Earth's Interior Earth's Interior Dynamic Study Module
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is the best evidence of Earth having a solidified inner core?
P waves travel faster in the inner core than in the outer core.
S waves do not pass directly through the core.
S waves are slower in the inner core than in the outer core.
S waves are focused at the center of the P-wave shadow zone.
P waves travel faster in the inner core than in the outer core.
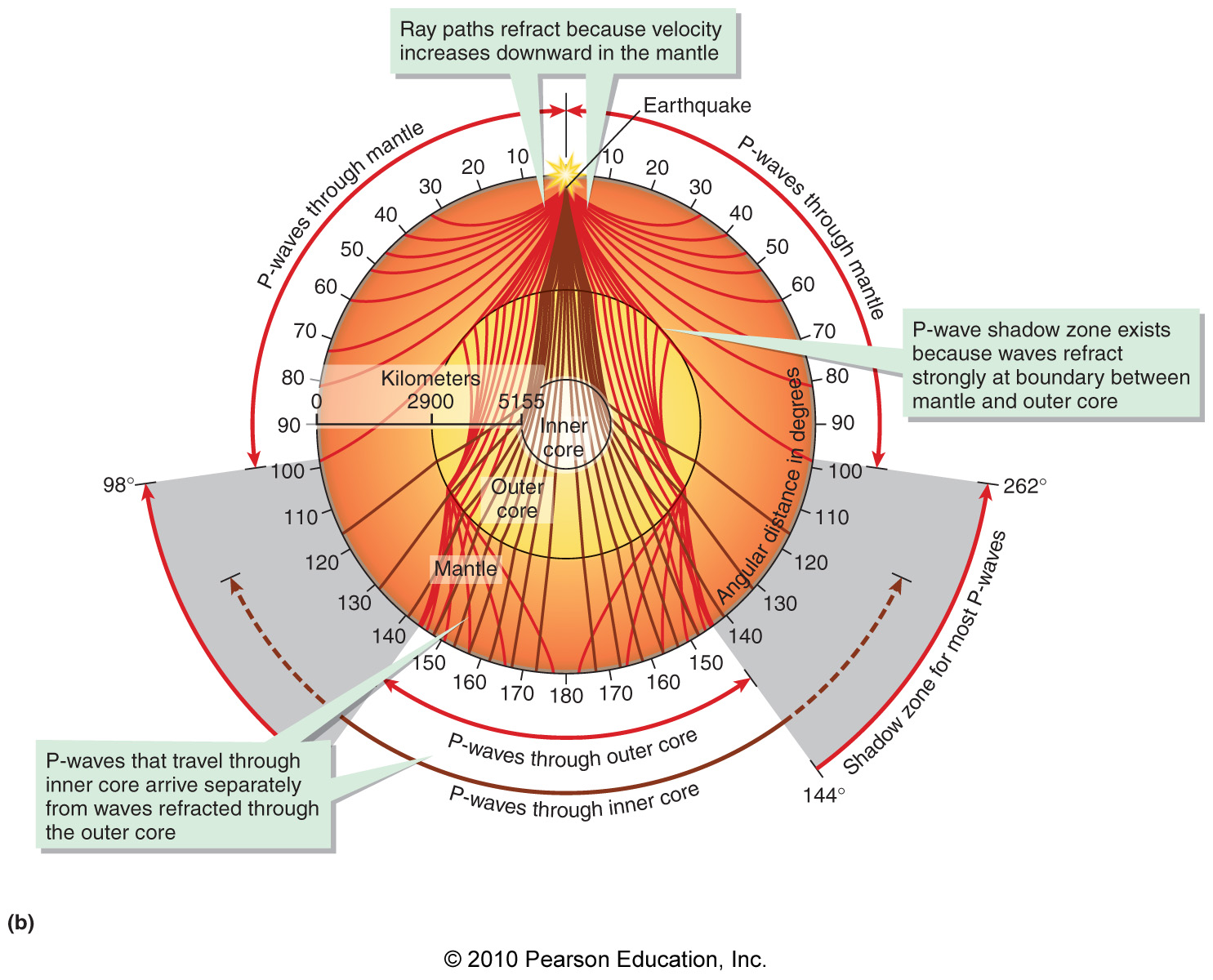
What causes the P-wave shadow zone?
Reflection of P waves at the boundary between the inner and outer cores
Lower P-wave velocities in the mantle than in the crust
Refraction of P waves crossing the mantle-outer core boundary
Reflection of P waves from the inner core-outer core boundary
Refraction of P waves crossing the mantle-outer core boundary.
