Introduction to brain structure and function
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Layers of the head
Scalp
Bone
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
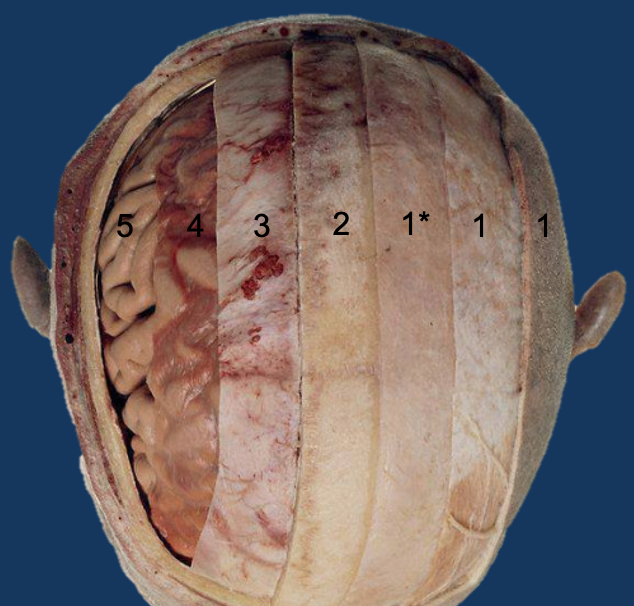
What are the 3 meninges?
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
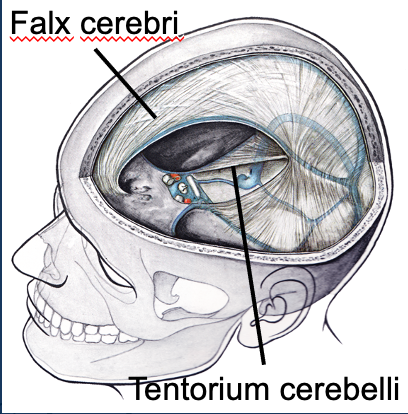
3 folds/reflections of the dura mater
Falx cerebri
Tentorium cerebelli
Falx cerebelli
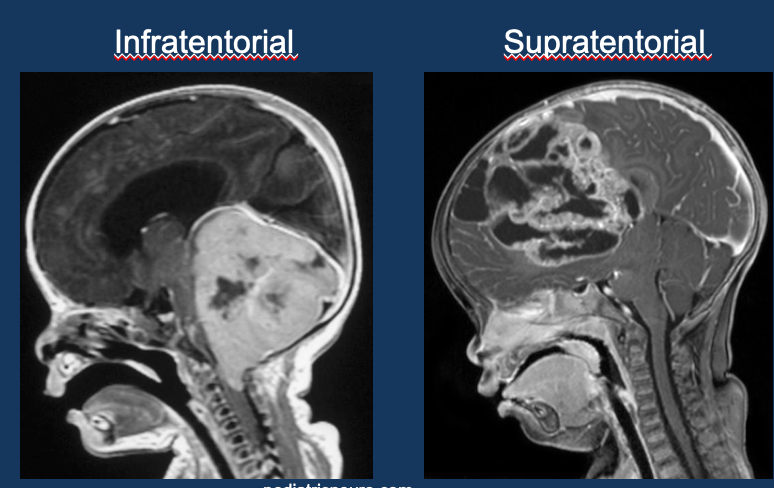
Types of tensorial tumours
Infratentorial
Supratentorial
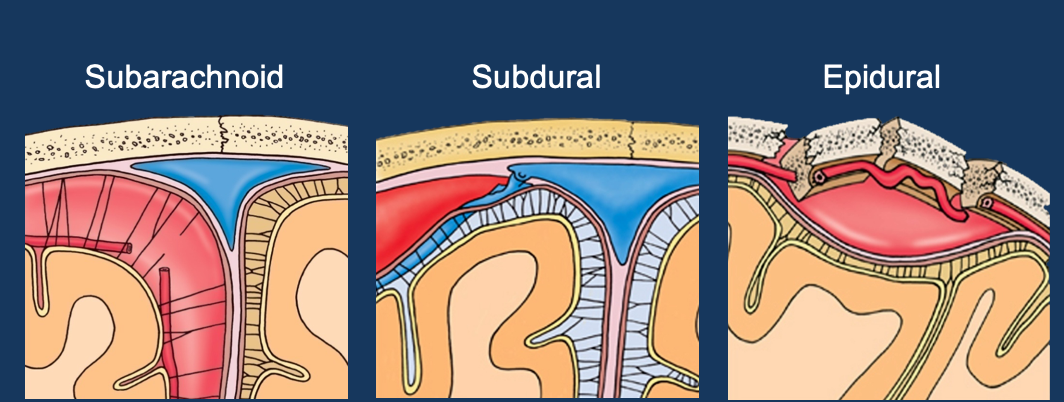
3 types of meningeal haematomas
subarachnoid
subdural
epidural
Which meningeal layer has blood vessels and cerebral spinal fluid?
