chapter 20 + 21 electrochemistry and equilibria
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
oxidation number of cl
-1 (except when combined with O or F)
ox number of H
-1 in metal hydrides, +1 in everything else
ox number of O
-2 except in peroxides (-1) or OF2 (+2)
balancing redox reactions in acidic/basic solutions
divide the reaction into half reactions
balance the atoms in each half reaction
balance the O by adding H2O
balance the H by adding hydride ions (in acid) or OH (bases)
balance the charges by adding electrons
put the reactions back together and multiply
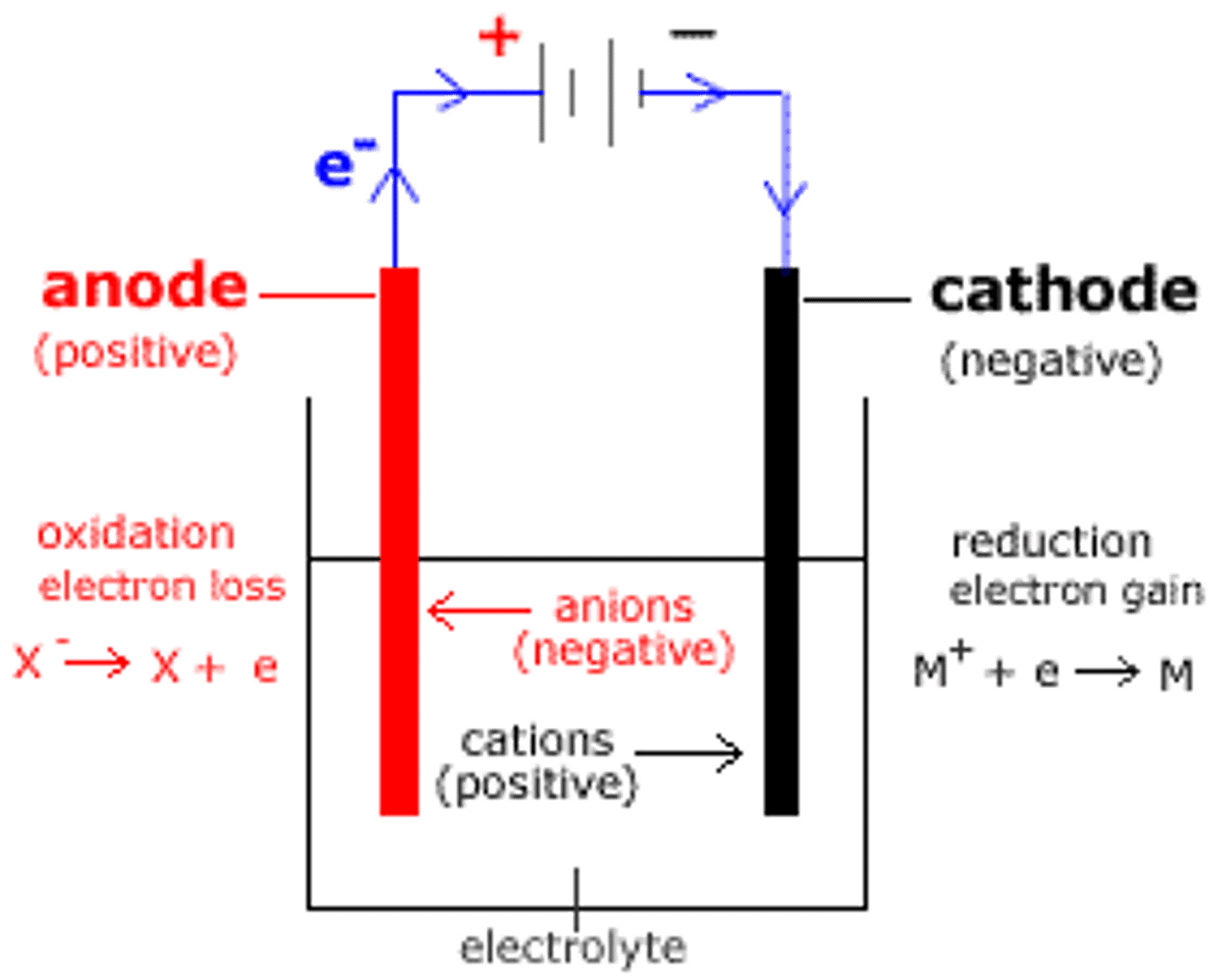
