Dominance: Incomplete Dominance, Codominance and Overdominance
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is dominance?
Interaction between genes at the same locus
2 versions of the same gene
What are the 3 subgroups of dominance?
Incomplete dominace
Codominace
Overdominace
How does this relate to the Mendel theory?
It acknowledges dominace, but not the different types of dominance
How are alleles in the different types of dominance, different from each other?
Due to slight differences in DNA sequence at same loci
What is the phenotype of heterozygotes in incomplete dominance?
It falls within a range (intermediate) between the phenotypes of the 2 homozygotes
Therefore, which theory does incomplete dominance represent?
Blending theory
What is the phenotypic ratio of incomplete dominance?
1:2:1
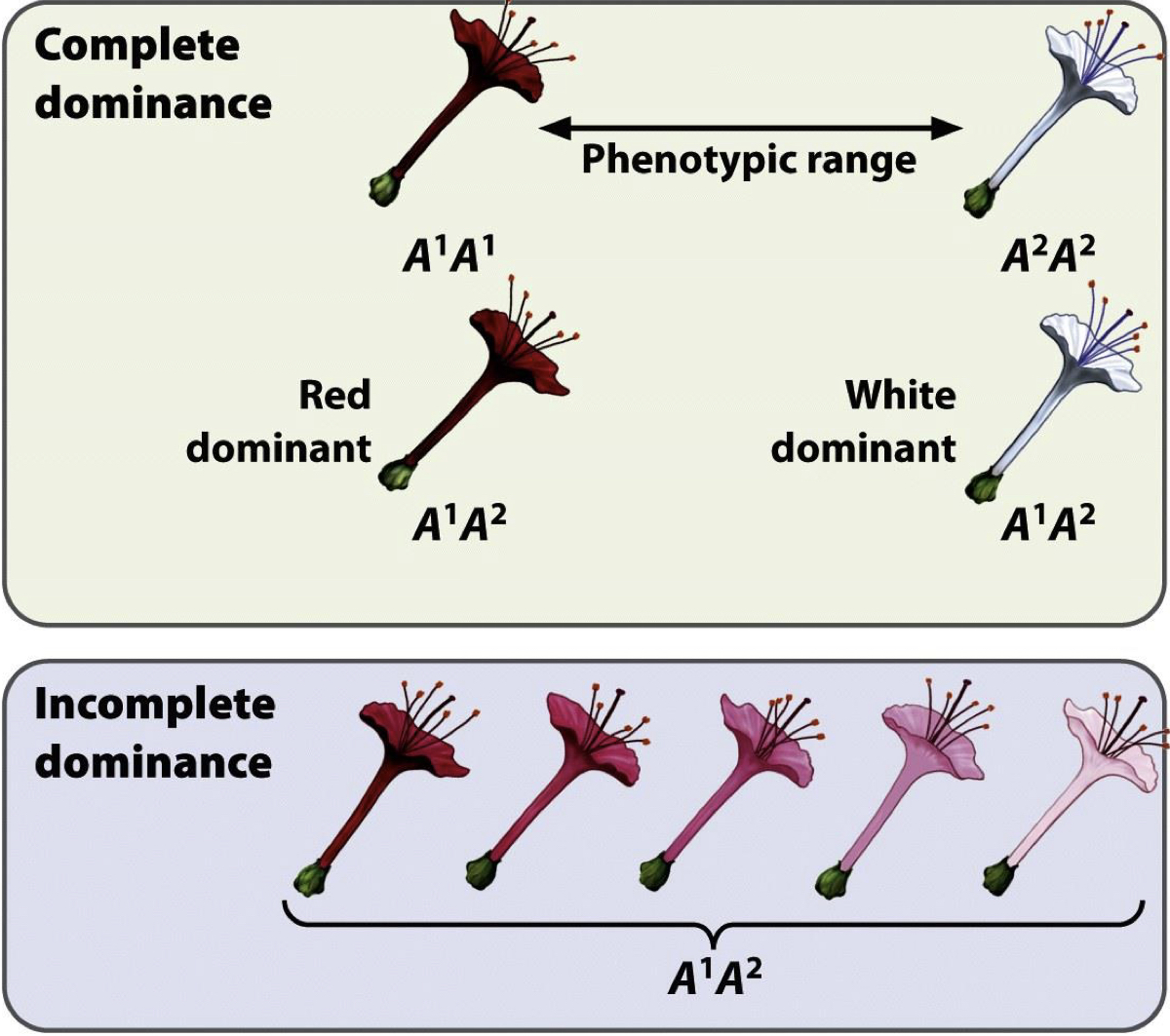
2 diagrams showing incomplete dominance
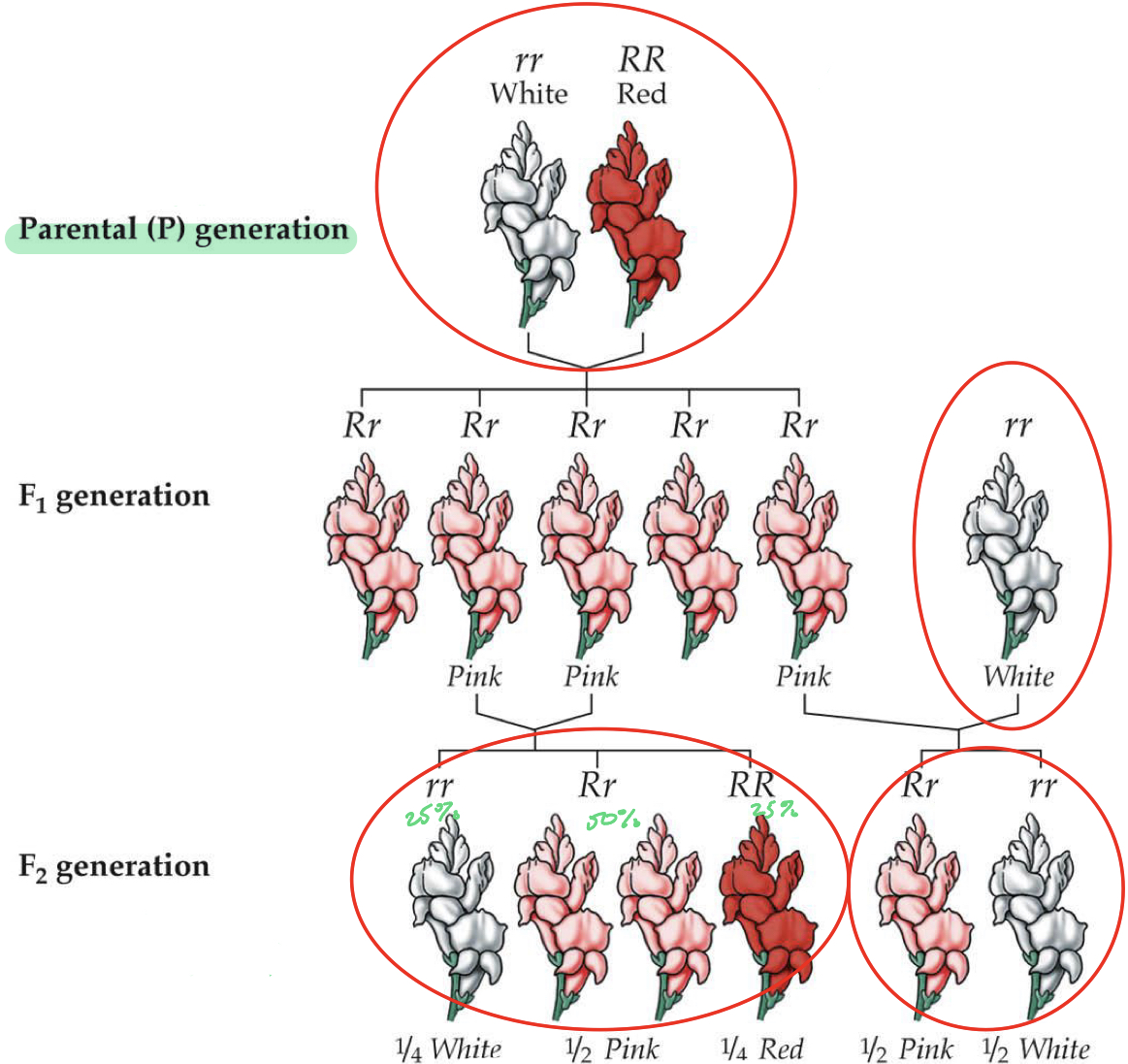
What is codominance and what is observed in heterozygote?