Arachnoid mater
Which meningeal layer protects the brain?
Dura mater
Contents of the arachnoid mater
blood vessels, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), and granulations to drain CSF back into the venous system
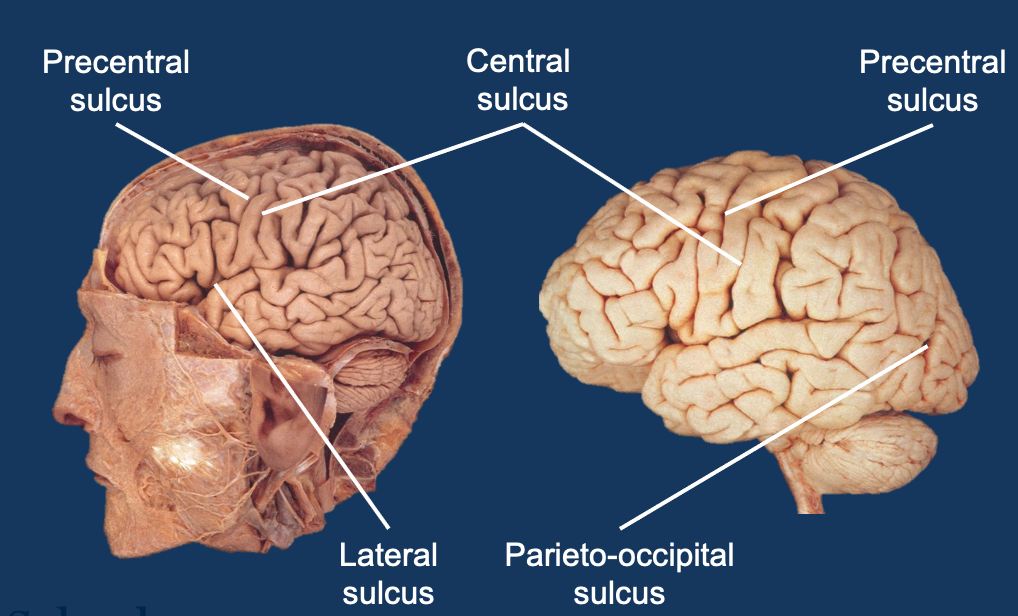
Sulcus on outside of brain
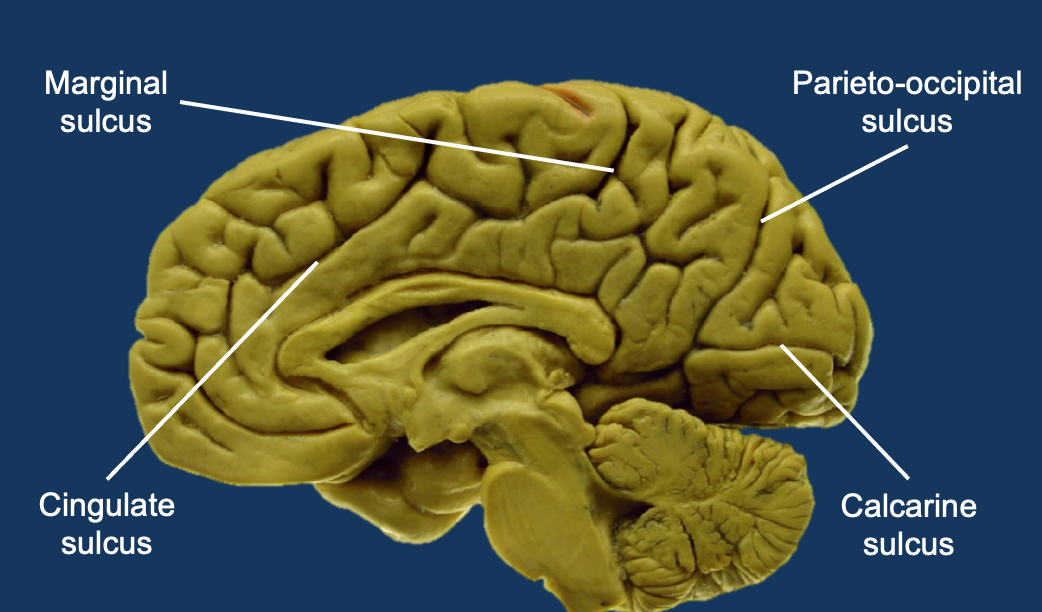
Sulcus on inside of brain
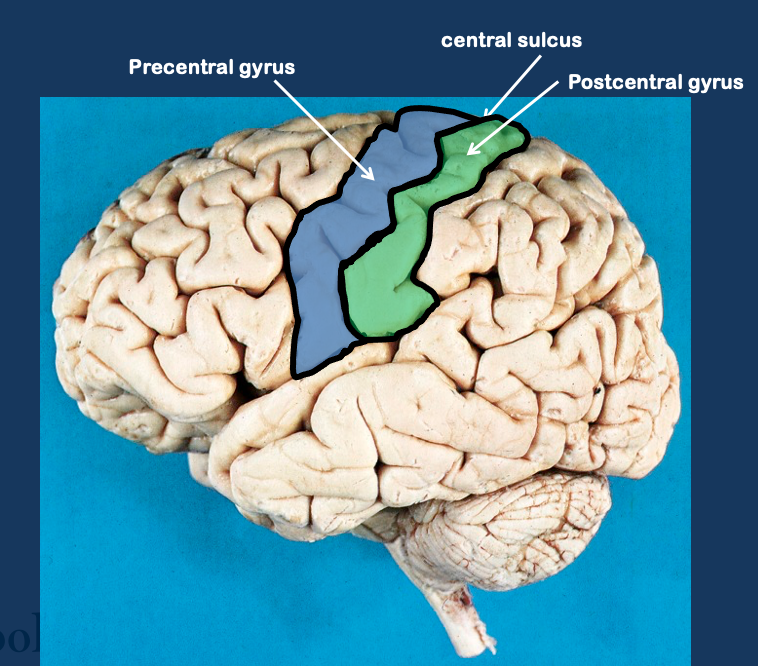
What is the cortical gyri?
Area including precentral gyrus - associated with motor complex (movement) and post central gyrus (sensation)
Separated by central sulcus
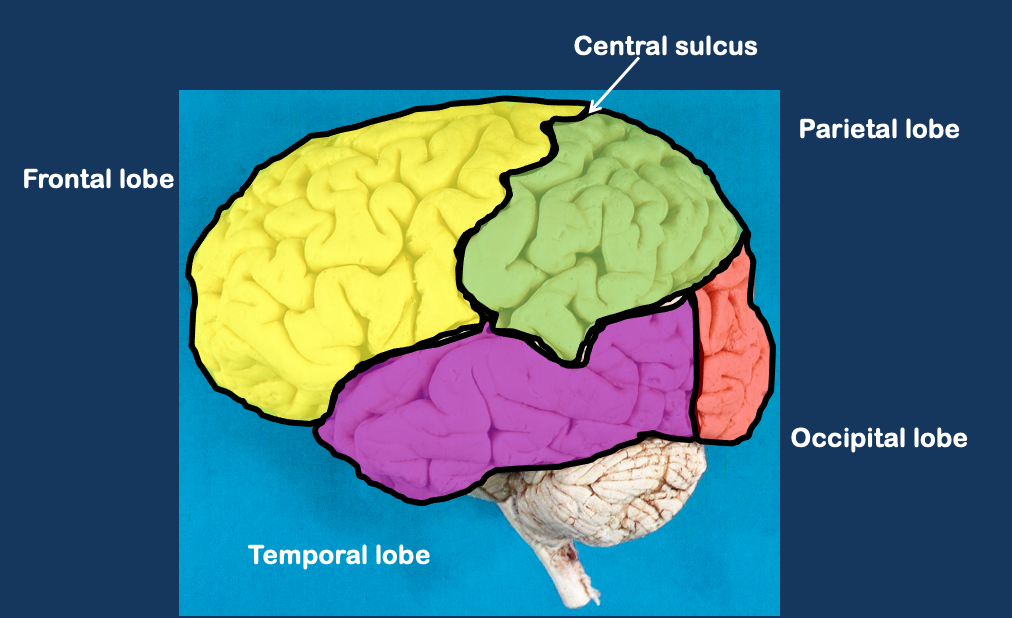
Cortical lobes (4)
Frontal - voluntary movement personality.