electrolysis cell
faraday's law
Q = I x t
Q= total charge (coulombs, C)
I= current in Amps (A)
t= time (s)
nerst equation
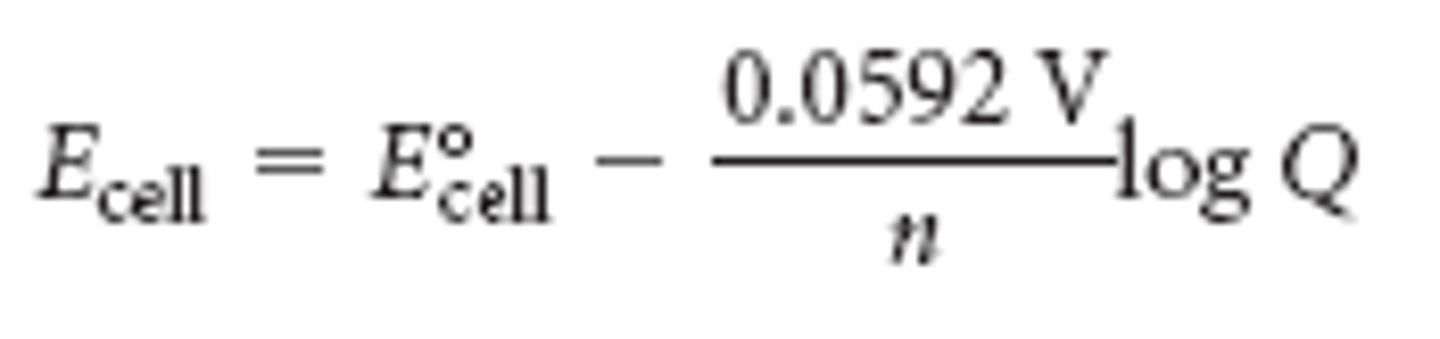
standard electrode potential
the voltage produced when a standard half cell is connected to a standard hydrogen electrode under standard conditions
standard cell potential
the difference in the standard electrode potential between two specified half cells
conjugate pair
an acid base pair on each side of an acid base neutralisation reaction that are related to each other by the difference of a hydrogen ion
pH
-log[H+]
Kw
ion product constant for water (1.0 x 10^-14)