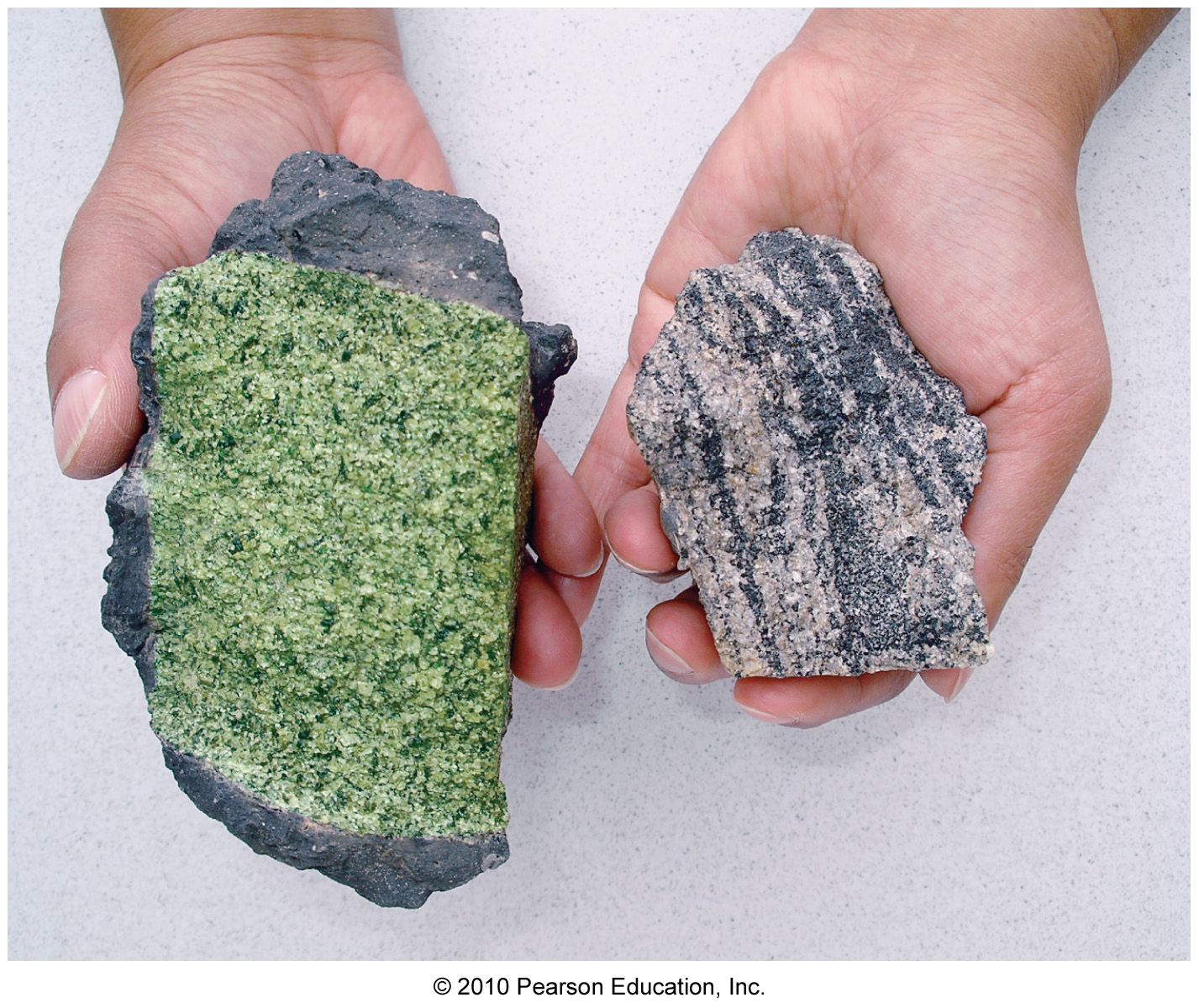
Which rock type listed below is probably closest in chemical composition to the upper mantle?
Peridotite
Shale
Granite
Andesite
Peridotite

What causes Earth's magnetic field?
Magnetic mineral grains in the inner core cause Earth’s magnetic field.
Weak electrical currents associated with hot, rising, mantle plumes cause Earth's magnetic field.
Weak electrical currents associated with fluid motions of molten iron in the outer core causes Earth's magnetic field.
Magnetization of oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the atmospheric ozone layer by solar radiation causes Earth's magnetic field.
Weak electrical currents associated with fluid motions of molten iron in the outer core cause Earth's magnetic field.