Parietal - senses
Occipital - vision
Temporal - memory, speech
Hindbrain structural development (rhombencephalon)
Metencephalon → Pons + Cerebellum
Myelencephalon → Medulla oblongata
Midbrain structural development (mesencephalon)
Mesencephalon → Tectum (colliculi), Tegmentum + Cerebral peduncles
Forebrain structural development (prosencephalon)
Diencephalon → Thalamus + Hypothalamus
Telencephalon → Basal ganglia and cortex
Centre of brain structures
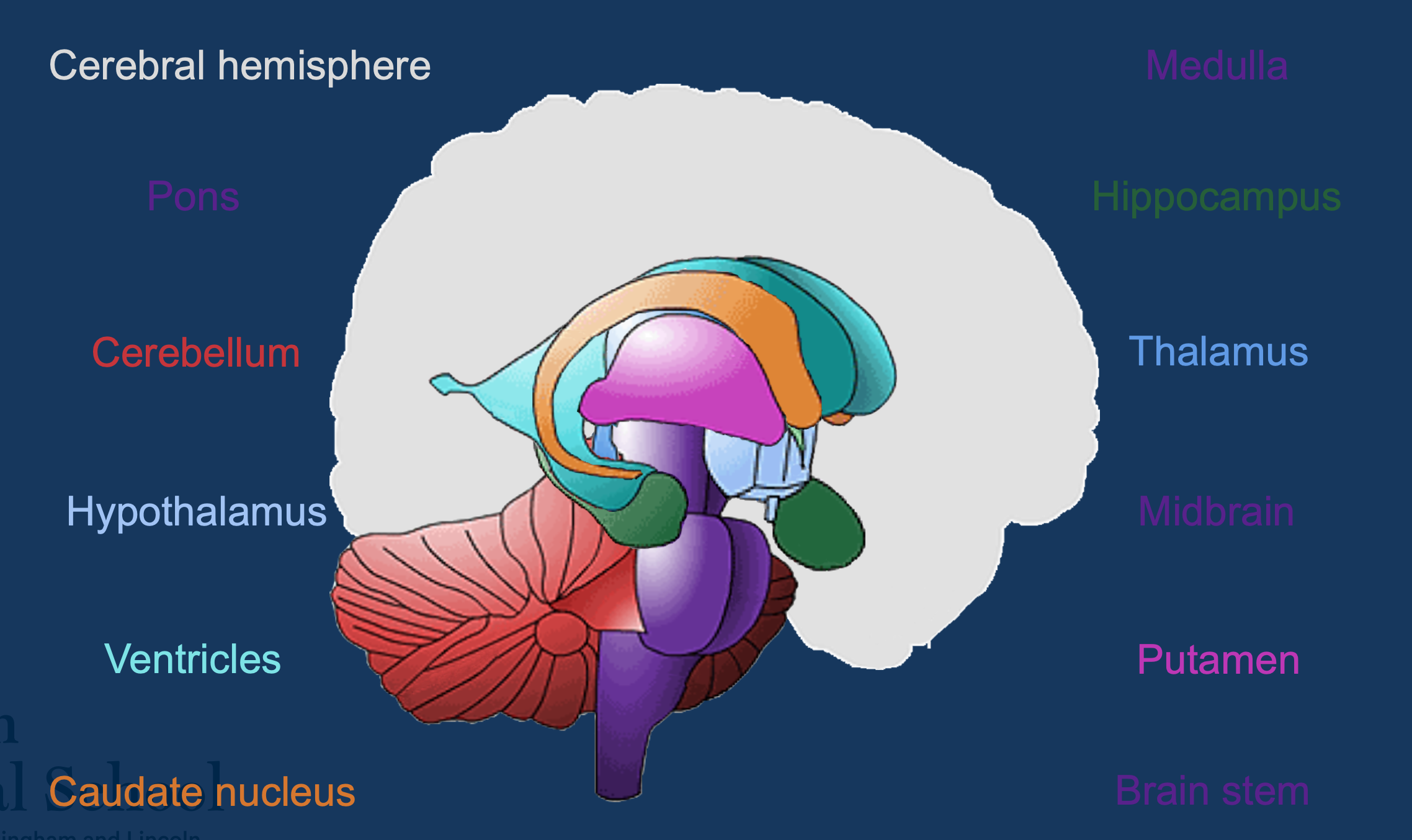
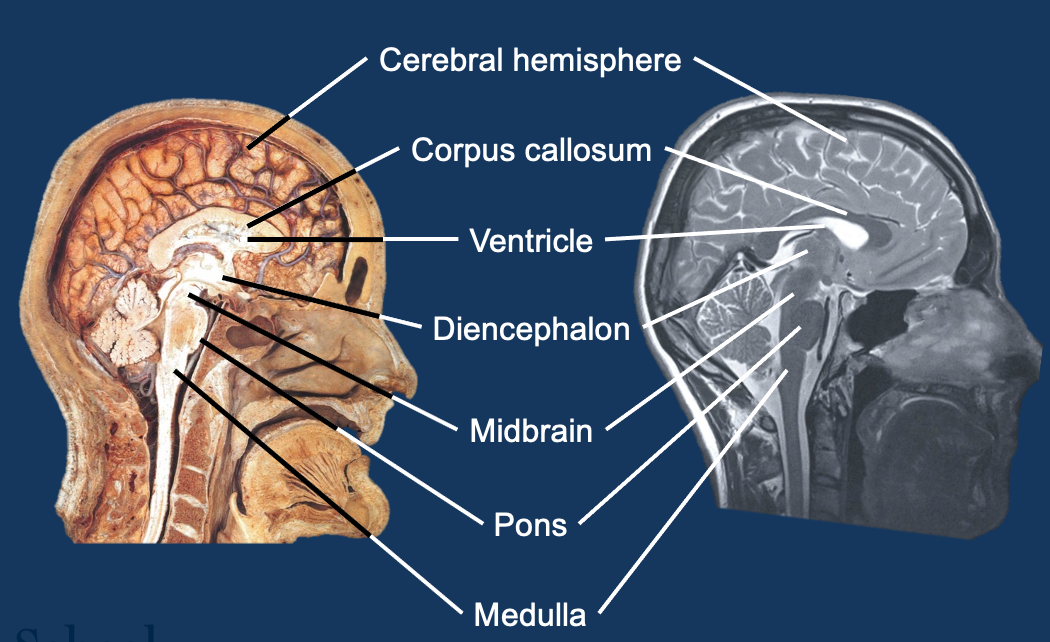
Structures found from the top of the head to the bottom of spinal cord