Neither allele masks the other
In heteozygote: Effects of both alleles are observed without blending
What is a real life example of codominace and how does it present it?
Example: Blood type
Represent by:
IA and IB = codominant
BUT IA and IB are completely dominant over i
How are different blood types determined?
By the antigen type
Antigen A (controlled by allele IA)
Antigen B (controlled by allele IB)
Antigen O (controlled by allele i)
Therefore, type A and type B phenotype can be resulted from which genotypes?
Homozygous dominant
Heterozygous with i
IA i
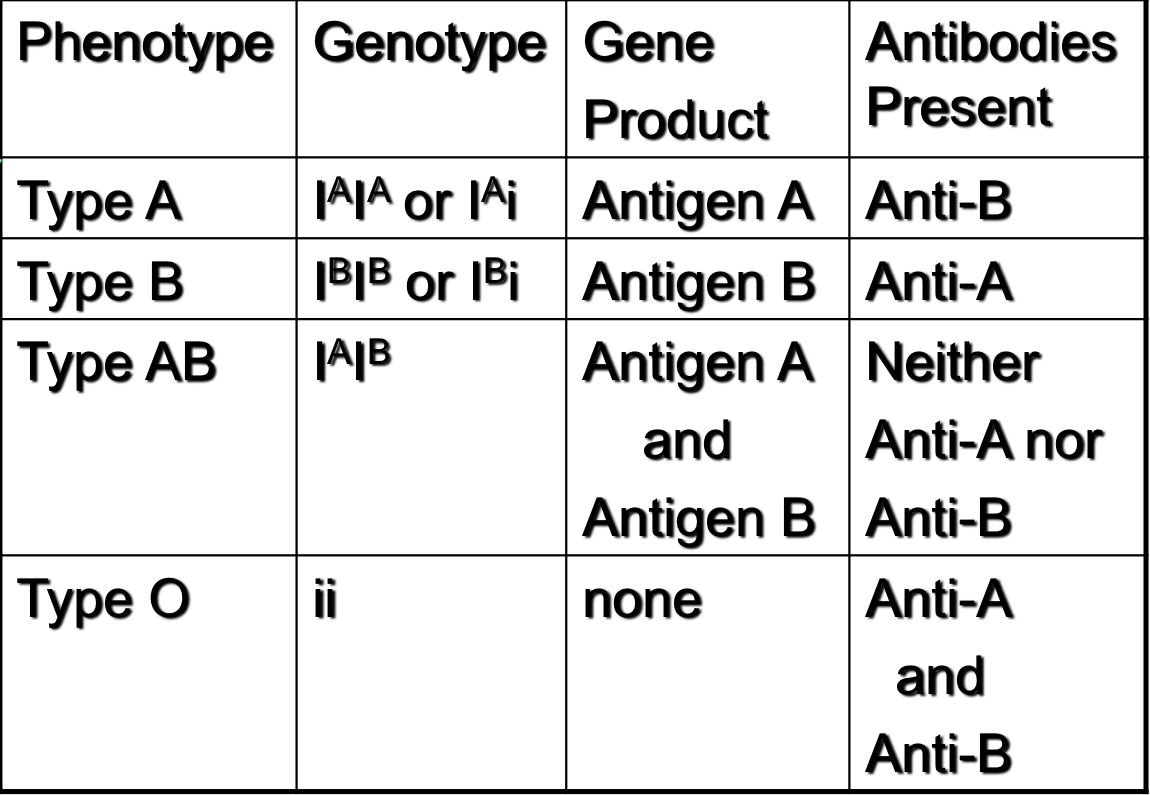
Table that represents codominance
-
What is overdominance?
In which a heterozygotes is more vigorous than both types of homozygotes
What is overdominance also called?
Heterozygous advantage
What is an example of overdominance?
Sickle cell anemia
Autosomal recessive disorder
Affected individuals produce abnormal forms of hemoglobin
Sickle cell anemia
HbA = Normal hemoglobin, hemoglobin A
HbS = Abnormal hemoglobin, hemoglobin S
Q: How does it represent overdominance
Because
HbA HbS individuals are “better” than
HbS HbS because they do not suffer from sickle cell anemia
HbA HbA, because they are more resistant to malaria
What is heterosis (hybrid vigor)
When offspring is
Phenotypically stronger
Larger
More vigorous