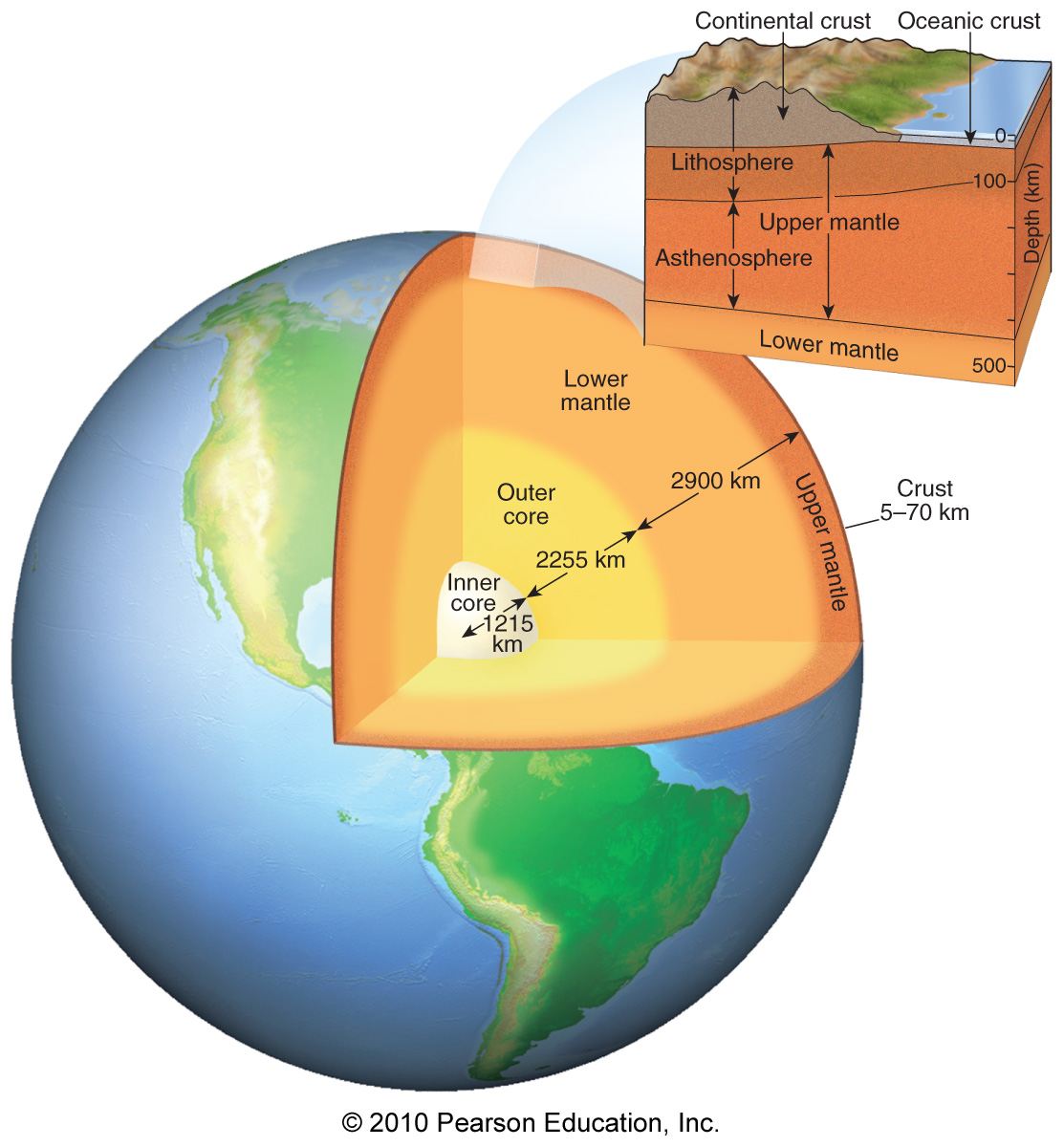
Which layer of Earth does not transmit S waves?
Deep mantle
Outer mantle
Inner crust
Outer core
Outer core
S (secondary) waves do not pass through liquids; they only pass through solids. The absence of S waves in the outer core indicates its liquid state.
Which of the following best characterizes how the diameter of Earth's core and the nature of the outer core were discovered?
By studying P-wave speeds, which are higher in the outer core than in the lower mantle
By using the ratio of iron meteorites to stony meteorites to deduce the relative diameters of the core and mantle
Through analysis of the P-wave and S-wave shadow zones
Through analysis of crystalline iron found in lavas erupted from the deepest known hot spots
Through analysis of the P-wave and S-wave shadow zones
Which layer of Earth is very dense and solid and consists most likely of an iron-rich alloy?
Outer core
Inner core
Mantle
Crust
Inner core
Where does Earth's magnetic field originate?
Outer core
Crust
Inner core
Mantle
Outer core
Which layer of Earth transmits P earthquake waves but not S earthquake waves?
Inner core
Mantle
Crust
Outer core
Outer core
Which of the following are probably major components of Earth's inner core?
Solid iron silicates and magnesium silicates
Crystalline iron and nickel
Solidified uranium and other very heavy elements
Liquid iron-nickel-sulfur alloy
Crystalline iron and nickel
Which of the following includes the zone called the “asthenosphere” (the “weak sphere”)?