[H+][OH-]
Ka
acid dissociation constant; high = likely to dissociate (ionize), small = unlikely/less dissociation
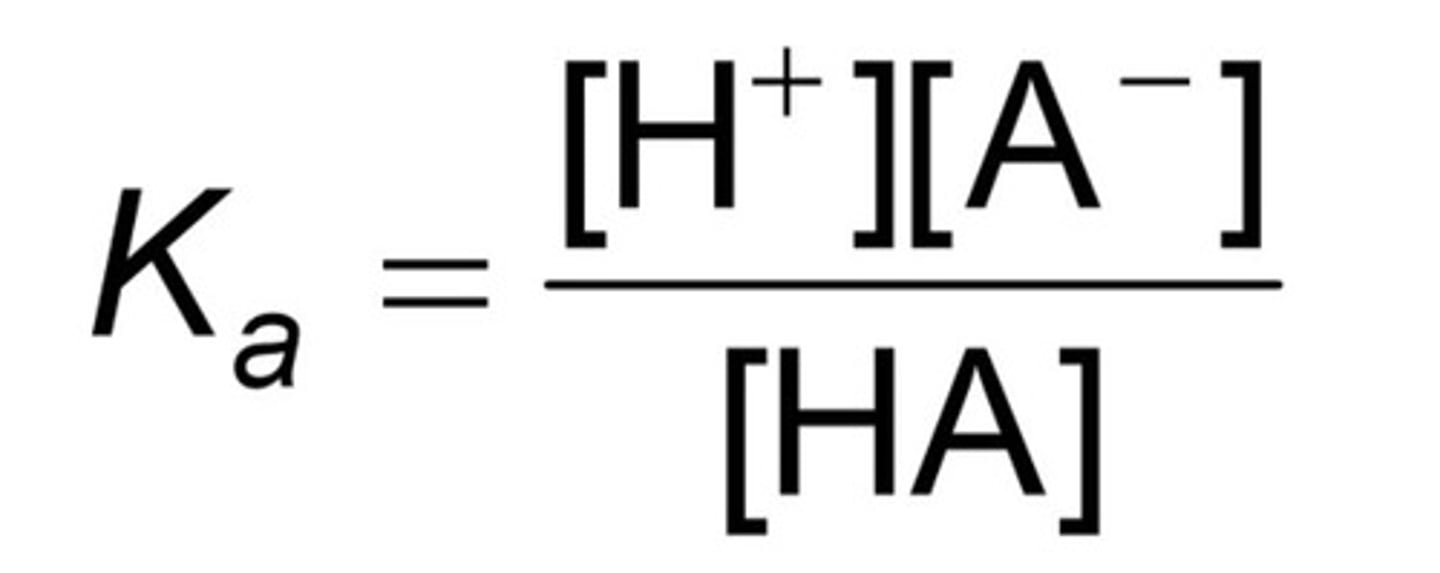
buffer solution
a solution that minimizes changes in pH when moderate amounts of an acid or base are added
calculating pH of a buffer solution
pH=pKa+log (conjugate base/weak acid)
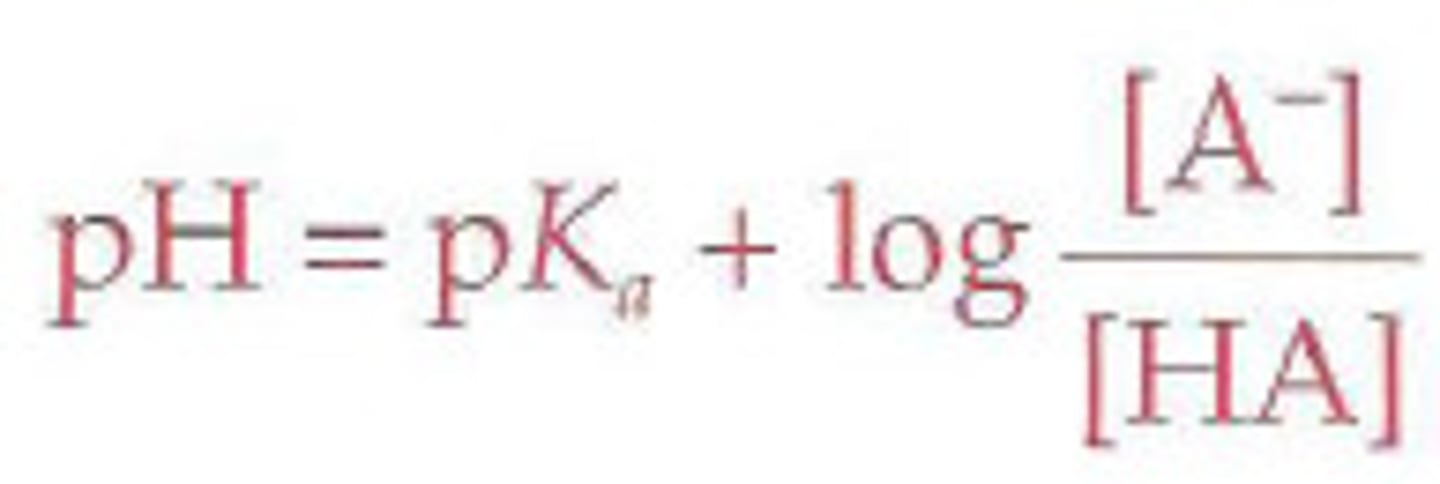
Ksp
solubility product constant
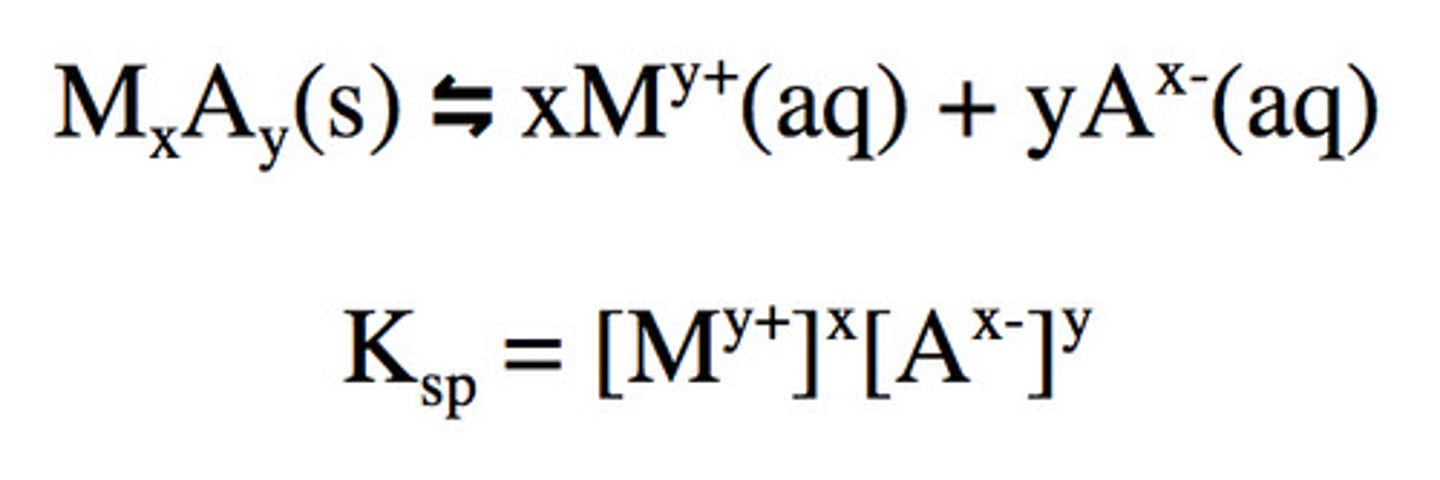
common ion effect
a decrease in the solubility of an ionic compound caused by the addition of a common ion
Kpc
partition coefficient
[X(solvent A)]/[X(solvent B)]