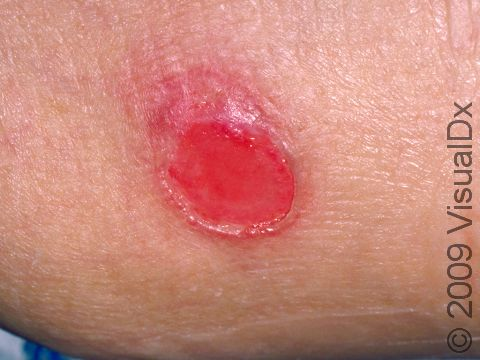
34
New cards
Skin Function
* Protection
* Temperature
* Sensation
* Regulation
* Temperature
* Sensation
* Regulation
35
New cards
Stage III Pressure Injury
Full thickness tissue loss. Subcutaneous fat may be visible but bone, tendon, or muscle are not exposed. Slough may be present but does not obscure the depth of the tissue loss.
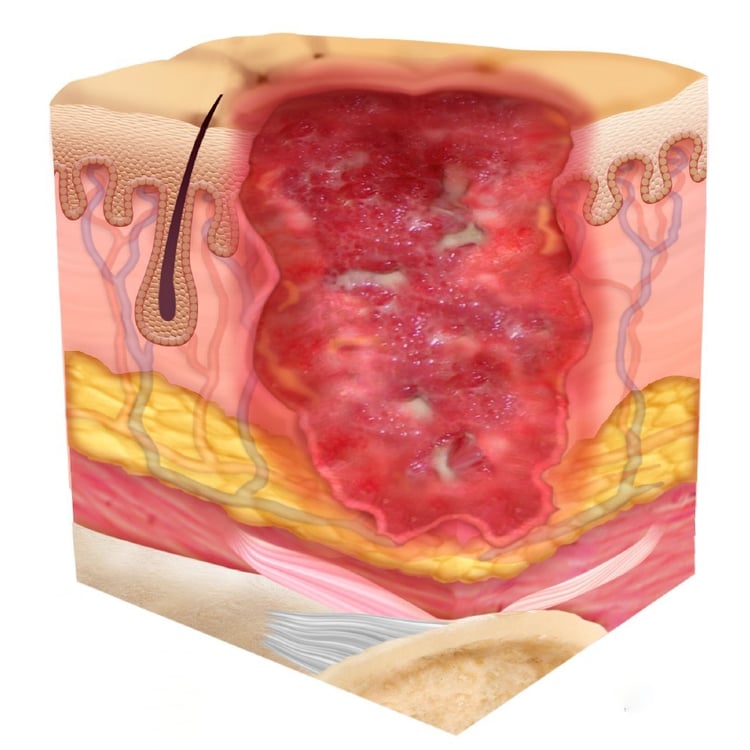
36
New cards
Stage IV Pressure Injury
Full thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle. Slough or eschar may be present. Often undermining or tunneling. Can extend into muscle and/or supporting structures. (Ex. fascia, tendon, or joint capsule.)
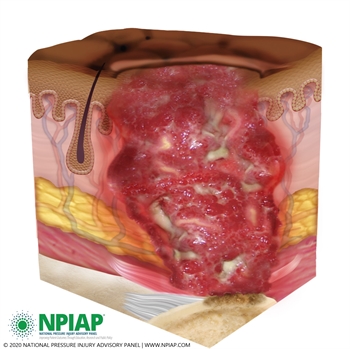
37
New cards
Slough
Wet necrotic tissue. Tan or yellow.
38
New cards
Eschar
Dry necrotic tissue. Black.
39
New cards
Deep-Tissue Pressure Injury
Purple or maroon localized area of discolored intact skin or blood-filled blister due to damage of underlying soft tissue from pressure and/or shear. The area may be preceded by tissue that is painful, firm, mushy, boggy, warmer or cooler as compared to adjacent tissue.