Crust
Upper mantle
Outer core
Inner core
Upper mantle
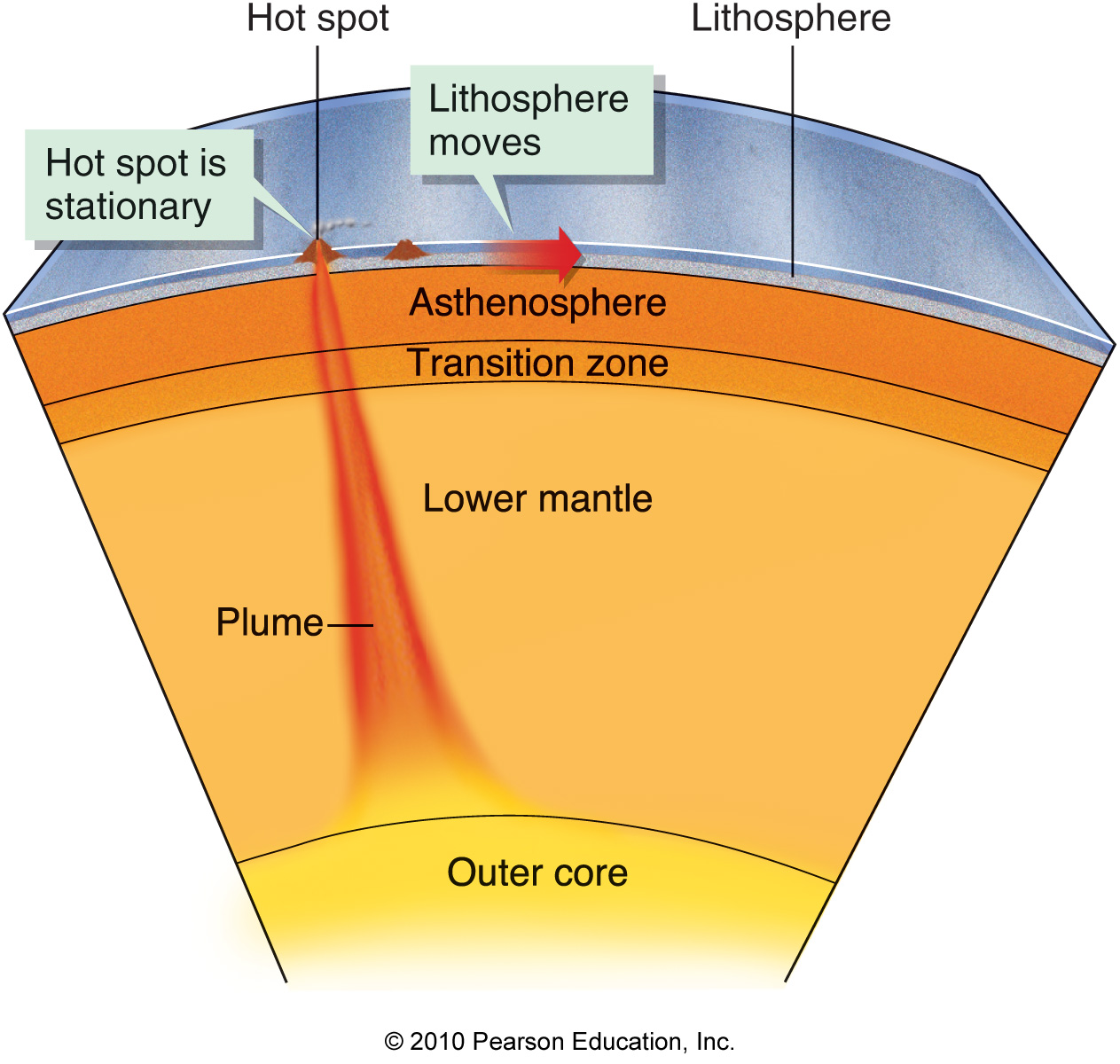
Which of the following is the result of convection within the mantle?
Warm rock rises as tabular sheets.
Warm rock rises as narrow pipe-like plumes.
Cool rock rises as tabular sheets.
Cool rock rises as vertical, pipe-like masses
Warm rock rises as narrow pipe-like plumes.
Which of Earth's layers is marked at its top by the Mohorovičić discontinuity?
Mantle
Outer core
Crust
Inner core
Mantle
Which one of the following best characterizes the asthenosphere?
A layer of soft, solid magnesium silicates and molten iron droplets at the base of the mantle
The zone in the mantle from which hot-spot magmas are melted
A zone of softened peridotite in the upper mantle
A zone of hardened, silicate rock at the base of the oceanic crust
A zone of softened peridotite in the upper mantle.