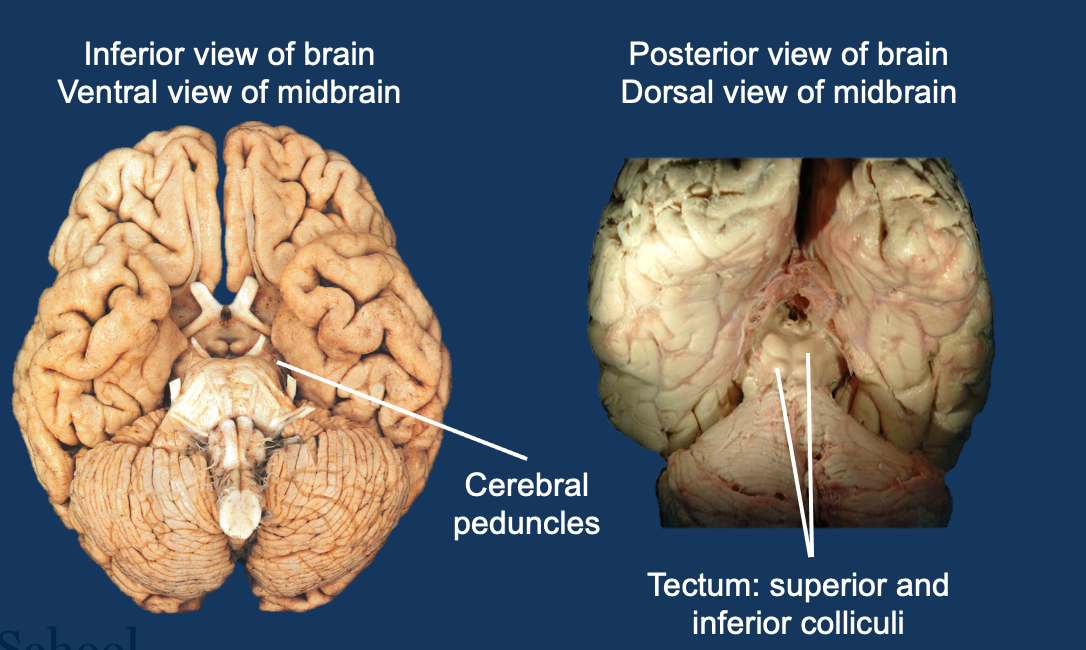
Structures of the mid brain
Cerebral peduncles
Tectum: superior(vision)and inferior colliculi (hearing)
Superior colliculi is closer to the middle
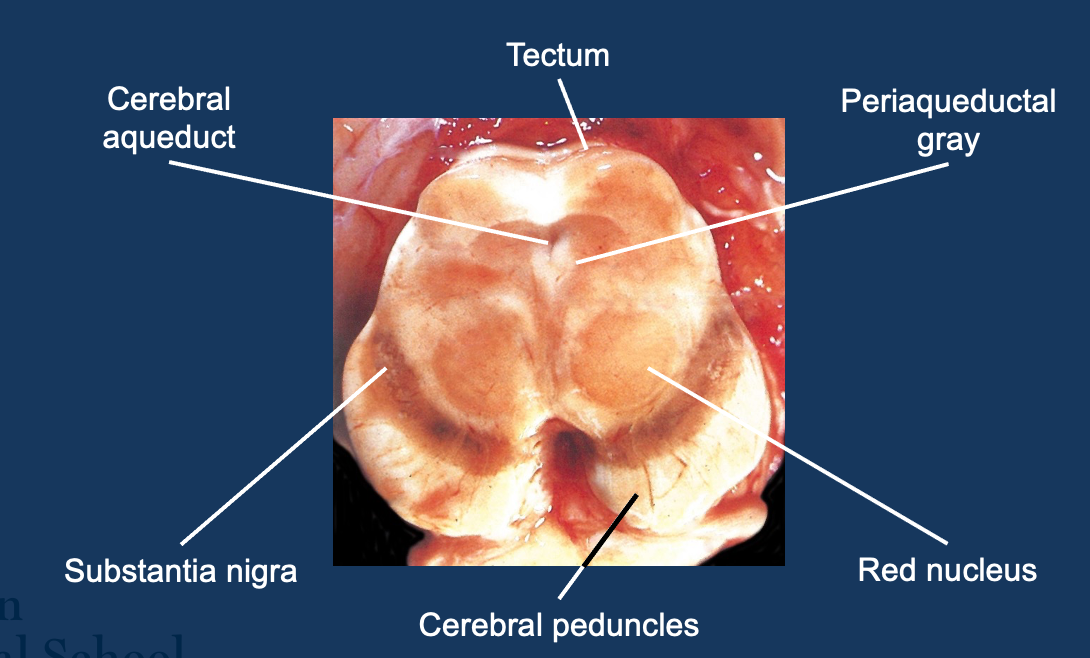
Transverse midbrain
Tectum
Cerebral aqueduct
Periaqueductal gray
Substantia nigra (motor function, Parkinson’s)
Red nucleus (3rd cranial nerve for the eyes)
Cerebral peduncles
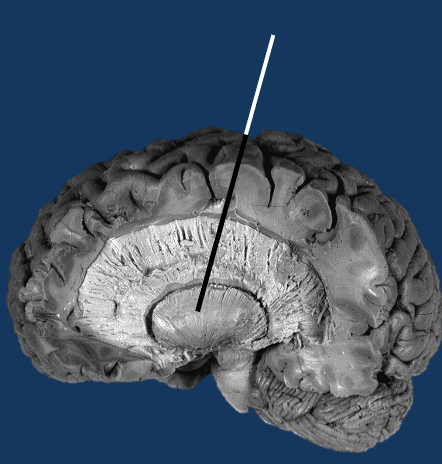
What is this structure?
Putamen
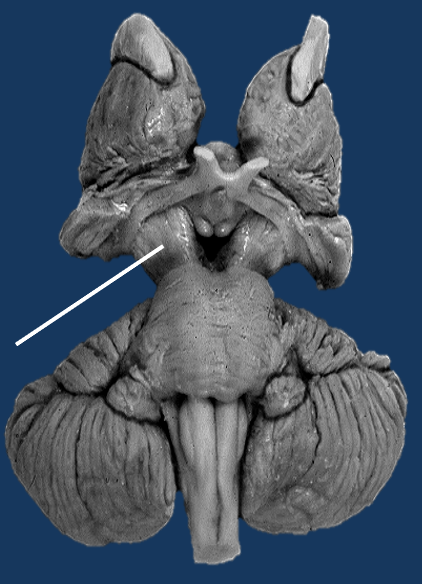
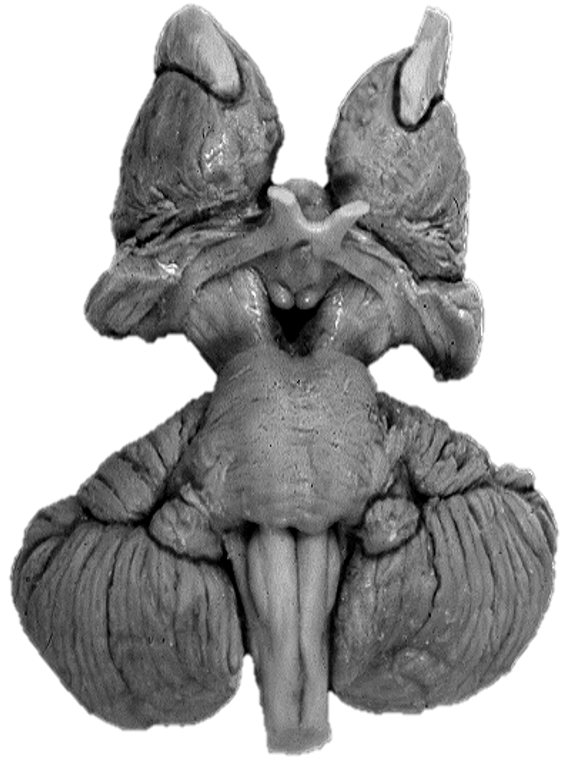
What is this structure?
Cerebral peduncles

What is this?