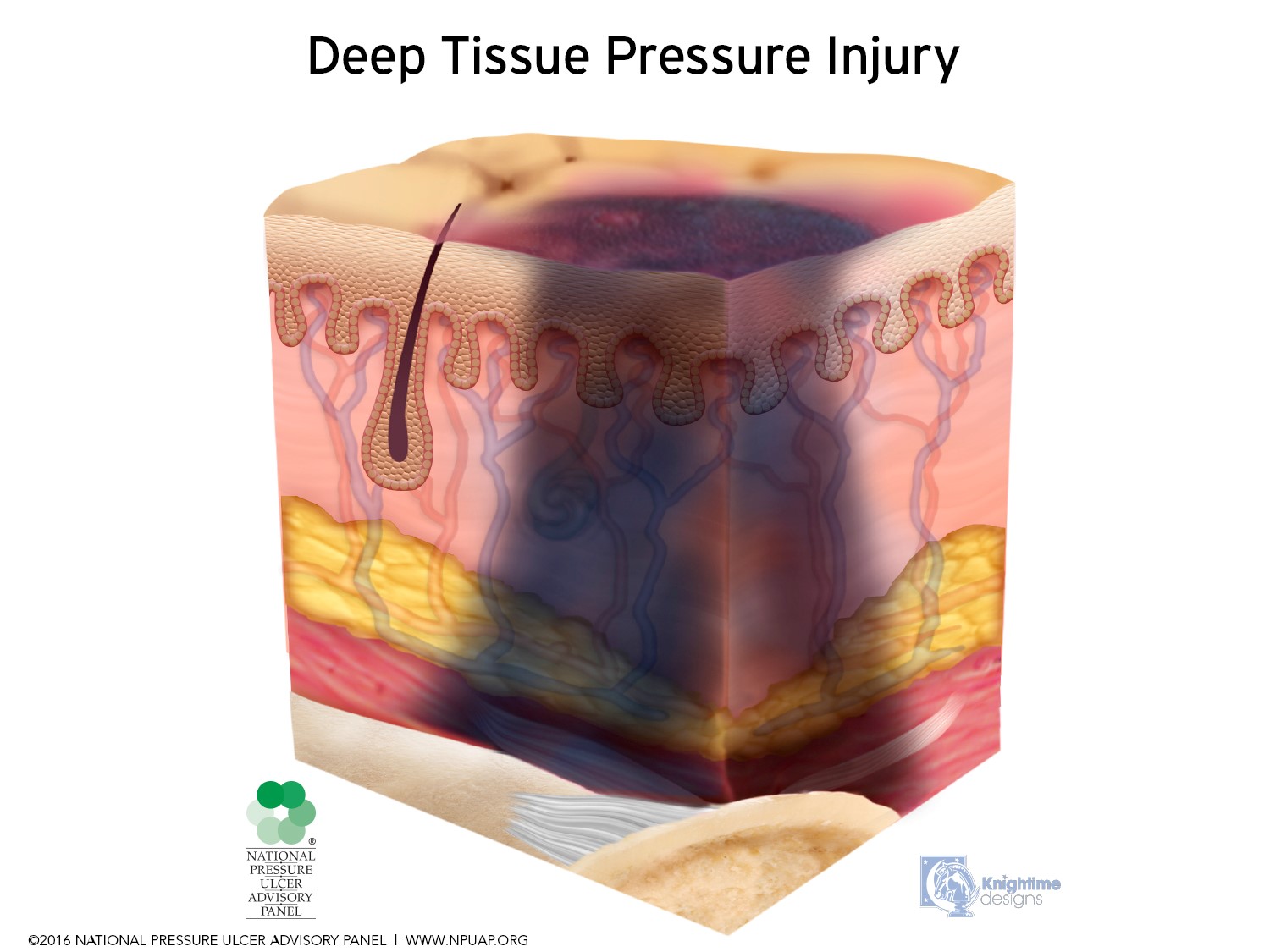
40
New cards
Unstageable Pressure Injury
Full-thickness tissue loss in which the actual depth of the ulcer is completely obscured by slough or eschar in the wound bed.
