genome
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Genome size and content doesn’t predict
Complexity
Gene content and genome size are correlated
In bacteria not eukaryotes
Genomes bloated with
Noncoding dna
Our genome is 50% “parasites” –
Transposable elements
Exact same sequence
Is recent insertion
Prokaryotes
Efficient at screening for junk and deletions
Can select for low mutation rate
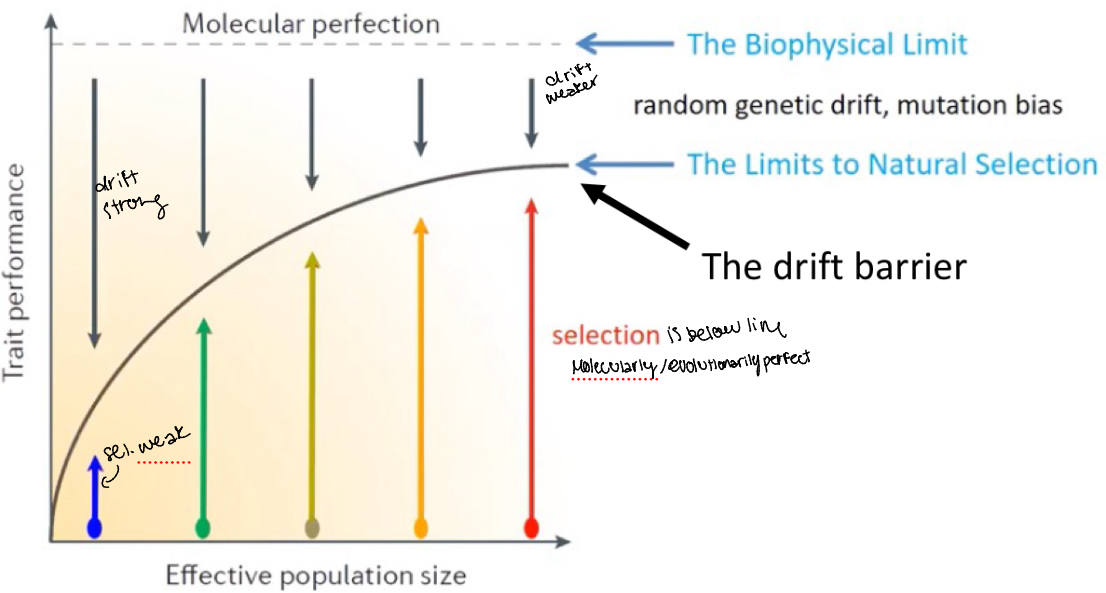
Drift barrier hypothesis
• Selection is most efficient at high Ne
• There is a “barrier” to whether or not selection can act on a mutation/variant – the barrier is imposed by drift
• For species with large Ne, this barrier will be ”low” – selection can act on mutations with relatively weak effects
• For species with small Ne, this barrier is “high” – selection can only act on mutations with relatively strong effects
• Predictions include some of the data just shown
Where do new genes come from?
• What is a gene?
• De novo gene birth is rare
• Gene duplication is common
Fate of duplicate genes – most are lost
Pseudogenes
Fate of duplicate genes – repetitive function
Resistance against pesticides in plants
Fate of duplicate genes - neofunctionalization
Duplicate acquires new function
Fate of duplicate genes - subfunctionalization
Duplicate expressed at different time points
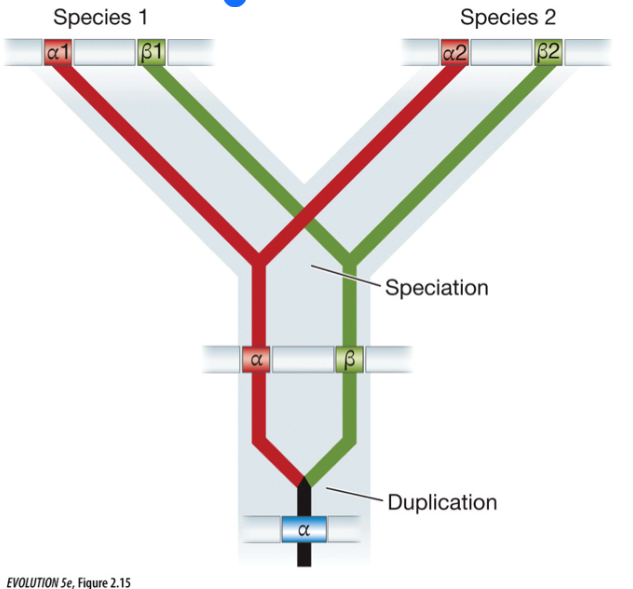
Gene family evolution
Build trees using duplicates