Hind brain
Summary

Ventricular system
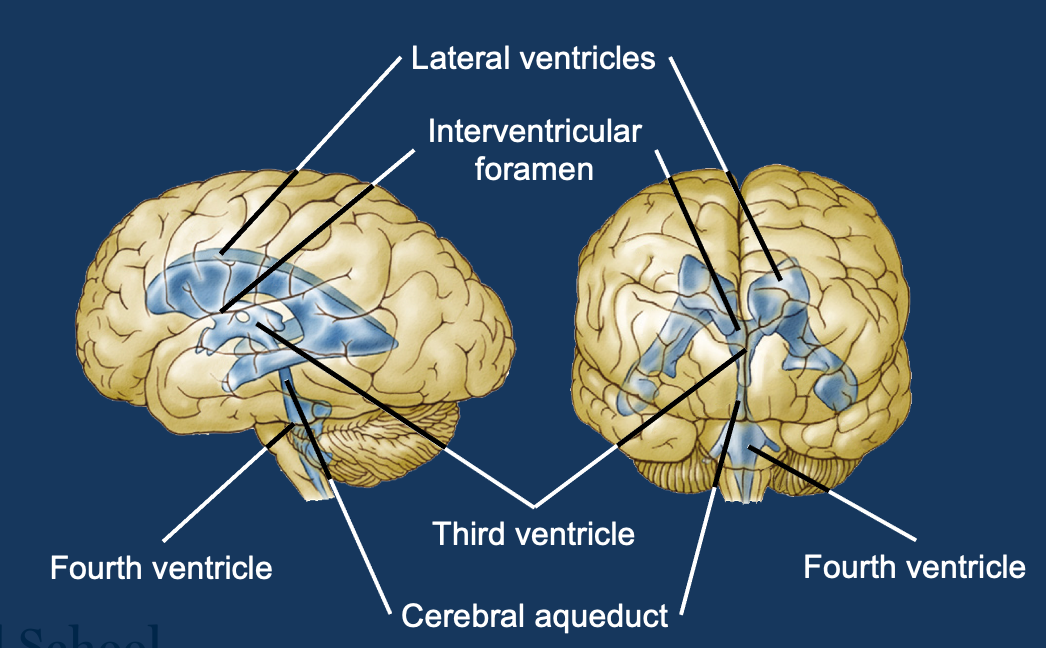
Function of cerebral spinal fluid
Fills ventricles, colour-less liquid that baths the brain, assists in circulating substances, it provides cushioning and absorbs shock
What is the choroid plexus?
Group of cells that line the ventricles
produces CSF
induces CSF circulation
acts as a medium of exchange between extra cellular fluid and blood stream
Structures involved in CSF circulation
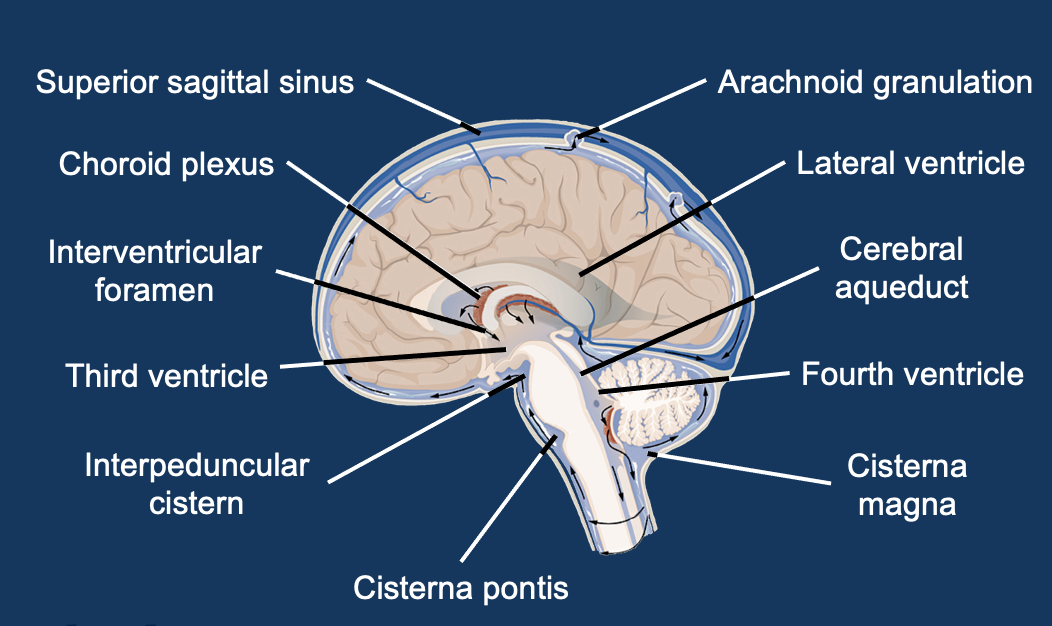
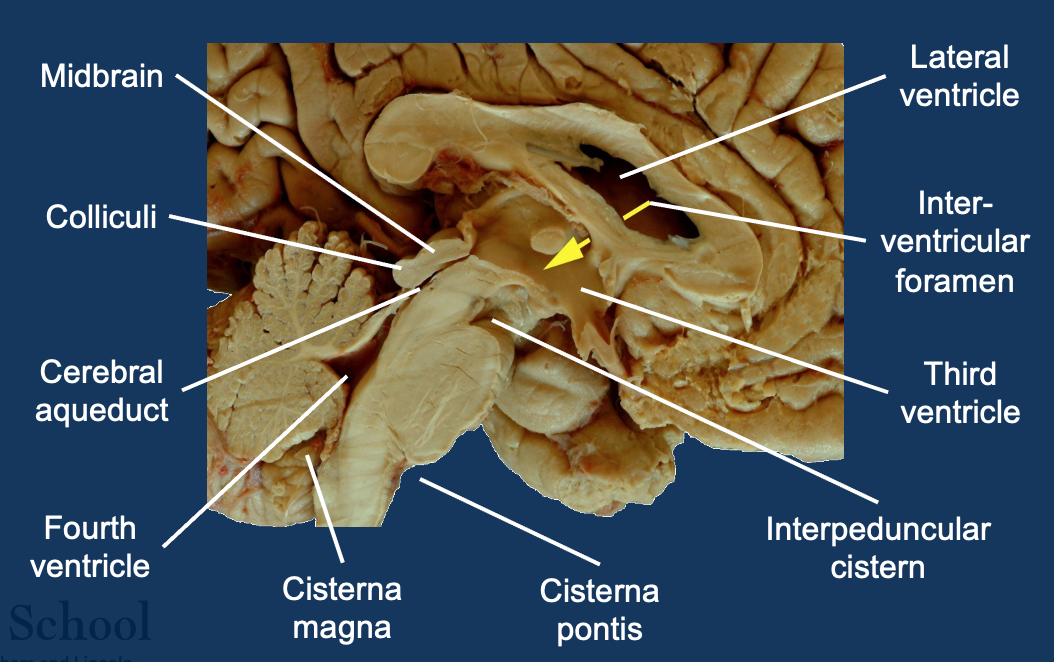
CSF circulation (midbrain)
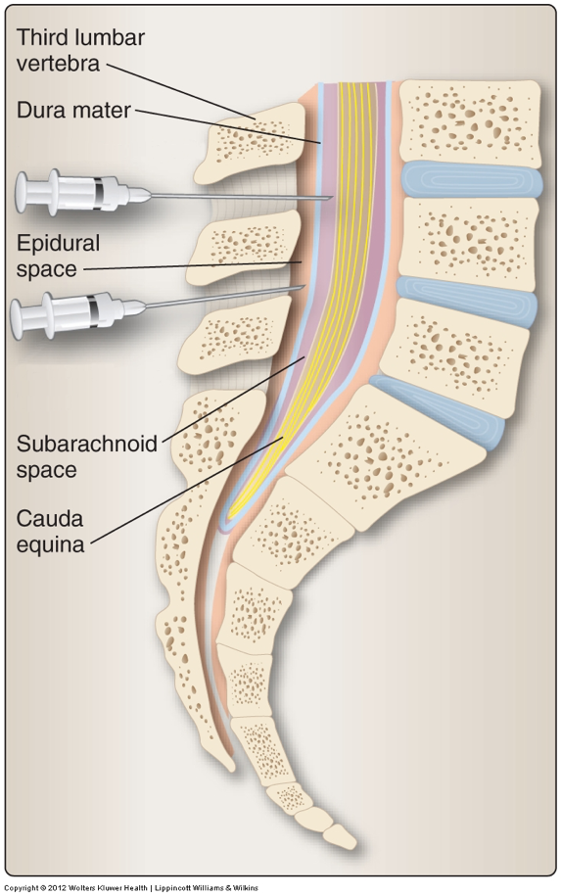
Vertebral level for safe CSF sampling, adult vs infants
Adults: L3-L4/ L4-L5
Infants: at or below L4-L5
What is this structure?