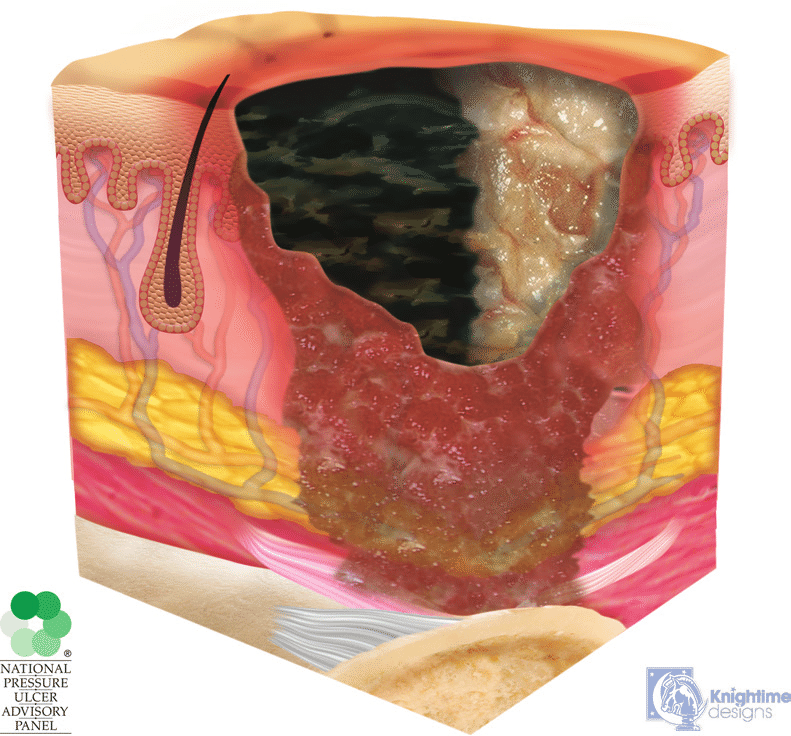
41
New cards
Acute Wound
Wounds that proceed through an orderly and timely reparative process that results in sustained restoration of anatomical and functional integrity. Caused by trauma or incision.
42
New cards
Chronic Wound
Wound that fails to proceed through an orderly and timely process to produce integrity.
43
New cards
Primary Wound Closure
* Surgical incision with sutures or staples
* Minimal scar formation
* Minimal scar formation
44
New cards
Secondary Wound Closure
* Wound edges are not closed
* Intentional for wounds that have tissue loss
* Heals by granulation tissue formation, wound contraction, and epithelialization
* Intentional for wounds that have tissue loss
* Heals by granulation tissue formation, wound contraction, and epithelialization
45
New cards
Tertiary Wound Closure
* Wound that is left open for several days; then wound edges are approximated.
46
New cards
Partial Thickness Wound Repair
1. Inflammatory response
2. Epithelial proliferation and migration
3. Reestablishment of the epidermal layers
47
New cards
Full-Thickness Wound Repair
1. Hemostasis
2. Inflammatory phase
3. Proliferation
4. Remodeling
48
New cards
Inflammatory Response
Damaged tissue/mast cells secrete histamine resulting in vasodilation. Redness and swelling with moderate serous exudate. Generally limited to 24 hours.
49
New cards
Epithelial Proliferation and Migration
Start at wound edges, cells migrate across the wounded soon after the wound occurs.
50
New cards
Hemostasis
Controls blood loss, establishes bacterial control, and seal the defect. Blood vessels constrict and platelet gather to stop bleeding.
51
New cards
Reestablishment of the epidermal layers
Cells slowly reestablish normal thickness and appear as dry pink tissue.
52
New cards
Proliferation
Occurs 3-4 days after injury and can last for two weeks wound fills with granulation tissue, wound contraction, and wound resurfacing by means of epithelialization.
53
New cards
Remodeling
Collagen scar continues to reorganize and gain strength. Begins several weeks post-injury and depends on depth/extent.
54
New cards
Partial Thickness
Shallow, involving loss of epidermis and possible loss of dermis.
55
New cards
Full Thickness
Extend into the dermis and heal by scar formation because deeper structure. Do not regenerate. Ex. Stage III and IV pressure injuries.
56
New cards
Internal Hemorrhage
* Hematoma-collection of blood
* Large bruise (ecchymosis)
* Large bruise (ecchymosis)
57
New cards
External Hemorrhage
* Blood-soaked dressing
* Pooling underneath the patient
* Pooling underneath the patient
58
New cards
Dehiscence
* Partial or total separation of the wound layers
* Occurs after coughing, vomiting, straining
* Patient ports a pop sensation or something “gave way”
* Possible serosanguineous drainage.