Ventricular system - 3rd ventricle
CSF summary

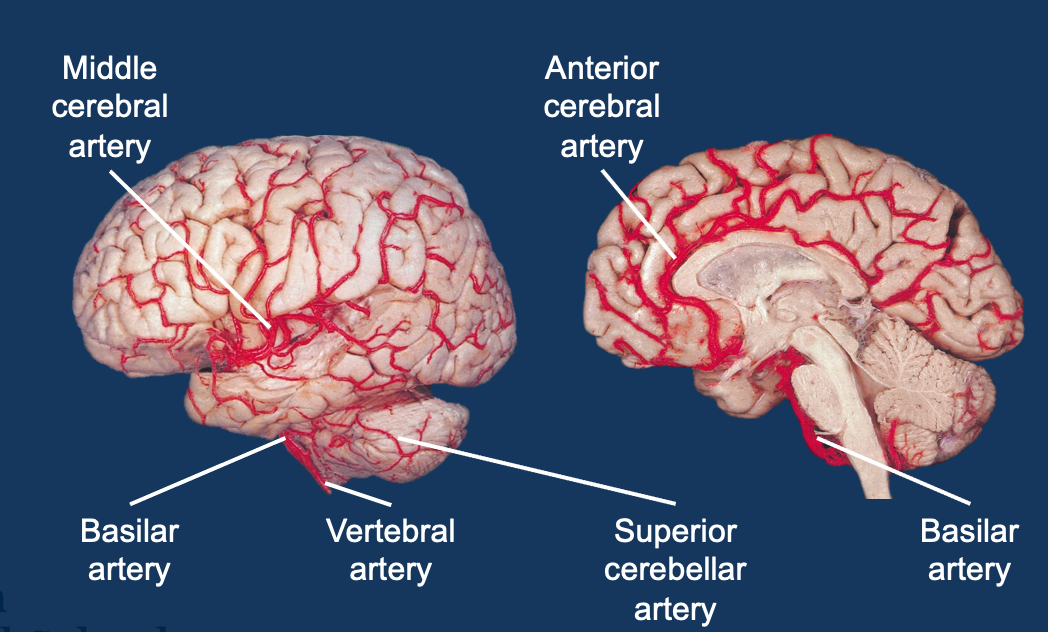
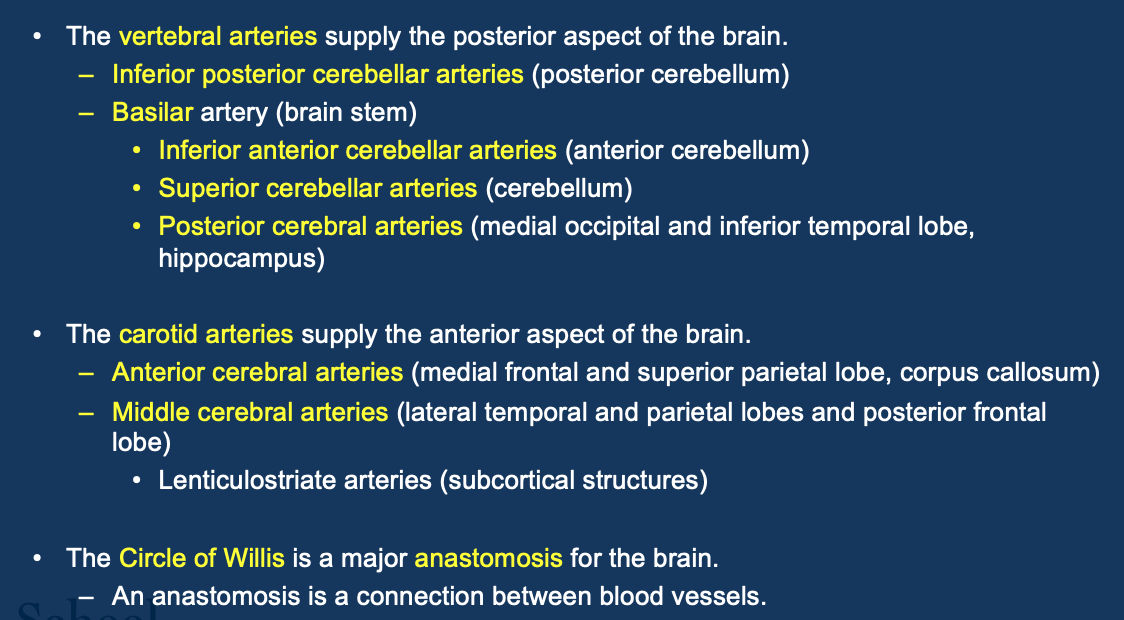
Describe the blood supply to the brain
Dual supply - internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries
Internal carotid - Anterior and middle cerebral arteries (terminal)