* Occurs after coughing, vomiting, straining
* Patient ports a pop sensation or something “gave way”
* Possible serosanguineous drainage.
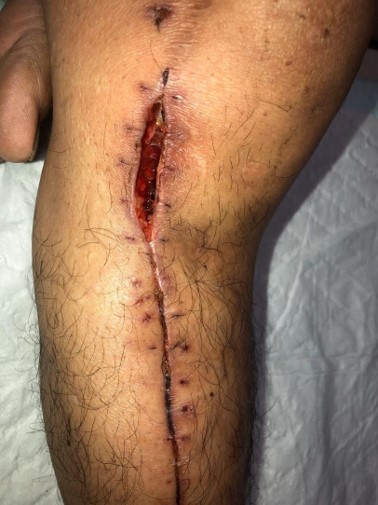
59
New cards
Evisceration
* Emergency
* Protrusion of visceral organs
* Caused by poor wound healing or suturing
* Notify the provider, keep the patient NPO, and cover site with sterile saline gauzes.
* Protrusion of visceral organs
* Caused by poor wound healing or suturing
* Notify the provider, keep the patient NPO, and cover site with sterile saline gauzes.
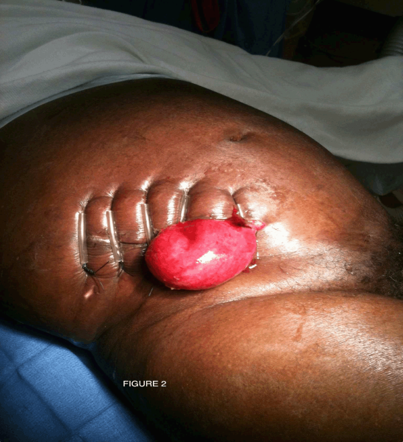
60
New cards
Infection
* A wound that has excessive exudate (drainage) provides an environment that supports bacteria growth, macerates the peri-wound skin, and slows the healing process.
* Signs and Symptoms:
* Erythema
* An increased amount of wound drainage
* Change in appearance of wound drainage (purulent and odorous)
* Fever and an increase in WBC count
* Wound culture
* Signs and Symptoms:
* Erythema
* An increased amount of wound drainage
* Change in appearance of wound drainage (purulent and odorous)
* Fever and an increase in WBC count
* Wound culture
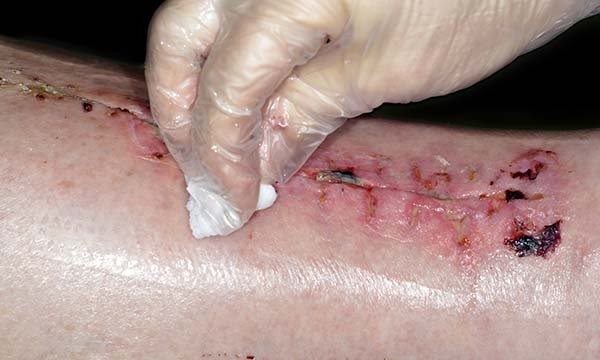
61
New cards
Surgical Drain Function
* Provide a means for fluid or blood that accumulates within a wound bed to drain out of the body
* Surgeon inserts it into or near a surgical wound if there is a large amount of drainage
* Removes excess wound fluid and promotes wound healing in the wound bed allowing it to heal from the inside out.
* Surgeon inserts it into or near a surgical wound if there is a large amount of drainage
* Removes excess wound fluid and promotes wound healing in the wound bed allowing it to heal from the inside out.