Vertebral - unite to form basilar artery→ posterior cerebral arteries
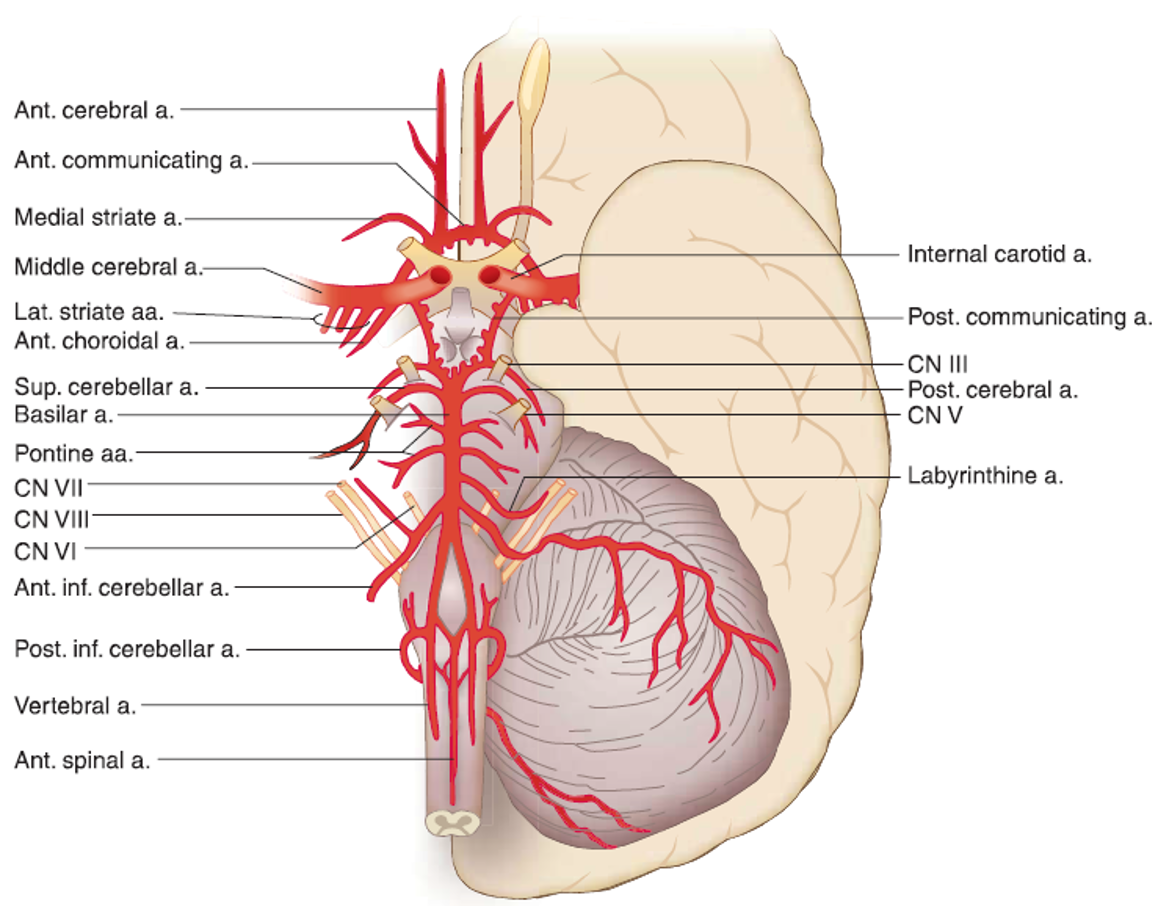
Circle of Willis
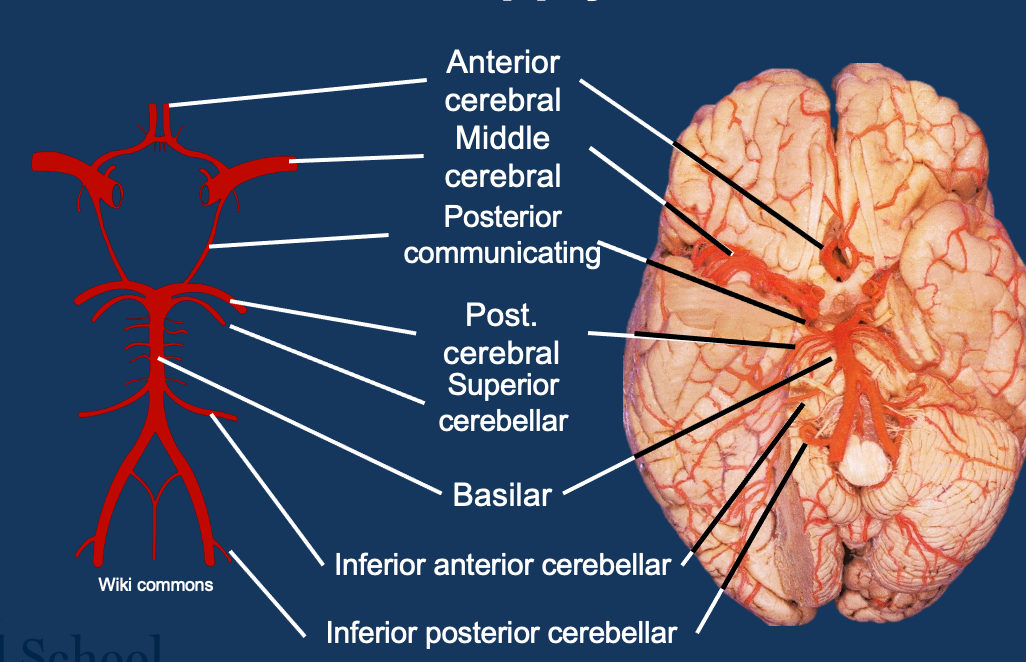
Arterial territories
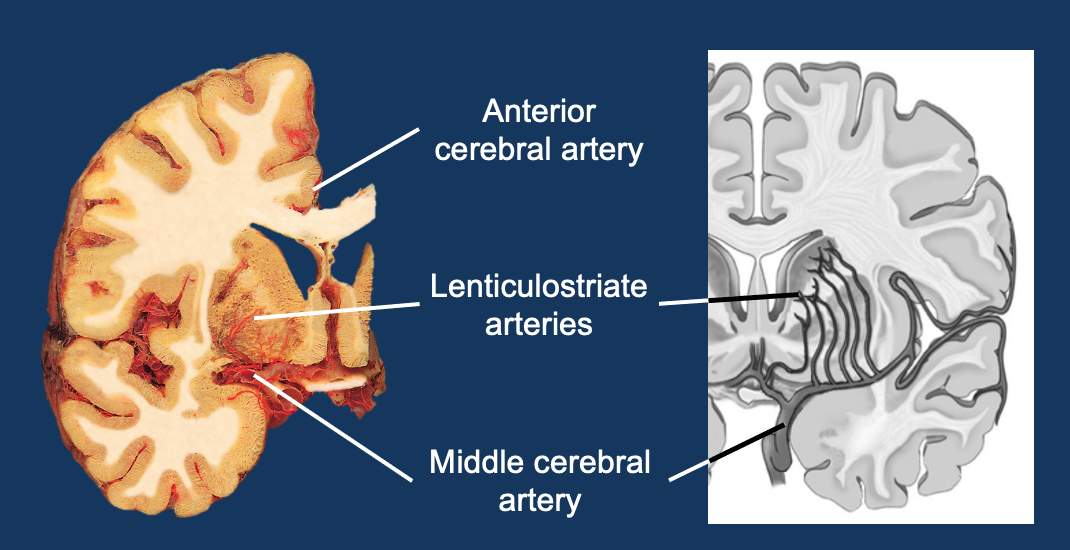
Subcortical blood supply
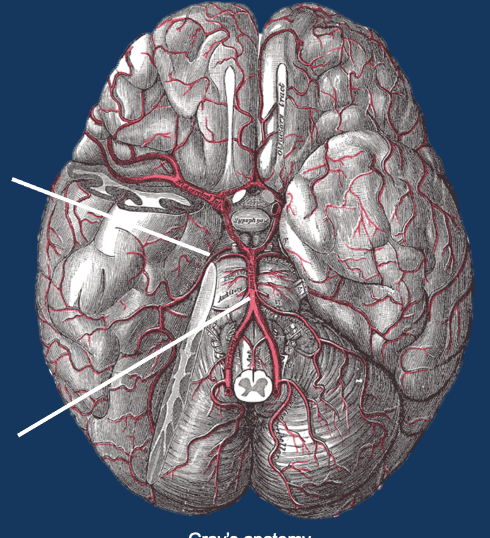
What are these arteries?