62
New cards
Jackson Pratt Drain

63
New cards
Hemovac
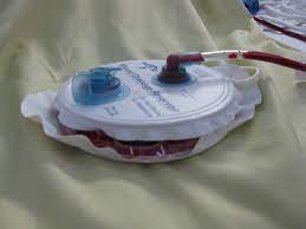
64
New cards
Penrose Drain
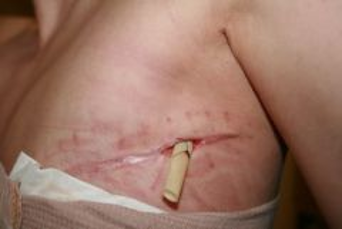
65
New cards
Debridement
* Removal of nonviable, necrotic tissue
* Necessary to rid the wound of a source of infection
* Enables visualization of the wound bed
* Provides a clean base necessary for healing
* Necessary to rid the wound of a source of infection
* Enables visualization of the wound bed
* Provides a clean base necessary for healing
66
New cards
Autolytic Debridement (Slow Method)
* Adding moisture to the wound to make the dead tissue liquify and easy to remove with dressing changes.
* Hydrocolloids, hydrogels, and transparent films.
* Hydrocolloids, hydrogels, and transparent films.
67
New cards
Mechanical Debridement
* Can damage healthy tissue as well
* Wet to dry dressing technique (wet gauze first and layer with dry gauze)
* Pulls off viable and nonviable tissue with each dressing change.
* PAINFUL
* Wet to dry dressing technique (wet gauze first and layer with dry gauze)
* Pulls off viable and nonviable tissue with each dressing change.
* PAINFUL
68
New cards
Chemical Debridement
* Application of a prescribed topical agent that chemically liquefies necrotic tissues with enzymes.
* Some enzymes dissolve and engulf devitalized tissue within the wound.
* Dakin solution breaks down and loosens dead tissue in a wound.
* Some enzymes dissolve and engulf devitalized tissue within the wound.
* Dakin solution breaks down and loosens dead tissue in a wound.
69
New cards
Biological Debridement
* Sterile maggots eat the dead tissue only.
70
New cards
Surgical Debridement
* Removal of tissue with a scalpel, scissors, or other sharp instrument.
71
New cards
High Pressure Wound Irrigation
* Type of debridement
* Pulse lavage
* Whirlpool treatments
* Pulse lavage
* Whirlpool treatments
72
New cards
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis
Skin irritation caused by prolonged exposure to feces or urine.
73
New cards
Gauze Dressing
* Oldest and most common dressings.
* Absorbent and wicks away wound exudate.
* Can be used to clean or pack wounds.
* Purpose is to provide moisture to the wound, yet allow wound drainage to be wicked into the dry cover pad.
* Absorbent and wicks away wound exudate.
* Can be used to clean or pack wounds.
* Purpose is to provide moisture to the wound, yet allow wound drainage to be wicked into the dry cover pad.
74
New cards
Self Adhesive Transparent Film Dressing
* Traps moisture over a wound, providing a moist environment to ensure epithelial cell growth.
* Ideal for small, superficial wounds. (Ex. Stage 1)
* Serves as a barrier to external fluids and bacteria but still allows the wound surface to breathe as oxygen passes through.
* Ideal for small, superficial wounds. (Ex. Stage 1)
* Serves as a barrier to external fluids and bacteria but still allows the wound surface to breathe as oxygen passes through.
75
New cards
Hydrocolloid Dressing
* Dressings with complete formulations of colloids and adhesive components. Support healing in clean granulating wounds and automatically debride necrotic tissue.
* Impenetrable to bacteria ad other contaminants.
* Self-adhesive and mold to the wound.
* Good for shallow to moderately deep wounds.
* Impenetrable to bacteria ad other contaminants.
* Self-adhesive and mold to the wound.
* Good for shallow to moderately deep wounds.
76
New cards
Hydrogel With Foam
* Gauze/sheet dressings with gel.
* Indicated for use in partial thickness wounds, deep wound with exudate, necrotic wounds, burns, and radiation damaged skin.
* Softens necrotic tissue, soothing, and does not adhere to the would.
* May require a secondary dressing.
* Indicated for use in partial thickness wounds, deep wound with exudate, necrotic wounds, burns, and radiation damaged skin.
* Softens necrotic tissue, soothing, and does not adhere to the would.
* May require a secondary dressing.
77
New cards
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
* Application of negative pressure wound through suction to facilitate healing and collect fluid.
* Draws edges of the wound together.
* Draws edges of the wound together.
78
New cards
Wound Irrigation
* Using irrigation syringe to flush the wound with a constant, low-pressure flow of solution.
* Cleanses the wound of exudate and debris.
* Good for deep, open, or inaccessible wounds.
* Requires sterile technique.
* Cleanses the wound of exudate and debris.
* Good for deep, open, or inaccessible wounds.
* Requires sterile technique.
79
New cards
Nutrition for Wound Healing
* More calories
* Protein
* Vitamin C
* Vitamin A
* Zinc
* Fluid
* Protein
* Vitamin C
* Vitamin A
* Zinc
* Fluid
80
New cards
Binders and Bandages
* Support underlying muscles and incisions, lessening muscle stress.
* Promote early ambulation, controlling pain, and recovery experiments.
* Promote early ambulation, controlling pain, and recovery experiments.
81
New cards
Hot Therapy
* Vasodilation
* Reduces blood viscosity
* Reduced muscle tension
* Increased tissue metabolism
* Increased capillary permeability
* Improves blood flow to injured body part
* Promotes delivery of nutrients and removal of wastes
* Improves deliver of leukocytes and antibiotics to wound sote
* Promotes muscle relaxation
* Reduces pain from spasm or stiffness
* Provides local warmth
* Reduces blood viscosity
* Reduced muscle tension
* Increased tissue metabolism
* Increased capillary permeability
* Improves blood flow to injured body part
* Promotes delivery of nutrients and removal of wastes
* Improves deliver of leukocytes and antibiotics to wound sote
* Promotes muscle relaxation
* Reduces pain from spasm or stiffness
* Provides local warmth
82
New cards
Cold Therapy
* Local anesthesia
* Reduced cell metabolism
* Increased blood viscosity
* Decreased muscle tension
* Reduces blood flow to injured site, preventing edema formation.
* Reduces inflammation
* Reduces localized pain
* Reduces oxygen needs of tissues
* Promotes blood coagulation at injury site
* Relieves pain
* Reduced cell metabolism
* Increased blood viscosity
* Decreased muscle tension
* Reduces blood flow to injured site, preventing edema formation.
* Reduces inflammation
* Reduces localized pain
* Reduces oxygen needs of tissues
* Promotes blood coagulation at injury site
* Relieves pain
83
New cards
True
True or False: Hot and cold therapy should be applied for no more than 20 minutes.
84
New cards
Risk Factors for Pressure Injury Development
* Impaired sensory perception
* Impaired mobility
* Altered level of consciousness
* Moisture
* Friction and shear
* Impaired mobility
* Altered level of consciousness
* Moisture
* Friction and shear
85
New cards
Braden Scale
* Measures the risk for the development of pressure injuries
* The higher the score, the less likely a patient is to develop a pressure injury.
*
* The higher the score, the less likely a patient is to develop a pressure injury.
*
86
New cards
Medical Device Pressure Injuries
Occurs when the skin or underlying tissues are subjected to sustained pressure or shear from medical devices or equipment. Ex. Nasal cannula.
87
New cards
Considerations for Older Adults
* More comorbidities
* Decreased subcutaneous tissue which reduces padding protection over bony prominences
* Aging skin has decreased epidermal turnover and healing requires more time
* Diminished inflammatory response
* Decreased collagen
* Reduces elasticity
* Thinning of underlying muscles
* Decreased subcutaneous tissue which reduces padding protection over bony prominences
* Aging skin has decreased epidermal turnover and healing requires more time
* Diminished inflammatory response
* Decreased collagen
* Reduces elasticity
* Thinning of underlying muscles
88
New cards
True
True or False: Shear + Friction = Superficial damage
89
New cards
True
True or False: Pressure Intensity + Pressure Duration + Tissue Tolerance = Deep Damage
90
New cards
Serous
Clear, watery plasma
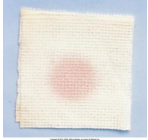
91
New cards
Purulent
* Thick, yellow, green, tan, or brown.
* Indicates infection
* Indicates infection
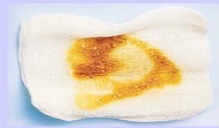
92
New cards
Serosangiuneous
* Pale, red, watery.