Posterior and basilar
How can you visualise arteries?
Angiograms
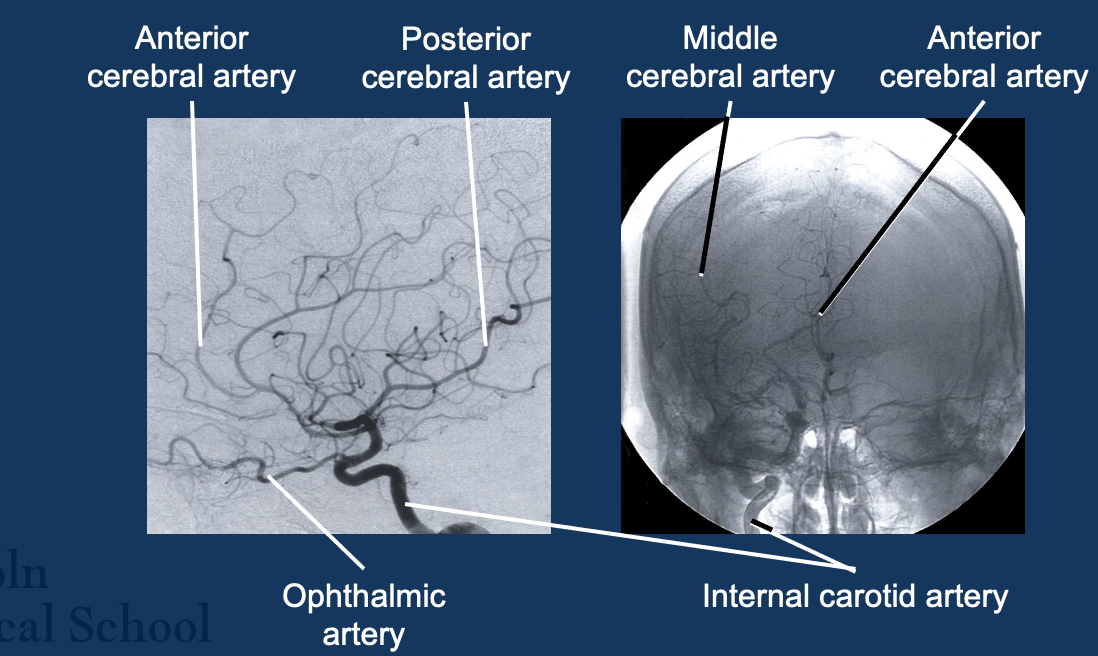
Arterial supply summary
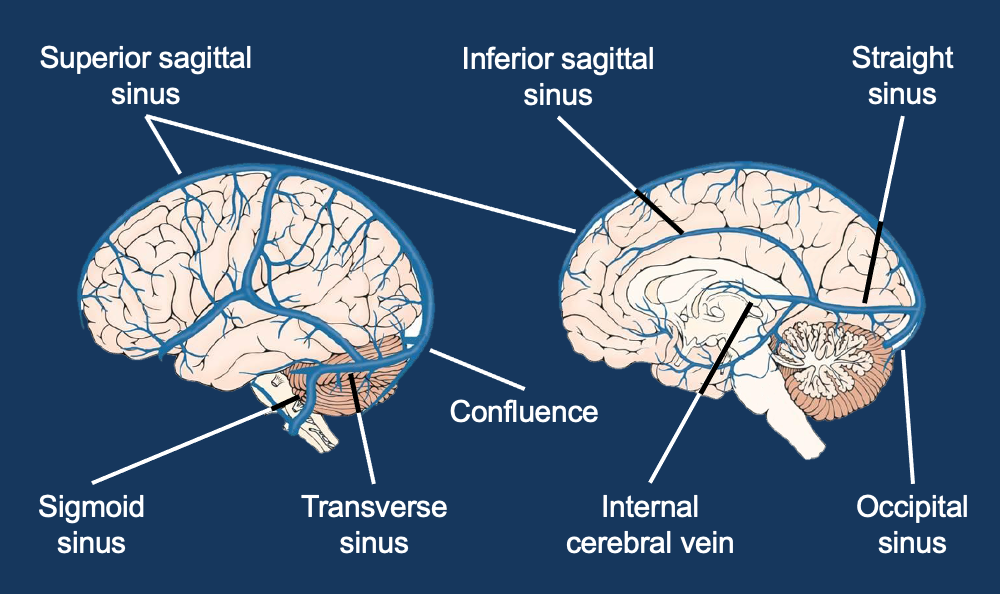
Venous drainage of brain
What are these veins?
Superior sagittal and sigmoid sinuses
Venous drainage summary

What is the blood brain barrier?
an interface that ensures the circulatory system (blood) is kept separate from the extracellular fluid/CSF
Maintained by pericytes and astrocytes
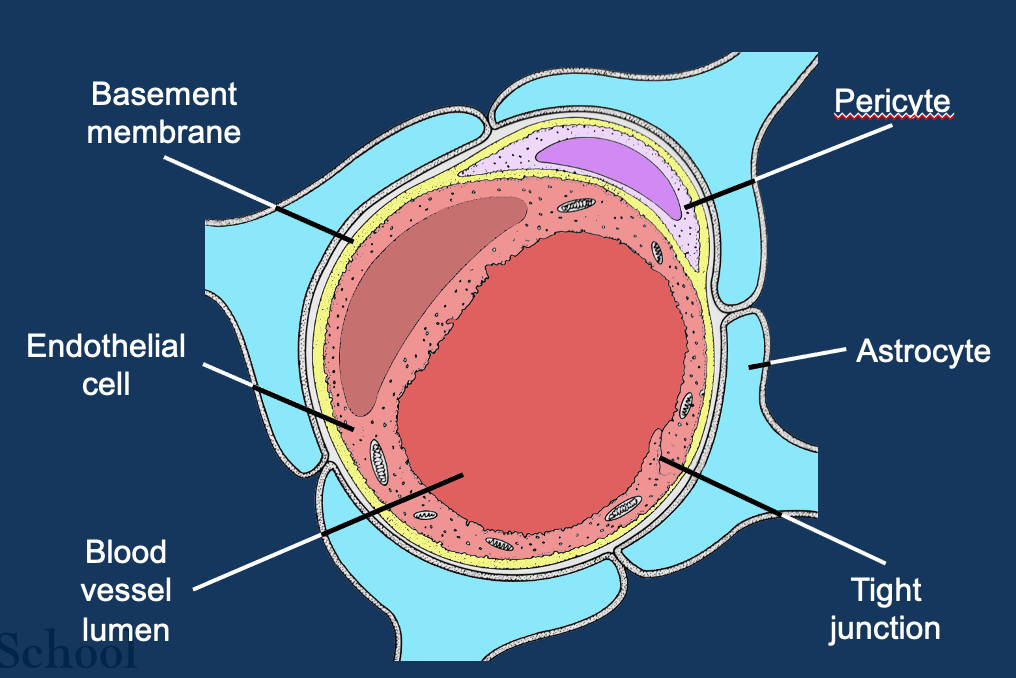
Which molecules can cross the BBB?
Small molecules - oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose, select amino acids
BBB summary