* Mixture of serous and sanguineous
* Common and normal early in healing
* Mixture of serous and sanguineous
* Common and normal early in healing
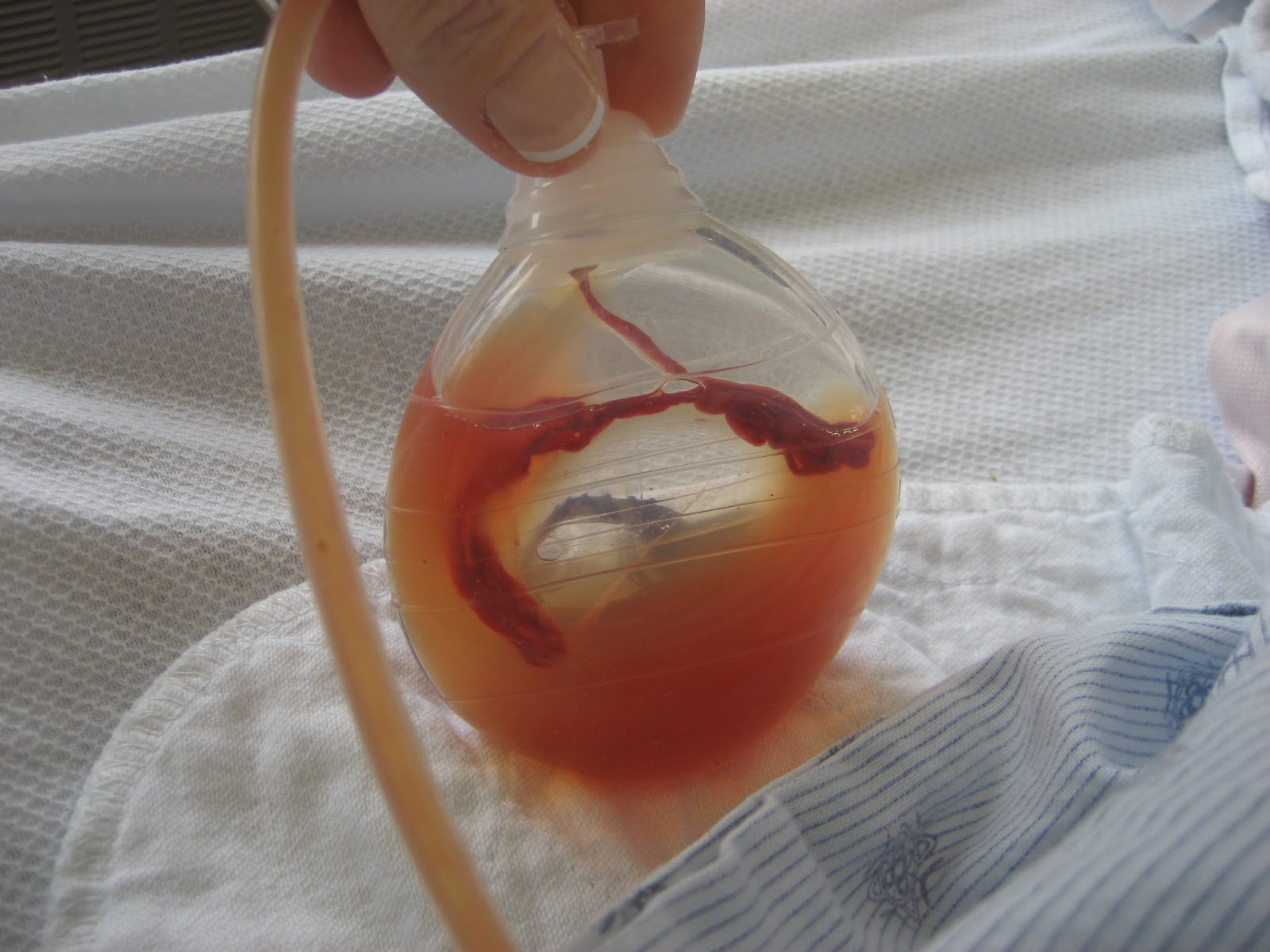
93
New cards
Sanguineous
* Bright red
* Indicates active bleeding
* Indicates active bleeding
